Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mental Status Examination
Uploaded by
Udaya SreeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mental Status Examination
Uploaded by
Udaya SreeCopyright:
Available Formats
MAMATA COLLEGE OF NURSING KHAMMAM Date: Time: SUBJECT: CLINICAL SPECIALTY PSYCHIATRY- II TOPIC : MENTAL STATUS EXAMINATION GUIDE:
MRS.ASHA KUMARI ASST. PROFESSOR PRESENTED BY: UDAYA SREE.G M.Sc. (N) II YEAR SEMINAR ON MENTAL STATUS EXAMINATION
MES is used to identify the persons present mental status. DEFINITION Assessment of general motor behavior, thought, emotional functioning along with evaluation of insight and judgment of the patients present status. -BIMLA KAPOOR, 2002 Systematic evaluation of behavior, emotions, cognitive functions of an individual. -K. LALITHA, 2007 ASPECTS OF MES 1. General behavior and appearance 2. Speech or talk 3. Mood or affect 4. Thought 5. Perceptual changes 6. Orientation 7. Memory 8. Judgment 9. Insight 10. Attention 11. Concentration GENERAL BEHAVIOUR Well kempt/ moderately kempt/ ill kempt/ overtly kempt Conscious/ cloudy/ withdrawn/ stupor/ drowsy/ unconscious or coma Nature of medication being received by the client The degree of cooperativeness/ non cooperativeness Understanding 1
Effect of drugs Alert/ woken up from sleep; looks comfortable/ uncomfortable Dressing: adequate/ any peculiarities Comprehension: intact/ impaired Mode of entry: come willingly/ persuaded/brought by using physical force Eye to eye contact: maintained/ difficult/ not maintained Psychomotor activity Attitudes towards examiner: cooperative/ guardedness/ hostility/ attentiveness Rapport: spontaneous/ difficult/ not established/ empathetic relationship Gestures: grimace/tics or mannerisms/ normal/odd/ exaggerated/ compulsion/ rituals Posture: open or closed / catatonic posture Physique and body built: height and weight Gait: staggering/ small steps/ confident walk Facial expressions: closed eyes, sad looks or happy looks on the face Motor activity: normal/ increased/decreased Extra pyramidal symptoms/ abnormal movements,(tics/ tremors/ akathisia) Sleep and eating pattern Pseudo seizures, possession state Compulsive acts, rituals or habits(eg nail biting) Reaction time
SPEECH OR TALK Initiation: spontaneous/ speaks when spoken to/ minimal/ mute/ hesitant or mumbled Talk: relevant/coherent/ spontaneous/ retarded/ irrelevant/ some times off targeted Tone and volume: tempo/ modulations/increased / decreased / low/ high/ normal pitch Speech activity: unusual pattern/ unusual words Rate: normal/ rapid or over talkative / talking little/ slow Productivity: monosyllabic/ pressured speech/ elaborate replies Stream: normal/ circumstantiality/ tangentiality Coherence: fully coherent/ loosening of association Others: rhyming/ echolalia/perseverance/ neologism/ clang association Sample of speech: responses to open-ended questions Speech pattern to: frighten/command/ distract
MOOD OR EFFECT It is a pervasive feeling tone which is sustained. Affect is the subjective immediate experience of emotions Appearance is the index of mind Intensity of happiness Sadness Irritability Anger Suspiciousness 2
Fear Worry Restlessness Labile Blurred Flattened moods Consistency of mood and related to the topic Shallowness/ superficiality/ absence of mood/ euphoria Reactivity Diurnal variations Congruity Liability Subjective and objective feeling
THOUGHT PROCESS Observation of the clients attitudes towards various people and things in the environment in the forms of ideas Stream: flight of ideas/ circumstantiality/ perseverance/thought block/ tangentiality/ clang association/neologism/racy thought/ unclear thinking/ poverty of thoughts or retardation of thoughts Content: Delusions Phobias Guilty Hypochondriasis Religiosity Obsessions Grandiose Form: normal/ formal thought disorders Ideas: hopelessness/worthlessness/ suicidal ideas/ helplessness Poverty/reference/ control/ bizarre/ persecution Doubts/ impulsive rituals Thoughts alienation phenomenon: thought insertion/ withdrawal/ thought broadcasting Obsessions/ compulsions/ thought images Abstract thinking: ability to assume a mental set voluntarily Shift voluntarily from one aspect of situation to another Keep in mind simultaneously the various aspects of a situations PERCEPTION 3
