Professional Documents
Culture Documents
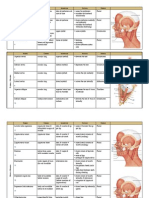
Lower Limb Anatomy Tables
Uploaded by
kep1313Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lower Limb Anatomy Tables
Uploaded by
kep1313Copyright:
Available Formats
SUMMARY: HIP: Flex: Iliopsoas, rectus femoris, sartorius Extend: hamstring, gluteus maximus Abduct: gluteus medius and
and minimus Rotate laterally: obturator internus, gemelli, piriformis Adduct: adductor muscles of medial thigh KNEE Flex: hamstrings, gracilis, Sartorius Extend: quadriceps femoris Rotate medially: semitendinosus, semimembranosus Rotate laterally: biceps femoris ANKLE Plantarflex: gastrocnemius, soleus, tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallucis longus Dorsiflex: tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum longus, extensor hallucis longus, fibularis tertius INTERTARSAL Evert: fibularis longus, fibularis brevis, fibularis tertius Invert: tibialis anterior, tibialis posterior METATARSOPHALANGEAL Flex: Interossei, lumbricals Extend: extensor digitorum longus, extensor digitorum brevis Abduct: dorsal interossei Adduct: plantar interossei INTERPHALANGEAL Flex: flexor digitorum longus, flexor digitorum brevis Extend: extensor digitorum longus, extensor digitorum brevis
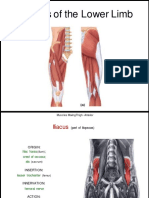
Muscle Iliacus: large triangular muscle Psoas
Proximal attachment Upper 2/3 of concavity of iliac fossa and iliac crest Transverse processes of lumbar vertebrae, sides of bodies of T12-L5 vertebrate
Distal attachment Lateral side of tendon of psoas major, lesser trochanter of femur Lesser trochanter of femur
Nerve supply Branches of femoral nerve Lumbar plexus via ventral branches of L2-L4 nerves (ventral rami of lumbar nerves L1-L3)
Action Flex thigh at hip joint
Flex thigh at hip joint
Iliopsoas
Passes under inguinal ligament to attach to lesser trochanter of femur
Flexes thigh at hip joint
Muscles of gluteal region: Muscle Gluteus maximus: large quadrilateral muscles which forms prominence of buttock and covers Proximal attachment Ilu posterior to posterior gluteal line, dorsal surface of sacrum and coccyx, and Distal attachment Iliotibial tract, gluteal tuberosity of femur Nerve supply Inferior gluteal nerve Action Extends thigh at hip LABS 1
ischial tuberosity Gluteus medius: triangular muscles between maximus and minimus Gluteus minimus: - deep to gluteus medius Tensor fasciae latae
sacrotuberous ligament Gluteal surface of ala of ilium
Greater trochanter
Superior gluteal nerve
Abducts thigh at hip
Bone of ala of ilium ASIS and anterior iliac crest
Obturator internus
Piriformis: triangular muscle passes through greater sciatic foramen; separates inferior and superior gluteal vessels and nerves Quadratus femoris: 4 sided muscles just inferior to tendon of obturator inters
Pelvic surface of obturator membrane and surrounding bones Anterior surface of sacrum (pelvic surface)
Greater trochanter Iliotibial tract that attaches to lateral condyle of tibia Greater trochanter Greater trochanter
Superior gluteal nerve Superior gluteal nerve
Abducts thigh at hip Abducts thigh at hip; Stabilizes knee in extension Laterally rotates thigh at hip joint Laterally rotates thigh
Don't need to know Don't need to know
Lateral border of ischial tuberosity
Intertrochanter ic crest
Don't need to know
Laterally rotates thigh at hip joint
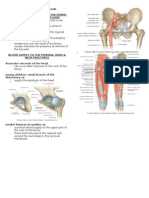
