Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FDI Types, Methods and Incentives
Uploaded by
Jesse JhangraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FDI Types, Methods and Incentives
Uploaded by
Jesse JhangraCopyright:
Available Formats
Foreign direct investment (FDI) refers to long term participation by country A into country B.
It usually involves participation in management, joint-venture, transfer of technology and expertise. There are two types of FDI: inward foreign direct investment and outward foreign direct investment, resulting in a net FDI inflow (positive or negative) and "stock of foreign direct investment", which is the cumulative number for a given period. Direct investment excludes investment through purchase of shares
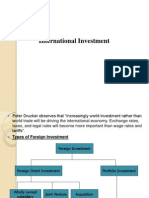
Types
A foreign direct investor may be classified in any sector of the economy and could be any one of the following:[citation needed]
an individual; a group of related individuals; an incorporated or unincorporated entity; a public company or private company; a group of related enterprises; a government body; an estate (law), trust or other societal organisation; or any combination of the above.
Methods
The foreign direct investor may acquire voting power of an enterprise in an economy through any of the following methods:
by incorporating a wholly owned subsidiary or company by acquiring shares in an associated enterprise through a merger or an acquisition of an unrelated enterprise participating in an equity joint venture with another investor or enterprise
Foreign direct investment incentives may take the following forms:[citation needed]
low corporate tax and income tax rates tax holidays other types of tax concessions preferential tariffs special economic zones EPZ - Export Processing Zones Bonded Warehouses Maquiladoras investment financial subsidies soft loan or loan guarantees free land or land subsidies
relocation & expatriation subsidies job training & employment subsidies infrastructure subsidies R&D support
Foreign direct investment in India
A recent UNCTAD survey projected India as the second most important FDI destination (after China) for transnational corporations during 2010-2012. As per the data, the sectors which attracted higher inflows were services, telecommunication, construction activities and computer software and hardware. Mauritius, Singapore, the US and the UK were among the leading sources of FDI. FDI for 2009-10 at USD 25.88 billion was lower by five per cent from USD 27.33 billion in the previous fiscal. Foreign direct investment in August dipped by about 60 per cent to USD 1.33 billion, the lowest in 2010 fiscal, industry department data released showed.
In economics, foreign portfolio investment is the entry of funds into a country where foreigners make purchases in the countrys stock and bond markets, sometimes for speculation.[1] It is a usually short term investment (sometimes less than a year, or with involvement in the management of the company), as opposed to the longer term Foreign Direct Investment partnership (possibly through joint venture), involving transfer of technology and "know-how Institutional investors are organizations which pool large sums of money and invest those sums in securities, real property and other investment assets. They can also include operating companies which decide to invest its profits to some degree in these types of assets. Types of typical investors include banks, insurance companies, retirement or pension funds, hedge funds, investment advisors and mutual funds. Their role in the economy is to act as highly specialized investors on behalf of others. For instance, an ordinary person will have a pension from his employer. The employer gives that person's pension contributions to a fund. The fund will buy shares in a company, or some other financial product. Funds are useful because they will hold a broad portfolio of investments in many companies. This spreads risk, so if one company fails, it will be only a small part of the whole fund's investment. Institutional investors will have a lot of influence in the management of corporations because they will be entitled to exercise the voting rights in a company. They can actively engage in corporate governance. Furthermore, because institutional investors have the freedom to buy and sell shares, they can play a large part in which companies stay solvent, and which go under. Influencing the conduct of listed companies, and providing them with capital are all part of the job of investment management.
