Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pdfa1 2
Uploaded by
aizat0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
656 views1 pageScalar quantity Physical quantity which has magnitude only. Vector Quantity Physical quantity which has both magnitude and direction. Force addition of forces 3N+4N=5N magnitude of each force is represented by its length.
Original Description:
Original Title
pdfa1_2
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentScalar quantity Physical quantity which has magnitude only. Vector Quantity Physical quantity which has both magnitude and direction. Force addition of forces 3N+4N=5N magnitude of each force is represented by its length.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
656 views1 pagePdfa1 2
Uploaded by
aizatScalar quantity Physical quantity which has magnitude only. Vector Quantity Physical quantity which has both magnitude and direction. Force addition of forces 3N+4N=5N magnitude of each force is represented by its length.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Chapter 1
Transparency
2
Introduction To Physics
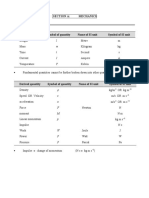
Scalar Quantities & Vector Quantities
Scalar Quantity Vector Quantity
Physical quantity which has Physical quantity which has
magnitude only. both magnitude and direction.
Distance Displacement
Speed Velocity
Mass Weight
Energy Momentum
Temperature Pressure
Time Impulse
Electric current Acceleration
Power Deceleration
Density Force
Example
Mass of 1 kg has Velocity of 400 km h−1
no direction has direction (due East)
Scalar addition Vector addition
1.1 kg + 1.1 kg 2 m s−1 + 2 m s−1
= 2.2 kg 2 m s−1 ≠ 4 m s−1
2 m s−1
Addition of forces
5N
3N+4N=5N 3N
Magnitude of each force is represented by its length.
4N
© Marshall Cavendish ( Malaysia ) Sdn. Bhd.
You might also like
- Chapter 1 - Physical Quantities and Measurement - Nov 2015.docx UpdatedDocument26 pagesChapter 1 - Physical Quantities and Measurement - Nov 2015.docx Updateddannypro13No ratings yet
- Edexcel GCSE Physics Mind MapsDocument38 pagesEdexcel GCSE Physics Mind MapsDanmin YuNo ratings yet
- Base Quantities & Derived QuantitiesDocument1 pageBase Quantities & Derived Quantitiesjgd2080No ratings yet
- CSEC Physics - Definitions and FormulaeDocument39 pagesCSEC Physics - Definitions and FormulaeA.BensonNo ratings yet
- Understanding Physics: Study of All Natural PhenomenonDocument14 pagesUnderstanding Physics: Study of All Natural PhenomenonbatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- DownloadfilephysicsDocument37 pagesDownloadfilephysicsdeonkrobyNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Physics Syllabus Overview 2023-25Document7 pagesGrade 9 Physics Syllabus Overview 2023-25Aarti AkelaNo ratings yet
- Hasan Sayginel: Edexcel IAL Physics Unit 1Document22 pagesHasan Sayginel: Edexcel IAL Physics Unit 1Dusty ClaneNo ratings yet
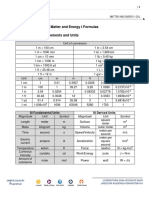
- Topic 2. Measurements and Units: Matter and Energy I FormulasDocument5 pagesTopic 2. Measurements and Units: Matter and Energy I FormulasGaelNo ratings yet
- BAB 2. Chapter 1 Part 2Document28 pagesBAB 2. Chapter 1 Part 2Evi NadilahNo ratings yet
- 1 6 Momentum (from-Reference-Book)Document10 pages1 6 Momentum (from-Reference-Book)M IqtadarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Physical Quantities and Measurement Lecturer Only1Document45 pagesChapter 1 Physical Quantities and Measurement Lecturer Only1Jerome FizzowNo ratings yet
- CHEL04A - Transes in BiochemistryDocument7 pagesCHEL04A - Transes in BiochemistryMikhaella GwenckyNo ratings yet
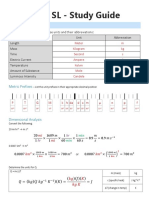
- Ib Physics SL Study GuideDocument34 pagesIb Physics SL Study Guideapi-298716691100% (1)