Illusions Hallucinations: auditory/ visual/ olfactory/gustatory/tactile Modalities Abnormal vestibular sensations Passivity (somatic 0 9 presence of strange sensations described by the patient as being imposed on the body by some external agency, patient will be passive recipient o Depersonalization/ derealisation o o o o o CONGNITIVE FUNCTIONS Level of consciousness: conscious or alert/ confusion/ clouding/delirium/ stupor/coma Time: correct time/ orientation to date/ day/ month/ year/season Place: area name/ city/ nation/ location Person: himself and recognizes self Attention: normally reacting to the call/ aroused/aroused with difficulty/sustained ( digits counting forward and back ward test) Concentration: normally sustained/ sustained with difficulty/ distractibility Name of months and weeks days( forward and back ward) Memory: Immediate memory: telling and ask the client to grasp and repeat immediately Recent memory: ask the client who brought him to hospital, when he came, give an address to memorize and ask to recall 15 minutes later Remote memory: personal events like marriage date, situations during marriage or the job, impersonal events- situation related to environment. Events related to illness- with what complaints the illness started, where he has taken treatment. Intelligence: It is the ability to think logically, act rationally and deal effectively with the environment Enquire about clients- scholastic performance general knowledge and general information Arithmetic ability Interpretation of proverbs Similarities and dissimilarities between paired objects Refer to psychologist to carry out intelligence tests INSIGHT It is the degree of awareness and understanding that the patient has regarding his illness. Clinical rating of insight on point scale Complete denial of illness Slight awareness of being sick and needing help, but denying it at the same time Awareness of being sick, due to something unknown in self Awareness of being sick but it is attributed to external or physical factors Intellectual insight: awareness of being ill and the symptoms or failures in social adjustment are due to own particular irrational feelings/ thoughts. 4
True emotional insight: the awareness leads to significant changes in the future behavior and personality
JUDGEMENT Judgement is based on his knowledge, educational levels, intelligence, alert. Judgement is made regard to client and his social setting. It is the ability to assess a situation correctly and act appropriately within that situation For example, testing by means of interpreting proverbs giving a problematic situation and asking for salvation of problem Types: Social judgement Test judgement- asking the client, to test certain situations Personal judgement ABSTRACTABILITY Similarity, differences, interpretation of given situation
SUMMARY Mental status examination is very important for to detect behavioral abnormalities of the client. It is used to identify the persons present mental status. It consist of general behavior, speech, mood, perceptions, orientation, memory, judgement, insight, attention and concentration. BIBLIOGRAPHY
K.P. Neeraja. Essentials of mental health and psychiatric nursing, Volume-1; Jayapee brothers publication, 2008 Bimla Kapoor. Psychiatric nursing, Volume-2, Pearsons publications, 2005 Sreevani. Psychiatric nursing, Volume-1, Suresh kumar publications 2004 Mary C. Townson. Psychiatric and mental health nursing, Jayapee brothers publications, 2009
Madhavi K. Essentials of mental health and psychiatric nursing for nurses, Vijams series publications, 2009: 34- 42
5
MAMATA COLLEGE OF NURSING KHAMMAM Date: Time: SUBJECT: CLINICAL SPECIALTY PSYCHIATRY- II TOPIC : MENTAL STATUS EXAMINATION GUIDE: MRS.ASHA KUMARI ASST. PROFESSOR PRESENTED BY: UDAYA SREE.G M.Sc. (N) II YEAR
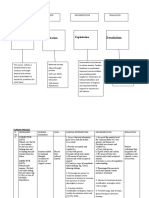
MASTER PLAN ON MENTAL STATUS EXAMINATION I. II. III. Introduction Definition Aspects of mental status examination
i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. vii. viii. ix. x. xi. General behavior and appearance Speech or talk Mood or affect Thought Perceptual changes Orientation Memory Judgment Insight Attention Concentration
