Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pdfa4 5
Uploaded by
aizatOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pdfa4 5
Uploaded by
aizatCopyright:
Available Formats
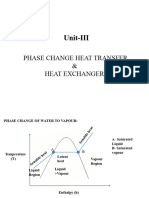
Chapter 4
Transparency
33
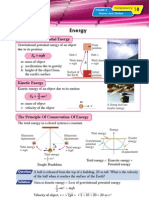
Heat
Specific Latent Heat (II)
Latent Heat Of Vaporisation
Latent Cooling Curve
heat Temperature
Q
Gas
Liquid Vapour Condensaton (Condensation)
point Liquid
Latent heat of vaporisation, + gas Liquid
Q = mlv Solidification (Solidification)
point Liquid
where m: mass + gas Solid
lf : specific latent heat
of vaporisation Time
The specific latent heat of vaporisation (lv) of a substance is the amount of heat
required to convert a unit mass of the liquid into gas without change in temperature.
The latent heat of vaporisation is required to break up molecules in the liquid state to
molecules in the gaseous state at boiling point.
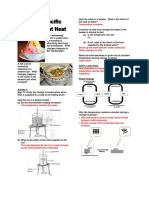
Experiment To Determine Specific Latent Heat Of Vaporisation (lv)
Power supply At the boiling point of water,
Latent heat of vaporisation absorbed by water
= Electric energy supplied
Boiling water mlv = Pt
Electric heater
where
m: mass of water converted to steam
Balance
P: electric power supply
t: time taken
Hence, lv = Pt
m
Applications Of Latent Heat
Latent heat of vaporisation is used to
cook (by steaming) food faster.
Latent heat of vaporisation is
used in an autoclave to sterilise
hospital equipment.
© Marshall Cavendish ( Malaysia ) Sdn. Bhd.
You might also like
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Grade 9 Academic Geography GlossaryDocument14 pagesGrade 9 Academic Geography Glossaryrickeyw60% (5)
- The Natural Hygiene Diet A Beginners GuideDocument16 pagesThe Natural Hygiene Diet A Beginners GuidePeachNo ratings yet
- Discharge Standards in Dubai PDFDocument6 pagesDischarge Standards in Dubai PDFHRK65No ratings yet
- Herofus GuideDocument24 pagesHerofus Guidepalolo tepitoNo ratings yet
- Specific Latent Heat (I) : Heating Ice To Form VapourDocument1 pageSpecific Latent Heat (I) : Heating Ice To Form VapouraizatNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Specific Latent HeatDocument18 pages4.3 Specific Latent HeatkhodijahaminNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics O Level Note 27-Nov-2023Document13 pagesThermal Physics O Level Note 27-Nov-2023aliayanraza5No ratings yet
- Heat Capacity Latent Heat: What Is Cooking All About?Document76 pagesHeat Capacity Latent Heat: What Is Cooking All About?Gkid GkidNo ratings yet
- U.3.1. Thermal EnergyDocument40 pagesU.3.1. Thermal EnergyClaudia Ruelas0% (1)
- Unit IIIDocument62 pagesUnit IIIBharathi KannaNo ratings yet
- Latent Heat of VaporizationDocument11 pagesLatent Heat of VaporizationEsther Faith GabrielNo ratings yet
- 2022 CH2213 Lecture29Document9 pages2022 CH2213 Lecture29KuNaL aGaLeNo ratings yet
- 8.21 The Physics of Energy: Mit OpencoursewareDocument34 pages8.21 The Physics of Energy: Mit OpencoursewareywoodyNo ratings yet
- Third Generation PV and Other Ways To Utilize Solar EnergyDocument8 pagesThird Generation PV and Other Ways To Utilize Solar EnergyFarjad KhanNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Answer Specific Latent Heat Module 2021Document12 pages4.3 Answer Specific Latent Heat Module 2021黎珮琴No ratings yet
- Chem 320 Vapor Pressure of H2oDocument2 pagesChem 320 Vapor Pressure of H2olinwryn qNo ratings yet
- LG 4.2 Phase ChangeDocument7 pagesLG 4.2 Phase ChangeapngbnNo ratings yet
- Presentation FZKDocument12 pagesPresentation FZKHanis AqilahNo ratings yet
- Merginbcjcg ResultmergedDocument104 pagesMerginbcjcg ResultmergedjkjkNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Heat TreatmentDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Heat TreatmentNIDHI NAIRNo ratings yet
- Clausius-Clapeyron Equation: Liquid SolidDocument28 pagesClausius-Clapeyron Equation: Liquid SolidDiki AriNo ratings yet
- Latent Heat 1Document3 pagesLatent Heat 1Betts pearlsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 18Document8 pagesLecture 18Outis WongNo ratings yet
- What Is The Melting Point of This Substance? The Boiling Point?Document18 pagesWhat Is The Melting Point of This Substance? The Boiling Point?annisa fitriNo ratings yet
- Pdfa4 3Document1 pagePdfa4 3aizatNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes (G - 11) (ch-5)Document8 pagesPhysics Notes (G - 11) (ch-5)Khin Khin ThanNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 (Physics)Document2 pagesActivity 4 (Physics)Dudekula Shareef AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Form 4 PDFDocument25 pagesChapter 2 Form 4 PDFCikFasyareena MaoNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Atom: Wan Nur Syazwani Wan Mohd LudinDocument35 pagesThe Structure of The Atom: Wan Nur Syazwani Wan Mohd LudinSyaz LudinNo ratings yet
