Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EMTL Weekly
Uploaded by
vikramvsuCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EMTL Weekly
Uploaded by
vikramvsuCopyright:
Available Formats
NARAYANA ENGINEERING COLLEGE:: GUDUR DEPARTMENT OF ECE ACADEMIC YEAR: 2012-13 SUB: EM THEORY AND TRANSMISSION LINES YEAR:
II B.Tech(ECE), II-SEM Name of the staff: V.Ajay Kishan/T.Pratap QUESTIONS QUESTIONS FOR EXAM DATE SCHEDULED ON - 09-01-2013 1. a) Define electric field of point charge. Express electric field of point charge Q at a distance r meters in vector form. [April/May-07 set-2, Aug/Sep - 08, set 3] b) A charge of -0.3C is located at A(25,-30,15)cm and a second charge of 0.5C is located at B (-10, 8, 12) cm. Find the electric field strength, E, at a point P (15, 20, 50) cm [Nov 2008, Set1, May 2009, set 3] 2. a)Derive the relationship between E and V. [April/May-04 set-2] b) Point charges -1nc,4nc,3nc are located at (0,0,0)(0,0,1)(1,0,0) . Find the energy in the system. [April/May-08 set-2, Aug/Sep - 07, set 2] 3 a) Discuss the salient features and limitations of Gausss law [April/May-08 set-2, Aug/Sep 07, set 2] b) Derive Poissons and Laplaces equations starting from gauss law 4. .a) Define the electric potential V at a point due to an electric charge and an electric dipole b) A point charge 5nc is located at (-3,4,0) while line y=1,z=1 carries uniform charge 2nc/m. Find if V=0V at O( 0,0,0) find v at A(5,0,1). [April/May-08 set-4, Nov 06, set 3]
5 a) State Coulombs law. Discuss about the Coulomb vector force or point charges say Q1 and Q2 with suitable examples. [April/May-07 set-3,Aug/Sep - 07,set 1, May 05 set 4 ] b) Point charges 1mc and 2mc are located at (3,2,-1) and (-1,-1,4) respectively. Find the electric force on a 10nc point charge located at (0,3,1).what will be the Electric field intensity at that point. [April/May-08 set-2,Aug/Sep - 07,set 2] 6) a) Derive the expression for E at any point in free space due to an electric dipole. [April/May-05 set-1, Nov - 03,set 3 Nov 07 set 4 ] b) Point charges Q1 = 1 nC, Q2= -2nC Q3 =3nC and Q4 = -4 nc are positioned one at a time in the order (0, 0, 0,) (1, 0, 0) (0, 0,-1) and (0, 0, 1) respectively. Calculate the energy in the system after each charge is positioned. [April/May-08 set-3, Nov - 05, set 1] 7) a) Derive an expression for the electric field intensity due to an infinite length line charge along the Z-axis at an arbitrary point P(x,y,z) . [Nov -06, Set-1] b) A point charge of 15nC is situated at the origin and another point charge of -12nCis located a the point (3, 3, 3). Find E and V at tha point (0,-3,-3). [April/May-06 set-2]
8) a) Define (i) Line charge (ii) Surface charge and (iii) volume charge . Give the electric field intensity equations due to each of the charge distributions L, S and v b) Find the total charge inside a volume having volume charge density as 10z2 e -0.1x sin ey C/m3. The volume is defined between -2<x<2, 0<y<1 and 3<z<4 ? [April/May-08, Set-3]
9.a) Define conductivity of a material [April/May-08, Set-3] 2 b) If J= (2cosar+sina) A/m . Calculate the current passing through i) A hemi spherical shell of radius 20 cm 0<</2 , 0<<2, ii) A spherical shell of radius 10 cm. 10. Explain about Linear, Isotropic and homogeneous dielectrics 11. Explain the equation of continuity for time varying fields . [April 09 set 1 May-10,Set 2 ,set 4 ] [April/May-04,Set-1,Nov/dec-04,set 2 ]
12. Derive Poissons and Laplaces Equations starting from Gauss law [April/May-08 set-2,Aug/Sep - 07,set 2] 13. Find the potential volume charge density at P(0.5,1.5,1) Iin free space given the potential field (a) V=2x2-y2-z2. [April/May-08 set-2,Aug/Sep - 07,set 2 ] 14. a) What is capacitance? Differentiate between isotropic and anisotropic materials [Aug/Sep - 07,set 4] b) Determine the capacitance of a capacitor consisting of two parallel metal plates 30cm30cm surface area separated by 5mm in air. What is the total energy stored by the capacitor if the capacitoris charged to potential difference of 500V.What is energy density? [April/May-08 set-4,Nov 06, set 3] 15. In a cylindrical conductor of radius 2mm the current density varies with distance from the axis according to J = 103 e -400r A/m2.Find the total current I. [April/May-07 set-3, Nov 06, set 2] QUESTIONS FOR EXAM DATE SCHEDULED ON 06-02-2013