Iliotibial band: thickened band of fascia lata extending from the tubercle of ilia crest to the lateral condyle of the tibia. Serves as tendon fro the gluteus maximus and TFL. Attaches inferiorly to the lateral plateau of the tibia Vascularization of gluteal region: Descending aorta bifurcates into the common iliac artery which provides blood to lower extremities Common iliac bifurcates into the internal and external iliac arteries External iliac artery: becomes femoral Internal iliac artery is major blood supply to pelvis and gluteal regions Internal iliac splits into superior and inferior gluteal arteries o Superior gluteal artery: Supplies blood to obturator internus and piriformis muscles Supplies blood to muscles and skin in gluteal region, including TFL o Inferior gluteal artery: terminal branch of internal iliac artery Supplies blood to muscles of gluteal region and forms anastomoses with blood vessels around hip joint Major branches of sacral plexus: Anterior: 1. Pudendal 2. Tibial: innervates posterior thigh muscles, posterior leg muscles, and foot, forms the sciatic nerve with common fibular nerve Posterior 1. Superior gluteal: innervate gluteus medius and minimus (L4-S1) 2. Inferior gluteal: innervates gluteus maximus (L5-S2) 3. Common fibular: portion of sciatic nerve that innervates lateral and anterior muscles compartments of leg
Posterior compartment of thigh
Refereed to as hamstrings, can also rotate the knee and attached proximally to ischial tuberosity (except short head) Supplied by deep (femoral) artery of thigh and the femoral artery Proximal Attach Ischial tuberosity Lateral supracondylar line of femur Ischial tuberosity Ischial tuberosity Distal attachment Head of fibula Head of fibula Nerve supply Tibial division of sciatic nerve Common fibular division of sciatic nerve Tibial nerve Action Extends thigh at hip; flexes leg at knee Flexes leg at knee joint Labs 1 1
Muscle Biceps femoris, long head Biceps femoris, short head Semimembranosus: flat tendon extending length of proximal half Semitendinosus: has a cord like tendon on its distal half
Posterior part of medial condyle of tibia Medial surface of superior part of tibia
Extends thigh at hip, flexes leg at knee Extends thigh at hip, flexes leg at knee
Tibial nerve
Anterior compartment of the thigh Include the quadriceps which attach to the patella by the quadriceps femoris tendon and to the tibia by the patellar ligament Primarily extensors the leg at the knee 2 secondarily flex the thigh at hip Innervated by femoral nerve Supplied by femoral artery and deep artery of the thigh Iliopsoas: starts as 2 muscles from posterior abdominal wall, fuses into one muscle at about level of inguinal ligament and attaches the lesser trochanter of femur. Deepest muscle of femoral triangle Femoral triangle: o Boundaries: Inguinal ligament: base of triangle Sartorius: lateral boundary Adductor longus muscle: medial boundary o Inferiorly, fascial sleeve extends rom apex of triangle and continuous with adductor canal o Contains Femoral nerve and Femoral artery, vein, lymphatics at they pass beneath inguinal ligament and to the anterior thigh o Contains: (from lateral to medial) N - femoral nerve: originates as branch from lumbar plexus A- femoral artery: continuation of external iliac artery V - Femoral vein: continues at the external iliac vein E - empty space (femoral canal) L - Lymphatics o Femoral sheath: contains femoral vessels, femoral branch of genitofemoral nerve and lymphatics Femoral nerve is outside this sheath Muscle Sartorius: longest muscles, upper 1/3 forms lateral boundary of femoral triangle Rectus femoris Vastus lateralis: head of quads on lateral side of ant Proximal attachment ASIS Distal attachment Superior part of medial surface of tibia Quadriceps femoris tendon Quadriceps femoris tendon Nerve Femoral nerve Femoral nerve Femoral nerve Action Flexes and laterally rotates thigh, flexes leg Extends leg, flex thigh Extends leg Labs 2
