Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NDT AND EDDY CURRENT TESTING
Uploaded by
Tonyo AyshiyuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NDT AND EDDY CURRENT TESTING
Uploaded by
Tonyo AyshiyuCopyright:
Available Formats
NDT AND EDDY CURRENT TESTING After reading this section you will be able to do the following:
Explain how eddy currents are used in NDT. Explain why NDT is so important to our society.
Nondestructive testing (NDT) means exactly what the words say. NDT literally means testing materials without destroying them. In other words, we can look for defects in a variety of metallic materials using eddy currents and never harm the material that we are testing. This is important because if we destroy the material we are testing, it does not do much good to test it in the first place. NDT is very important because often the defects that we are looking for are not visible because paint or some other coating may cover them. There might also be defects that are so small they cannot be seen with our eyes or any other visual method of inspection. Therefore, inspection methods such as eddy current inspection have been developed to detect the defects. Try an Eddy Current Experiment In the experiment below you will use eddy current testing to detect cracks in a block of metal. You will notice that you are using a coil of wire wrapped around a piece of iron to generate the magnetic field that caused the eddy currents to form in the metal. In the field of NDT the coil is called the inspection probe. The magnetic field that is generated by the eddy currents can be detected using this same probe. We can monitor the magnetic field being produced by these eddy currents with an instrument called an eddyscope. If there is a change in the magnetic field from the eddy currents, we can tell that we have found some sort of defect in the material that we are testing. When the instrument sees a change in the magnetic field generated by the eddy currents, it displays a change in the signal on the screen.
As long as the material being tested is very uniform in every way, the eddy currents will be uniform and consistent. If there is some defect in the material such as a crack, the eddy currents will be disturbed from their normal circular shapes. NDT technicians use many different types of eddy current testing equipment. Some are simple coils that are held on a piece of metal. Others use special probes, like the one shown above, that are pushed inside of tube such as those in heat exchanger units. The technicians on the right are performing an eddy current inspection on the tube of a heat exchanger. Heat exchangers are used in places like nuclear power plants. Radioactive water from the reactor is circulated through the tubes and cooling water that will be returned to a river or lake is circulated on the outside of the tubes. It is very important that the radioactive water and the cooling water do not mix. Therefore, technicians perform eddy current inspections on the tubes to
find and defects that may be present before they become leaks in the tubing.
Review 1. NDT stands for "Nondestructive Testing." 2. NDT methods are used to test materials and parts without harming them. 3. Eddy current testing is just one of the methods used by technicians to find defects before they cause problems. EDDY CURRENTS After reading this section you will be able to do the following:
Explain what an Eddy Current is. Discuss the one requirement necessary for a current to be induced into an object.
In the discussion on the previous page you learned learned about electromagnetic induction. You learned that anytime a conductor was placed in a changing magnetic field that electrical current was generated in the conductor. We talked about the conductor being a piece of wire that is often wrapped into a coil, but the conductor does not need to be in the shape of a coil and does not even need to be wire. It could be a piece of flat steel, aluminum plate, or any other conductive object. The only requirement is that the object must be able to conduct electrical current.
When current is induced in a conductor such as the square piece of metal shown above, the induced current often flows in small circles that are strongest at the surface and penetrate a short distance into the material. These current flow patterns are thought to resemble eddies in a stream, which are the tornado looking swirls of the water that we sometimes see. Because of this presumed resemblance, the electrical currents were named eddy currents. Uses of eddy currents Just like in our transformer experiment, these induced eddy currents generate their own magnetic field. After all, this is an actual electrical current and any current flowing in a conductor produces a magnetic field, right? The detection and measurements of the strength of the magnetic fields produced by the eddy currents makes it possible for us to learn things about conductive materials without even contacting them. For example, the electrical conductivity of a material can be determined by the strength of the eddy currents that form. Also since cracks and other breaks in the surface of a material will prevent eddy currents from forming in that region of the surface, eddy currents can be used to detect cracks in materials.
This is referred to as eddy current testing in the field of nondestructive testing (NDT). NDT technicians and engineers use eddy current testing to find cracks and other flaws in part of airplanes and other systems where bad things can happen if the part breaks. On the next page you will learn more about eddy current testing and be able to try an inspection yourself.
