Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pancreas: Function
Uploaded by
itsankurzOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pancreas: Function
Uploaded by
itsankurzCopyright:
Available Formats
Pancreas: Function
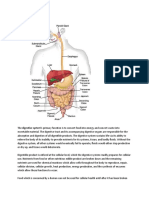
The pancreas is a small organ, approximately six inches long, located in the upper abdomen, and adjacent to the small intestine. It lies toward your back. Because it is so deep within your body, doctors have difficulty diagnosing disease in the pancreas.
The Pancreas
Completes the job of breaking down protein, carbohydrates, and fats using digestive juices of pancreas combined with juices from the intestines. Secretes hormones that affect the level of sugar in the blood. Produces chemicals that neutralize stomach acids that pass from the stomach into the small intestine by using substances in pancreatic juice. Contains Islets of Langerhans, which are tiny groups of specialized cells that are scattered throughout the organ.
o
These cells secrete: Glucagonraises the level of glucose (sugar) in the blood
Insulinstimulates cells to use glucose Somatostatinmay regulate the secretion of glucagons and insulin.
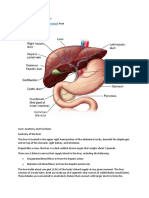
What are the functions of the liver? The liver regulates most chemical levels in the blood and excretes a product called bile, w further digestion and absorption. All of the blood leaving the stomach and intestines passes t breaks down the nutrients and drugs in the blood into forms that are easier to use for the re been identified with the liver. Some of the more well-known functions include the following: Production of bile, which helps carry away waste and break down fats in the small intestine during digestion.
Production of certain proteins for blood plasma. Production of cholesterol and special proteins to help carry fats through the body. Conversion of excess glucose into glycogen for storage. (This glycogen can later be converted back to glucose for energy.) Regulation of blood levels of amino acids, which form the building blocks of proteins. Processing of hemoglobin for use of its iron content. (The liver stores iron.) Conversion of poisonous ammonia to urea. (Urea is one of the end products of protein metabolism that is excreted in the urine.)
Clearing the blood of drugs and other poisonous substances. Regulating blood clotting. Resisting infections by producing immune factors and removing bacteria from the blood stream. When the liver has broken down harmful substances, they are excreted into the bile or blood. Bile by-products enter the intestine and ultimately leave the body in the feces. Blood by-products are filtered out by the kidneys and leave the body in the form of urine.
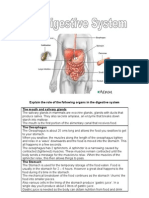
The stomach's main function is digestion. It does this by: Storing the food we eat.
Breaking down the food into a liquidly mixture called chyme. Mixing enzymes which is are chemicals that break down food. Slowly empties that liquidly mixture into the small intestine.
The stomach uses pepsin (enzyme) and peptidase (another enzyme) to break down proteins in your food. The acid released by the stomach doesn't break down food it only provides a good environment for the enzymes to work in. By this point the food is mushy and the stomach then passes this mixture on to the small intestine which will further break down the food. The stomach mixed the food with stomach acid to break it down and digest it.
Function of the Small Intestine
The small intestine is responsible for absorbing most of the nutrients found within your food. By the time ingested food reaches the small intestine, it has been mechanically broken down into a liquid. As this liquid flows across the inner surface of the small intestine (which has many small folds to increase the surface area), nutrients within the food come into contact with the many small blood vessels that surround the small intestine. This blood then leaves the small intestine, carrying away nutrients, water electrolytes, vitamins, minerals, fats and medications to the entire body. It can take three to six hours for a meal to pass from one end of the small intestine to the other, and that is dependent on the makeup of the food passing through; meals containing a lot of fiber move more quickly.
Functions of Large Intstine
The large intestine takes about 16 hours to finish the digestion of the food. It removes water and any remaining absorbable nutrients from the food before sending the indigestible matter to the rectum. The colon absorbs vitamins which are created by the colonic bacteria - such as vitamin K (especially important as the daily ingestion of vitamin K is not normally enough to maintain adequate blood coagulation), vitamin B12, thiamine and riboflavin. It also compacts feces, and stores fecal matter in the rectum until it can be discharged via the anus in defecation.