- Science Reviewer PhysicsDocument3 pagesScience Reviewer PhysicsZeus FrancisNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics Chapter 4 NotesDocument6 pagesO Level Physics Chapter 4 NoteshelloNo ratings yet
- (PHY) Chapter 4 - Mass, Weight, DensityDocument6 pages(PHY) Chapter 4 - Mass, Weight, Densitymicole.kohNo ratings yet
- Energy Key Terms and ConceptsDocument13 pagesEnergy Key Terms and Conceptsrumbi16No ratings yet
- Unit IV Quantum MechanicsDocument15 pagesUnit IV Quantum MechanicsYash100% (1)
- List of Physical Quantities: Base Quantity Symbol Description CommentsDocument12 pagesList of Physical Quantities: Base Quantity Symbol Description CommentsAnas ImdadNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Waves Physics For Engg PDFDocument24 pagesMechanical Waves Physics For Engg PDFMicah Aranay50% (2)
- ICSE Physics Formulas GuideDocument12 pagesICSE Physics Formulas GuideRekhaBhandariNo ratings yet
- Elementary physics measurement and scientific investigationDocument5 pagesElementary physics measurement and scientific investigationJacqueline Lim ?No ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 1 F4 KSSM (SPM Notes 4.0)Document5 pagesPhysics Chapter 1 F4 KSSM (SPM Notes 4.0)harwezelNo ratings yet
- Science FormDocument6 pagesScience FormMahesh GowdaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Physical QuantityDocument12 pages1.1 Physical QuantityFATIHAH BINTI MOKHTAR MoeNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 1: "Engineering Mechanics"Document18 pagesLecture # 1: "Engineering Mechanics"Razaq Khan MandokhailNo ratings yet
- 332physics 2016 Unit 3 Head Start Lecture - Post Lecture - Upload P1Document162 pages332physics 2016 Unit 3 Head Start Lecture - Post Lecture - Upload P1lolz0037No ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 3 f4 KSSM (SPM Notes 4.0)Document18 pagesPhysics Chapter 3 f4 KSSM (SPM Notes 4.0)Dhievakar ParamesivanNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Force and Motion 1Document15 pages4.2 Force and Motion 1velavan0% (1)
- Chapter 2 Kinematic 413Document61 pagesChapter 2 Kinematic 413ِAladin S HamidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 MeasurementDocument25 pagesChapter 1 MeasurementRachael HoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Physical Quantities, Units & Dimensions 1.1 Physical QuantitiesDocument5 pagesChapter 1: Physical Quantities, Units & Dimensions 1.1 Physical QuantitiesAAAANo ratings yet
- Engineering MechanicsDocument22 pagesEngineering MechanicsNieve ArhoNo ratings yet
- Physics 110 Biological Physics: DR Alaa S Hamid Professor of PhysicsDocument36 pagesPhysics 110 Biological Physics: DR Alaa S Hamid Professor of PhysicsِAladin S HamidNo ratings yet
- Equations To Learn (Combined) Year 10 VersionDocument1 pageEquations To Learn (Combined) Year 10 VersionSteve RamseyNo ratings yet
- Welcome To PhysicsDocument12 pagesWelcome To PhysicsjuanmanuelbustillogNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Energy and Momentum FormulasDocument26 pagesKinetic Energy and Momentum FormulasWan MajdahNo ratings yet
- Form Three Physics Handbook-1Document94 pagesForm Three Physics Handbook-1Kisaka G100% (1)
- 2 Forces and Weight LessonDocument9 pages2 Forces and Weight LessonXavier RaghunananNo ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument48 pagesPhysics NotesAshley LimNo ratings yet
- Forceeq1 DelDocument3 pagesForceeq1 Delbinilj04No ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Mass Weight DensityDocument2 pagesChapter 15 Mass Weight DensityAlexisNo ratings yet
- Sos (Kips Repeater Session 10june RS)Document8 pagesSos (Kips Repeater Session 10june RS)Muhammad UsamaNo ratings yet
- Sos (Kips Repeater Session 10june RS)Document8 pagesSos (Kips Repeater Session 10june RS)Muhammad UsamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Units and MeasuremntsDocument31 pagesChapter 1 Units and MeasuremntsAiman HakimNo ratings yet