ASIS, ilium superior to acetabulum Greater trochanter and lateral lip of linea
2 2
thigh Vastus medialis: head of quads on medial side of ant thigh Vastus intermedius: deep head of quads
aspera of femur Intertrochanteric line and medial lip of linea aspera of femur Femoral shaft, upper 2/3 of anterior and lateral surfaces
Quadriceps femoris tendon Quadriceps femoris tendon
Femoral nerve Femoral nerve
Extends leg
Extends leg
Medial compartment of thigh Primarily adductors the thigh at hip Most innervated by obturator nerve Supplied by obturator artery and dep artery o thigh Muscle Pectineus: forms part of posterior wall of femoral triangle. Located on floor of femoral triangle lateral to adductor longus and medial to Iliopsoas. Femoral vessels and greater saphenous vein lie anteriorly. Adductor brevis: triangular muscle deep to adductor longus, Adductor longus: triangular muscle, most anterior of adductors in same plane as pectineus Adductor magnus: fan shaped muscle Proximal attachment Superior ramus of pubis Distal attachment Pectineal line of femur inferior to less trochanter Nerve Femoral nerve, may receive branch from obturator nerve Action Adducts and flexes thigh Labs 2
Body and inferior ramus of pubis Body of pubis inferior in pubic crest Adductor: ischiopubic ramus Hamstring: ischial tuberosity Body and inferior ramus of pubis External surface of obturator membrane
Linea aspera of femur
Obturator
Adducts thigh at hip Adducts and medially rotates thigh Adducts thigh Hamstring: extends thigh Adducts thigh; flexes leg Lateral rotates thigh
Linea aspera
Obturator
Gracilis: long strap like, superficial muscle on medial side of thigh Obturator externus: seen between superior part of adductor magnus and superior pubic ramus
Adductor: linea aspera, femoral shaft Hamstring: adductor tubercle of femur Medial surface of proximal tibia Trochanteric fossa of femur
Adductor: obturator Hamstring: tibial Obturator
Don't need to know
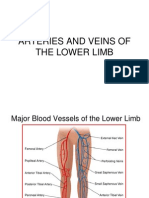
Major arteries of thigh: Obturator: arises fro internal iliac artery has anterior and posterior branches, passes through obturator foramen Femoral: continuation of external iliac artery with numerous branches to perineum, hip, thigh and knee Deep artery of thigh: arises from femoral artery; supplies hip and thigh
Ligaments: Sacrotuberous ligament (Lab 1): stout ligament spanning from ischial tuberosity and dorsum of the sacrum Posterior (flexor) compartment of leg Primarily flexors of foot at ankle (plantarflexion) and flexors of toes Several can flex the leg at knee or invert the foot Innervated by tibial nerve Posterior tibial artery (popliteal artery divides in to anterior and posterior tibial arteries) Muscle Gastrocnemius: large superficial muscle of calf region Proximal attachment Lateral head: lateral condyle of femur Medial head: popliteal surface of femur, superior to medial condyle of femur Posterior aspect of fibular head and shaft, posterior aspect of tibia Superior to lateral femoral condyle Distal attachment Posterior surface of calcaneus bone via calcaneal tendon Nerve Tibial Action Plantar flexes foot at ankle, flexes leg at knee Labs 3
Soleus: large muscle of calf deep to gastrocnemius Plantaris: very small muscle, long tendon and small muscle belly Deep Popliteus: triangular muscle of posterior compartment just below knee and deeply position, apex of muscle points laterally Flexor hallucis longus: tendon passes behind medial malleolus posterior to FDL Flexor digitorum longus: tendon lies between Tibialis posterior and FHL tendons at medial malleolus Tibialis posterior: tendon is first to pass posterior to medial malleolus
Posterior surface of calcaneus bone via calcaneal tendon