- Boiling PDFDocument11 pagesBoiling PDFRahul Kotadiya100% (1)
- Heat & Mass Transfer: Theory & ApplicationDocument11 pagesHeat & Mass Transfer: Theory & ApplicationMuhammad Nouman khanNo ratings yet
- Answer Seminar Ilmufree Form 4 Pyhsics MR Shafiee English VersionDocument11 pagesAnswer Seminar Ilmufree Form 4 Pyhsics MR Shafiee English Versionna jaeminNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document3 pagesLecture 5Dharmishtha PatelNo ratings yet
- HAAVINESH A - L GANESH Moe - THEME 3 HEAT 4.3 SPECIFIC LATENT HEAT - STUDENTDocument24 pagesHAAVINESH A - L GANESH Moe - THEME 3 HEAT 4.3 SPECIFIC LATENT HEAT - STUDENTHaavinesh Ganesh100% (1)
- Et - Sem - 1 - CH - 3 - Properties of Pure Substance - Sessional 1 21 SlidesDocument21 pagesEt - Sem - 1 - CH - 3 - Properties of Pure Substance - Sessional 1 21 SlidesJinit SanghviNo ratings yet
- Heat (Add Science) OkDocument35 pagesHeat (Add Science) OkJaswardi Anwar Bin Md Yaacob� IPGKKBNo ratings yet
- Latent Heat of Fusion:: For ExampleDocument5 pagesLatent Heat of Fusion:: For ExampleNajam RasheedNo ratings yet
- Heat and Energy: 4.1 Thermal EquilibriumDocument7 pagesHeat and Energy: 4.1 Thermal Equilibriumgrace_lo_1No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - ThermodynamicsDocument73 pagesLecture 1 - ThermodynamicsNgọc ĐàoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 PHY210Document2 pagesExperiment 5 PHY210Adinda Nur AdilaNo ratings yet
- Section 5Document5 pagesSection 5Hugo LauNo ratings yet
- Energy Transport: Ch. 9, 10 BirdDocument53 pagesEnergy Transport: Ch. 9, 10 BirdHadi SiddiqiNo ratings yet
- CH2043 - 7 - Phase Change Heat Transfer (Part 1 Boiling)Document28 pagesCH2043 - 7 - Phase Change Heat Transfer (Part 1 Boiling)Long NguyenNo ratings yet
- GEAS103 - ThermodynamicsDocument6 pagesGEAS103 - Thermodynamicscj gamatNo ratings yet
- Slaid Topik 6-Temperature and Heat2Document46 pagesSlaid Topik 6-Temperature and Heat2Md KhairulNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Convection 1Document22 pagesUnit 1 - Convection 1Londiwe NxumaloNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument20 pagesThermodynamicsRonieboy Baliber CairoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics: Custodio, Keyzel B. Paña, Kimberly Anne HDocument12 pagesChemical Engineering Thermodynamics: Custodio, Keyzel B. Paña, Kimberly Anne HMark William Almero GeronNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer TheoryDocument82 pagesHeat Transfer TheoryJayantNo ratings yet
- t6 Heat TransferDocument19 pagest6 Heat Transfersuehana15No ratings yet
- Calorimetry - Formula SheetDocument1 pageCalorimetry - Formula Sheetanushridey122005No ratings yet
- Thermo 2 Module 1 To 6 ReviewerDocument9 pagesThermo 2 Module 1 To 6 ReviewerJerome NuevoNo ratings yet
- Properties of SteamDocument26 pagesProperties of SteamAaditya NaikNo ratings yet
- HEAT p3p4 StudentsDocument23 pagesHEAT p3p4 StudentsSharvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- HT W 531 ForcedConv 1Document34 pagesHT W 531 ForcedConv 1Shaheer FarrukhNo ratings yet
- Pdfa4 1Document1 pagePdfa4 1aizatNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 1Document115 pagesThermodynamics 1Rajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 107 Latent Heat of FusionDocument4 pagesExperiment 107 Latent Heat of FusionJosh BarrogaNo ratings yet
- Pharma Engg. Heating & Cooling Time-CycleDocument2 pagesPharma Engg. Heating & Cooling Time-CyclepratikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Thermal Properties of MatterDocument9 pagesChapter 11 - Thermal Properties of MattergnkstarNo ratings yet
- Mixing and Cooling Modelling of Cryogenic Fuel in Liquid Fuel Rocket Engine TanksDocument5 pagesMixing and Cooling Modelling of Cryogenic Fuel in Liquid Fuel Rocket Engine Tanksait oubella marouaneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Boiling and CondensationDocument47 pagesChapter 11 - Boiling and CondensationhaqjmiNo ratings yet
- Calorimetry (Theory) Module-3Document5 pagesCalorimetry (Theory) Module-3Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Pdfa5 3Document1 pagePdfa5 3aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa5 2Document1 pagePdfa5 2aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa5 1Document1 pagePdfa5 1aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa5 3Document1 pagePdfa5 3aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa4 8Document1 pagePdfa4 8aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 7Document1 pagePdfa3 7aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 16Document1 pagePdfa2 16aizat100% (1)