Review 1. Any electrically conductive object will conduct an induced current if it is placed in a changing magnetic field. 2. Eddy currents are circular induced currents. 3. Eddy currents generate their own magnetic fields. ALTERNATING CURRENT After reading this section you will be able to do the following:
Define what AC stands for and what it means. Explain how AC is created and delivered to different places. Discuss the differences between AC and DC.
AC is short for alternating current. This means that the direction of current flowing in a circuit is constantly being reversed back and forth. This is done with any type of AC current/voltage source. The electrical current in your house is alternating current. This comes from power plants that are operated by the electric company. Those big wires you see stretching across the countryside are carrying AC current from the power plants to the loads, which are in our homes and businesses. The direction of current is switching back and forth 60 times each second.
This is a series circuit using an AC source of electricity. Notice that the light bulb still lights but the electron current is constantly reversing directions. The change in direction of the current flow happens so fast that the light bulb does not have a chance to stop glowing. The light bulb does not care if it is using DC or AC current. The circuit is delivering energy to the light bulb from the source, which, in this case, is a power plant.
Review 1. AC, or alternating current means the electrical current is alternating directions in a repetitive pattern. 2. AC is created by generators in power plants, and other sources. This AC current is delivered to our homes and businesses by the power lines we see everywhere. 3. The frequency of repetition of this current is 60 Hertz. This means the direction of the current changes sixty times every second. DIRECT CURRENT After reading this section you will be able to do the following:
Explain what DC stands for and what it means. Define what a good source of DC would be.
Now that we have a fairly good understanding of basic electricity terms and concepts, let's take a closer look at some more details of the electrical current itself. The battery we have been using for a current/voltage source generates direct current, which simply means the current flows in only one direction.
As long as electrons are flowing through the atoms of the circuit, work is being done. We can see that work is being done in this circuit because it lights the light bulb. The actual amount of electrons that are flowing is determined by the type and size of the battery as well as by the size and type of the light bulb. We could reverse the polarity of the battery by switching the contacts (wires), and the current would flow in the opposite direction and the bulb would still light. Either way the battery is connected to the circuit, current can only flow in one direction. Direct current (DC) can also be generated by means other than batteries. Solar cells, fuel cells, and even some types of generators can provide DC current.
Review 1. DC, or direct current means the electrical current is flowing in only one direction in a circuit. 2. Batteries are a good source of direct current (DC).
You might also like
- Eddy Current Inspection ApplicationDocument13 pagesEddy Current Inspection ApplicationRestu PutraNo ratings yet
- 1100 Gorman RT-UT Presentation For CTMS Oct 07Document29 pages1100 Gorman RT-UT Presentation For CTMS Oct 07Sagar NaduvinamaniNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing - Wikipedia PDFDocument26 pagesUltrasonic Testing - Wikipedia PDFKarthicWaitingNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Particle TestingDocument3 pagesMagnetic Particle TestingAnu AnoopNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing Ndt4 Rev 0: TWI LTD, Training & Examination ServicesDocument114 pagesUltrasonic Testing Ndt4 Rev 0: TWI LTD, Training & Examination Servicesphutd09No ratings yet
