Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pdfa4 1
Uploaded by
aizatOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pdfa4 1
Uploaded by
aizatCopyright:
Available Formats
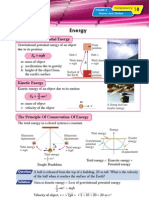
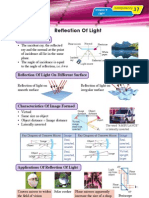
Chapter 4
Transparency
29
Heat
Thermal Equilibrium
Two objects are said to be in thermal equilibrium if there is no net heat flow between
them.
A and B not in θ1 θ2 Temperatures of object A and object B are θ 1
thermal contact A B and θ 2 respectively.
If object A and object C, and object B and
A and C in thermal A object C are in thermal equilibrium with each
equilibrium C other respectively, then object A and object B
are in thermal equilibrium.
B and C in thermal B
equilibrium C Hence, θ1 = θ2
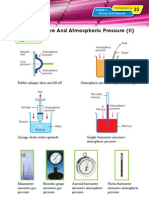
Calibration Of Temperature Scale Of A Liquid-In-Glass Thermometer
Steam point
The volume of the liquid in the
Ice point
Conical thermometer increases as the
Melting ice
flask temperature increases. As the
Steam volume of the liquid increases, the
Filter funnel Boiling length of the liquid also increases.
water
To determine ice point To determine steam point
100 ºC (Steam point)
Upper
fixed l100 − l0
point θ
l100 lθ − l0
l100 lθ lθ
Lower 0 ºC (Ice point)
l0
fixed
point l0 lθ − l0
Temperature θ = × 100 ºC
In melting ice In boiling water In warm water
l100 − l0
Types Of Liquid-In-Glass Thermometer
Clinical thermometer Alcohol-in-glass thermometer
© Marshall Cavendish ( Malaysia ) Sdn. Bhd.
You might also like
- Specific Latent Heat (I) : Heating Ice To Form VapourDocument1 pageSpecific Latent Heat (I) : Heating Ice To Form VapouraizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa4 3Document1 pagePdfa4 3aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 13Document1 pagePdfa2 13aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 16Document1 pagePdfa2 16aizat100% (1)
- Pdfa4 6Document1 pagePdfa4 6aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 12Document1 pagePdfa2 12aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 1Document1 pagePdfa3 1aizatNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Chemistry Calculation Practice Chapter 7: Acids and Bases 2017Document3 pagesForm 4 Chemistry Calculation Practice Chapter 7: Acids and Bases 2017khangsiean89No ratings yet
- Pdfa2 8Document1 pagePdfa2 8aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 3Document1 pagePdfa3 3aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 14Document1 pagePdfa2 14aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 7Document1 pagePdfa2 7aizatNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws GravitationDocument20 pagesNewton's Laws GravitationNoorleha Mohd Yusoff100% (1)
- Chemistry Qualitative Analysis NotesDocument9 pagesChemistry Qualitative Analysis NotesLim Yan Peng GaryNo ratings yet
- Test For Gases: Gas Test and Test ResultsDocument2 pagesTest For Gases: Gas Test and Test ResultsKhim YangNo ratings yet
- Notes For Qualitative AnalysisDocument1 pageNotes For Qualitative Analysissatty22No ratings yet
- Glossary SPM BiologyDocument11 pagesGlossary SPM BiologyMus Staqim Besut100% (1)
- CHEMISTRY FORM 4 SUMMARYDocument3 pagesCHEMISTRY FORM 4 SUMMARYNora MnNo ratings yet
- Section A p3Document8 pagesSection A p3Zunaidi JaafarNo ratings yet
- Jawaban 100 Kesalahan TatabahasaDocument4 pagesJawaban 100 Kesalahan Tatabahasaevelyn_lim_68No ratings yet
- Effect of Electrodes on Copper Chloride ElectrolysisDocument27 pagesEffect of Electrodes on Copper Chloride ElectrolysisHafizoh HarunNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY 2 (4551/2) : Answering Questions Techniques SECTION A: STRUCTURED QUESTIONS (5 Compulsory Questions)Document6 pagesBIOLOGY 2 (4551/2) : Answering Questions Techniques SECTION A: STRUCTURED QUESTIONS (5 Compulsory Questions)Jedidah Jong100% (2)
- Chemistry (The Mole)Document44 pagesChemistry (The Mole)Aisya AnwarNo ratings yet
- Science Form 2 Notes on Water Solutions Acids and AlkalisDocument17 pagesScience Form 2 Notes on Water Solutions Acids and AlkalisDhiipagesan Muniandy100% (1)
- Bio Past Year 2012Document7 pagesBio Past Year 2012Ismaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- Answer Gerak Gempur Chemistry 2013Document11 pagesAnswer Gerak Gempur Chemistry 2013ryder1man6433No ratings yet
- Activity Resources (Teacher's Edition) - 2 YearsDocument100 pagesActivity Resources (Teacher's Edition) - 2 YearsYenny Tiga100% (1)