IV. V.
Summary Bibliography
6
You might also like
- Mental Status ExaminationDocument35 pagesMental Status ExaminationSANU RAMASWAMY80% (10)
- Mental Status ExaminationDocument5 pagesMental Status ExaminationNhelia Santos Bañaga100% (3)
- Mental Status Examination FormatDocument7 pagesMental Status Examination FormatMala Rasaily100% (3)
- Mental Status Examination: Identification DataDocument5 pagesMental Status Examination: Identification Datailakkiya ilakkiyaNo ratings yet
- MMSE1Document4 pagesMMSE1nikithaa saravananNo ratings yet
- AUD: Understanding Alcohol Use DisorderDocument28 pagesAUD: Understanding Alcohol Use DisorderAkhilesh Parab0% (2)
- Mental Status Examination: Thwisha ShettyDocument4 pagesMental Status Examination: Thwisha ShettyThwisha Shetty100% (1)
- Mental status examination reveals schizophrenia symptoms in 46-year old maleDocument6 pagesMental status examination reveals schizophrenia symptoms in 46-year old maleMeenakshi Antil100% (1)
- OCD Case StudyDocument51 pagesOCD Case StudyEchuserang Froglet0% (1)
- Psychiatric Case PresentationDocument73 pagesPsychiatric Case PresentationRechie Gallo50% (2)
- Mental Status ExamDocument18 pagesMental Status Examlouradel100% (1)
- Case History and MSEDocument11 pagesCase History and MSESonia Soans100% (6)
- Mse Alcohol DependenceDocument4 pagesMse Alcohol DependenceFlavouring vlogs100% (1)
- Case Study on Severe Depression with PsychosisDocument33 pagesCase Study on Severe Depression with PsychosisPallavi KharadeNo ratings yet
- Process Recording: I Demographic DataDocument27 pagesProcess Recording: I Demographic DataKavita kumari100% (2)
- Case StudyDocument22 pagesCase StudyAru Verma0% (1)
- Mental State ExaminationDocument26 pagesMental State ExaminationAbdul Rahman Al Helou100% (1)
- Mrs. Sunanda's History and Mental Status Exam for DepressionDocument12 pagesMrs. Sunanda's History and Mental Status Exam for DepressionamitNo ratings yet
- Mental Status ExaminationDocument5 pagesMental Status Examinationdrhusnafadzil96% (23)
- Outline of Mental Status ExaminationDocument10 pagesOutline of Mental Status ExaminationMohammed Hosen100% (1)
- Somatoform DisordersDocument6 pagesSomatoform Disordersgeorgeloto12No ratings yet
- Psy Case StudyDocument81 pagesPsy Case StudyIOM BNSNo ratings yet
- Catatonia 171007211242Document49 pagesCatatonia 171007211242onen patoNo ratings yet
- MSE Acute PsychosisDocument4 pagesMSE Acute Psychosisilakkiya ilakkiyaNo ratings yet
- Process Recording FinalDocument32 pagesProcess Recording FinalRiteka SinghNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric History TakingDocument6 pagesPsychiatric History TakingNurul Nadzri100% (1)
- Mohd Rafi'uddin Hamidon 01200910 0070Document13 pagesMohd Rafi'uddin Hamidon 01200910 0070Mohd Rafi50% (2)
- Ocd CsDocument19 pagesOcd CsNiharika savita100% (3)
- Alcohol Dependence SyndromeDocument6 pagesAlcohol Dependence Syndromemaakkan100% (2)
- Case Presentation On CannabisDocument85 pagesCase Presentation On CannabisKisna BhurtelNo ratings yet
- 1.02 Psychiatric History and Mental Status Examination PDFDocument4 pages1.02 Psychiatric History and Mental Status Examination PDFEp-ep Jeffrey Sibayan Ramos100% (1)
- Understanding The Mental Status Examination: With The Help of VideosDocument38 pagesUnderstanding The Mental Status Examination: With The Help of Videosdev100% (1)
- The Psychiatric Mental Status Exam (MSE)Document4 pagesThe Psychiatric Mental Status Exam (MSE)dev100% (1)
- Case StudyDocument17 pagesCase Studyapi-508597583No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Dissociative... 2 JanDocument18 pagesNursing Care Plan Dissociative... 2 Janannu100% (1)
- Psychotherapy 2Document28 pagesPsychotherapy 2lehsem20006985No ratings yet
- Alcoholism Care PlanDocument11 pagesAlcoholism Care Planilakkiya ilakkiyaNo ratings yet
- Process Recording 2Document7 pagesProcess Recording 2Hardeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Tamboli Amit S. First Year MSC (Psychiatric) Nursing Mimh PuneDocument25 pagesPresented By: Tamboli Amit S. First Year MSC (Psychiatric) Nursing Mimh PuneAmit Tamboli100% (1)
- Mental Status ExamDocument2 pagesMental Status Examkristel_nicole18yahoNo ratings yet