1). a) State and prove Biot Savarts Law. [Nov-06,set 1] b) Find the total magnetic flux crossing a surface, = /2, 12 m and 0z5 m due to a vector magnetic potential = ( - 2/4) az, webers/m. 2)Derive an expression for magnetic field strength,H,due to a finite filamentary conductor carrying a current I and placed along Z-axis at a point P on Y-axis.Hence deduce the magnetic field strength for the length of the conductor extending from - to +. [Nov-06, Set-1] 3) For the finite length current element on the Z-axis use the biot savart law to derive H = I/4 (sin2-sin1) a .[April -07, set 1, April -07, set 4,]
4)Explain amperes circuital law.Specify the conditions to be met for determinig magnetic Field strength H based on Amperes circuital law [April -08, set 3, Nov -06, set 2,set 3]
5)a). what is the force experienced by a charge in a magnetic field. Obtain Lorentz Force equation. [April -08, set 2, April -06, set 3,] b).If a point charge of 4C moves with a velocity of 5ux+6uy-7uz m/s.Find the Force exerted if the Flux density is 5ux+7uy+9uz Wb/m2. 6) a)what is the inductance of a Solenoid and write the expression for its inductnce and also For magnetic field in a Solenoid.? [May -09,Set 1] b) Derive an expression for Force between two straight long parallel current carrying conductors [March -06,set 2, nov 05, set 1] 7) A steady current of 10A is established in a long straigth hollow aluminium conductor having Inner and outer radius of 1.5 cm and 3 cm respectively. Find the value of B as function of radius [Nov 08 set 3] 8)a). Derive an expression for magnets vector potential A for Surface currents [March -08,,set 2, nov 09, set 4] b). The magnetic vector potential of a current distribution in free space is given by A=15e- sin az Wb/m. Find H at (3, /4,-10) Also find the flux through = 5, 0/2, 0Z10 [March -08,,set 2, nov 09, set 1] 9. (a) Explain Faradays law for time varying fields. [April -07, set 4, Nov -06, set 4] (b) Verify the displacement current in the parallel plate capacitor is same as the conduction current in the conducting wires. 10 a) What is the inconsistency of amperes law? [April -08, set - 4, Aug -07, set 1] b) A circular loop conductor of radius 0.1m lies in the z=0 plane and has a resistance of 5 given B=0.20 sin 103t az T. determine the current 11 a) Differentiate conduction and displacement current densities [May-09, set 2] b) If =0 , = 2.5 o and = 10 o.determine whether the following pairs of fields satisfy Maxwells Equation or not. a. E = 2y ay V/m and H = 5x ax A/m. b. E = 100 sin 6107 t sinz ay V/m and H = -0.1328 cos 6 10 7 t cos z az ax A/m[May 09,set 1] 12. State and explain Maxwells equations. 13 Write down the maxwells equations for Harmonically varying fields [May 08, set 3] [May 08, set 2]
14. Obtain the integral form of Maxwells equations from Amperes circuital law in the generalized form. [Aug 07 , set 3, May -07,set 3] 15. what are the boundary conditions of magnetic field.Explain? [ May -10,set 1] 16. Derive the equation of continuity for time varying fields? [May -07, set 1]
QUESTIONS FOR EXAM DATE SCHEDULED ON EXAM DATE - 13-03-2013
1 a) Derive wave equations for source free regions. [April/May -02, set 1] b) If = 0, r = 9 for the medium in which a wave with a frequency f = 0.3GHz is propagating, determine propagation constant and intrinsic impedance of the medium when (i) = 0 and (ii) = 10 mho/s. 2.a)Explain about uniform plane waves. [Nov -06, set 1] b) Auniform plane wave at a frequency of 1 GHz is travelling in a large block of Teflon (= 1, r = 2.1, = 0) Determine , ,,. [Aug/ Sep -01,] 3. a) Derive the expression for the phase shift constant and attenuation constant of Plane wave propagating in lossy dielectric mediums. b) A plane wave propagating through a medium with r =8, r =2 has E=0.5exp(-0.33z)sin(10 8 t-z)a x v/m determine wave velocity, impedance and ,magnetic field intensity. [Aug/ Sep -04 Nov 08 set 3] 4 a) For good dielectrics derive the expressions for , , , . [May/ 08 , set-1 Nov 06 set-2] b) Find , , , for ferrite at 10Ghz r =9, r=4, =10ms/m. [Aug/ Sep -07 set 3,] 5 a) Explain wave propagation in a conducting medium. [April/May 08 , set-4] b) A large copper conductor (r = 1 r=1, =5.8x107s/m) support a uniform plane wave at 60Hz. Determine the ratio of conduction current to displacement current compute the attenuation constant.Propagation constant, intrinsic impedance, wave length and phase velocity of propagation [Aug/ Sep -08,set 3] 6 Explain wave propagation in a lossless medium. [Aug/sep 07 , set-1]
