Professional Documents
Culture Documents
01chapter 1 Psychology
Uploaded by
aiklussOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
01chapter 1 Psychology
Uploaded by
aiklussCopyright:
Available Formats
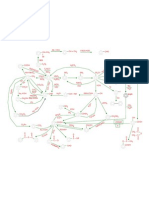
Chapter one What is Psychology?
Fields of Psychology Developmental psychology
Physiological Psychology
Experimental psychology
Personality Psychology
Clinical and Counseling Psychology Clinical: Counseling:
Social Psychology
Industrial and Organizational (I/O) Psychology
Enduring Issues What are the principle issues common to many subfields of psychology? Person-Situation Internal factors:
External factors:
Heredity-Environment Nature: Nurture:
Stability-Change
Diversity-Universality
Mind-Body
Psychology as a Science Scientific method:
Theory:
Hypotheses:
Science vs. Non-science
Other Social Sciences Sociology: : Anthropology Political Science: The Growth of Psychology Wilhelm Wundt (1879) and Edward Bradford Titchener: Structuralism Concerned with identifying the units of conscious experience William James: Functionalism Concerned with the ongoing use of conscious experience
Sigmund Freud: Psychodynamic psychology Focuses on the unconscious determinants of behavior
John Broadus Watson: Behaviorism Concerned with observable, quantifiable, measurable behavior Burthus Fredrick Skinner: Behaviorism revisited Focused on the role of reinforcement Gestalt Psychology Defined psychology as: the study of the immediate experience of the whole organism -THE WHOLE IS DIFFERENT THAN THE SUM OF ITS PARTS
Existential and Humanistic Psychology Existentialism
Humanists
Cognitive Psychology Concerned with memory, thinking, language, learning, and decision making; mental processing Evolutionary Psychology Focuses on the adaptive values of mental processes and behavior patterns and what function they serve
Positive Psychology Emphasizes and studies the origins and nurturance of mental wellness Multiple Perspectives of Psychology Today
Women in Psychology
Successful explanations of human functioning at one level need not invalidate explanations at other levels
Human Diversity Gender:
Feminist Psychology
Race and ethnicity Race: Ethnicity:
Culture
Research Methods in Psychology 1. Naturalistic Observation Studied non-intrusively in its natural environment
2. Case Studies Intensive analysis and description of an individual or small group hoping to find commonalties between that individual and the entire population
3. Surveys Asking predetermined questions using an interview or questionnaire Wording effects: 4. Correlational Research Used to investigate and clarify the relationships between variables 5. Experimental Research Enables the researcher to focus on the possible effects of one or more factors by: 1) 2)
Independent and Dependent variables Independent: Dependent:
Experimental condition/group:
Control condition/group:
Experimenter Bias:
Random Assignment:
6. Multimethod Research
The Importance of Sampling Representative sample:
Random sample:
Human Diversity and Research
Ethics and Psychology Milgram study
APA code of ethics requires Informed consent from participants o The nature of the study in clearly understandable language o Must be documented o Risks, possible adverse effects, and limitation on confidentiality o If participation is course credit then alternative must be offered o Cannot deceive related to risks or unpleasant emotional experiences o Deception can only be used when absolutely necessary