- Planar Flaw Height Sizing by Ultrasonics: Standard Guide ForDocument22 pagesPlanar Flaw Height Sizing by Ultrasonics: Standard Guide ForAnonymous gQTQ8cbUNo ratings yet
- RadiographyDocument41 pagesRadiographybhavin178No ratings yet
- List of StandardsDocument6 pagesList of StandardsShahazad ShaikNo ratings yet
- Eddy Current InspectionDocument7 pagesEddy Current InspectionAl BorromeoNo ratings yet
- DGS DGS MethodDocument6 pagesDGS DGS MethodAlzaki AbdullahNo ratings yet
- AGR Field Operations TD Focus-Scan Data SheetDocument2 pagesAGR Field Operations TD Focus-Scan Data SheetJeganeswaranNo ratings yet
- 67229-BS 6072-1981 Method For Magnetic Particle Flaw DetectionDocument35 pages67229-BS 6072-1981 Method For Magnetic Particle Flaw DetectionANNADURAINo ratings yet
- Magnetic Particle Examination ProcedureDocument5 pagesMagnetic Particle Examination ProcedureShankey JAlanNo ratings yet
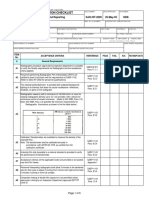
- Interpretation of EN 1712 Acceptance CriteriaDocument4 pagesInterpretation of EN 1712 Acceptance CriteriaYuzi VengamNo ratings yet
- RFT Theory of Operation ExplainedDocument6 pagesRFT Theory of Operation ExplainedPradeep Kumar BowmarajuNo ratings yet
- Saudi Aramco Inspection Checklist: Radiographic Film Evaluation and Reporting SAIC-RT-2009 25-May-05 NdeDocument6 pagesSaudi Aramco Inspection Checklist: Radiographic Film Evaluation and Reporting SAIC-RT-2009 25-May-05 NdeSergey KichenkoNo ratings yet
- Doc. Eddy Current Testing Basic PrincipleDocument43 pagesDoc. Eddy Current Testing Basic PrincipleCepi Sindang KamulanNo ratings yet
- EMAT Inspection Services PDFDocument1 pageEMAT Inspection Services PDFCepi Sindang KamulanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3, Eddy Current NDEDocument49 pagesLecture 3, Eddy Current NDEMirza Safeer AhmadNo ratings yet
- ANDT InspectionsDocument98 pagesANDT InspectionsHerris SimamoraNo ratings yet
- API 934 Minutes Fluor ATT CDocument28 pagesAPI 934 Minutes Fluor ATT CAnonymous rUs4PjYo5No ratings yet
- Iso 14096 1 2005Document18 pagesIso 14096 1 2005RONALD ALFONSO PACHECO TORRESNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Particle TestingDocument3 pagesMagnetic Particle TestingKurniawanNo ratings yet
- Phased Array CiorauDocument9 pagesPhased Array Ciorausolrac4371No ratings yet
- Iso 16809Document44 pagesIso 16809edcaabayNo ratings yet
- Asme Sec 5 TofdDocument6 pagesAsme Sec 5 TofdarsalanhaqNo ratings yet
- Eddy Current Testing Level II Course 40 Hours Hands-OnDocument1 pageEddy Current Testing Level II Course 40 Hours Hands-OnMai Sỹ HảiNo ratings yet
- E2700-09 Standard Practice For Contact Ultrasonic Testing of Welds Using Phased ArraysDocument9 pagesE2700-09 Standard Practice For Contact Ultrasonic Testing of Welds Using Phased Arrayskenvn100% (1)
- ID Creep Wave Detection and Sizing Principles ExplainedDocument22 pagesID Creep Wave Detection and Sizing Principles Explainednathaniel ekaikoNo ratings yet
- 109428-BS en 583-4-2002Document18 pages109428-BS en 583-4-2002Nensha KagasawaNo ratings yet
- Quality - NDT and NDE Present-OKDocument60 pagesQuality - NDT and NDE Present-OKMan Nguyen TheNo ratings yet
- TOFD Sizing Defect by Creep WaveDocument6 pagesTOFD Sizing Defect by Creep WaveLương Hồ VũNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Flaws in Tube Butt Welds Using an Innovative RT TechniqueDocument3 pagesEvaluating Flaws in Tube Butt Welds Using an Innovative RT TechniquesubhashpkdNo ratings yet
- NDT MT nds1Document41 pagesNDT MT nds1sathi11189No ratings yet
- Inspection Report Bifab Ut On Duplex Stainless Steel Piping PDFDocument11 pagesInspection Report Bifab Ut On Duplex Stainless Steel Piping PDFquiron2014No ratings yet
