Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Eyes
Uploaded by
Phương MiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Eyes
Uploaded by
Phương MiCopyright:
Available Formats
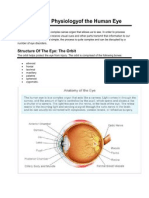
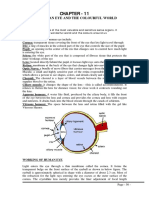
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9.
posterior compartment ora serrata ciliary muscle ciliary zonules canal of Schlemm pupil anterior chamber cornea iris
10. lens cortex 11. lens nucleus 12. ciliary process 13. conjunctiva 14. inferior oblique muscule 15. inferior rectus muscule 16. medial rectus muscle 17. retinal arteries and veins 18. optic disc 19. dura mater 20. central retinal artery 21. central retinal vein 22. optical nerve 23. vorticose vein 24. bulbar sheath 25. macula 26. fovea 27. sclera 28. choroid 29. superior rectus muscule 30. retina
The eyes are the sensory organ in charge of visual function. Thanks to the human eye's new learn and recognize the surrounding environment, creating conditions for growing minds. The structure of the
eyes consists of three parts: the eyeball, eyeball protection unit, the nervous and visual analysis of regional centers.
Eyeball
Eyeballs are spherical, the length axis of the eyeball in adults is 20-24 mm. Axis of the eyeball is shorter or longer will influencing spherical refractive myopia or hyperopic.
The sheath of the eyeball consisting of
The cornea Is a transparent membrane, very tough, no blood vessels with spherical Cap account for 1/5 the front of the eyeball. The diameter of the cornea has five classes, since in addition to the included: Epithelium: is the epithelium layer slices without the horns. Bowman membrane: a membrane which acts as the base of the epithelium. Parenchyma; took 9/10 corneal Descemet membrane-thickness: very tough. The endothelial cell layer: only one Cornea is nurtured through osmosis from the blood vessels around the edge from tears and hydraulic fluid. The dominant neurological sense of the cornea consists of multiple branches of development from the ophthalmic nerve V1. Sclera Is a fibrous tissue is very tough; white took 4/5 after the eyeball. Sclera is made from several layers of thick, fibrous band crossover knit together very firm whose mission is to protect the membrane and the inner environment. The thickness of sclera changes depends on the region. Thick sclera as in polar (1-1, 35 mm), thin is in sticking by the users, only about 0, 3 mm. At the edge of the thick sclera has a diameter of 1, 5 mm hole cover has to have more small holes to the optic nerve fibers pass through. Choroid Choroid or the called the choroid coat, consisting of three parts is the IRIS, ciliary body and choroid. Where the IRIS and ciliary body are called first choroid coat and choroid is called after choroid coat. The mission of the choroid coat is brought up with bridges and air with pressure. The IRIS
Has a coin-shaped hole in the middle. The front is the rear limits of anterior chamber. They are black, blue or brown which depending on the race. The back of the IRIS is dark brown and the limits of posterior chamber. In the middle of the IRIS has a round hole called pupils. On histology, IRIS consists of three main layers: The front of the endothelial layer continues with endothelial layer of the cornea. Buffer layer: smooth muscle fibers of sphincter Prince has co co, due to the nerve of the dominant III and spokes has a flexible contract, due to the sympathetic nerves that govern this class is also the pigment carrying cells decide which color the IRIS The epithelial layer on the back, including the highly rated pigment bearing cells, as the back of the IRIS is dark brown. The primary role of the IRIS is adjusted to the light energy to the retina by altering the size of the pupils.
You might also like
- Dme C1Document7 pagesDme C1taliya. shvetzNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye 3 Classes Objects 1. Master The Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye 2. Relationship With Clinical DiseasesDocument181 pagesThe Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye 3 Classes Objects 1. Master The Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye 2. Relationship With Clinical DiseasessanjivdasNo ratings yet
- EyeballDocument14 pagesEyeballMirko BelanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Eye: By: Dr. Lubna ShahDocument36 pagesAnatomy of Eye: By: Dr. Lubna ShahRida ShahNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument45 pagesUntitledc/risaaq yuusuf ColoowNo ratings yet
- Eye and AdnexaDocument22 pagesEye and AdnexaWadabiNo ratings yet
- 04 The Uveal TractDocument8 pages04 The Uveal TractmoraadoreneNo ratings yet
- EyeballDocument38 pagesEyeballTahaani Bilqis ZoraayaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of OPHTHALMOLOGYDocument40 pagesAnatomy of OPHTHALMOLOGYhenok birukNo ratings yet