- Chemsitry FolioDocument32 pagesChemsitry FolioJoeyee NgNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Force and Motion (Teacher)Document58 pagesChapter 2 Force and Motion (Teacher)Fahmi Ami100% (1)
- Bio PekaDocument27 pagesBio PekaEmderellaNo ratings yet
- Science F3 C8-PPT-Part I Dynamo and GeneratorDocument36 pagesScience F3 C8-PPT-Part I Dynamo and GeneratorRebecca Choong Xin Hui100% (2)
- Dear MR Kilmer Form 5 SPMDocument4 pagesDear MR Kilmer Form 5 SPMenesusNo ratings yet
- STPM Mathematics Trial Exam Marking SchemeDocument10 pagesSTPM Mathematics Trial Exam Marking SchemeMichelles JimNo ratings yet
- BELONGS TO: .. : Chemistry SPM - Quick Review F4Document8 pagesBELONGS TO: .. : Chemistry SPM - Quick Review F4Anis Wahida Mohamad100% (1)
- Form 5 Science: Microorganisms and Their Effects On Living ThingsDocument54 pagesForm 5 Science: Microorganisms and Their Effects On Living Thingsnicky1213aNo ratings yet
- Experiment Design - A Property of A Spring - OscillationDocument3 pagesExperiment Design - A Property of A Spring - Oscillationapi-241231725No ratings yet
- 2010 Chemistry Perak (Gerak Gempur)Document67 pages2010 Chemistry Perak (Gerak Gempur)qalanisNo ratings yet
- Physics-Lesson 2.6impulse, Impulsive Force and Safety Features in VehiclesDocument7 pagesPhysics-Lesson 2.6impulse, Impulsive Force and Safety Features in VehiclesRais RahimiNo ratings yet
- Solve Quadratic EquationsDocument4 pagesSolve Quadratic EquationsFazlina MustafaNo ratings yet
- Carbon CompoundDocument16 pagesCarbon CompoundAidah AmirNo ratings yet
- Body Coordination FORM 4 SCIENCEDocument15 pagesBody Coordination FORM 4 SCIENCESiti NorhayatiNo ratings yet
- Literature Sample SPMDocument1 pageLiterature Sample SPMKogilan Bama Daven100% (2)
- Form 4 Science Chapter 8Document6 pagesForm 4 Science Chapter 8elineNo ratings yet
- Energy in a Peanut CaloriesDocument3 pagesEnergy in a Peanut CaloriesjopaudecruNo ratings yet
- Solubility and temperatureDocument122 pagesSolubility and temperatureVANESSA VOON MoeNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 4 Form 4 DEFINITIONDocument3 pagesPhysics Chapter 4 Form 4 DEFINITIONAnnie HonNo ratings yet
- Chem U5 A2 EdexcelDocument48 pagesChem U5 A2 EdexcelReez SinhaNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 3 SPMDocument13 pagesPhysics Paper 3 SPMChaste TanNo ratings yet
- Tanjong RhuDocument6 pagesTanjong RhuHao WeiNo ratings yet
- Science Form 1 NoteDocument5 pagesScience Form 1 NoteDaniel ChanNo ratings yet
- Angle Properties Cheat SheetDocument1 pageAngle Properties Cheat SheetTan Guodong50% (2)
- Literature Component Notes Form 5Document16 pagesLiterature Component Notes Form 5Nabila Abdul MukthiNo ratings yet
- 2018 April 二年级英文试卷 附答案 2018-06-27Document22 pages2018 April 二年级英文试卷 附答案 2018-06-27ya wenNo ratings yet
- Seminar Add Maths F4 1-4 PDFDocument18 pagesSeminar Add Maths F4 1-4 PDFAnonymous bwVxI8Y8WNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Science Chapter 1 PDFDocument20 pagesForm 5 Science Chapter 1 PDFfrez_kingdom100% (1)
- Form 4 Physics Chapter 4 HeatDocument34 pagesForm 4 Physics Chapter 4 HeatTang VincentNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 HeatDocument30 pagesChapter 4 HeatosamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Heat Teacher's GuideDocument34 pagesChapter 4 Heat Teacher's GuidehermanwongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Thermal Properties of MatterDocument6 pagesChapter 11 - Thermal Properties of MatterFirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Heat Teacher's GuideDocument34 pagesChapter 4 Heat Teacher's GuideAhmad Zaidi100% (9)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Pdfa5 3Document1 pagePdfa5 3aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa5 3Document1 pagePdfa5 3aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa5 2Document1 pagePdfa5 2aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa4 7Document1 pagePdfa4 7aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa5 1Document1 pagePdfa5 1aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa4 8Document1 pagePdfa4 8aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa4 5Document1 pagePdfa4 5aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 2Document1 pagePdfa3 2aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 6Document1 pagePdfa3 6aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa4 2Document1 pagePdfa4 2aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 11Document1 pagePdfa2 11aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 7Document1 pagePdfa3 7aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 5Document1 pagePdfa3 5aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 3Document1 pagePdfa3 3aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 1Document1 pagePdfa3 1aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 4Document1 pagePdfa3 4aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 12Document1 pagePdfa2 12aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 15Document1 pagePdfa2 15aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 10Document1 pagePdfa2 10aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 14Document1 pagePdfa2 14aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 9Document1 pagePdfa2 9aizat100% (1)
- Pdfa2 8Document1 pagePdfa2 8aizatNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics - DPP 10 (Of Lec 14) - (Lakshya JEE 2023)Document3 pagesRay Optics - DPP 10 (Of Lec 14) - (Lakshya JEE 2023)rambhaiya888No ratings yet
- A Review Porosity in Aluminum WeldingDocument10 pagesA Review Porosity in Aluminum WeldingBenny TavlovichNo ratings yet
- Specific Surface Area (BET Method)Document3 pagesSpecific Surface Area (BET Method)kawtherahmedNo ratings yet
- Advanced Waterflooding: 5 D T II C 5-Day Training Course by Pavel BedrikovetskyDocument15 pagesAdvanced Waterflooding: 5 D T II C 5-Day Training Course by Pavel Bedrikovetskybu7amudNo ratings yet
- Design & Construction of MicropilesDocument49 pagesDesign & Construction of MicropilesHRC100% (2)
- RAY Optics Past 5 Years Jee Main PyqDocument88 pagesRAY Optics Past 5 Years Jee Main PyqiitjeemotiNo ratings yet
- Astm D790-15Document12 pagesAstm D790-15Rodrigo Ampuero100% (2)
- Chapter 4 Optical ReceiversDocument49 pagesChapter 4 Optical ReceiversNguyễnMinhTháiNo ratings yet
- CHE 406 - Lecture 3 (1) MOMENTUM TRANSFERDocument31 pagesCHE 406 - Lecture 3 (1) MOMENTUM TRANSFERDietrich Jamiro DizonNo ratings yet
- KobyDocument1 pageKobyJeanette Bonifacio CorpuzNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Impact Engineering: Li Chen, Mingjin Cao, Qin FangDocument11 pagesInternational Journal of Impact Engineering: Li Chen, Mingjin Cao, Qin FangFattah Maulana AlanNo ratings yet
- Bending on Bar: Determining Modulus of ElasticityDocument5 pagesBending on Bar: Determining Modulus of ElasticityKhairul Anam HaliminNo ratings yet
- Industrial Trainning Gladni JammuDocument34 pagesIndustrial Trainning Gladni Jammumohasan aliNo ratings yet
- Metal Eng. Tech. ExamDocument3 pagesMetal Eng. Tech. ExamEahbm KaduNo ratings yet
- Pds Insulyte 9Document1 pagePds Insulyte 9pulakjaiswal85No ratings yet
- BS Iso 7619-1 2004 A1 2008Document20 pagesBS Iso 7619-1 2004 A1 2008Wan Cheung LaiNo ratings yet
- TDS LF-361Document2 pagesTDS LF-361ofershochetNo ratings yet
- BT Mix DesignDocument5 pagesBT Mix DesignGhaffar LaghariNo ratings yet
- Grillo Et Al - High-Field Emission Current Density From Ga2O3 Nanopillars (2019)Document6 pagesGrillo Et Al - High-Field Emission Current Density From Ga2O3 Nanopillars (2019)JulienBarratNo ratings yet
- Electric Dipole Induced Spin Resonance in Quantum DotsDocument11 pagesElectric Dipole Induced Spin Resonance in Quantum DotsLing XuNo ratings yet
- Transmission of Air in Air Conditioning Ducts: LessonDocument18 pagesTransmission of Air in Air Conditioning Ducts: Lessoncaptainhass100% (1)
- 188 - Formability Limits by Wrinkling in Sheet Metal Forming PDFDocument12 pages188 - Formability Limits by Wrinkling in Sheet Metal Forming PDFasifNo ratings yet
- 3.7.12. Metal Matrix Composites: Matrices and Processing: T.W.ClyneDocument14 pages3.7.12. Metal Matrix Composites: Matrices and Processing: T.W.ClyneVizay KumarNo ratings yet
- 1 Normal StressDocument40 pages1 Normal StressTerise SangalangNo ratings yet
- Mousam Nagar Physics ProjectDocument21 pagesMousam Nagar Physics Projectsherin johnsonNo ratings yet
- Compressive Strength of Concrete & Concrete Cubes - What - How - CivilDigitalDocument13 pagesCompressive Strength of Concrete & Concrete Cubes - What - How - CivilDigitalArdhi TaNo ratings yet
- Advance StructuresDocument6 pagesAdvance StructuresManju NishaNo ratings yet
- 4 - Lec 3 - 1 MaterialDocument55 pages4 - Lec 3 - 1 MaterialMohd Shukri IsmailNo ratings yet
- 06 08 Jet Kulkarni PDFDocument13 pages06 08 Jet Kulkarni PDFRicardo Horacio LoreficeNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Strength AgaroseDocument9 pagesMechanical Strength AgaroseHyunjung KimNo ratings yet