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Magnificent 10 For Men by MrLocario-1Document31 pagesThe Magnificent 10 For Men by MrLocario-1Mauricio Cesar Molina Arteta100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Heat Wave Action Plan RMC 2017Document30 pagesHeat Wave Action Plan RMC 2017Saarthak BadaniNo ratings yet
- 10 Definite IntegrationDocument36 pages10 Definite IntegrationaiklussNo ratings yet
- Lumafusion Shortcuts LandscapeDocument2 pagesLumafusion Shortcuts Landscapepocho clashNo ratings yet
- Polystylism in The Context of Postmodern Music. Alfred Schnittke's Concerti GrossiDocument17 pagesPolystylism in The Context of Postmodern Music. Alfred Schnittke's Concerti Grossiwei wuNo ratings yet
- Mini Lecture and Activity Sheets in English For Academic and Professional Purposes Quarter 4, Week 5Document11 pagesMini Lecture and Activity Sheets in English For Academic and Professional Purposes Quarter 4, Week 5EllaNo ratings yet
- CRUSADE of PRAYERS 1-170 Litany 1-6 For The Key To Paradise For DistributionDocument264 pagesCRUSADE of PRAYERS 1-170 Litany 1-6 For The Key To Paradise For DistributionJESUS IS RETURNING DURING OUR GENERATION100% (10)
- 70 Solutions To Common Writing Mistakes-ManteshDocument68 pages70 Solutions To Common Writing Mistakes-ManteshbuntopsihNo ratings yet
- Benzene Road MapDocument1 pageBenzene Road MapSahib RandhawaNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamic 2Document74 pagesAerodynamic 2aiklussNo ratings yet
- Origin of Super Massive Black HolesDocument5 pagesOrigin of Super Massive Black HolesaiklussNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 (Qus. & Ans.)Document15 pagesGrade 4 (Qus. & Ans.)aiklussNo ratings yet
- Accounts - II (Qus. Paper)Document8 pagesAccounts - II (Qus. Paper)aikluss0% (1)
- 218 39 Solutions Instructor Manual Chapter 1 World MechanismsDocument6 pages218 39 Solutions Instructor Manual Chapter 1 World MechanismsaiklussNo ratings yet
- Practice Set 1 (Synonyms)Document6 pagesPractice Set 1 (Synonyms)aiklussNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 (Qus. & Ans.)Document16 pagesGrade 3 (Qus. & Ans.)aiklussNo ratings yet
- E M Problem Set 1 Suggested Time: 30-60 Mins. Grade: IV Topic: ArithmeticDocument2 pagesE M Problem Set 1 Suggested Time: 30-60 Mins. Grade: IV Topic: ArithmeticaiklussNo ratings yet
- Apmo 2005Document1 pageApmo 2005aiklussNo ratings yet
- E M Problem Set 1 Suggested Time: 30-60 Mins. Grade: IV Topic: ArithmeticDocument2 pagesE M Problem Set 1 Suggested Time: 30-60 Mins. Grade: IV Topic: ArithmeticaiklussNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 (Qus. & Ans.)Document17 pagesGrade 5 (Qus. & Ans.)aiklussNo ratings yet
- Part II-Ch. 6 - Early Perspectives of The CurriculumDocument43 pagesPart II-Ch. 6 - Early Perspectives of The CurriculumaiklussNo ratings yet
- Benzene Road MapDocument1 pageBenzene Road MapSahib RandhawaNo ratings yet
- PCMI Lesson Study VersionVDocument10 pagesPCMI Lesson Study VersionVaiklussNo ratings yet
- Rev 19 3 2011Document28 pagesRev 19 3 2011aiklussNo ratings yet
- 07car Assmnt & MBTI - McCaulleyDocument22 pages07car Assmnt & MBTI - McCaulleyaiklussNo ratings yet
- Ar2011 12Document337 pagesAr2011 12Bhaskar KumarNo ratings yet
- Cog Ability & Non Ability Trait DeterminantsDocument7 pagesCog Ability & Non Ability Trait DeterminantsaiklussNo ratings yet
- 1999 New York State Grade 8 Mathematics Statewide Assessment Technical ReportDocument54 pages1999 New York State Grade 8 Mathematics Statewide Assessment Technical ReportaiklussNo ratings yet