- AtpdDocument48 pagesAtpddrkadiyala2100% (1)
- MSE Sample PDFDocument5 pagesMSE Sample PDFSam Raven AndresNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Case PresentationDocument52 pagesPsychiatric Case PresentationdoreenNo ratings yet
- Alcoholic CaseDocument14 pagesAlcoholic Caseharshitha dNo ratings yet
- Legal Aspect of Mental Health NursingDocument37 pagesLegal Aspect of Mental Health NursingRita Pokharel80% (5)
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With SchizophreniaDocument14 pagesNursing Care Plan For A Patient With SchizophreniaJerilee SoCute WattsNo ratings yet
- Recreational Therapy Presentee: Sukhdeep Kaur Msc. (N) 1 YearDocument26 pagesRecreational Therapy Presentee: Sukhdeep Kaur Msc. (N) 1 YearSatbir GillNo ratings yet
- Mental Status ExaminationDocument13 pagesMental Status ExaminationJosé Ramón Pérez-Accino100% (1)
- Case StudyDocument9 pagesCase StudyKavita KavNo ratings yet
- Case Study On OCD: Sri Lakshmi College of NursingDocument49 pagesCase Study On OCD: Sri Lakshmi College of NursingveereshNo ratings yet
- Causes and Treatment of ManiaDocument11 pagesCauses and Treatment of ManiaGEETA MOHAN100% (2)
- Format MSEDocument3 pagesFormat MSESubir Banerjee0% (1)
- PTSD Case Study 3bsn 6Document20 pagesPTSD Case Study 3bsn 6Danielle Quemuel Viray100% (3)
- History and MSEDocument13 pagesHistory and MSEG.Sangeetha bnchNo ratings yet
- Case On Mental RetardationDocument31 pagesCase On Mental Retardationassej_mine2491% (22)
- Psychiatric History & MSE: Bivin JB Department of Psychiatric Nursing Mar Baselios College of NursingDocument56 pagesPsychiatric History & MSE: Bivin JB Department of Psychiatric Nursing Mar Baselios College of NursingHardeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Psychosocial Assessment Techniques for Psychiatric NursingDocument44 pagesPsychosocial Assessment Techniques for Psychiatric NursingHershey Cordero Briones100% (1)
- Mental Health Assessment GuideDocument5 pagesMental Health Assessment GuideJaka Carina CalicaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Psychiatric History Taking and Mental Status ExaminationDocument56 pagesUnderstanding Psychiatric History Taking and Mental Status ExaminationHardeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Consumer Protection ActDocument5 pagesConsumer Protection ActUdaya Sree100% (4)
- ManiaDocument12 pagesManiaUdaya Sree100% (4)
- Legal and Ethical Issues in NursingDocument35 pagesLegal and Ethical Issues in NursingUdaya Sree86% (7)
- Hospital Planing and OrganizationDocument15 pagesHospital Planing and OrganizationUdaya SreeNo ratings yet
- EdemaDocument3 pagesEdemaUdaya SreeNo ratings yet
- Introduction of AdministrationDocument12 pagesIntroduction of AdministrationUdaya Sree100% (1)
- Seminar On Committee ReportsDocument11 pagesSeminar On Committee ReportsUdaya Sree100% (2)
- Health Care Delivery SystemDocument16 pagesHealth Care Delivery SystemUdaya Sree100% (4)
- Ethical and Legal Issues in Mental Health NursingDocument18 pagesEthical and Legal Issues in Mental Health NursingUdaya Sree80% (5)
- Legal and Ethical IssuesDocument22 pagesLegal and Ethical IssuesUdaya Sree100% (4)
- Seminar On Cancer: Submitted To Submitted byDocument13 pagesSeminar On Cancer: Submitted To Submitted byUdaya SreeNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric EmergenciesDocument10 pagesPsychiatric EmergenciesUdaya Sree100% (1)
- Human Resource For HealthDocument19 pagesHuman Resource For HealthUdaya Sree100% (3)
- Norms of Staffing in NursingDocument34 pagesNorms of Staffing in NursingUdaya Sree86% (22)
- Credentialing Process ExplainedDocument51 pagesCredentialing Process ExplainedUdaya Sree100% (2)
- INFECTION CONTROL: PREVENTING CROSS-CONTAMINATIONDocument23 pagesINFECTION CONTROL: PREVENTING CROSS-CONTAMINATIONUdaya Sree67% (3)
- Disaster ManagementDocument15 pagesDisaster ManagementUdaya Sree100% (1)
- Geriatic ConsiderationsDocument19 pagesGeriatic ConsiderationsUdaya SreeNo ratings yet
- Accountability in NursingDocument14 pagesAccountability in NursingUdaya Sree100% (2)
- Ascension 2010 04Document12 pagesAscension 2010 04José SmitNo ratings yet
- How to Excel at Math and ScienceDocument3 pagesHow to Excel at Math and Sciencemohdzamrimurah_gmail100% (1)