Tibial
Plantar flexes foot at ankle
Posterior surface of calcaneus bone via calcaneal tendon
Tibial
Identify only
Lateral condyle of femur and lateral meniscus
Posterior surface of tibia
Tibial
Unlocks knee at beginning of flexion = laterally rotate femur on fixed tibia, or medially rotate tibia on fixed femur Flexes big toe
Posterior surface of fibula and interosseous membrane
Distal phalanx of big toe
Tibial
Posterior surface of Tibia
Distal phalanges of lateral 4 digits (digits 2-5)
Tibial
Flexes lateral 4 toes
Interosseous membrane, posterior surface of tibia and fibula
Navicular, cuneiform bones, metatarsals 2-4
Tibial
Plantar flexes foot at ankle and inverts foot at subtalar joints
Anterior (extensor) compartment of leg Primarily extensors of foot at the ankle (dorsiflexion) and extensors of toes Several can invert foot, and fibularis tertius can weakly evert the foot
Muscle
Innervated the by the deep fibular nerve (common fibular nerve divides into superficial and deep branches) Supplied by anterior tibial artery Proximal attachment Lateral condyle and surface of tibia, interosseous membrane Fibula and lateral tibial condyle Anterior surface of fibula and interosseous membrane Distal part of fibula Distal attachment Medial cuneiform and base of metatarsal 1 Nerve Deep fibular nerve Action Dorsiflexes foot at ankle and inverts foot at subtalar joint Labs 3
Tibialis anterior: large muscle, its tendon passes on medial side of dorsum of foot to insert in tarsal bone Extensor digitorum longus: 4 tendons attaching to phalanges 2-6 Extensor hallucis longus: tendon lies between tibialis anterior (medial) and EDL (lateral) Fibularis (peroneus) tertius: lowest arising part of EDL that sends tendon to tuberosity of 5th metatarsal
Middle and distal phalanges of digits 2-5 (lateral 4 digits) Distal phalanx of great toe
Deep fibular nerve Deep fibular nerve
Extends lateral 4 toes
Extends great toe and dorsiflexes at ankle
Base of 5th metatarsal
Deep fibular nerve
Everts foot at ankle
Lateral (fibular) compartment of leg Primarily able to evert the foot (supination -plantar surface faces laterally) and weakly plantar flex foot at ankle Innervated by superficial fibular nerve Supplied by fibular artery (branch of posterior tibial artery) Muscle Fibularis (peroneus) longus: lies superficial to FB muscles, tendon wraps around sole of foot from lateral to medial to insert on tarsal bone Fibularis (peroneus) brevis: lies deep to fibularis longus, attaches to tuberosity on base of 5th metatarsal Proximal attachment Head and superior 2/3 of lateral surface of fibula Inferior 2/3 of lateral surface of fibula Distal attachment Base of 1st metatarsal and medial cuneiform Nerve Superficial fibular nerve Action Everts foot at subtalar joints and plantar flexes foot at ankle Labs 3
Dorsal surface of tuberosity on lateral side of 5th metatarsal
Superficial fibular nerve
Everts foot at subtalar joints and plantar flexes foot at ankle
Dorsum (extensor) surface of foot Muscle Extensor digitorum brevis: dorsum of foot under long tendons, arise from lateral side 4 tendons for digits 2-5 Extensor hallucis brevis: medial head of EDB with tendon going to big toe Plantar (flexor) surface of foot
Proximal attachment Lateral calcaneus Lateral calcaneus
Distal attachment Digits 2-4
Nerve Deep fibular nerve Deep fibular nerve
Action Extends digits 2-4 (extension of middle 3 toes) Extension of big toe
Labs 3
Digit 1
Muscle Flexor digitorum brevis: deep to plantar aponeurosis arising from calcaneus and giving rise to 4 tendons Quadratus plantae: muscle parallel and dep to FDB, inserts into tendon of FDL, lateral plantar artery and nerve pass obliquely between FDB and QP Abductor hallucis: Abductor digiti minimi Flexor hallucis brevis Flexor digiti minimi brevis Adductor hallucis Lumbricals (4 muscles) Dorsal interossei Plantar interossei