- Ophtha - Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye 2007Document57 pagesOphtha - Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye 2007api-3856051100% (2)
- Eye & EarDocument44 pagesEye & EardrmanojkulNo ratings yet
- Eye and Ear HistologyDocument28 pagesEye and Ear Histologyirakozehugue14No ratings yet
- The Eye Pre-Lab: s94 s98 Index of ImagesDocument13 pagesThe Eye Pre-Lab: s94 s98 Index of ImagesAndi KasiantoNo ratings yet
- Histology of The EyeDocument91 pagesHistology of The EyeFazira EkmaNo ratings yet
- Cornea: Points From Snell's Ocular Anatomy Compiled by Dr. AliDocument14 pagesCornea: Points From Snell's Ocular Anatomy Compiled by Dr. Ali9999999999999-567421No ratings yet
- Histology of Cornea & RetinaDocument14 pagesHistology of Cornea & RetinaSandhya KurupNo ratings yet
- EyeDocument10 pagesEyeGIRSHINI A/P PRABURAM (B21361136)No ratings yet
- Lo Week 3 Blok Sss - April 2Document12 pagesLo Week 3 Blok Sss - April 2mellyNo ratings yet
- MD PW 1,2 Eyelids and AnatomyDocument84 pagesMD PW 1,2 Eyelids and Anatomytaliya. shvetzNo ratings yet
- 2.eyes HistologyDocument23 pages2.eyes Histologyqty9jgkpnzNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology 2Document235 pagesOphthalmology 2yididiyagirma30No ratings yet
- Eye HistologyDocument9 pagesEye HistologyDayagNo ratings yet
- Animal VertebrateDocument10 pagesAnimal VertebrateAbdullahi AwwalNo ratings yet
- 1 AnatomyDocument58 pages1 AnatomyBemnet NuruNo ratings yet
- Unit 13 Sence OrganDocument132 pagesUnit 13 Sence OrganChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- Orbital and Ocular Anatomy: Abdulrahman Al-Muammar, MD, FRCSC King Saud UniversityDocument45 pagesOrbital and Ocular Anatomy: Abdulrahman Al-Muammar, MD, FRCSC King Saud UniversityAriyanie NurtaniaNo ratings yet
- Ocular and Visual Science: Nor Shahahidah BT Shahabudin Semester 3Document44 pagesOcular and Visual Science: Nor Shahahidah BT Shahabudin Semester 3sheedah_damuloNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Retina: by DR - Ashok Kumar ValuroutuDocument49 pagesAnatomy of Retina: by DR - Ashok Kumar ValuroutuanamariaboariuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of The EYEDocument50 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of The EYEapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Bab I Pendahuluan: 1.1 Latar BelakangDocument10 pagesBab I Pendahuluan: 1.1 Latar BelakangromaNo ratings yet
- EyeDocument9 pagesEyeMont HanaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Eye of RabbitDocument3 pagesNotes On Eye of RabbitShailesh NiroulaNo ratings yet
- Organs of VisionDocument3 pagesOrgans of VisionNarasimha Murthy100% (1)
- PBL Eye No1,2,3Document9 pagesPBL Eye No1,2,3adelaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyeDocument55 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EyeWahyu Caesar Ramdani100% (1)
- Anatomy & Physiology: Lecturer: Tatyana V. RyazantsevaDocument70 pagesAnatomy & Physiology: Lecturer: Tatyana V. RyazantsevaArif MohammadNo ratings yet
- The Eye HistologyDocument16 pagesThe Eye HistologyFarah AkhwanisNo ratings yet
- Histology of EyeDocument24 pagesHistology of EyeRitvik Sharma100% (1)
- Eye and VisionDocument19 pagesEye and VisionVincent PolicarNo ratings yet
- Eye Histo Lo Gy: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Karim Al-Jashamy IMS/MSU 2010Document16 pagesEye Histo Lo Gy: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Karim Al-Jashamy IMS/MSU 2010audiNo ratings yet
- Resume Ulkus CorneaDocument10 pagesResume Ulkus CorneaNita RosianiNo ratings yet
- 2019 Dr. Sahillah Anatomi Dan Fisiologi MataDocument29 pages2019 Dr. Sahillah Anatomi Dan Fisiologi MataWahyu FajarNo ratings yet
- نسخة Opthalmology AnatomyDocument25 pagesنسخة Opthalmology AnatomyMhm MhmNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Special Senses Part 1-VisionDocument47 pagesLecture 6 Special Senses Part 1-VisionMoses Jr KazevuNo ratings yet
- Yoga & Eye - Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument73 pagesYoga & Eye - Anatomy and Physiologysachi sharma0% (1)
- Ocular AnatomyDocument56 pagesOcular AnatomyJulianto KeceNo ratings yet
- Dimensions: ThicknessDocument5 pagesDimensions: ThicknesskalaranjiniNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Human EyeDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Human EyeMaryy Basilio100% (2)
- The RetinaDocument6 pagesThe RetinaSourav RanjanNo ratings yet
- IrisDocument26 pagesIrisJaspreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyeDocument51 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EyeANTONIONo ratings yet
- Ocular PhysiologyDocument80 pagesOcular PhysiologyKenny KayNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy & Physiology of Lens: DR Prabhjot SinghDocument76 pagesThe Anatomy & Physiology of Lens: DR Prabhjot SinghPrabhjot SinghNo ratings yet