Institutional investor types
Pension fund Mutual fund Investment trust Unit trust and Unit Investment Trust Investment banking Hedge fund Sovereign wealth fund Endowment fund Private equity firms Insurance companies
You might also like
- ACCT 1115 - Final Review SolutionsDocument13 pagesACCT 1115 - Final Review SolutionsMarcelo BorgesNo ratings yet
- Importance of Communication in Our Daily LifeDocument4 pagesImportance of Communication in Our Daily LifeJesse Jhangra33% (3)
- DCF and Trading Multiple Valuation of Acquisition OpportunitiesDocument4 pagesDCF and Trading Multiple Valuation of Acquisition Opportunitiesfranky1000No ratings yet
- Bills Buying and Selling RatesDocument2 pagesBills Buying and Selling RatesEnamul Haque100% (1)
- Corporate Governance MCQs on Risk Management, CSR and DirectorsDocument8 pagesCorporate Governance MCQs on Risk Management, CSR and DirectorsMusharafmushammad67% (6)
- FDIDocument26 pagesFDIKumar SwamyNo ratings yet
- Banking and InsuranceDocument20 pagesBanking and Insurancebeena antuNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Letter 102/3/2020: Question BankDocument303 pagesTutorial Letter 102/3/2020: Question Bankdivyesh mehtaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Foreign Direct Investment: Management Joint-Venture Transfer of Technology Expertise InvestmentDocument31 pagesChapter 1: Foreign Direct Investment: Management Joint-Venture Transfer of Technology Expertise InvestmentHarikrishnan Nair100% (1)
- Foreign Direct InvestmentDocument13 pagesForeign Direct InvestmentGaurav GuptaNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument3 pagesIntroductionbhamidipati_bNo ratings yet
- Foreign Direct InvestmentDocument10 pagesForeign Direct InvestmentminshengNo ratings yet
- Difference Between FDI & Portfolio Investment: PurposesDocument6 pagesDifference Between FDI & Portfolio Investment: PurposesNupur MathurNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance SystemDocument16 pagesCorporate Governance SystemRajib RoyNo ratings yet
- Mod 4 BeDocument25 pagesMod 4 BePratha JainNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument7 pagesNew Microsoft Word Documentshubham aroraNo ratings yet
- Foreign Direct InvestmentDocument41 pagesForeign Direct Investmentatul kumarNo ratings yet
- Foreign Direct InvestmentDocument4 pagesForeign Direct InvestmentprasanjeetbNo ratings yet
- Main Project of FdiDocument34 pagesMain Project of FdiBhaven H ThakrarNo ratings yet
- The Different Types of FDI InvestorsDocument1 pageThe Different Types of FDI Investorsjyoti90No ratings yet
- What Is A Forei-WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesWhat Is A Forei-WPS OfficeShây Lâh ÃmpúãñNo ratings yet
- FDI in India Case Study WalmartDocument32 pagesFDI in India Case Study WalmartSaad KhanNo ratings yet
- Foreign Direct Investment & It'S Impact On Indian Economy: Presented byDocument11 pagesForeign Direct Investment & It'S Impact On Indian Economy: Presented byhemal_sNo ratings yet
- Foreign Direct Investments (FDI)Document7 pagesForeign Direct Investments (FDI)Rajsandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Foreign Direct InvestmentDocument9 pagesForeign Direct Investmentchhayamotwani103No ratings yet
- FDI Growth Factors and RisksDocument9 pagesFDI Growth Factors and RiskshuyenNo ratings yet
- Yagnesh EcoDocument29 pagesYagnesh EcoRaven McguireNo ratings yet
- 5fdi Report GlobalDocument10 pages5fdi Report GlobalroseNo ratings yet
- What Is Foreign Investment?: Foreign Direct Investments Include Long-Term Physical Investments Made byDocument7 pagesWhat Is Foreign Investment?: Foreign Direct Investments Include Long-Term Physical Investments Made bychuchu tvNo ratings yet
- Foreign Direct Investment and Its Growth in IndiaDocument75 pagesForeign Direct Investment and Its Growth in IndiaRohit SoniNo ratings yet
- An Analytical Study of Foreign Direct Investment in IndiaDocument90 pagesAn Analytical Study of Foreign Direct Investment in Indiasunil ps50% (2)
- Unit_V__International_Capital_MovementsDocument27 pagesUnit_V__International_Capital_Movementsnuk.2021018028No ratings yet
- International Equity Market PDFDocument16 pagesInternational Equity Market PDFShreyas Dicholkar0% (1)
- Trend Analysis of FDI in IndiaDocument66 pagesTrend Analysis of FDI in IndiaRajat Goyal100% (4)
- Foreign Direct InvestmentDocument8 pagesForeign Direct InvestmentpratikpawarNo ratings yet
