Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter5 Bonding in Polyatomic Molecules
Uploaded by
Rhonda HaleCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter5 Bonding in Polyatomic Molecules
Uploaded by
Rhonda HaleCopyright:
Available Formats
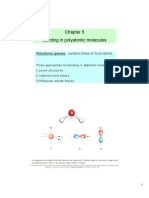
Chapter 5 Bonding in polyatomic molecules
Polyatomic species: contains three or more atoms
Three approaches to bonding in diatomic molecules 1. Lewis structures 2. Valence bond theory 3. Molecular orbital theory
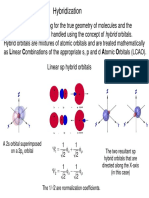
Orbital hybridization - sp
sp _ hybrid =
1 ( 2 s + 2 px ) 2
sp _ hybrid =
Hybrid orbitals generated by mixing the characters of atomic orbitals
1 ( 2 s 2 px ) 2
Orbital hybridization sp2
sp 2 _ hybrid =
1 2 2 s + 2 px 3 3
sp 2 _ hybrid =
1 1 1 2 s 2 px + 2 p y 3 6 2
sp 2 _ hybrid =
1 1 1 2 s 2 px 2 p y 3 6 2
sp3 hybrid orbitals one s and three p atomic orbitals mix to form a set of four orbitals with different directional properties
sp 3 _ hybrid = sp 3 _ hybrid =
1 2 s + 2 px + 2 p y + 2 p z 2 1 2 s + 2 p x 2 p y 2 p z 2
) )
sp 3 _ hybrid = sp 3 _ hybrid =
1 2 s 2 p x + 2 p y 2 p z 2 1 2 s 2 p x 2 p y 2 p z 2
) )
sp3d hybrid orbitals one s, three p, and one d atomic orbitals mix to form a set of five orbitals with different directional properties
[Ni(CN)5]3-
Valence bond theory multiple bonding in polyatomic molecules
Valence bond theory multiple bonding in polyatomic molecules
Valence bond theory multiple bonding in polyatomic molecules
Molecular orbital theory: ligand group orbital approach in triatomic molecules
10
11
Molecular orbital theory: BF3
12
Consider the S3 operation (=C3h) on the pz orbitals in the F3 fragment.
C3 2 2 S3 3 S3 C3 3 S3 1 Unique, S32
The resulting wavefunction contributions from the S3 and S32 operations are 3 and 2, respectively.
1 S3 2 Unique, S3 1
3 h
2 S3 2
1 S3 2 2 3
13
BF3 3 Resonance Structures
The presence of the resonance contributions account for the partial double bond character in BF3
14
SF6
15
Find number of unchanged radial 2p orbitals that are unchanged under each Oh symmetry operation. 1 C2 Note the C2 axis bisect the planes containing 4 p orbitals. The C2 axis contains no 2p orbitals.
4 6
C2
E 6
C3 0
C2 0
C4 2
C2 i S4 (C42) 2 0 0
S6 0
h 4
d 2
Use the reduction formula to find the resulting symmetries: a1g, t1u, eg Could derive the equations for the LGOs for the F6 fragment.
16
1 ( 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 ) 6 1 (t1u )1 = ( 1 6 ) 2 1 (t1u ) 2 = ( 2 4 ) 2 1 (t1u )3 = ( 3 5 ) 12 (eg )1 = (2 1 2 3 4 5 + 2 6 ) 12 1 (eg ) 2 = ( 2 3 + 4 5 ) 2
(a1g ) =
Three-center twoelectron interactions
17
18
19
20
You might also like
- Handbook of Physics in Medicine and Biology PDFDocument521 pagesHandbook of Physics in Medicine and Biology PDFYudi TrigunaNo ratings yet
- Outlines: Theory Calculation Conclusion ReferencesDocument31 pagesOutlines: Theory Calculation Conclusion ReferencesYè Paing Oo100% (3)
- Quantum+No (1) +&+Periodic+TableDocument19 pagesQuantum+No (1) +&+Periodic+TableKunalSinghNo ratings yet
- (Solutions) Kittel - Introduction To Solid State Physics 8Th EditionDocument60 pages(Solutions) Kittel - Introduction To Solid State Physics 8Th EditionCody Foster0% (1)
- Practical Yield Line DesignDocument175 pagesPractical Yield Line DesignGan Chin Phang100% (1)
- Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Lattice DynamicsDocument73 pagesLecture Notes Chapter 1 Lattice Dynamicsd460023100% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics Equation SheetDocument11 pagesFluid Mechanics Equation SheetJerone Manley0% (1)
- CH 09Document114 pagesCH 09ddubbah100% (2)
- Experiment 3 - Jet ImpactDocument18 pagesExperiment 3 - Jet ImpactKhairil Ikram75% (4)
- Finite Element MethodDocument32 pagesFinite Element MethodParvind LolldharryNo ratings yet