Proximal Distal attachment attachment Calcaneus Middle phalanges tuberosity of lateral 4 digits
Nerve Tibial nerve
Action Flexes lateral 4 digits
Labs 4
Plantar surface of calcaneus
Tendon of flexor digitorum longus
Tibial nerve
Assist FDL in flexing digits 25
Large muscle on medial side of the sole, visible and palpable as prominent bulge. Belongs to most superficial layer of muscles of foot Relatively slender muscles in lateral part of the sole of foot. First layer of muscle of foot Layer 3, medial side of foot, plantar surface s of cuboid and lateral cuneiforms to proximal phalanx of first digit Layer 3, attaches proximally to base of metatarsal 5 and distally to base of proximal phalanx 5, lateral side of foot Layer 3, between FHB and FDMB, 2 heads: transvers and oblique 4 slender muscles, 2 layer. Name is sequence from the medial aspect of the foot. First lumbricals is most medial of the 4. 4 muscles arranged around 2nd toe as central axis of foot, layer 4 3 muscles arranged around 2nd toe at central axis of foot, layer 4
Gait
Involves swing phase and stance phase (when foot is weight bearing) Walking produces pelvic tilt and rotation, hip and knee flexion/extension and a smoothly coordinated interaction btwn pelvis, hip, knee, ankle, and foot Swing phase o Occurs rom pre-swing toe-off (TO) position, with acceleration though the initial swing the mid-sing (MSW) and terminal swing phase o Limb decelerates to the heel strike (HS) phase when foot meets the ground Stance phase o Occurs from the heel strike position to the flat foot (FF) position, to the mid-stance (MST) phase, and then the heel off (HO) o Forward thrust to toe-off position and the heels trike position for the opposite foot
Gait cycle Toe off (TO) to Mid swing (MSW)
MSW to heel strike (HS) HS to flat foot (FF)
Muscle actions Hip flexors accelerate thigh Knee is flexed Foot dorsiflexed to clear ground Knee extended rapidly Foot dorsiflexed Hip flexed Knee extended Ankle is neutral position but foot plantarflexes flat on ground Limb extensors stabilize weight bearing joints
Phase Swing
Swing Stance
FF to mid stance (MST)
MST to heel-off (HO)
HO to Toe-Off
Body moves forward Extensors support limb while other limb is in swing phase Hip abductors control pelvic tilt Body continues forward Planar flexors contract as weight moves from heel to metatarsal heads Hip abductors control pelvic tilt Push off as opposite heel strikes ground Plantarflexors exert thrust Knee flexes Foot goes into dorsiflexed position at beginning of HO to plantarflexed as toes push off at TO Hip abductors relax while hip flexors ready for swing face
Stance
Stance
Stance
You might also like
- Mnemonics AnatomyDocument32 pagesMnemonics Anatomyjspradeepscribd75% (4)
- Table of Upper Limb JointsDocument3 pagesTable of Upper Limb JointsVijay Pradeep100% (2)
- Myofascial Muscle Chains - P. Jonckheere, Et Al., (Trigger, 1998) WWDocument308 pagesMyofascial Muscle Chains - P. Jonckheere, Et Al., (Trigger, 1998) WW1cucu0100% (5)
- Myofascial Meridians Trigger Points Tend To Develop Along "Myofascial Meridians"Document4 pagesMyofascial Meridians Trigger Points Tend To Develop Along "Myofascial Meridians"Corduneanu MonalisaNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy CheatsheetDocument302 pagesGross Anatomy CheatsheetNobody2015100% (1)
- Muscles of Lower LimbsDocument7 pagesMuscles of Lower LimbsFong Yu-hengNo ratings yet