- The Lens - Applied Anatomy and Embryology: Chapter - 1Document7 pagesThe Lens - Applied Anatomy and Embryology: Chapter - 1Reza AkbarNo ratings yet
- Ophtha LectureDocument634 pagesOphtha LectureIb YasNo ratings yet
- Eyes and Vision PresentationDocument142 pagesEyes and Vision Presentationrhimineecat71100% (1)
- Anatomy & Physiology: DR - Turlea CristianDocument71 pagesAnatomy & Physiology: DR - Turlea CristianGermanyNo ratings yet
- Low Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsFrom EverandLow Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Eye and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Eye and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Delta R DetectionDocument2 pagesDelta R DetectionPhương MiNo ratings yet
- Academic Writing Examples 1 - 5Document6 pagesAcademic Writing Examples 1 - 5Jedsan LiangphapaipunNo ratings yet
- General Training Writing Sample Task - Task 1Document1 pageGeneral Training Writing Sample Task - Task 1Phương MiNo ratings yet
- QuizDocument3 pagesQuizPhương MiNo ratings yet
- Physiological VisualDocument1 pagePhysiological VisualPhương MiNo ratings yet
- Nes-Grade 9 - Unit 1: Edited By: Aliaa MuhammedDocument25 pagesNes-Grade 9 - Unit 1: Edited By: Aliaa MuhammedMagd OsamaNo ratings yet
- Handout (Sample)Document22 pagesHandout (Sample)judssalangsangNo ratings yet
- Eyelids, Conjunctiva, Cornea and Sclera: McquestionsDocument52 pagesEyelids, Conjunctiva, Cornea and Sclera: McquestionsHawwi Ismail100% (1)
- Light-Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument10 pagesLight-Human Eye and The Colourful WorldsidztoucheNo ratings yet
- The Eye: OphthalmologyDocument12 pagesThe Eye: OphthalmologyAshley DayagNo ratings yet
- QB U10 Fill in Blanks EngDocument14 pagesQB U10 Fill in Blanks Engsuetki pang100% (1)
- Class10 Science Unit11 NCERT TextBook English EditionDocument12 pagesClass10 Science Unit11 NCERT TextBook English Editionshraddha0603No ratings yet
- OphthalmologyDocument2 pagesOphthalmologyJohn Christopher LucesNo ratings yet
- Pig EyeDocument6 pagesPig Eyeaims_sluNo ratings yet
- Mature CataractDocument24 pagesMature CataractmethadamayNo ratings yet
- Visual SystemDocument7 pagesVisual SystemJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- 11.human Eye and Colourful WorldDocument19 pages11.human Eye and Colourful WorldJagpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Bio5 1Document7 pagesBio5 1HarmonyChuiNo ratings yet
- 2 3 1 A Visualperception by Javier PrietoDocument4 pages2 3 1 A Visualperception by Javier Prietoapi-268997163No ratings yet
- Optics of The Eye: Distances Between Surfaces (MM)Document24 pagesOptics of The Eye: Distances Between Surfaces (MM)Boussad CHAIBNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Crystalline Lens - Abdelmonem Hamed EditionDocument16 pagesChapter 5 Crystalline Lens - Abdelmonem Hamed EditionAbdelmonem HamedNo ratings yet
- L. Obj. 1.6Document2 pagesL. Obj. 1.6Lee DahlanNo ratings yet
- Biológia Angol Nyelven: Emelt Szintű Írásbeli Érettségi VizsgaDocument7 pagesBiológia Angol Nyelven: Emelt Szintű Írásbeli Érettségi VizsgaDsanNo ratings yet
- OphthoBook 1-6.0Document180 pagesOphthoBook 1-6.0David Cheng100% (1)
- Lecture Outline: See Separate Powerpoint Slides For All Figures and Tables Pre-Inserted Into Powerpoint Without NotesDocument73 pagesLecture Outline: See Separate Powerpoint Slides For All Figures and Tables Pre-Inserted Into Powerpoint Without NotesAngelika DomondonNo ratings yet
- Contact Lenses Resource Guide: ConnectionDocument44 pagesContact Lenses Resource Guide: ConnectionproxyNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and Colourful WorldDocument27 pagesHuman Eye and Colourful WorldSreejith SurendranNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Development, and Physiology of The Visual System PDFDocument23 pagesAnatomy, Development, and Physiology of The Visual System PDFNivedha AvoodaiappanNo ratings yet
- Sharad Coaching: Sense Organs 1 Marks QuestionsDocument8 pagesSharad Coaching: Sense Organs 1 Marks QuestionsArnav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Function of The EyeDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Function of The EyeAljhon DelfinNo ratings yet
- Psychology Notes Class 11thDocument2 pagesPsychology Notes Class 11thSheeraz KhanNo ratings yet
- Organs of VisionDocument3 pagesOrgans of VisionNarasimha Murthy100% (1)
- Eye Care IntroductionDocument66 pagesEye Care IntroductionEdeti RoneNo ratings yet
- PHY - Sense NotesDocument32 pagesPHY - Sense NotesAbhijith S. PNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 11: The Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument23 pagesChapter - 11: The Human Eye and The Colourful WorldVarunveer DubeyNo ratings yet