- Bonding Notes2Document20 pagesBonding Notes2M Nur M. MahmudNo ratings yet
- HW08SDocument11 pagesHW08SMani Ratnam RaiNo ratings yet
- Polyatomic Molecular Orbital TheoryDocument29 pagesPolyatomic Molecular Orbital TheoryShamila HussainNo ratings yet
- Ch. 11 Review Power Point CHEM 180Document15 pagesCh. 11 Review Power Point CHEM 180Muhammad Nazif AzmiNo ratings yet
- Ch3 ExamplesDocument11 pagesCh3 ExamplesMariana LizethNo ratings yet
- Chem 373 - Lecture 24: Applications of Valence Bond TheoryDocument22 pagesChem 373 - Lecture 24: Applications of Valence Bond TheoryNuansak3No ratings yet
- IC Chemistry 2006 IIAInorg ADocument12 pagesIC Chemistry 2006 IIAInorg ASuman DebnathNo ratings yet
- On The Spin-Liquid Phase of One-Dimensional Spin-1 Bosons: Ournal of Statistical Mechanics: Theory and ExperimentDocument17 pagesOn The Spin-Liquid Phase of One-Dimensional Spin-1 Bosons: Ournal of Statistical Mechanics: Theory and ExperimentGravvolNo ratings yet
- On A Generalized Oscillator System: Interbasis ExpansionsDocument23 pagesOn A Generalized Oscillator System: Interbasis Expansionstestonly261No ratings yet
- Tutorial PDFDocument50 pagesTutorial PDFvasudevan m.vNo ratings yet
- Polar CoordinatesDocument22 pagesPolar CoordinatesSyed Kamran HaiderNo ratings yet
- Pchem10e Solutions Ch10 AtkinsonDocument32 pagesPchem10e Solutions Ch10 Atkinson동글No ratings yet
- Atomic Orbital Functions and Quantum NumbersDocument10 pagesAtomic Orbital Functions and Quantum NumbersReviaNo ratings yet
- MIT OCW Principles of Inorganic Chemistry II Lecture on Octahedral ML6 Sigma ComplexesDocument7 pagesMIT OCW Principles of Inorganic Chemistry II Lecture on Octahedral ML6 Sigma Complexessanskarid94No ratings yet
- Abstract CosmologyDocument32 pagesAbstract CosmologyIan BeardsleyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To High Energy Physics by Dan KabatDocument235 pagesIntroduction To High Energy Physics by Dan KabatAtanu GayenNo ratings yet
- Vladimir E. Korepin and Ovidiu I. Pâtu - XXX Spin Chain: From Bethe Solution To Open ProblemsDocument12 pagesVladimir E. Korepin and Ovidiu I. Pâtu - XXX Spin Chain: From Bethe Solution To Open ProblemsPo48HSDNo ratings yet
- Contact of screw surfaces with displaced axesDocument10 pagesContact of screw surfaces with displaced axesAHMED WALIDNo ratings yet
- Group Theory in a NutshellDocument7 pagesGroup Theory in a NutshellcyrimathewNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Solid State Physics - Kittel, Charles - 8ed Solucionario PDFDocument61 pagesIntroduction To Solid State Physics - Kittel, Charles - 8ed Solucionario PDFmanuelomar87No ratings yet
- Abstract Cosmology: Ian Beardsley, 2022Document34 pagesAbstract Cosmology: Ian Beardsley, 2022Ian BeardsleyNo ratings yet
- Physics Letters A: Emmanuel YombaDocument11 pagesPhysics Letters A: Emmanuel YombaadilNo ratings yet
- Iit Jee 2005 MatDocument7 pagesIit Jee 2005 MatLokesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 2010 Set B Paper 3 RVHS Promo (Solutions)Document12 pages2010 Set B Paper 3 RVHS Promo (Solutions)Lim Kew ChongNo ratings yet
- Кинематический винт. J.SviglerDocument2 pagesКинематический винт. J.SviglerSergey ManakovNo ratings yet
- Molecular Orbital Theory of Octahedral Complexes (1)Document7 pagesMolecular Orbital Theory of Octahedral Complexes (1)Vasudev M SNo ratings yet
- Shankar ErrataDocument3 pagesShankar ErrataJuan CapellaNo ratings yet
- Thermo Stat3Document4 pagesThermo Stat3Hagere EthiopiaNo ratings yet
- Miessler-Fischer-Tarr5e SM CH 02 CM FinalDocument17 pagesMiessler-Fischer-Tarr5e SM CH 02 CM FinalKatieYoung100% (2)
- Test of Equal CovarianceDocument5 pagesTest of Equal CovarianceMinNo ratings yet
- Abstract CosmologyDocument35 pagesAbstract CosmologyIan BeardsleyNo ratings yet
- Periodic Soliton Solutions To The Davey-Stewartson EquationDocument8 pagesPeriodic Soliton Solutions To The Davey-Stewartson EquationcherineNo ratings yet