- Table of Lower Limb Muscles 01Document6 pagesTable of Lower Limb Muscles 01Nick JacobNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb: Muscle Table + PicturesDocument3 pagesLower Limb: Muscle Table + Picturesrichard_yin_397% (31)
- Muscle ChartDocument16 pagesMuscle Chartphinee1692% (13)
- List of Mnemonics For Upper Limbs-1Document6 pagesList of Mnemonics For Upper Limbs-1chitrojan142269% (13)
- N O I A N: AME Rigin Nsertion Ction ErveDocument16 pagesN O I A N: AME Rigin Nsertion Ction ErveJulie Brookelle Jacquinot100% (7)
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Hip JointDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of the Hip JointSundaraBharathiNo ratings yet
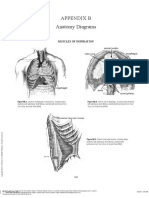
- Anatomy Diagrams: Appendix BDocument4 pagesAnatomy Diagrams: Appendix BHannah Marie OsorioNo ratings yet
- Lower LimbDocument9 pagesLower LimbCrishu Razvi100% (4)
- Blood Suppply of Lower LimbDocument8 pagesBlood Suppply of Lower LimbCamille Magdirila100% (1)
- Anatomy MnemonicsDocument69 pagesAnatomy MnemonicsGovindSoni100% (2)
- L14-Arteries of The Lower Limb-DoneDocument47 pagesL14-Arteries of The Lower Limb-Doneyakuza444No ratings yet
- Muscles of The Upper Limb Made EasyDocument7 pagesMuscles of The Upper Limb Made Easynss92% (26)
- Mnemonic For Forearm Muscles and BoneDocument2 pagesMnemonic For Forearm Muscles and BoneLaura Tapia89% (28)
- Gluteal and thigh muscle functionsDocument7 pagesGluteal and thigh muscle functionsOskar BrugrandNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb Anatomy Flashcards - QuizletDocument5 pagesLower Limb Anatomy Flashcards - QuizletAsif HanifNo ratings yet
- Summary of Nerves of Lower LimbDocument6 pagesSummary of Nerves of Lower LimbYusri Arif100% (6)
- Posterior Muscle GroupsDocument6 pagesPosterior Muscle GroupsMarina CasavecchiaNo ratings yet
- A GUIDE TO THE MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMBDocument9 pagesA GUIDE TO THE MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMBVirronChahalNo ratings yet
- Popliteal Fossa AnatomyDocument27 pagesPopliteal Fossa AnatomyAira Maranan100% (1)
- MOINA Flashcards (Upper Limb)Document63 pagesMOINA Flashcards (Upper Limb)jnthnrsj50% (2)
- Lower Limb Mnemonics (Highlighted)Document8 pagesLower Limb Mnemonics (Highlighted)Saajid Amra100% (5)
- Univ of Michigan - Gross Anatomy - Muscles TablesDocument41 pagesUniv of Michigan - Gross Anatomy - Muscles TablesDarren Lim100% (1)
- Gluteal RegionDocument34 pagesGluteal Regionlion2chNo ratings yet
- Table of Upper Limb MusclesDocument7 pagesTable of Upper Limb MusclesLjubica Nikolic100% (7)
- Muscle Origins, Insertions, Actions, and InterventionsDocument15 pagesMuscle Origins, Insertions, Actions, and InterventionsJoseph Kachelman100% (3)
- Clinical Notes of Lower LimbDocument5 pagesClinical Notes of Lower Limbbeia21100% (1)
- Table of Lower Limb MusclesDocument7 pagesTable of Lower Limb MuscleskavindukarunarathnaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lower LimbDocument43 pagesAnatomy Lower LimbYasif Abbas100% (2)
- Muscle Chart Upper ExtremityDocument3 pagesMuscle Chart Upper Extremitykep1313100% (1)
- Upper Limbs Blood Supply and NervesDocument6 pagesUpper Limbs Blood Supply and Nervesmarksterxxx78% (9)
- Lower Limb & HipDocument9 pagesLower Limb & HipENo ratings yet
- Trunk Wall: Muscle Charts: Cheat Sheet (English Terminology)Document13 pagesTrunk Wall: Muscle Charts: Cheat Sheet (English Terminology)Galo Pillajo100% (4)
- PS 01 - Lower Limb Muscles Table From Gray'sDocument4 pagesPS 01 - Lower Limb Muscles Table From Gray'szivp610% (1)
- Mnemonics Head NeckDocument8 pagesMnemonics Head NeckMartin Susanto, MD100% (2)
- Trigger Points Quick Reference Student ResourceDocument129 pagesTrigger Points Quick Reference Student ResourceViviana Rolón100% (2)