The large intestine differs in physical form from the small intestine in being much wider and in showing the longitudinal layer of the muscularis have been reduced to 3 straplike structures known as the taeniae coli. The wall of the large intestine is lined with simple columnar epithelium. Instead of having the evaginations of the small intestine (villi), the large intestine has invaginations (the intestinal glands). While both the small intestine and the large intestine have goblet cells, they are abundant in the large intestine. The appendix is attached to its inferior surface of the cecum. It contains the least of lymphoid tissue. It is a part of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue, which gives the appendix an important role in immunity. Appendicitis is the result of a blockage that traps infectious material in the lumen. The appendix can be removed with no apparent damage or consequence to the patient. The large intestine extends from the ileocecal junction to the anus and is about 4.9 ft long. On the surface, bands of longitudinal muscle fibers called taeniae coli, each about 1/5 in wide, can be identified. There are three bands, and they start at the base of the appendix and extend from the cecum to the rectum. Along the sides of the taeniae, tags of peritoneum filled with fat, called epiploic appendages (or appendices epiploicae) are found. The sacculations, called haustra, are characteristic features of the large intestine, and distinguish it from the small intestine.
You might also like
- A Simple Guide to Pancreas Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Pancreas Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Alimentary Tract of The Digestive System MouthDocument5 pagesDigestive System Alimentary Tract of The Digestive System MouthJoNo ratings yet
- Digestive System ReadingDocument6 pagesDigestive System ReadingcholzNo ratings yet
- Nutrition-GSCI1045 Lecture - Week 4Document12 pagesNutrition-GSCI1045 Lecture - Week 4Nicholas ObasiNo ratings yet
- Digestive System GuideDocument4 pagesDigestive System Guidesebastian voieiabetNo ratings yet
- Structure of Digestive SystemDocument8 pagesStructure of Digestive System32 Mhd RayisNo ratings yet
- Structure of Digestive SystemDocument8 pagesStructure of Digestive System32 Mhd RayisNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption of Food in ManDocument3 pagesDigestion and Absorption of Food in Mancd78x8xbsxNo ratings yet
- Organs of The Digestive SystemDocument28 pagesOrgans of The Digestive SystemMitch TiangeNo ratings yet
- The Human Digestive SystemDocument37 pagesThe Human Digestive SystemEvangeline Basilan GarciaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology - October 2-4Document15 pagesAnatomy & Physiology - October 2-4Ayessa Camelle DumileNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesAnatomy and Physiologydaculareyndel04No ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesDigestive SystemSevdaNo ratings yet
- Food Nutrient Digestion AbsorptionDocument34 pagesFood Nutrient Digestion AbsorptionvinodhknatrajanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Human Digestive System: The Mouth and PharynxDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Human Digestive System: The Mouth and Pharynxitachi278No ratings yet
- Digestive System Breaks Down Food for Cellular UseDocument11 pagesDigestive System Breaks Down Food for Cellular UsePia Sempron100% (1)
- Running Head: 1: The Process of Human DigestionDocument5 pagesRunning Head: 1: The Process of Human Digestiongmelendez2No ratings yet
- Digestion and AbsorptionDocument3 pagesDigestion and AbsorptionDJ DannyNo ratings yet
- Maui Jullian Removed A MessageDocument3 pagesMaui Jullian Removed A MessageGio LlanosNo ratings yet
- DocDocument4 pagesDocAnonymous eMOb79RNt5No ratings yet
- Human Digestive SystemDocument29 pagesHuman Digestive SystemRagini Dubey100% (1)
- AnaphyDocument5 pagesAnaphyAnne BrazilNo ratings yet