- 9-12 Math I Student Edition Unit 1 Function FamiliesDocument61 pages9-12 Math I Student Edition Unit 1 Function FamiliesSharyahna McNeilNo ratings yet
- Student's Worksheet 4, Cartesian Product Content Worksheet (CW2)Document2 pagesStudent's Worksheet 4, Cartesian Product Content Worksheet (CW2)aiklussNo ratings yet
- Mcqs Class ViDocument47 pagesMcqs Class Viaikluss100% (1)
- Rate of Change, Tangent Line and DifferentiationDocument18 pagesRate of Change, Tangent Line and DifferentiationaiklussNo ratings yet
- Math Class XDocument101 pagesMath Class Xaikluss0% (1)
- Jae 198547030505Document5 pagesJae 198547030505aiklussNo ratings yet
- 04 - JTC Template On Project ProposalDocument10 pages04 - JTC Template On Project Proposalbakelm alqamisNo ratings yet
- Class Homework Chapter 1Document9 pagesClass Homework Chapter 1Ela BallıoğluNo ratings yet
- CSEC English SBA GuideDocument5 pagesCSEC English SBA GuideElijah Kevy DavidNo ratings yet
- Ujian NasionalDocument41 pagesUjian NasionalKeisha SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Guerrero vs Benitez tenancy disputeDocument1 pageGuerrero vs Benitez tenancy disputeAb CastilNo ratings yet
- TAFJ-H2 InstallDocument11 pagesTAFJ-H2 InstallMrCHANTHANo ratings yet
- Dell Market ResearchDocument27 pagesDell Market ResearchNaved Deshmukh0% (1)
- Engaged Listening Worksheet 3 - 24Document3 pagesEngaged Listening Worksheet 3 - 24John BennettNo ratings yet
- FIN 1050 - Final ExamDocument6 pagesFIN 1050 - Final ExamKathi100% (1)
- AefiDocument38 pagesAefizedregga2No ratings yet
- Group Handling - Pre Registration Activity: Submited To-Submitted byDocument12 pagesGroup Handling - Pre Registration Activity: Submited To-Submitted byharshal kushwahNo ratings yet
- Hays Grading System: Group Activity 3 Groups KH PS Acct TS JG PGDocument1 pageHays Grading System: Group Activity 3 Groups KH PS Acct TS JG PGkuku129No ratings yet
- JSP - How To Edit Table of Data Displayed Using JSP When Clicked On Edit ButtonDocument8 pagesJSP - How To Edit Table of Data Displayed Using JSP When Clicked On Edit Buttonrithuik1598No ratings yet
- MCQ CH 5-Electricity and Magnetism SL Level: (30 Marks)Document11 pagesMCQ CH 5-Electricity and Magnetism SL Level: (30 Marks)Hiya ShahNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of GingerDocument24 pagesPharmacology of GingerArkene LevyNo ratings yet
- Instafin LogbookDocument4 pagesInstafin LogbookAnonymous gV9BmXXHNo ratings yet
- Terrestrial EcosystemDocument13 pagesTerrestrial Ecosystemailene burceNo ratings yet
- Basic Unix Commands: Cat - List A FileDocument3 pagesBasic Unix Commands: Cat - List A Filekathir_tkNo ratings yet
- OutliningDocument17 pagesOutliningJohn Mark TabbadNo ratings yet
- Compiled May 5, 2017 Case DigestDocument16 pagesCompiled May 5, 2017 Case DigestGrace CastilloNo ratings yet
- Molly C. Dwyer Clerk of CourtDocument3 pagesMolly C. Dwyer Clerk of CourtL. A. PatersonNo ratings yet
- Study of Storm and Sewer Drains For Rajarhat (Ward No 4) in West Bengal Using Sewergems SoftwareDocument47 pagesStudy of Storm and Sewer Drains For Rajarhat (Ward No 4) in West Bengal Using Sewergems SoftwareRuben Dario Posada BNo ratings yet
- Ecological Modernization Theory: Taking Stock, Moving ForwardDocument19 pagesEcological Modernization Theory: Taking Stock, Moving ForwardFritzner PIERRENo ratings yet
- The Principle of Subsidiarity and Catholic Ecclesiology - ImplicatDocument218 pagesThe Principle of Subsidiarity and Catholic Ecclesiology - ImplicatJonathanKiehlNo ratings yet