Professional Documents
Culture Documents
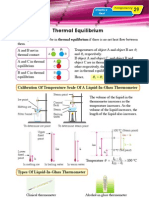
Specific Latent Heat (I) : Heating Ice To Form Vapour
Uploaded by
aizatOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Specific Latent Heat (I) : Heating Ice To Form Vapour
Uploaded by
aizatCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 4
Transparency
32
Heat
Specific Latent Heat (I)
Heating Ice To Form Vapour
Stirrer
Hot Boiling
water water
Ice
Latent Heat Of Fusion
Heating Curve
Latent Temperature
heat
Q Gas
Liquid
+ gas
Boiling
Solid Liquid point (Vaporisation)
Solid +
Liquid Liquid
Latent heat of fusion,
Melting
(Melting)
Q = mlf point
Solid
where m: mass
lf : specific latent heat Time
of fusion
The specific latent heat of fusion (lf) of a substance is the amount of heat required to
convert a unit mass of a solid to liquid without change in temperature.
The latent heat of fusion is required to break up molecules in the solid state to molecules
in the liquid state at the same temperature (melting point).
Latent heat is absorbed An iceberg melts due to Latent heat of ice is used
from the drink to melt the dissipation of latent to preserve food.
the ice cubes. heat to the surroundings.
© Marshall Cavendish ( Malaysia ) Sdn. Bhd.
You might also like
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Chemistry Exercise - Chap 3Document2 pagesChemistry Exercise - Chap 3eddielawNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument27 pagesAtomic StructureZekZanaNo ratings yet
- Activity Resources (Teacher's Edition) - 2 YearsDocument100 pagesActivity Resources (Teacher's Edition) - 2 YearsYenny Tiga100% (1)
- Newton's Laws GravitationDocument20 pagesNewton's Laws GravitationNoorleha Mohd Yusoff100% (1)
- Notes Updates SaltsDocument32 pagesNotes Updates SaltsLim Jing YeeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 2011 No LogoDocument96 pagesChemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 2011 No Logohome8008100% (2)
- SPM Pecutan Kimia Berfokus t5 Cohort 2021Document28 pagesSPM Pecutan Kimia Berfokus t5 Cohort 2021Wardati Najihah MohamedNo ratings yet
- Solubility and temperatureDocument122 pagesSolubility and temperatureVANESSA VOON MoeNo ratings yet
- English to Indonesian opposites word list under 40 charactersDocument2 pagesEnglish to Indonesian opposites word list under 40 charactersAstri DesmayantiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Qualitative Analysis NotesDocument9 pagesChemistry Qualitative Analysis NotesLim Yan Peng GaryNo ratings yet
- Test For Gases: Gas Test and Test ResultsDocument2 pagesTest For Gases: Gas Test and Test ResultsKhim YangNo ratings yet
- Notes For Qualitative AnalysisDocument1 pageNotes For Qualitative Analysissatty22No ratings yet
- Pdfa4 1Document1 pagePdfa4 1aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa4 3Document1 pagePdfa4 3aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 13Document1 pagePdfa2 13aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 16Document1 pagePdfa2 16aizat100% (1)
- Pdfa4 6Document1 pagePdfa4 6aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 14Document1 pagePdfa2 14aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 3Document1 pagePdfa3 3aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 8Document1 pagePdfa2 8aizatNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Chemistry Calculation Practice Chapter 7: Acids and Bases 2017Document3 pagesForm 4 Chemistry Calculation Practice Chapter 7: Acids and Bases 2017khangsiean89No ratings yet
- Pdfa3 1Document1 pagePdfa3 1aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 7Document1 pagePdfa2 7aizatNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY FORM 4 SUMMARYDocument3 pagesCHEMISTRY FORM 4 SUMMARYNora MnNo ratings yet
- Science Form 2 Notes on Water Solutions Acids and AlkalisDocument17 pagesScience Form 2 Notes on Water Solutions Acids and AlkalisDhiipagesan Muniandy100% (1)
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument10 pagesAcids, Bases and Saltsshehryar khanNo ratings yet
- Heat Changes in Chemical Reactions ExperimentDocument9 pagesHeat Changes in Chemical Reactions ExperimentnursyidNo ratings yet
- TB Science F1 Chapter 3Document35 pagesTB Science F1 Chapter 3wienna1987No ratings yet
- Chemistry (Chapter 3 - Notes)Document2 pagesChemistry (Chapter 3 - Notes)Daniel Wong Sai Meng100% (1)
- Chapter 7: Dynamic: Types of ForceDocument54 pagesChapter 7: Dynamic: Types of ForceNur Azila ZabidiNo ratings yet
- Bio PekaDocument27 pagesBio PekaEmderellaNo ratings yet
- Science Form 5 Synthetic Materials in IndustryDocument10 pagesScience Form 5 Synthetic Materials in Industrydebbycley100% (11)
- BIOLOGY 2 (4551/2) : Answering Questions Techniques SECTION A: STRUCTURED QUESTIONS (5 Compulsory Questions)Document6 pagesBIOLOGY 2 (4551/2) : Answering Questions Techniques SECTION A: STRUCTURED QUESTIONS (5 Compulsory Questions)Jedidah Jong100% (2)