- Introduction To Lower Limb FinalDocument52 pagesIntroduction To Lower Limb FinalRafique Ahmed100% (3)
- Lower LimbDocument6 pagesLower LimbYusri Arif100% (1)
- Gluteal and Thigh Muscle Origins, Insertions and FunctionsDocument3 pagesGluteal and Thigh Muscle Origins, Insertions and FunctionsKathleen CunananNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb Anatomy Class NotesDocument87 pagesLower Limb Anatomy Class NotesSalina Amir88% (16)
- Lower Limp MnemonicsDocument6 pagesLower Limp MnemonicsScott Yee67% (6)
- Lower Limp MnemonicsDocument6 pagesLower Limp MnemonicsScott Yee67% (6)
- Netter Atlas UL ChartsDocument4 pagesNetter Atlas UL ChartsJUSASB100% (1)
- Bio 22 Post-Lab - The Muscular System (New Ver.)Document33 pagesBio 22 Post-Lab - The Muscular System (New Ver.)Arah Sacdalan92% (12)
- Muscle of Upper LimbsDocument5 pagesMuscle of Upper LimbsFong Yu-heng100% (1)
- Lower Limb: Muscle Charts: Cheat Sheet (English Terminology)Document9 pagesLower Limb: Muscle Charts: Cheat Sheet (English Terminology)yinose7198No ratings yet
- Muscle CardsDocument9 pagesMuscle Cardsapi-328688284No ratings yet
- Anatomy MnemonicsDocument63 pagesAnatomy MnemonicsAnnapurna DangetiNo ratings yet
- Origin and Insertion MusclesDocument5 pagesOrigin and Insertion MusclesStephenMontoyaNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb Muscle FunctionsDocument35 pagesLower Limb Muscle FunctionsDerek Prasai100% (1)
- Anatomy MnemonicsDocument15 pagesAnatomy Mnemonicskolintang1No ratings yet
- Upper Extremity Circulation and NervesDocument35 pagesUpper Extremity Circulation and NervesMarie100% (1)
- Anatomy: 1800 Multiple Choice QuestionsFrom EverandAnatomy: 1800 Multiple Choice QuestionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (15)
- Tips For Studying MusclesDocument2 pagesTips For Studying Musclesapi-19510625100% (11)
- Atlas of Botulinum Toxin Injection (3rd Edition) - 2019Document18 pagesAtlas of Botulinum Toxin Injection (3rd Edition) - 2019RelviGuzmanApazaNo ratings yet
- Axial Muscles PDFDocument32 pagesAxial Muscles PDFTegar Syaiful Qodar100% (1)
- Lower Limb Lab SheetDocument3 pagesLower Limb Lab SheetKelly TrainorNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Mnemonics PDFDocument31 pagesAnatomy Mnemonics PDFNonoy JoyaNo ratings yet
- Bio 102 Handout Muscular SysDocument3 pagesBio 102 Handout Muscular Sysgjsup100% (1)
- Lower Limb Test QuestionsDocument19 pagesLower Limb Test QuestionsKazim Hussain50% (2)
- Lower Limb ReviewDocument24 pagesLower Limb ReviewRyan SilberNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb - Clinical AnatomyDocument18 pagesLower Limb - Clinical Anatomyewijayapala100% (2)
- Popliteal Fossa: By: Dr. Sana KashifDocument18 pagesPopliteal Fossa: By: Dr. Sana KashifUSAMA AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Anatomy MCQ 2Document63 pagesAnatomy MCQ 2Pirabakar MahendranNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb & HipDocument9 pagesLower Limb & HipENo ratings yet
- LL Round UpDocument309 pagesLL Round UpTapiwanashe MoyoNo ratings yet
- Case Studies 9Document7 pagesCase Studies 9kep1313No ratings yet
- Case Studies 8Document7 pagesCase Studies 8kep1313No ratings yet
- Case Studies 7Document6 pagesCase Studies 7kep1313No ratings yet
- Case Studies 10Document5 pagesCase Studies 10kep1313No ratings yet
- Case Studies 6Document8 pagesCase Studies 6kep1313No ratings yet
- SeizuresDocument3 pagesSeizureskep1313No ratings yet
- Case Studies 2Document4 pagesCase Studies 2kep1313No ratings yet
- Case Studies 4Document4 pagesCase Studies 4kep1313No ratings yet
- Neurology Notes For Clerkship ReviewDocument22 pagesNeurology Notes For Clerkship Reviewkep1313No ratings yet
