Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Case Study Presentation For Va
Uploaded by
api-217889657Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Case Study Presentation For Va
Uploaded by
api-217889657Copyright:
Available Formats
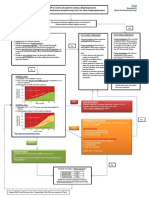
ETIOLOGY
Abnormal immune
SIGNS & SYMPTOMS
Bloody diarrhea with
response resulting in inflammatory damage of GI mucosa Genetic susceptibility Association with exsmokers
PATHOLOGY
Chronic inflammation of
colonic mucosa Involves entire colon
mucus Abdominal and/or rectal pain Fever Weight loss Possibly constipation and rectal spasm Arthritis Dermatological changes Ocular manifestations
Admission diagnosis: Bloody diarrhea Admitted to Acute Medicine Pt complaints at admission:
2 weeks of abdominal pain and bloody
diarrhea
constant pain (rated 10/10 at admission); no increase in pain after
eating 10-15 lb wt loss in past 2 weeks sore throat and odynophagia Cough productive of greenish mucous
CT of abdomen/pelvis
Diffuse colonic wall thickening Consistent with pancolitis Erosive sacroiliitis Consistent with ulcerative colitis
VITALS:
Temperature: 100.6 Pulse: 119
Suspected SIRS/Sepsis
Age: 65 years Gender: Male Married Branch of Service: Air Force H/O 25 pack a year smoking; quit 8 years ago Drinks EtOH very rarely Anthropometrics:
Height: 180.3 cm Weight: 86 kg BMI: 26.5
Hypertension Sinusitis Hyperlipidemia Knee pain
204 202 200 198 196 194 192 190 188 186 184 182 1/1/2012 2/1/2012
Weight
Pt lost 9# in 1 month (4.5% of body weight)
Weight loss was likely due in part to dehydration Pt reports UBW of 200 lbs Current wt overweight at 110% of IBW, BMI of 26.5
3/1/2012 4/1/2012 5/1/2012 6/1/2012
Mother: died of some sort of metastatic cancer 9 siblings: died in fire during WWII 1 brother: died of MI at age 66 1 sister: died of renal failure 1 brother: still living
Abnormal NUTR Related Lab Tests Albumin Sodium Potassium Chloride Glucose WBC CRP Hematocrit
Patients value 2.1 g/dL 133 mEq/L 2.7 mEq/L 94 mEq/L 120 mg/dL 12.69x103 185 mg/L 30.9%
Normal value
Diagnosis
3.2-5.0 g/dL 135-145 mEq/L 3.5-5.0 mEq/L 100-106 mEq/L 60-115 mg/dL 3.8-11x103 <10 mg/L 42-52%
Severe depletion Hyponatremia, likely due to diarrhea Hypokalemia, likely due to diarrhea Hypochloremia, associated with hypokalemia Likely due to stress High, likely due to inflammation High, likely due to inflammation Low, likely due to loss of blood
Hemoglobin
10.2 g/dL
14-18 g/dL
Low, likely due to loss of blood
Pt considers himself a good cook and reports eating well at home Pt reported a poor appetite for 1 week PTA due to GI pain Pt tries to use Mrs. Dash and pepper since he has HTN, but still adds salt at the table. No Food Allergies
Severe diarrhea can result in malabsorption of all nutrients (especially Fe, Zn, Mg, and electrolytes) When infection/inflammation are present or when pt is febrile, energy and protein needs are higher (up to 150% of normal requirements)
In adults, enteral nutrition is recommended when use of medications is not feasible & additional nutrition is needed to improve or maintain nutritional status TPN is not necessary in most cases Energy needs estimated using HarrisBenedict or Mifflin-St. Jeor (stress factor 1.31.5) Protein needs are as high as 1.5-1.75 g/kg
Low-residue, lactose free diet Small, frequent meals Fat reduced with added MCT if steatorrhea is present Restriction of gas-producing, spicy, or fried foods & caffeinated beverages Add fiber and lactose as tolerated
Low fiber is generally only necessary during acute exacerbation or if stricture is present
All pts should receive a multivitamin
Increase protein intake Consider protein supplement or high protein formula Iron supplementation
Clear liquids until GI bleeding stops IV therapy to correct electrolyte imbalances
120 cc/hr of NS + 20 mEq KCl
Pt still on clear liquids & tolerating it well. Pt states he is eating 100% of his food and feels hungry DIAGNOSES:
Inadequate oral intake related to decreased ability to consume sufficient energy as evidenced by estimated energy intake from diet less than estimated nutritional needs.