- Unit 2.3 Algebraic Struct Part-3Document19 pagesUnit 2.3 Algebraic Struct Part-3Vikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Peskin Chapter 4Document34 pagesPeskin Chapter 4Gary OaksNo ratings yet
- Unit 4.3 Algebraic Struct Part-3Document22 pagesUnit 4.3 Algebraic Struct Part-3johntyles9No ratings yet
- Benzene Quantum SystemsDocument10 pagesBenzene Quantum SystemsNigletNo ratings yet
- CHM 451 F-12 Exam 3 AnswersDocument10 pagesCHM 451 F-12 Exam 3 AnswersAbdul Mueez Lone100% (1)
- TUTORIAL - Triple Integral PDFDocument2 pagesTUTORIAL - Triple Integral PDFAbdur Rashid100% (1)
- HYBRIDIZATION OF ATOMIC ORBITALS (Inorganic MoleculesDocument21 pagesHYBRIDIZATION OF ATOMIC ORBITALS (Inorganic MoleculesROGELIO RIVERANo ratings yet
- Ahn 1986Document16 pagesAhn 1986achmad muzammilNo ratings yet
- Peskin Chapter 4Document34 pagesPeskin Chapter 4Bd BdNo ratings yet
- FIITJEE JEE(Advanced)-2013 Paper SolutionsDocument8 pagesFIITJEE JEE(Advanced)-2013 Paper Solutionsullasagw100% (1)
- Non-Relativistic Scattering of A Spin-1/2 Particle Off A Self-Dual MonopoleDocument8 pagesNon-Relativistic Scattering of A Spin-1/2 Particle Off A Self-Dual MonopoleBayer MitrovicNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1. Filippov Systems: Sliding Solutions and Bifurcations Yuri A. KuznetsovDocument13 pagesLecture 1. Filippov Systems: Sliding Solutions and Bifurcations Yuri A. KuznetsovFelipe Antonio Gallego LópezNo ratings yet
- Molecular Orbital TheoryDocument14 pagesMolecular Orbital TheoryElectro_LiteNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2 - Quantum Mechanical Model of AtomDocument8 pagesUnit - 2 - Quantum Mechanical Model of AtomShyamala HNo ratings yet
- Two-Body Phase SpaceDocument9 pagesTwo-Body Phase Spacezcapg17No ratings yet
- Guidelines of The Answer!: X X X XDocument3 pagesGuidelines of The Answer!: X X X Xsidik17No ratings yet
- Alternative (Su (3) ) Model of Leptonic Color and Dark Matter: SciencedirectDocument15 pagesAlternative (Su (3) ) Model of Leptonic Color and Dark Matter: Sciencedirectlong maneNo ratings yet
- Type IIB Flux Compactifications On Twistor Bundles: Ali ImaanpurDocument12 pagesType IIB Flux Compactifications On Twistor Bundles: Ali ImaanpurcrocoaliNo ratings yet
- Compton Scattering in Scalar ElectrodynamicsDocument4 pagesCompton Scattering in Scalar ElectrodynamicsMichael BravermanNo ratings yet
- CH101 Lecture 3Document52 pagesCH101 Lecture 3api-3819150No ratings yet
- 2010 AJC Paper 1solDocument6 pages2010 AJC Paper 1solnothingtodo1992No ratings yet
- Root Locus 1Document19 pagesRoot Locus 1Jeeva Suria Rajah100% (1)
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Commensurabilities among Lattices in PU (1,n). (AM-132), Volume 132From EverandCommensurabilities among Lattices in PU (1,n). (AM-132), Volume 132No ratings yet
- Grafik Kimsik 2Document6 pagesGrafik Kimsik 2Rhonda HaleNo ratings yet
- Grafik Kimsik 2Document6 pagesGrafik Kimsik 2Rhonda HaleNo ratings yet
- Conformasi CycloalkanaDocument52 pagesConformasi CycloalkanaRhonda HaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter6metallic and Ionic SolidsDocument31 pagesChapter6metallic and Ionic SolidsRhonda HaleNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Reaction 2012 - Part-1Document80 pagesInorganic Reaction 2012 - Part-1Rhonda HaleNo ratings yet
- Are Humans Responsible For Global WarmingDocument6 pagesAre Humans Responsible For Global WarmingRhonda HaleNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument29 pagesIntroductionRhonda HaleNo ratings yet
- The Gelation of Polyvinyl Alcohol With Borax: Jeff Maciborski Tony Salamone 5/1/01 Instructor - Dr. MarandDocument6 pagesThe Gelation of Polyvinyl Alcohol With Borax: Jeff Maciborski Tony Salamone 5/1/01 Instructor - Dr. MarandDian Eka FajriyantoNo ratings yet