- Notebook 1: Lindsey ShrinerDocument3 pagesNotebook 1: Lindsey Shrinerapi-338662480No ratings yet
- Units and Dimensions: Physical QuantitiesDocument17 pagesUnits and Dimensions: Physical Quantitiesfirozalam011No ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument69 pagesFluid MechanicsMARSHALNo ratings yet
- NLMSYP23Document12 pagesNLMSYP23Venky reddyNo ratings yet
- Table of Units - Dimensional FormulaeDocument8 pagesTable of Units - Dimensional Formulaehorlersunkanmey BNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 A2 Physics Problems STEM-N ASICODocument11 pagesPhysics 1 A2 Physics Problems STEM-N ASICOChristian Paul A. AsicoNo ratings yet
- PHYS Module 2 PhotoMasterDocument25 pagesPHYS Module 2 PhotoMasterPrathmesh Sinha100% (1)
- 1 - Physical Quantities and UnitsDocument49 pages1 - Physical Quantities and UnitsNurul AtikaNo ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument29 pagesPhysics NotesAlicia TanNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS IAS: Unit 01 Mechanics - Topic 01 MechanicsDocument23 pagesPHYSICS IAS: Unit 01 Mechanics - Topic 01 Mechanicsමේනුක සූවින්දNo ratings yet
- Bansal Units and MeasurementsDocument24 pagesBansal Units and MeasurementsAmbition Study Centre ButiboriNo ratings yet
- Phy With ShahrierApon PDFDocument34 pagesPhy With ShahrierApon PDFShahrier AponNo ratings yet
- Pdfa5 3Document1 pagePdfa5 3aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 7Document1 pagePdfa3 7aizatNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Pdfa3 6Document1 pagePdfa3 6aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa4 5Document1 pagePdfa4 5aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa5 1Document1 pagePdfa5 1aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa5 3Document1 pagePdfa5 3aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa5 2Document1 pagePdfa5 2aizatNo ratings yet
- Specific Latent Heat (I) : Heating Ice To Form VapourDocument1 pageSpecific Latent Heat (I) : Heating Ice To Form VapouraizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa4 7Document1 pagePdfa4 7aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 5Document1 pagePdfa3 5aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa4 8Document1 pagePdfa4 8aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa4 6Document1 pagePdfa4 6aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa4 3Document1 pagePdfa4 3aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa4 2Document1 pagePdfa4 2aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 1Document1 pagePdfa3 1aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa4 1Document1 pagePdfa4 1aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 15Document1 pagePdfa2 15aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 16Document1 pagePdfa2 16aizat100% (1)
- Pdfa3 3Document1 pagePdfa3 3aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 4Document1 pagePdfa3 4aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa3 2Document1 pagePdfa3 2aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 14Document1 pagePdfa2 14aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 12Document1 pagePdfa2 12aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 13Document1 pagePdfa2 13aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 11Document1 pagePdfa2 11aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 9Document1 pagePdfa2 9aizat100% (1)
- Pdfa2 10Document1 pagePdfa2 10aizatNo ratings yet
- Pdfa2 8Document1 pagePdfa2 8aizatNo ratings yet
- Area CapacitanceDocument7 pagesArea CapacitancesivanagendraNo ratings yet