- NON-DESTRUCTIVE TESTING: OVERVIEW OF LIQUID PENETRANT AND MAGNETIC PARTICLE INSPECTIONDocument30 pagesNON-DESTRUCTIVE TESTING: OVERVIEW OF LIQUID PENETRANT AND MAGNETIC PARTICLE INSPECTIONshuklahouseNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Examination Austenitic and Dissimilar WeldsDocument6 pagesUltrasonic Examination Austenitic and Dissimilar WeldshocimtmNo ratings yet
- NDE Associates, Inc. - Ultrasonic Testing - Phased ArrayDocument2 pagesNDE Associates, Inc. - Ultrasonic Testing - Phased Arrayaldeanucu3203No ratings yet
- Ruane MTDocument40 pagesRuane MT9703422499No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Acoustic Transducers (Emats) : Standard Guide ForDocument8 pagesElectromagnetic Acoustic Transducers (Emats) : Standard Guide ForEric GozzerNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic TestingDocument134 pagesUltrasonic TestingWoodrow FoxNo ratings yet
- Study of The Factors Affecting The Sensitivity of Liquid PenetrantDocument59 pagesStudy of The Factors Affecting The Sensitivity of Liquid PenetrantfallalovaldesNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic 4Document3 pagesUltrasonic 4nsbirwalNo ratings yet
- E 1065 - 99-UT-transdDocument22 pagesE 1065 - 99-UT-transdDemian PereiraNo ratings yet
- ACFM® & TSC Products OverviewDocument27 pagesACFM® & TSC Products OverviewStu SutcliffeNo ratings yet
- PT VariousDocument159 pagesPT VariousShyam Sundar GayenNo ratings yet
- Neutron Radiography: A Guide to Non-Destructive Testing Using NeutronsDocument29 pagesNeutron Radiography: A Guide to Non-Destructive Testing Using NeutronsKaitlyn SmallfootNo ratings yet
- E390-11 Standard Reference Radiographs For Steel Fusion WeldsDocument4 pagesE390-11 Standard Reference Radiographs For Steel Fusion WeldsAhmed Shaban KotbNo ratings yet
- Asnt Liii Otline Ut & PTDocument3 pagesAsnt Liii Otline Ut & PTMohammed RizwanNo ratings yet
- Corrosion and Materials in Hydrocarbon Production: A Compendium of Operational and Engineering AspectsFrom EverandCorrosion and Materials in Hydrocarbon Production: A Compendium of Operational and Engineering AspectsNo ratings yet
- Impact of Non-Destructive Testing: Proceedings of the 28th Annual British Conference on Non-Destructive Testing, Sheffield, UK, 18-21 September 1989From EverandImpact of Non-Destructive Testing: Proceedings of the 28th Annual British Conference on Non-Destructive Testing, Sheffield, UK, 18-21 September 1989C. BrookNo ratings yet
- Radiation Safety of X Ray Generators and Other Radiation Sources Used for Inspection Purposes and for Non-medical Human Imaging: Specific Safety GuideFrom EverandRadiation Safety of X Ray Generators and Other Radiation Sources Used for Inspection Purposes and for Non-medical Human Imaging: Specific Safety GuideNo ratings yet
- ECE00 - Basic Electronics (Laboratory) Activity 6: InductorsDocument7 pagesECE00 - Basic Electronics (Laboratory) Activity 6: InductorsKpop Challenge By GodsNo ratings yet
- NDT Method & AcceptanceDocument1 pageNDT Method & AcceptanceTonyo Ayshiyu100% (8)
- Introduction to the Six Most Common NDT MethodsDocument34 pagesIntroduction to the Six Most Common NDT MethodsNanditha Mandava ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- Guided Wave UTDocument5 pagesGuided Wave UTTonyo Ayshiyu100% (1)
- Computer Radiography Wall ThicknessDocument36 pagesComputer Radiography Wall ThicknessTonyo Ayshiyu100% (3)
- Procedure Using UT SlideDocument1 pageProcedure Using UT SlideTonyo Ayshiyu100% (3)
- Useful Radiography Formulas GuideDocument1 pageUseful Radiography Formulas GuideTonyo Ayshiyu100% (9)
- DAC Distance Amplitude CurveDocument2 pagesDAC Distance Amplitude CurveTonyo Ayshiyu81% (16)
- UT Flaw Detection For Technicians by J.C.druryDocument100 pagesUT Flaw Detection For Technicians by J.C.druryTonyo Ayshiyu96% (23)
- AWS - Use of Measuring ToolsDocument33 pagesAWS - Use of Measuring ToolsTonyo Ayshiyu100% (11)
- Ultrasonic and Radiography Techniques for Finding Depth and Safe DistancesDocument1 pageUltrasonic and Radiography Techniques for Finding Depth and Safe DistancesTonyo Ayshiyu100% (6)