7. Explain skin depth and derive an expression for depth of penetration for a good conductor? [Aug/sep 07 , set-4] 8.Determine the phase velocity of propagation, attenuation constant,phase constant and intrinsic impedance For a forward travelling wave in a large block of copper at 1 MHz((r = 1r=1, =5.8x107s/m). Determine the distance the wave must travel to be attenuated by a factor of 100(40 dB) [April/May -08 set 2 , Nov 06 set3]
9(a) Obtain an expression for the reflection coefficient where a wave is incident normally on a perfect conductor. (b) Define Brewster and critical angles. And Total internal Reflection .
[May-09, set 1]
10.(a) derive an expression for Brewster angle when a wave is parallely polarized and what happen for Brewster angle when wave is perpendicularly polarized. [May-10, set 3 April 08 set 2] (b) What is the total internal reflection and obtain the expression for the total internal reflection angle . [April 06 set 2] 11 a) Derive a suitable expression for transmission coefficient when a plane wave incident at some angle at the interface of two media. Consider parallel polarization only. [May-09, set 4, Nov 06 set 2] b) A uniform plane wave is incident from air onto glass at an angle from the normal of 30 0. Determine the fraction of the incident power that is reflected and transmitted for parallel polarization. Assume glass has refractive index n2=1.45 12 a) Derive a suitable expression for reflection coefficient when a plane wave incident normally at the interface of two different media. [May-10, set 2] b) Derive expression for reflection and transmission coefficients of an EM wave when it is incident normally on a dielectric. [ April 08 set 3] 13 a) Define surface impedance and explain how it exists. [May-10, set 1] b) State and prove poyntings theorem with regard to EM wave propagation [May-10, set 4, set 1] 14 a) Determine the resultant Electric and Magnetic fields of plane wave when it is incident normally on a perfect conductor . [May-09, set 3] b) A Plane wave traveling in a medium of r=1, r=1 has an electric field intensity of 100,V/m. Determine the energy density in the magnetic field and also the total energy density. 15. a) Explain the significances of Poynting theorem and Poynting vector. [May-9, set 4] b) A plane wave traveling in a free space has an average Poynting vector of 5N/m2. Find the average energy density. 16.a)Derive an expression for Brewster angle when a wave is parallely polarized. [May-07 set 1] b) A uniform plane wave is incident from air onto glass at an angle from the normal of 300 Determine the fraction of incident power that is reflected and transmitted for parallel polarization. Assume glass has refractive index n2=1.45 [May-10, set 3] . 17(a) Explain different types of transmission lines. What are limitations to the maximum power that they can handle. [April -08, set 1, Nov -06, set 4] b) A coaxial cable with an outer diameter of 8mm has 50ohms characteristic impedance. If dielectric constant of the insulation is 1.60, calculate the inner diameter.. [May 08 set 1,Nov 06 set 3] 18.(a) A transmission line operating at 500Mhz has zo = 80 ohms, = 0.04Np/m, =1.5rad/m find line parameters R,L,C,G. [May 07 set 2,April 07 set1] (b) What is meant by the polarization of wave? When the wave is linearly polarized and circularly polarized.
19. a) Derive the expression for characteristic impedance of a transmission line in terms of primary constants of the line [May 09 set 1] b) A telephone line has the following primary constant R=10.15 ohms/km, L= 3.93mH/km, C = 0.00797F/km and G = 0.29mho. at frequency of 796HZ determine the Zo of the line, propagation constant. QUESTIONS FOR EXAM DATE SCHEDULED ON - 03-04-2013 1 a) Explain the concept of Infinite line. [May 09 set 4] b) A transmission line operating at =106 rad/s has =8 db/m, =1 rad/m and Zo = 60+j40 and is 2m long If the line is connected to a source of 10v, internal resistance of 40 and terminated by a load of 20+j50 determine the input impedance, the sending end current, and current at the middle of the line.