- Body of HumanDocument14 pagesBody of HumanArlene Joy BuqueNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of GITDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of GITyassyrnNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument9 pagesDigestive SystemhlorenoNo ratings yet
- Colon's A & PDocument2 pagesColon's A & PGrace DonatoNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive SystemDocument11 pagesHuman Digestive SystemSyeda NafeezaNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive SystemDocument11 pagesHuman Digestive SystemSyeda NafeezaNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument26 pagesDigestive Systemapi-208253906100% (1)
- The Digestive System Study GuideDocument6 pagesThe Digestive System Study GuideMohamed ArafaNo ratings yet
- 5-Digestive SystemDocument8 pages5-Digestive Systemsuperjomar24No ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyernestoNo ratings yet
- Digestive System and Process of DigestionDocument4 pagesDigestive System and Process of DigestionSid QNo ratings yet
- What Is The Digestive System?Document9 pagesWhat Is The Digestive System?sri wiqayatul fajariyahNo ratings yet
- CP Dianne Ana PhysioDocument5 pagesCP Dianne Ana PhysioyangreinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The ColonDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The ColonMenchie Vivas-AlotNo ratings yet
- Organ Tubuh Manusia EnglishDocument6 pagesOrgan Tubuh Manusia EnglishL-Viva'An Ri-l SpqNo ratings yet
- Digestive SysytemDocument3 pagesDigestive Sysytemleomar3090No ratings yet
- Science Project - Digestive SystemDocument28 pagesScience Project - Digestive Systemapi-35222133565% (17)
- LiverDocument3 pagesLiverrahniNo ratings yet
- Ulcerative Colitis FinalDocument13 pagesUlcerative Colitis FinalAngelique100% (1)
- Master HerbalistDocument91 pagesMaster HerbalistVázsonyi Júlia50% (2)
- Vsmmc-Or 2009Document3 pagesVsmmc-Or 2009june allenNo ratings yet
- Digestive System DraftDocument39 pagesDigestive System DraftDiosa BakingNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Digestive SystemDocument9 pagesOverview of The Digestive SystemMehmet SaylıkNo ratings yet
- Modular Handout and Worksheet For April 19-21-2023Document5 pagesModular Handout and Worksheet For April 19-21-2023ccam88743No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Digestive System and Circulatory SystemDocument17 pagesAnatomy of The Digestive System and Circulatory SystemRafael Quieta Claro Jr.No ratings yet
- Tgs Bhs - InggrisDocument3 pagesTgs Bhs - InggrisErizka Aprilia P LNo ratings yet
- Diet Assessment 1 0Document7 pagesDiet Assessment 1 0DanRenwickNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - DigestionDocument17 pagesChapter 6 - DigestionTrisha100% (1)
- Digestive and Respiratory Systems OverviewDocument36 pagesDigestive and Respiratory Systems Overviewapa@No ratings yet
- ANATOMY & PHY OF THE GIDocument8 pagesANATOMY & PHY OF THE GIElsy MayjoNo ratings yet
- What Is The Digestive System?Document9 pagesWhat Is The Digestive System?sri wiqayatul fajariyahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of the Digestive SystemJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- Chemically Digested To Small Molecules That AreDocument14 pagesChemically Digested To Small Molecules That AreVarun WadhwaNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal SystemDocument3 pagesGastrointestinal SystemxhemhaeNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Digestion DefinitionDocument4 pagesDigestive System: Digestion Definitiondina aribahNo ratings yet
- What Is The Digestive SystemkeahDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Digestive SystemkeahJanine GuillermoNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System 1Document2 pagesThe Digestive System 1Sebastian RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Digestive System: Tongue MusclesDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Digestive System: Tongue Musclesbarbiegirl9497No ratings yet
- Excel BasicsDocument17 pagesExcel BasicsitsankurzNo ratings yet
- Yogesh NegiDocument2 pagesYogesh NegiitsankurzNo ratings yet