- Journal Pre-Proofs: Applied Thermal EngineeringDocument40 pagesJournal Pre-Proofs: Applied Thermal EngineeringDedi AfandiNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Pressure Drop in Vertical Pneumatic ConveyorsDocument9 pagesPrediction of Pressure Drop in Vertical Pneumatic ConveyorshendrobamaNo ratings yet
- Dead Weight TesterDocument10 pagesDead Weight TesterrajputashiNo ratings yet
- Analytical Model of An Ultrasonic Cross-Correlation Flow Meter, Part 1 - ..Document7 pagesAnalytical Model of An Ultrasonic Cross-Correlation Flow Meter, Part 1 - ..Thiago TavaresNo ratings yet
- Super X/Xi Series VRF: Variable Refrigerant Flow SystemsDocument104 pagesSuper X/Xi Series VRF: Variable Refrigerant Flow SystemsIván CovarrubiasNo ratings yet
- DIY Colloidal Silver Generator Circuit DesignDocument6 pagesDIY Colloidal Silver Generator Circuit DesignБориз Марсовец УалалгаманатинагахаNo ratings yet
- Untitled 3Document7 pagesUntitled 3Yoonjin HwangNo ratings yet
- Device Coordination PDFDocument89 pagesDevice Coordination PDFMothafukin MorrisseyNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Forces, Materials, and DevicesDocument18 pagesMagnetic Forces, Materials, and DevicesJefry Pasaribu GoratNo ratings yet
- Ee Module 4 April 2012Document3 pagesEe Module 4 April 2012Znevba QuintanoNo ratings yet
- Thermal Conductivity of Composite Slab: Vishwakarma Institute Technology, Pune ofDocument7 pagesThermal Conductivity of Composite Slab: Vishwakarma Institute Technology, Pune ofHussain MagarNo ratings yet
- Mycbseeguide Test GeneratorDocument3 pagesMycbseeguide Test GeneratorRAJESH SHARMANo ratings yet
- Repuestos EX2000Document10 pagesRepuestos EX2000Jhonathan RodriguezNo ratings yet
- ASTM C127 - Specific Gravity and Absorption of Coarse AggregateDocument5 pagesASTM C127 - Specific Gravity and Absorption of Coarse AggregateIsaac ArturoNo ratings yet
- 'Ulyhfrq: Instruction ManualDocument36 pages'Ulyhfrq: Instruction ManualAndri kuswandiNo ratings yet
- UEi Test Instruments - Multimeters DataSheetDocument6 pagesUEi Test Instruments - Multimeters DataSheetAleksandar PantelićNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1, B, Introduction To Heat TransferDocument68 pagesChapter 1, B, Introduction To Heat Transfer01094255175 01094255175No ratings yet
- Module 5 Print 2Document16 pagesModule 5 Print 2Merrie Anne Pascual BagsicNo ratings yet
- Edoc-What Is Capacitor Bank Testing and Why Is DoneDocument8 pagesEdoc-What Is Capacitor Bank Testing and Why Is DoneEl Comedor BenedictNo ratings yet
- A Lecture On Autotransformers For Power Engineering StudentsDocument6 pagesA Lecture On Autotransformers For Power Engineering StudentsBojanNo ratings yet
- 5-KW Solar System QuotationDocument1 page5-KW Solar System QuotationKidzee KidzeeNo ratings yet
- The Plasma-Sheath Boundary Region - R.N.franklinDocument13 pagesThe Plasma-Sheath Boundary Region - R.N.franklingkwltnaosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-Different Types of ForcesDocument56 pagesLesson 1-Different Types of Forcesclyde domingoNo ratings yet
- MMAN2300 Mock Exam QS 1Document15 pagesMMAN2300 Mock Exam QS 1Aaron HoytashNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Kinematics - Motion in 1DDocument4 pagesLesson 3: Kinematics - Motion in 1DErika SoriñoNo ratings yet
- ABB Motors and Technical Data Sheet - DOL Generators: No. Data Unit RemarksDocument1 pageABB Motors and Technical Data Sheet - DOL Generators: No. Data Unit Remarksarash esmaeiliNo ratings yet
- Must Read ONGC Fluid Mechanics Questions With AnswersDocument5 pagesMust Read ONGC Fluid Mechanics Questions With AnswersIgbereyivwe TejiriNo ratings yet
- Munters Misting Humidifiers Electrolux Ovlaznuvaci - MX2700 - ENDocument2 pagesMunters Misting Humidifiers Electrolux Ovlaznuvaci - MX2700 - ENIfti NiaziNo ratings yet
- DTR 1500 Eng - 12.2019Document39 pagesDTR 1500 Eng - 12.2019diogo_airjNo ratings yet