- Case Studies 5Document4 pagesCase Studies 5kep1313No ratings yet
- Case Studies 1Document11 pagesCase Studies 1kep1313No ratings yet
- Case Studies 3Document4 pagesCase Studies 3kep1313No ratings yet
- Virology 1 3Document5 pagesVirology 1 3kep1313No ratings yet
- Week 5 Learning ObjectivesDocument34 pagesWeek 5 Learning Objectiveskep1313No ratings yet
- Biochem MedicineDocument27 pagesBiochem Medicinekep1313No ratings yet
- Week 2 Learning ObjectivesDocument21 pagesWeek 2 Learning Objectiveskep1313No ratings yet
- Physiology - BSDocument14 pagesPhysiology - BSkep1313No ratings yet
- Case 1: Cystic FibrosisDocument5 pagesCase 1: Cystic Fibrosiskep1313No ratings yet
- Psychiatry - BSDocument15 pagesPsychiatry - BSkep1313No ratings yet
- Week 4 Learning ObjectivesDocument24 pagesWeek 4 Learning Objectiveskep1313No ratings yet
- Week 3 Learning ObjectivesDocument12 pagesWeek 3 Learning Objectiveskep1313100% (1)
- Case 1: Cystic FibrosisDocument5 pagesCase 1: Cystic Fibrosiskep1313No ratings yet
- Biochem MedicineDocument27 pagesBiochem Medicinekep1313No ratings yet
- Genetics - MMDocument25 pagesGenetics - MMkep1313No ratings yet
- Physiology - BSDocument14 pagesPhysiology - BSkep1313No ratings yet
- MicroanatomyDocument59 pagesMicroanatomykep1313No ratings yet
- Preventative Medicine PM - BSDocument22 pagesPreventative Medicine PM - BSkep1313No ratings yet
- Biogenic AminesDocument5 pagesBiogenic Amineskep1313No ratings yet
- 2-5-10 Introduction To Acute LeukemiaDocument3 pages2-5-10 Introduction To Acute Leukemiakep1313No ratings yet
- 2-5-10 HCT For Immunodeficiency and Autoimmune DisordersDocument2 pages2-5-10 HCT For Immunodeficiency and Autoimmune Disorderskep1313No ratings yet
- Pectoralis Biceps Obliques Rectus Abdominus Deltoid QuadricepsDocument2 pagesPectoralis Biceps Obliques Rectus Abdominus Deltoid QuadricepsAni BayindiryanNo ratings yet
- Acara 3 - QORI NURUL HUSNAIDA PDFDocument5 pagesAcara 3 - QORI NURUL HUSNAIDA PDFQori HusnaidaNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The Anterior Thigh - Quadriceps - TeachMeAnatomyDocument4 pagesMuscles of The Anterior Thigh - Quadriceps - TeachMeAnatomyو عجلت اليك ربي لترضيNo ratings yet
- Exercise 12 Answer Sheet AbellanaornopiaDocument5 pagesExercise 12 Answer Sheet AbellanaornopiaMarlie TobiseNo ratings yet
- Table Summary For Gross Anatomy of Upper LimbDocument20 pagesTable Summary For Gross Anatomy of Upper Limbafifah zabidiNo ratings yet
- Clavicle (Bone and Attachments) Flow ChartDocument2 pagesClavicle (Bone and Attachments) Flow Chartshree niwasNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Regio Antebrachii Et Manus (Lo 1)Document24 pagesAnatomi Regio Antebrachii Et Manus (Lo 1)Warni PutriNo ratings yet
- Dumbbell Lunge Exercise for Strong QuadsDocument1 pageDumbbell Lunge Exercise for Strong QuadsRAM NAIDU CHOPPANo ratings yet
- DTM Trigger-Point-Referred-Pain-Guide-Interactive PDFDocument439 pagesDTM Trigger-Point-Referred-Pain-Guide-Interactive PDFleokeoNo ratings yet
- LE Muscles OINADocument5 pagesLE Muscles OINAUshuaia Chely FilomenoNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb Muscles Nerve Flow ChartDocument4 pagesLower Limb Muscles Nerve Flow ChartRiyazNo ratings yet
- Elbow Approaches and AnatomyDocument5 pagesElbow Approaches and Anatomyhaitham alkhamaisehNo ratings yet
- Anatomy HWDocument4 pagesAnatomy HWTassnime SebaeiNo ratings yet
- Functions of Human MuscleDocument4 pagesFunctions of Human MuscleCatherine EscartinNo ratings yet
- Lab 7-Analysis 1 - 2Document7 pagesLab 7-Analysis 1 - 2api-402694883No ratings yet
- Cat Dissection ManualDocument30 pagesCat Dissection ManualJezebel MolinoNo ratings yet