- Flexinet Solutions Appointment LetterDocument2 pagesFlexinet Solutions Appointment LetteritsankurzNo ratings yet
- ExcelDocument23 pagesExcelitsankurzNo ratings yet
- Physicst ScientistDocument6 pagesPhysicst Scientistitsankurz0% (1)
- Benefits of ReadingDocument5 pagesBenefits of ReadingitsankurzNo ratings yet
- Lumbering in CanadaDocument2 pagesLumbering in Canadaitsankurz67% (3)
- Subject Complaint Against Garbage Picker in My Shop Gaytri Computers, Main Bazaar, Sanjauli, Shimla - 6Document1 pageSubject Complaint Against Garbage Picker in My Shop Gaytri Computers, Main Bazaar, Sanjauli, Shimla - 6itsankurzNo ratings yet
- Vandana Kumari: Career ObjectiveDocument2 pagesVandana Kumari: Career ObjectiveitsankurzNo ratings yet
- Famous SikhDocument6 pagesFamous SikhitsankurzNo ratings yet
- Power StationsDocument13 pagesPower StationsitsankurzNo ratings yet
- AkbarDocument17 pagesAkbaritsankurzNo ratings yet
- Types of NutrientsDocument5 pagesTypes of NutrientsitsankurzNo ratings yet
- Types of Energy PicsDocument3 pagesTypes of Energy PicsitsankurzNo ratings yet
- Benefits of ReadingDocument5 pagesBenefits of ReadingitsankurzNo ratings yet
- NalandaDocument4 pagesNalandaitsankurzNo ratings yet
- FESTIDocument12 pagesFESTIitsankurzNo ratings yet
- India From 200bc To Ad300Document6 pagesIndia From 200bc To Ad300itsankurzNo ratings yet
- Application Form For Appointment of Supervisors (On Contract) in Labour BureauDocument2 pagesApplication Form For Appointment of Supervisors (On Contract) in Labour BureauitsankurzNo ratings yet
- AddDocument1 pageAdditsankurzNo ratings yet
- IELTS ESSAYS - Doc1Document2 pagesIELTS ESSAYS - Doc1itsankurzNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint AdvantagesDocument2 pagesPowerpoint AdvantagesitsankurzNo ratings yet
- Salochana PDFDocument2 pagesSalochana PDFitsankurzNo ratings yet
- QuestionnaireDocument1 pageQuestionnaireitsankurzNo ratings yet
- Importance Of Sleep - 6 Reasons To Get Enough Rest For Health And Well-BeingDocument9 pagesImportance Of Sleep - 6 Reasons To Get Enough Rest For Health And Well-BeingitsankurzNo ratings yet
- Bhandral NoticeDocument6 pagesBhandral NoticeitsankurzNo ratings yet
- Ankylosaurs, Ceratopsians, Dino-Birds & More: 5 Types of DinosaursDocument2 pagesAnkylosaurs, Ceratopsians, Dino-Birds & More: 5 Types of DinosaursitsankurzNo ratings yet
- Cancer 123Document10 pagesCancer 123itsankurzNo ratings yet
- Pics DishesDocument3 pagesPics DishesitsankurzNo ratings yet
- Tundra Land Taiga Land: Temperate Grasslands Desert and Semi DesertDocument2 pagesTundra Land Taiga Land: Temperate Grasslands Desert and Semi DesertitsankurzNo ratings yet
- Why Farts SmellDocument6 pagesWhy Farts SmellRonanNo ratings yet
- THE Gastro-Intestinal TractDocument51 pagesTHE Gastro-Intestinal TractandrewNo ratings yet
- Ben's Trevo Presentation SlideDocument69 pagesBen's Trevo Presentation SlideBenNo ratings yet
- Selective and Total Vagotomy Plus Pyloroplasty:: Comparative Gastric Secretion in Dogs Evesht, CharmlDocument5 pagesSelective and Total Vagotomy Plus Pyloroplasty:: Comparative Gastric Secretion in Dogs Evesht, CharmlAlexander VigenNo ratings yet
- Urogenital System of The VertebratesDocument51 pagesUrogenital System of The VertebratesFaye Nadine Cabural100% (1)
- NCP (Stoma)Document2 pagesNCP (Stoma)Markren BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 PT Science 6 MELCs BasedDocument4 pagesQuarter 2 PT Science 6 MELCs BasedG6 MapagmahalNo ratings yet
- Magnesium deficiency core instigator of pathology; transdermal Mg a new modalityDocument2 pagesMagnesium deficiency core instigator of pathology; transdermal Mg a new modalitykpraj01100% (1)
- Digestive System: MouthDocument3 pagesDigestive System: MouthTOt's VinNo ratings yet
- Science (Digestion) Notes/ActivityDocument4 pagesScience (Digestion) Notes/ActivityHi HelloNo ratings yet
- The Great Cholesterol MythDocument11 pagesThe Great Cholesterol Mythpantera neagră100% (1)
- Reflection On The Digestive SystemDocument2 pagesReflection On The Digestive SystemJulianne MercolitaNo ratings yet