- Features - Venture CapitalDocument19 pagesFeatures - Venture CapitalnavinpoddarNo ratings yet
- C PCPPPPP PP PPPP PDocument2 pagesC PCPPPPP PP PPPP PSandeep ReddyNo ratings yet
- Current Trends in FdiDocument14 pagesCurrent Trends in Fdipunitrnair100% (1)
- Eco Project ReportDocument23 pagesEco Project ReportRohit PalNo ratings yet
- Foreign Direct InvestmentDocument2 pagesForeign Direct InvestmentTanmay VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Investment Law F.D.Document26 pagesInvestment Law F.D.Abhishek K. SinghNo ratings yet
- RAVALIDocument53 pagesRAVALIhemangiNo ratings yet
- International InvestmentDocument16 pagesInternational Investmentmisty_nairNo ratings yet
- Buisnes EnvioDocument18 pagesBuisnes EnvioAparna A D NairNo ratings yet
- From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesFrom Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaJaseena PrettyNo ratings yet
- SM Project .FinalDocument40 pagesSM Project .Finalaniketbhosale_012No ratings yet
- Final Project MBADocument13 pagesFinal Project MBAdivya chandru100% (1)
- FDI determinants and methodsDocument12 pagesFDI determinants and methodsabcNo ratings yet
- FDI in India Case Study WalmartDocument32 pagesFDI in India Case Study WalmartDhawal Khandelwal33% (3)
- CompilationDocument27 pagesCompilationRikki Marie PajaresNo ratings yet
- MNCs and Their Impact on Host CountriesDocument8 pagesMNCs and Their Impact on Host CountriesRikki Marie PajaresNo ratings yet
- Module 4 If NotesDocument31 pagesModule 4 If Notesanon_433140562No ratings yet
- Foreign Institutional Investments and Its Influence On Equity Stock Market in IndiaDocument14 pagesForeign Institutional Investments and Its Influence On Equity Stock Market in IndiaNeha KumariNo ratings yet
- Fast Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) : Project By-Arpita Hirawat ROLL NO. - 946 ROOM NO. - 38Document5 pagesFast Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) : Project By-Arpita Hirawat ROLL NO. - 946 ROOM NO. - 38arpita_hirawatNo ratings yet
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)Document5 pagesForeign Direct Investment (FDI)Nguyên HàNo ratings yet
- Seminar on Energy SourcesDocument7 pagesSeminar on Energy SourcesRamesh GargNo ratings yet
- Ahmad Husnain FDI IBDocument5 pagesAhmad Husnain FDI IBChaudhary Ahmad HusnainNo ratings yet
- Final Project On Fdi in IndiaDocument66 pagesFinal Project On Fdi in Indiasantosh_boyeNo ratings yet
- SM Assignment 1Document25 pagesSM Assignment 1Utkarsh AryanNo ratings yet
- Full Report On Reasons For FDIDocument19 pagesFull Report On Reasons For FDIKrishnapalsinh Indrajitsinh VirparaNo ratings yet
- Types of Foreign Direct Investment: An Overview: Outward FDIDocument7 pagesTypes of Foreign Direct Investment: An Overview: Outward FDIRitu MakkarNo ratings yet
- Project Report On FdiDocument15 pagesProject Report On FdiAkshata ZopayNo ratings yet
- Fdi Eco Project (Quillbot)Document4 pagesFdi Eco Project (Quillbot)ANANDA PADMANABAN SURESHNo ratings yet
- Development Financing AssingmentDocument21 pagesDevelopment Financing AssingmentucheNo ratings yet
- Foreign Direct InvestmentDocument3 pagesForeign Direct InvestmentkalaiselvanmaduraiNo ratings yet
- Executive Summary On Global Capital Flows (Overview of FDI in and From India)Document6 pagesExecutive Summary On Global Capital Flows (Overview of FDI in and From India)Basant SinhaNo ratings yet
- FDI in MediaDocument6 pagesFDI in MediaJesse JhangraNo ratings yet
- Meaning of HRPDocument4 pagesMeaning of HRPJesse JhangraNo ratings yet
- LeadsDocument15 pagesLeadsJesse JhangraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 NotesDocument7 pagesChapter 1 NotesJesse JhangraNo ratings yet
- News AgenciesDocument2 pagesNews AgenciesJesse Jhangra0% (1)
- Inclusive GrowthDocument32 pagesInclusive GrowthJesse Jhangra67% (3)
- The Prasar Bharati ActDocument2 pagesThe Prasar Bharati ActJesse Jhangra100% (1)
- Media OrganizationDocument3 pagesMedia OrganizationJesse JhangraNo ratings yet
- Air - DD CodeDocument4 pagesAir - DD CodeJesse JhangraNo ratings yet
- EVENTS AND EVENT MANAGEMENTDocument41 pagesEVENTS AND EVENT MANAGEMENTJesse JhangraNo ratings yet
- EditorialDocument5 pagesEditorialJesse JhangraNo ratings yet
- Depth of FieldDocument1 pageDepth of FieldJesse JhangraNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow ManagementDocument5 pagesCash Flow ManagementDEEPAK GROVERNo ratings yet