Increased protein needs related to increased demand for nutrient (colitis, slight proteinuria) as evidenced by decreased albumin indicating increased metabolic needs.
RECOMMENDATIONS: Advance diet as tolerated to eventual healthful diet Provide Resource Breeze TID. Will change to Boost supplements when diet is advanced. If unable to advance diet past clear liquids in 1-2 days, consider nutrition support
2200-2500 kcal/day
Mifflin-St. Jeor, using current wt and AF/IF of 1.31.5
103-129 gram protein/day
Using current wt and 1.2-1.5 g/kg
Pt transferred to MICU Pts diet changed from clear liquids to NPO Pt receiving ice chips to aid with sore throat
Pt states abdominal pain is improving Bleeding has ceased, but sudden diarrhea persists Body Temperature decreases (99.4 F) Diet changed to General/Healthy Diet
PO intake slowly improves
On 6/29/2012, nursing notes report 100% of meals eaten
Pt moved from MICU to floor
No hematochezia Afebrile Pt eating general/healthy diet with good appetite Diet instructions upon discharge:
Resume previous diet
May eat yogurt to re-populate gut flora
DRUG Acetaminophen Ciprofloxacin
Purpose Pain reliever Antibiotic
Interactions Caffeine rate of absorption and effect of drug Ensure adequate fluid intake; Dont take drug with milk; Drug causes caffeine effect May cause dry mouth, metallic taste, N/V, & diarrhea; May take with meals to GI distress but food drug bioavailability. May cause GI irritation, N/V, abdominal pain, diarrhea, & flatulence. --
Metronidazole
Antibiotic
Potassium Chloride Cherry Lozenge
Electrolyte, Mineral supplement Relieve sore throat
Ondansetron
Anti-nauseant
May cause dry mouth, abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea, headache & fatigue
Nutrition Care Indicator Weight
Albumin Sodium Potassium Chloride Glucose WBC Hematocrit Hemoglobin
Before 189.6 lbs
2.1 g/dL (1.7 g/dL) 133 mEq/L 2.7 mEq/L 94 mEq/L 120 mg/dL 12.69x103 30.9% (28.7%) 10.2 g/dL (9.4 g/dL)
After 197.31 lbs
none 141 mEq/L 3.9 mEq/L 105 mEq/L 110 mg/dL 7.6x103 33% 10.4 g/dL
Nutrition Goals:
Advance diet as tolerated to a general, healthy dietMET Pt to consume 75% or more of all meals/supplementMET
Expected Outcomes:
Albumin to gradually increase toward 3.2 g/dLUNSURE
Prevent Further Wt lossMET
Recommend monitoring albumin more frequently Education at discharge concerning colitis diet tips Prescribe iron supplement for patient
Nelms, M. N., Sucher, K., Lacey, K., & Roth, S. L. (2011). Nutrition Therapy & Pathiophysiology (2nd ed.). Belmont, CA: Wadsworth. American Dietetic Association. (2011). Pocket Guide for International Dietetics & Nutrition Terminology Reference Manual(3rd ed.). Chicago, IL: Author. Pronsky, Z. M., & Crowe, J. P. (2010). Food-Medication Interactions (16th ed.). Birchrunville, PA: FoodMedication Interactions. Charney, P., & Malone, A. M. (2009). ADA Pocket Guide to Nutrition Assessment (2nd ed.). Chicago, IL: American Dietetic Association. Lee, R. D., & Nieman, D. C. (2010). Nutritional Assessment (5th ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Volunteer ExperiencesDocument3 pagesVolunteer Experiencesapi-217889657No ratings yet
- Iron OutlineDocument1 pageIron Outlineapi-217889657No ratings yet
- Condensed Introduction To Sports Nutrition PresentationDocument25 pagesCondensed Introduction To Sports Nutrition Presentationapi-217889657No ratings yet
- Resveratrol OutlineDocument1 pageResveratrol Outlineapi-217889657No ratings yet
- Powerpoint Topic 3Document42 pagesPowerpoint Topic 3api-217889657No ratings yet
- Journal ClubDocument12 pagesJournal Clubapi-217889657No ratings yet
- Summary Report Written DefenseDocument41 pagesSummary Report Written Defenseapi-217889657No ratings yet
- Final Oral PresentationDocument33 pagesFinal Oral Presentationapi-217889657No ratings yet
- Strength Room FuelingDocument1 pageStrength Room Fuelingapi-217889657No ratings yet