- Explain Ingestion, Absorption, Assimilation, and Excretion S8LTDocument20 pagesExplain Ingestion, Absorption, Assimilation, and Excretion S8LTJoseph Gabriel Genuino Cruz100% (1)
- The Paleo Primer: A Second HelpingDocument59 pagesThe Paleo Primer: A Second HelpingPrimalBlueprintNo ratings yet
- DATABASE SPRINGER LINk 4Document81 pagesDATABASE SPRINGER LINk 4Melinda Tri PutriNo ratings yet
- Radio PillDocument4 pagesRadio PillsaranyaammuNo ratings yet
- Upper Primary Integrated Science Syllabus, Jan 2012 FinalDocument36 pagesUpper Primary Integrated Science Syllabus, Jan 2012 Finaldayas1979100% (4)
- Soal Bahasa Inggris Kelas Xi: Multiple ChoiceDocument14 pagesSoal Bahasa Inggris Kelas Xi: Multiple ChoiceSilmi TahariNo ratings yet
- Grossing, Staging, and Reporting: An Integrated Manual of Modern Surgical PathologyDocument6 pagesGrossing, Staging, and Reporting: An Integrated Manual of Modern Surgical PathologySOUMYA DEYNo ratings yet
- The Human Digestive SystemDocument20 pagesThe Human Digestive SystemAzfar ZackNo ratings yet
- Ferret Medicine and SurgeryDocument545 pagesFerret Medicine and SurgeryTayná P DobnerNo ratings yet
- Limitless - Upgrade Your Brain and Unlock Your Exceptional LifeDocument22 pagesLimitless - Upgrade Your Brain and Unlock Your Exceptional LifeJB Arquero100% (2)
- Drugs Used in IBDDocument44 pagesDrugs Used in IBDBegmuhammet BabayevNo ratings yet
- PBL NMR 1Document5 pagesPBL NMR 1andiNo ratings yet
- Tao Garden 5H-MA Smart Water-Drinking GuideDocument3 pagesTao Garden 5H-MA Smart Water-Drinking GuideUniversal Healing Tao100% (4)
- Intestinal ObstructionDocument12 pagesIntestinal ObstructionKamMappatao100% (1)
- A Guide To Aim Global Business - TanzaniaDocument37 pagesA Guide To Aim Global Business - TanzaniaWa Tu LeeNo ratings yet
- Intestinal ObstructionDocument48 pagesIntestinal ObstructionMahmoud AbuAwadNo ratings yet
- Git PathologyDocument113 pagesGit PathologyanggitaNo ratings yet
- Surgery SyllabusDocument23 pagesSurgery SyllabusNajmul Hassan MubarakNo ratings yet
- The Fast800 Diet: Discover the Ideal Fasting Formula to Shed Pounds, Fight Disease, and Boost Your Overall HealthFrom EverandThe Fast800 Diet: Discover the Ideal Fasting Formula to Shed Pounds, Fight Disease, and Boost Your Overall HealthRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (37)
- The Raw Food Detox Diet: The Five-Step Plan for Vibrant Health and Maximum Weight LossFrom EverandThe Raw Food Detox Diet: The Five-Step Plan for Vibrant Health and Maximum Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (22)
- The Diabetes Code: Prevent and Reverse Type 2 Diabetes NaturallyFrom EverandThe Diabetes Code: Prevent and Reverse Type 2 Diabetes NaturallyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Summary: Fast Like a Girl: A Woman’s Guide to Using the Healing Power of Fasting to Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Balance Hormones: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Fast Like a Girl: A Woman’s Guide to Using the Healing Power of Fasting to Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Balance Hormones: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Power Souping: 3-Day Detox, 3-Week Weight-Loss PlanFrom EverandPower Souping: 3-Day Detox, 3-Week Weight-Loss PlanRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Summary of Mary Claire Haver's The Galveston DietFrom EverandSummary of Mary Claire Haver's The Galveston DietRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Glucose Goddess Method: A 4-Week Guide to Cutting Cravings, Getting Your Energy Back, and Feeling AmazingFrom EverandGlucose Goddess Method: A 4-Week Guide to Cutting Cravings, Getting Your Energy Back, and Feeling AmazingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (59)
- Forever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellFrom EverandForever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellNo ratings yet
- Eat to Lose, Eat to Win: Your Grab-n-Go Action Plan for a Slimmer, Healthier YouFrom EverandEat to Lose, Eat to Win: Your Grab-n-Go Action Plan for a Slimmer, Healthier YouNo ratings yet