- Consumerism: Consumerism Is A Social and Economic Order That Encourages The Purchase of Goods and Services inDocument2 pagesConsumerism: Consumerism Is A Social and Economic Order That Encourages The Purchase of Goods and Services inJesse JhangraNo ratings yet
- Understanding TVDocument16 pagesUnderstanding TVJesse JhangraNo ratings yet
- Common Legal TermsDocument31 pagesCommon Legal TermsJesse JhangraNo ratings yet
- New MediaDocument13 pagesNew MediaJesse JhangraNo ratings yet
- Media RegulationDocument8 pagesMedia RegulationJesse JhangraNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development of Advertising in IndiaDocument14 pagesGrowth and Development of Advertising in IndiaJesse Jhangra100% (1)
- SamplingDocument12 pagesSamplingJesse JhangraNo ratings yet
- Cyber Crimes & SecurityDocument4 pagesCyber Crimes & SecurityJesse JhangraNo ratings yet
- Internet: - The Term Internet Has Been Coined From Two Terms, I.e.Document11 pagesInternet: - The Term Internet Has Been Coined From Two Terms, I.e.Jesse JhangraNo ratings yet
- Dodgy Transaction: Powers of SEBIDocument11 pagesDodgy Transaction: Powers of SEBIJesse JhangraNo ratings yet
- Video ConferencingDocument5 pagesVideo ConferencingJesse JhangraNo ratings yet
- Web BrowserDocument3 pagesWeb BrowserJesse JhangraNo ratings yet
- IspDocument1 pageIspJesse JhangraNo ratings yet
- Challenges Facing India: Weak InfrastructureDocument3 pagesChallenges Facing India: Weak InfrastructureJesse JhangraNo ratings yet
- Consumerism: Consumerism Is A Social and Economic Order That Encourages The Purchase of Goods and Services inDocument2 pagesConsumerism: Consumerism Is A Social and Economic Order That Encourages The Purchase of Goods and Services inJesse JhangraNo ratings yet
- The Payment of Bonus Act, 1965Document15 pagesThe Payment of Bonus Act, 1965Raman GhaiNo ratings yet
- Stock Corp By-LawsDocument35 pagesStock Corp By-LawsAngelica Sanchez100% (3)
- PRMS FAQsDocument3 pagesPRMS FAQsfriendbceNo ratings yet
- Measuring National IncomeDocument71 pagesMeasuring National IncomeMayurRawoolNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Banking & Finance: Certificate Course in Digital BankingDocument6 pagesIndian Institute of Banking & Finance: Certificate Course in Digital BankingKay Aar Vee RajaNo ratings yet
- Uno Minda RameezDocument139 pagesUno Minda RameezRameez TkNo ratings yet
- Christopher P. Mittleman's LetterDocument5 pagesChristopher P. Mittleman's LetterDealBook100% (2)
- Registration flow and documentsDocument22 pagesRegistration flow and documentsmdzainiNo ratings yet
- HOME DEPOT - Debt StructureDocument3 pagesHOME DEPOT - Debt Structureluxi0No ratings yet
- Form 16 TDS Certificate SummaryDocument2 pagesForm 16 TDS Certificate SummaryPravin HireNo ratings yet
- International Taxation of Hybrid EntitiesDocument11 pagesInternational Taxation of Hybrid EntitiesNilormi MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Paper Accountingandcultureandmarket Zarzeski 1996.Document20 pagesPaper Accountingandcultureandmarket Zarzeski 1996.SorayaNo ratings yet
- Bata & AB BankDocument8 pagesBata & AB BankSaqeef RayhanNo ratings yet
- PUP Review Handout 3 OfficialDocument2 pagesPUP Review Handout 3 OfficialDonalyn CalipusNo ratings yet
- Internship Report On Grameen Bank - CompleteDocument65 pagesInternship Report On Grameen Bank - CompleteMishu100% (2)
- New Jeevan Anand (915) : Mr. YesDocument5 pagesNew Jeevan Anand (915) : Mr. YesPankaj YadavNo ratings yet
- Analyzation of Robinson's Clan's Three Months TransactionsDocument4 pagesAnalyzation of Robinson's Clan's Three Months TransactionsNoralyn de SilvaNo ratings yet
- Case Study Currency SwapsDocument2 pagesCase Study Currency SwapsSourav Maity100% (2)
- CREATE Bill Impact on Philippine Company TaxesDocument8 pagesCREATE Bill Impact on Philippine Company TaxesHanee Ruth BlueNo ratings yet
- The Asian Financial Crisis of 1997 1998 Revisited Causes Recovery and The Path Going ForwardDocument10 pagesThe Asian Financial Crisis of 1997 1998 Revisited Causes Recovery and The Path Going Forwardgreenam 14No ratings yet
- Ins - 21-1Document13 pagesIns - 21-1Siddharth Kulkarni100% (1)
- ECB & Fed A Comparison A Comparison: International Summer ProgramDocument40 pagesECB & Fed A Comparison A Comparison: International Summer Programsabiha12No ratings yet
- FAC121 - Direct Tax - Assignment 2 - Income From SalaryDocument4 pagesFAC121 - Direct Tax - Assignment 2 - Income From SalaryDeepak DhimanNo ratings yet
- Part Char 4Document9 pagesPart Char 4Denise Jeon25% (4)