- SMK Taman Tuanku Jaafar Biology Form 4 Exam 2020Document11 pagesSMK Taman Tuanku Jaafar Biology Form 4 Exam 2020Haslinda SheikhNo ratings yet
- Thermo chemistry: Exothermic vs Endothermic ReactionsDocument20 pagesThermo chemistry: Exothermic vs Endothermic ReactionsAzie Nurul Akhtar100% (1)
- Chemsitry FolioDocument32 pagesChemsitry FolioJoeyee NgNo ratings yet
- Group 1 and 17 Elements Properties and ReactionsDocument5 pagesGroup 1 and 17 Elements Properties and ReactionsLeong Kit WaiNo ratings yet
- Chem Form 5Document37 pagesChem Form 5Ashwin Boy Ash100% (1)
- PEKA Form 4 Chemistry Experiments ListDocument14 pagesPEKA Form 4 Chemistry Experiments Listmagentiran100% (1)
- Effect of Electrodes on Copper Chloride ElectrolysisDocument27 pagesEffect of Electrodes on Copper Chloride ElectrolysisHafizoh HarunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Chemical Bonds AnswerDocument12 pagesChapter 5 Chemical Bonds AnswerIvan Hoo Chean YiengNo ratings yet
- Answer Gerak Gempur Chemistry 2013Document11 pagesAnswer Gerak Gempur Chemistry 2013ryder1man6433No ratings yet
- Science Form 4 Chapter 5 5.2Document38 pagesScience Form 4 Chapter 5 5.2KSSM TSENo ratings yet
- Science Form 1 NoteDocument5 pagesScience Form 1 NoteDaniel ChanNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry and Oxidation and ReductionDocument32 pagesElectrochemistry and Oxidation and ReductionHajar Norasyikin Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- PMR 2012 Science 108 MantraDocument16 pagesPMR 2012 Science 108 MantraJun MingNo ratings yet
- Modul Defra Ting 5 Guru FinalDocument34 pagesModul Defra Ting 5 Guru FinalWeenaNo ratings yet
- Bombastic Words to Enhance Your SPM EssayDocument14 pagesBombastic Words to Enhance Your SPM EssayAmirul Asyraf100% (1)
- Topic 9 Manufactured Substances in Industry: 9.6 Composite MaterialsDocument5 pagesTopic 9 Manufactured Substances in Industry: 9.6 Composite MaterialsPutri MalayaNo ratings yet
- IT Chem F5 Topical Test 5 (BL)Document6 pagesIT Chem F5 Topical Test 5 (BL)Titim MohdNo ratings yet
- Chemistry (The Mole)Document44 pagesChemistry (The Mole)Aisya AnwarNo ratings yet
- 2A The Structure of The Atom-AnswerDocument6 pages2A The Structure of The Atom-AnswerSiti Nursahidah0% (1)
- Relative Atomic Mass & Relative Molecular MassDocument11 pagesRelative Atomic Mass & Relative Molecular Masscikgu aisyah100% (1)
- Acid Base and SaltDocument24 pagesAcid Base and Saltmanish100% (1)
- Dear MR Kilmer Form 5 SPMDocument4 pagesDear MR Kilmer Form 5 SPMenesusNo ratings yet
- Pdfa4 5Document1 pagePdfa4 5aizatNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Specific Latent HeatDocument18 pages4.3 Specific Latent HeatkhodijahaminNo ratings yet
- Concept Map of Solids and LiquidsDocument1 pageConcept Map of Solids and LiquidsKia SportageNo ratings yet
- HAAVINESH A - L GANESH Moe - THEME 3 HEAT 4.3 SPECIFIC LATENT HEAT - STUDENTDocument24 pagesHAAVINESH A - L GANESH Moe - THEME 3 HEAT 4.3 SPECIFIC LATENT HEAT - STUDENTHaavinesh Ganesh100% (1)
- Concept Map of Solids and LiquidsDocument1 pageConcept Map of Solids and LiquidsKia SportageNo ratings yet
- Pdfa5 3Document1 pagePdfa5 3aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa5 3Document1 pagePdfa5 3aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa5 1Document1 pagePdfa5 1aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa4 7Document1 pagePdfa4 7aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa4 8Document1 pagePdfa4 8aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa4 2Document1 pagePdfa4 2aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa5 2Document1 pagePdfa5 2aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa4 5Document1 pagePdfa4 5aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 5Document1 pagePdfa3 5aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 6Document1 pagePdfa3 6aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 4Document1 pagePdfa3 4aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 11Document1 pagePdfa2 11aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 7Document1 pagePdfa3 7aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 2Document1 pagePdfa3 2aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 3Document1 pagePdfa3 3aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 12Document1 pagePdfa2 12aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 10Document1 pagePdfa2 10aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 1Document1 pagePdfa3 1aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 15Document1 pagePdfa2 15aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 14Document1 pagePdfa2 14aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 9Document1 pagePdfa2 9aizat100% (1)
- Pdfa2 8Document1 pagePdfa2 8aizatNo ratings yet