- Manuscript FinalDocument23 pagesManuscript Finalapi-217889657No ratings yet
- Resume For Lifetime Fitness - Anna MitchellDocument2 pagesResume For Lifetime Fitness - Anna Mitchellapi-217889657No ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Sarcomas of The Head and Neck: Dr. DarwitoDocument60 pagesSarcomas of The Head and Neck: Dr. DarwitolaurasheerNo ratings yet
- Daftar Singkatan SMF JAntungDocument5 pagesDaftar Singkatan SMF JAntungBobby RahmantoNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma: by Tekia BuntynDocument18 pagesGlaucoma: by Tekia BuntynTekia BuntynNo ratings yet
- Case Study Week 1 Community Acquired Pneumonia 1Document6 pagesCase Study Week 1 Community Acquired Pneumonia 1Yuuki Chitose (tai-kun)No ratings yet
- PhotodermatosesDocument8 pagesPhotodermatosesIvan KurniadiNo ratings yet
- 307-Article Text-578-1-10-20210309 PDFDocument13 pages307-Article Text-578-1-10-20210309 PDFPUTRI LISTIANINo ratings yet
- 3 NURSING-CARE-PLAN FinaaalDocument7 pages3 NURSING-CARE-PLAN FinaaalSam PothNo ratings yet
- Bisphosphonate Treatment Break Guidance June 2017Document2 pagesBisphosphonate Treatment Break Guidance June 2017Usman Zafar QaziNo ratings yet
- PsoriasisDocument0 pagesPsoriasisaurax143No ratings yet
- Mixed Lymphocyte Culture / Reaction (MLC / MLR)Document2 pagesMixed Lymphocyte Culture / Reaction (MLC / MLR)Muthi KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Neural Mechanisms of CatatoniaDocument10 pagesStructure and Neural Mechanisms of CatatoniaAlejandra ToralNo ratings yet
- Approach To Nursing Assessment 1Document5 pagesApproach To Nursing Assessment 1Taiye OkondoNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology of Infectious DiseasesDocument69 pagesEpidemiology of Infectious Diseasesmus zaharaNo ratings yet
- 51-1606756076 TypDocument6 pages51-1606756076 TypbelaariyantiNo ratings yet
- Necessary Elements of A Dermatologic History and Physical Evaluation PDFDocument9 pagesNecessary Elements of A Dermatologic History and Physical Evaluation PDFkyle31No ratings yet
- Grand Rounds Facial Nerve ParalysisDocument86 pagesGrand Rounds Facial Nerve ParalysisA170riNo ratings yet
- DYSRHYTHMIASDocument9 pagesDYSRHYTHMIASgudobenNo ratings yet
- Final Update On Antenatal Steroids - DR PadmeshDocument66 pagesFinal Update On Antenatal Steroids - DR PadmeshAhalia NicuNo ratings yet
- The Bipolar Affective Disorder Dimension Scale (BADDS) - A Dimensional Scale For Rating Lifetime Psychopathology in Bipolar Spectrum DisordersDocument11 pagesThe Bipolar Affective Disorder Dimension Scale (BADDS) - A Dimensional Scale For Rating Lifetime Psychopathology in Bipolar Spectrum DisordersDM YazdaniNo ratings yet
- 15 English PPT Nursing 5 ADocument208 pages15 English PPT Nursing 5 ASinta WuLandari100% (1)
- Civic Drive, Filinvest City, Alabang 1781 Muntinlupa, PhilippinesDocument2 pagesCivic Drive, Filinvest City, Alabang 1781 Muntinlupa, PhilippinesRegulatory CPGNo ratings yet
- Homoeopathy in Breast Cancer: AbstractsDocument5 pagesHomoeopathy in Breast Cancer: Abstractskathir_cNo ratings yet
- GE Versana Balance Platinum BrosjyreDocument8 pagesGE Versana Balance Platinum BrosjyreRicky ImranNo ratings yet
- Placenta PreviaDocument11 pagesPlacenta PreviaKashmala ZiaNo ratings yet
- Paper 1Document11 pagesPaper 1api-499574410No ratings yet
- Sedation Under JCI StandardDocument36 pagesSedation Under JCI Standardกิ๊กกิ๊ก ค่าาาาNo ratings yet
- Hunter's Diseases of Occupations PDFDocument1,317 pagesHunter's Diseases of Occupations PDFLenny Rajagukguk86% (7)
- Modern TimesDocument58 pagesModern TimesMicah DomingoNo ratings yet
- English CourseDocument25 pagesEnglish CourseMaria Evy PurwitasariNo ratings yet
- Salubris Medical Center: National Highway, Brgy. Roxas, Solano, Nueva VizcayaDocument10 pagesSalubris Medical Center: National Highway, Brgy. Roxas, Solano, Nueva Vizcayajulie ann afanNo ratings yet