- Students' Preferred Learning Styles & Academic Performance: January 2016Document3 pagesStudents' Preferred Learning Styles & Academic Performance: January 2016Oliver C. ReromaNo ratings yet
- Constructivist Theory in Teaching MTB-MLEDocument4 pagesConstructivist Theory in Teaching MTB-MLEHya Balasabas - Dagangan100% (2)
- Maginhawa Perceptions StudiedDocument26 pagesMaginhawa Perceptions StudiedLaraNo ratings yet
- Pedagogy of Confidence - High Operational PracticesDocument8 pagesPedagogy of Confidence - High Operational Practicesapi-324270925No ratings yet
- Differences Between L1 and L2 AcquisitionDocument2 pagesDifferences Between L1 and L2 AcquisitionYazid YahyaNo ratings yet
- AI For BusinessDocument45 pagesAI For BusinessFaraz SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- MC Multiple Choice QuizDocument8 pagesMC Multiple Choice QuizRavishankar UlleNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: Activity 1: You Are To Answer The Following QuestionsDocument24 pagesUnit 4: Activity 1: You Are To Answer The Following QuestionsHarun IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Learning Episode 14 Utilizing Learning Management Systems: Participate and AssistDocument4 pagesLearning Episode 14 Utilizing Learning Management Systems: Participate and AssistLovely Rose MorenoNo ratings yet
- 1965, Pre-Writing The Stage of Discovery in The Writing ProcessDocument8 pages1965, Pre-Writing The Stage of Discovery in The Writing ProcessMarcelo Gules BorgesNo ratings yet
- Roles of Assessment in TeachingDocument8 pagesRoles of Assessment in Teachingdayah3101No ratings yet
- Department of Education: Detailed Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesDepartment of Education: Detailed Lesson PlanMelody Bagani FernandezNo ratings yet
- 7 E's LP Exemplar Bio. 8Document3 pages7 E's LP Exemplar Bio. 8ELLEN B.SINAHON100% (7)
- Studying Locally and Studying AbroadDocument2 pagesStudying Locally and Studying AbroadNixon ErnestNo ratings yet
- Educ 359 - Intro To Ell - Observation ChecklistDocument5 pagesEduc 359 - Intro To Ell - Observation Checklistapi-328213086No ratings yet
- Three Phases in Decision Making ProcessDocument42 pagesThree Phases in Decision Making Processvarunpatni10No ratings yet
- Educ 312 Prelim ModuleDocument32 pagesEduc 312 Prelim ModuleAljohn Sechico BacolodNo ratings yet
- Presentation Unpacking The MELCs For Module DevelopmentDocument30 pagesPresentation Unpacking The MELCs For Module DevelopmentLedie Lou Superales100% (5)
- Mandik Chapter 1Document21 pagesMandik Chapter 1GültekinNo ratings yet
- Understanding Meaning: Defining Expectations in Vocabulary TeachingDocument20 pagesUnderstanding Meaning: Defining Expectations in Vocabulary TeachingSolvex GevgelijaNo ratings yet
- Humss-Culminating Activity: Tala Senior High SchoolDocument3 pagesHumss-Culminating Activity: Tala Senior High SchoolRobert SamonteNo ratings yet
- University of West Alabama COE 5E Lesson Plan: Teacher: Date: Subject Area / Course / Grade Level: Materials: StandardsDocument2 pagesUniversity of West Alabama COE 5E Lesson Plan: Teacher: Date: Subject Area / Course / Grade Level: Materials: Standardsapi-618311699No ratings yet
- Homeroom Guidance (HG) Learning Activity Sheet (LAS) For Grade 8 Quarter 1-Week 1 To 7Document30 pagesHomeroom Guidance (HG) Learning Activity Sheet (LAS) For Grade 8 Quarter 1-Week 1 To 7Joy Victoria DasmariñasNo ratings yet
- Task Based Language LearningDocument2 pagesTask Based Language LearninglucianaparanoidNo ratings yet
- Art Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesArt Lesson Planapi-297642855No ratings yet
- Children's Assessment 1Document18 pagesChildren's Assessment 1ochieng onyinoNo ratings yet
- Flowcharts LPDocument7 pagesFlowcharts LPapi-292491710No ratings yet
- University of Rizal SystemDocument3 pagesUniversity of Rizal SystemJhonric M. LugtuNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (327)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsNo ratings yet
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (41)
- The Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossFrom EverandThe Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)