- Happy Gut: The Cleansing Program to Help You Lose Weight, Gain Energy, and Eliminate PainFrom EverandHappy Gut: The Cleansing Program to Help You Lose Weight, Gain Energy, and Eliminate PainRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (6)
- Keto Friendly Recipes: Easy Keto For Busy PeopleFrom EverandKeto Friendly Recipes: Easy Keto For Busy PeopleRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Allen Carr's Easy Way for Women to Lose Weight: The original Easyway methodFrom EverandAllen Carr's Easy Way for Women to Lose Weight: The original Easyway methodRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- The Arm: Inside the Billion-Dollar Mystery of the Most Valuable Commodity in SportsFrom EverandThe Arm: Inside the Billion-Dollar Mystery of the Most Valuable Commodity in SportsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (49)
- Metabolism Revolution: Lose 14 Pounds in 14 Days and Keep It Off for LifeFrom EverandMetabolism Revolution: Lose 14 Pounds in 14 Days and Keep It Off for LifeNo ratings yet
- Proteinaholic: How Our Obsession with Meat Is Killing Us and What We Can Do About ItFrom EverandProteinaholic: How Our Obsession with Meat Is Killing Us and What We Can Do About ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (19)
- Grit & Grace: Train the Mind, Train the Body, Own Your LifeFrom EverandGrit & Grace: Train the Mind, Train the Body, Own Your LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Lose Weight by Eating: 130 Amazing Clean-Eating Makeovers for Guilt-Free Comfort FoodFrom EverandLose Weight by Eating: 130 Amazing Clean-Eating Makeovers for Guilt-Free Comfort FoodRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Rapid Weight Loss Hypnosis: How to Lose Weight with Self-Hypnosis, Positive Affirmations, Guided Meditations, and Hypnotherapy to Stop Emotional Eating, Food Addiction, Binge Eating and MoreFrom EverandRapid Weight Loss Hypnosis: How to Lose Weight with Self-Hypnosis, Positive Affirmations, Guided Meditations, and Hypnotherapy to Stop Emotional Eating, Food Addiction, Binge Eating and MoreRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (17)
- The Candida Cure: The 90-Day Program to Balance Your Gut, Beat Candida, and Restore Vibrant HealthFrom EverandThe Candida Cure: The 90-Day Program to Balance Your Gut, Beat Candida, and Restore Vibrant HealthNo ratings yet
- How to Be Well: The 6 Keys to a Happy and Healthy LifeFrom EverandHow to Be Well: The 6 Keys to a Happy and Healthy LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Longevity Plan: Seven Life-Transforming Lessons from Ancient ChinaFrom EverandThe Longevity Plan: Seven Life-Transforming Lessons from Ancient ChinaNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Volumetrics Diet: Smart, Simple, Science-Based Strategies for Losing Weight and Keeping It OffFrom EverandThe Ultimate Volumetrics Diet: Smart, Simple, Science-Based Strategies for Losing Weight and Keeping It OffNo ratings yet
- Ultrametabolism: The Simple Plan for Automatic Weight LossFrom EverandUltrametabolism: The Simple Plan for Automatic Weight LossRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (28)
- The Toxin Solution: How Hidden Poisons in the Air, Water, Food, and Products We Use Are Destroying Our Health—AND WHAT WE CAN DO TO FIX ITFrom EverandThe Toxin Solution: How Hidden Poisons in the Air, Water, Food, and Products We Use Are Destroying Our Health—AND WHAT WE CAN DO TO FIX ITRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Brain Body Diet: 40 Days to a Lean, Calm, Energized, and Happy SelfFrom EverandBrain Body Diet: 40 Days to a Lean, Calm, Energized, and Happy SelfRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Think Yourself Thin: A 30-Day Guide to Permanent Weight LossFrom EverandThink Yourself Thin: A 30-Day Guide to Permanent Weight LossRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (22)
- Kintsugi Wellness: The Japanese Art of Nourishing Mind, Body, and SpiritFrom EverandKintsugi Wellness: The Japanese Art of Nourishing Mind, Body, and SpiritRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)