- Chapter5 Bonding in Polyatomic MoleculesDocument20 pagesChapter5 Bonding in Polyatomic MoleculesRhonda HaleNo ratings yet
- Scientific Communication: Presenting A Scientific ReportDocument40 pagesScientific Communication: Presenting A Scientific ReportRhonda HaleNo ratings yet
- Grammar Lesson 2Document15 pagesGrammar Lesson 2Rhonda HaleNo ratings yet
- Grammar Lesson 3Document23 pagesGrammar Lesson 3Rhonda HaleNo ratings yet
- PemisahanDocument35 pagesPemisahanRhonda HaleNo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1Rhonda HaleNo ratings yet
- 1 Metode TitrimetriDocument30 pages1 Metode TitrimetriRhonda HaleNo ratings yet
- Flow in Pipes and Closed ConduitsDocument31 pagesFlow in Pipes and Closed ConduitsRafael E. Becemberg LNo ratings yet
- Bag Bcs Primus t5 Data SheetDocument4 pagesBag Bcs Primus t5 Data SheetAyman ZarefyNo ratings yet
- Study Material: Free Master Class SeriesDocument13 pagesStudy Material: Free Master Class SeriesRizwan Salim100% (1)
- Physics: Unit: KPH0/4PH0 Science (Double Award) KSC0/4SC0 Paper: 1PDocument36 pagesPhysics: Unit: KPH0/4PH0 Science (Double Award) KSC0/4SC0 Paper: 1Pkhalil rehmanNo ratings yet
- Region Vii - Central Visayas Schools Division of Cebu Province S. Y. 2020-2021Document7 pagesRegion Vii - Central Visayas Schools Division of Cebu Province S. Y. 2020-2021Christian Jay R. LanuriasNo ratings yet
- Induced by Electron Motion : CurrentsDocument2 pagesInduced by Electron Motion : CurrentsJààd BenserhîrNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 FieldsDocument1 pageUnit 10 FieldsGajendraNo ratings yet
- Css Applied Mathematics 1 2009Document2 pagesCss Applied Mathematics 1 2009Bakhita MaryamNo ratings yet
- CHM 10 Chemistry For EngineersDocument6 pagesCHM 10 Chemistry For EngineersKim MoraNo ratings yet
- Numerical in Electrical, Mechanical, Electronic, Optical Materials From Different Books Along With Previous Year Papers of GATE, ES, CS and Other Exams.Document24 pagesNumerical in Electrical, Mechanical, Electronic, Optical Materials From Different Books Along With Previous Year Papers of GATE, ES, CS and Other Exams.Rehan Sharma100% (1)
- Objective Lab1Document27 pagesObjective Lab1Karthik MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Complex Permittivity (Dielectric Constant) of Solid Electrical Insulating Materials at Microwave Frequencies and Temperatures To 1650°CDocument16 pagesComplex Permittivity (Dielectric Constant) of Solid Electrical Insulating Materials at Microwave Frequencies and Temperatures To 1650°CROHIT100% (1)
- Module VI - ME205Document20 pagesModule VI - ME205Hari650No ratings yet
- FAPESP International - Issue1 2019 PDFDocument100 pagesFAPESP International - Issue1 2019 PDFholfmandNo ratings yet
- Quantum Entanglement LectureDocument4 pagesQuantum Entanglement LectureBasman BasmanNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: Objective: ApparatusDocument3 pagesExperiment No: Objective: ApparatusAfzaal FiazNo ratings yet
- Plan Ai2TS 2019 Class IX To XIDocument1 pagePlan Ai2TS 2019 Class IX To XIAmanNo ratings yet
- 5.60 Thermodynamics & Kinetics: Mit OpencoursewareDocument7 pages5.60 Thermodynamics & Kinetics: Mit OpencoursewarecaptainhassNo ratings yet
- LCA Lab1Document13 pagesLCA Lab1Rizwan HanifNo ratings yet
- Instructor: Arun Kumar Lecture - 1 Electromagnetic Waves and Quantum MechanicsDocument18 pagesInstructor: Arun Kumar Lecture - 1 Electromagnetic Waves and Quantum MechanicsShiv Kumar MeenaNo ratings yet
- Fatigue in The Shell of A Conveyor Drum: Ch. Affolter, G. Piskoty, R. Koller, M. Zgraggen, T.F. Ru TtiDocument15 pagesFatigue in The Shell of A Conveyor Drum: Ch. Affolter, G. Piskoty, R. Koller, M. Zgraggen, T.F. Ru TtiSamir KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Uit RGPV First Year SyllabusDocument19 pagesUit RGPV First Year SyllabusYasir MujtabaNo ratings yet