- Heat Transfer Chapter 6 SummaryDocument8 pagesHeat Transfer Chapter 6 SummaryJeremiah ValeraNo ratings yet
- PeDocument72 pagesPeRakesh NairNo ratings yet
- PSCExample1ASeminar JLS Jul05Document10 pagesPSCExample1ASeminar JLS Jul05Ekky CecilNo ratings yet
- M5 3-Unified09Document14 pagesM5 3-Unified09Chandana KarumanchiNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Chemical Engineering Unit OperationsDocument2 pagesIntroduction to Chemical Engineering Unit OperationsErwin CabangalNo ratings yet
- Mse630 f10 Hw1 SolDocument4 pagesMse630 f10 Hw1 SolLava Kumar BNo ratings yet
- Calculus 01 Tangents and NormalsDocument8 pagesCalculus 01 Tangents and NormalseliseudesafateNo ratings yet
- DeLanda - Matter MattersDocument16 pagesDeLanda - Matter MattersPorrie W WatanakulchaiNo ratings yet
- ANSYS Autodyn Composite ModelingDocument70 pagesANSYS Autodyn Composite Modelinggustavo5150No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Thermodynamics Fundamentals of ThermodynamicsDocument32 pagesFundamentals of Thermodynamics Fundamentals of ThermodynamicsYep IdidthisNo ratings yet
- Basic KinematicsDocument5 pagesBasic KinematicsKeniel YaoNo ratings yet
- INTRO TO AUTOMOBILE ENGINESDocument2 pagesINTRO TO AUTOMOBILE ENGINESamardeepbediNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Reduction Cobalt-Chromium Spinel Oxides. Stoichiometric Cobalt ChromiteDocument6 pagesHydrogen Reduction Cobalt-Chromium Spinel Oxides. Stoichiometric Cobalt ChromiteDuongNo ratings yet
- MCE IGCSE Physics TWB C03 - Full SolutionsDocument2 pagesMCE IGCSE Physics TWB C03 - Full SolutionsXIN ZHANGNo ratings yet
- MOTIONDocument6 pagesMOTIONAnthropophobe NyctophileNo ratings yet
- Gas Pipeline Hydrodynamic Analysis Based On Beggs-Brill CorrelationDocument7 pagesGas Pipeline Hydrodynamic Analysis Based On Beggs-Brill CorrelationsriadelilaNo ratings yet
- Voidage V2 API Model: Voidage (Built-In) Calculation in EDEMDocument5 pagesVoidage V2 API Model: Voidage (Built-In) Calculation in EDEMPeter MwangiNo ratings yet
- NafionDocument9 pagesNafionAlejandro BedollaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Metal Forming PDFDocument68 pagesLecture Notes - Metal Forming PDFIrfan KhanNo ratings yet
- Problem 4.63 - Fox - Mecânica Dos FluidosDocument1 pageProblem 4.63 - Fox - Mecânica Dos FluidosBruno AlbuquerqueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 48 Applications of Matrices and Determinants: EXERCISE 201 Page 545Document32 pagesChapter 48 Applications of Matrices and Determinants: EXERCISE 201 Page 545Sadio Abdi NasirNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic ProcessesDocument13 pagesThermodynamic ProcessesS Jayasuriya100% (1)
- Subject Code: PH 3151 Subject Title: Engineering Physics 05-03-2022 Max. Marks 100 Semester: I Time: 1:45 - 4:45 PMDocument1 pageSubject Code: PH 3151 Subject Title: Engineering Physics 05-03-2022 Max. Marks 100 Semester: I Time: 1:45 - 4:45 PMWittin PrinceNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument18 pagesLaws of MotionJhen BonNo ratings yet
- Part 12 Fundamentals of Ultrasonic Phased ArraysDocument7 pagesPart 12 Fundamentals of Ultrasonic Phased ArraysWahyu RiyandiNo ratings yet
- Switching Over Voltage When Disconnecting A Combined 400 KV Cable Overhead LineDocument10 pagesSwitching Over Voltage When Disconnecting A Combined 400 KV Cable Overhead LineJon Ivanc100% (1)
- Lecture 2 - Process Control (P1)Document30 pagesLecture 2 - Process Control (P1)Elia SaadNo ratings yet
- 5) 35473408 PDFDocument436 pages5) 35473408 PDFSubinDesarNo ratings yet
- Lab Practice #13 How Does A Thermometer Works? ADocument1 pageLab Practice #13 How Does A Thermometer Works? ABayonettaLinNo ratings yet
- ★★Electron RF Linacs for Industrial Applications - ICABU11 - 17 - 포스텍Document34 pages★★Electron RF Linacs for Industrial Applications - ICABU11 - 17 - 포스텍KoseokhoNo ratings yet