- Pdfa4 7Document1 pagePdfa4 7aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa4 3Document1 pagePdfa4 3aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa4 2Document1 pagePdfa4 2aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa4 6Document1 pagePdfa4 6aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa4 1Document1 pagePdfa4 1aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 5Document1 pagePdfa3 5aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 6Document1 pagePdfa3 6aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 2Document1 pagePdfa3 2aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 4Document1 pagePdfa3 4aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 14Document1 pagePdfa2 14aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 1Document1 pagePdfa3 1aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 3Document1 pagePdfa3 3aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 15Document1 pagePdfa2 15aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 10Document1 pagePdfa2 10aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 8Document1 pagePdfa2 8aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 13Document1 pagePdfa2 13aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 12Document1 pagePdfa2 12aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 11Document1 pagePdfa2 11aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 9Document1 pagePdfa2 9aizat100% (1)
- Petroleum Development Oman: P.O. Box: 81, Muscat Postal Code: 118 Sultanate of OmanDocument51 pagesPetroleum Development Oman: P.O. Box: 81, Muscat Postal Code: 118 Sultanate of OmanJose Angelo JunioNo ratings yet
- Water Cycle Lesson Plan 3 and 4Document4 pagesWater Cycle Lesson Plan 3 and 4api-314207089No ratings yet
- Q. Explain Water Pollution and Function of State Pollution Control Board Under The Water Act 1974Document2 pagesQ. Explain Water Pollution and Function of State Pollution Control Board Under The Water Act 1974Adan HoodaNo ratings yet
- Caustic SodaDocument5 pagesCaustic SodaamitNo ratings yet
- Spill Kits SorbentsDocument14 pagesSpill Kits SorbentsMahmoudNo ratings yet
- Research Paper - Egipto and LegaspiDocument20 pagesResearch Paper - Egipto and LegaspilololotrolNo ratings yet
- POTWC 22 Combined LinkedDocument106 pagesPOTWC 22 Combined LinkedHeidi TieuNo ratings yet
- 1.project ReportDocument33 pages1.project ReportDeepika GuptaNo ratings yet
- From Geographical Gridlock To Economic Impasse-The Chronicle of Kuttanadu: A Region De-RangedDocument76 pagesFrom Geographical Gridlock To Economic Impasse-The Chronicle of Kuttanadu: A Region De-RangedSanthosh T VargheseNo ratings yet
- Proposed Municipal Fishery Management PlanDocument48 pagesProposed Municipal Fishery Management PlananakbalayanNo ratings yet
- Aits 2324 FT I Jeem LD OfflineDocument15 pagesAits 2324 FT I Jeem LD OfflineVishnuNo ratings yet
- Aqua Glo Series III ManualDocument8 pagesAqua Glo Series III Manualtruckman1000No ratings yet
- Bahan Turbine ENERGY LautDocument15 pagesBahan Turbine ENERGY Lautakhmadmarufnur609No ratings yet
- Msds MG Sulfat PDFDocument2 pagesMsds MG Sulfat PDFAlmahyra AptkNo ratings yet
- Process For Refining of Used Lubricating OilDocument8 pagesProcess For Refining of Used Lubricating OilSubrata Banerjee100% (2)
- Earth & Rockfill DamsDocument21 pagesEarth & Rockfill DamsshrikantharleNo ratings yet
- Sciencedirect: Analysis of Water Mist Fire Suppression System Applied On Cellulose FireDocument8 pagesSciencedirect: Analysis of Water Mist Fire Suppression System Applied On Cellulose FireS.M.Touhidur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Dynamic City Doc CaseStudyTirupur JanDocument39 pagesDynamic City Doc CaseStudyTirupur JanVaishu ArvindNo ratings yet
- KawasanDocument2 pagesKawasanSel TopiaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Earth and Life Science: Exogenic ProcessesDocument2 pagesLesson Plan Earth and Life Science: Exogenic ProcessesNuevalyn Quijano FernandoNo ratings yet
- OS Coll. Vol. 1 p392-P-Nitrobenzoic AcidDocument3 pagesOS Coll. Vol. 1 p392-P-Nitrobenzoic Acidsunil_vaman_joshiNo ratings yet
- 03 Mixing TheoryDocument25 pages03 Mixing TheoryDoni KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Interchar 963: Acrylic IntumescentDocument4 pagesInterchar 963: Acrylic IntumescentImran MulaniNo ratings yet
- Agents of ErosionDocument1 pageAgents of ErosionJoya Sugue AlforqueNo ratings yet
- Geography FinishedDocument42 pagesGeography FinishedStork0% (1)
- Thesis of FYPDocument15 pagesThesis of FYPkhadija khanNo ratings yet