2 a) Define following terms and explain their physical significance. [May 08 set 3, April 09 set1] i)Attenuation constant ii) Characteristic impedance iii) Phase function iv) Phase velocity as applied to a transmission line b) At 8MHz Zo=40-j2 and propagation constant is 0.01+j0.18 per meter. Find the primary constants 3.a) Justify that an Infinite line is equivalent to a Finite Line terminated in its characteristic Impedance [May 06 set 1 ] b) A low transmission line of 100 characteristic impedance is connected to a load of 300 . Calculate the reflection coefficient and Standing wave ratio. 4. a) Derive the relationship between phase velocity and group velocity in transmission line theory. [May 09 set 3,April 09 set2] 0 b) The characteristic impedance of a certain line is 710 -16 when the frequency is 1 KHz. At this frequency the attenuation is 0.01neper/km and the phase function is 0.035 Radians/km. Calculate the resistance, the leakage, the inductance and the capacitance/km and velocity of propagation. 5. a) Derive the characterstic Impedance of a transmission line in terms of its line constants [May 08, set 3] b)Discuss the losses in transmission lines [April -08, set 1, Nov -06, set 4] State and explain a).Lossless transmission line and b). Distortionless line.[May 10 set 3]
6.
7. a) What is Loading. Explain different types of loading? [May 08 set 4] b) A telephone wire 20 km long has the following constants per loop km resistance 90 , capacitance o.o62 F, inductance of 0.001H. and leakage = 1.5 10-6 mhos.The line is terminated in its characterstic impedance and a potential difference of 2.1 Vhaving a frequency of 1000Hz is applied at the sending end Calculate i) . characterstic Impedance ii) Wavelength. Iii) velocity of propagation. [May 08, set 04]
8. (a) Draw the T & equivalent circuits of transmission line and define elements of those equivalent circuits. [April -07, set 1] (b) A low loss transmission line of 100 characteristic impedance is connected to a load of 300 . Calculate the reflection coefficient and standing wave ratio. Derive the relationships used. 9. (a) Explain about salient features of smith chart. [April -07, set 3, Nov -09, set 2] (b) A load ZL = 80 j 100 is located at Z = 0 on a lossless 50 line. The frequency is 200 MHz and the wavelength on the line is 2m. (i) If the line is 0.8m in length, use the smith chart to find the input impedance 10 a) explain the significance and utility of /8, /4, /2 line [April -08, set 2, Nov -04, set 3] b) A low transmission line of 100 characteristic impedance is connected to a load of 400 . Calculate the reflection coefficient and standing wave ratio. Derive the relation used. 11 a) Describe all the characteristics of UHF lines [April -08, set 4, Nov -07, set 1,May 06,set2,May 04,05 set1] b) Explain the significance and design of single stub impedance matching. Discuss the factors on which stub length depends. 12 a) Define the reflection coefficient and derive the expression for the input impedance transmission line in terms of reflection coefficient. [April -08, set 1, May -06, set 4] b) Explain with sketches how the input impedance varies with the frequency 13 a) Derive the expression for the input impedance of a transmission line of length l [April -07, set 2, May -07, set 1] b) Explain the applications of Smith chart. [April -07, set 3, Nov -06, set 4] 14 a) Explain the designing of double stub [April -09, set 3, Nov -06, set 4] b) Short circuited and open circuited measurements at frequency of 5 KHz on a line length 100 km yields the following results. ZOC =570 -480
ZSC =720 340 Find the characteristic impedance and propagation constant of the line.
UNIT I II III IV V VI VII VIII
SET1 5 2 7 4 4 4 7 4
SET2 11 7 4 2 2 4 2 4
SET3 6 3 5 2 4 4 5 4
SET4 3 1 4 3 3 3 5 5
You might also like
- College Level Math Practice TestDocument17 pagesCollege Level Math Practice TestHarsha Kasaragod100% (1)
- Thumb Rules For Civil Engineers PDFDocument4 pagesThumb Rules For Civil Engineers PDFA KNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsFrom EverandElectricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Oracle Process Manufacturing Master SetupsDocument42 pagesOracle Process Manufacturing Master SetupsMadhuri Uppala100% (2)
- Translating Mathematical PhrasesDocument16 pagesTranslating Mathematical PhrasesApple Jean Yecyec AlagNo ratings yet
- Topsoe Ammonia 4 Start Up Worlds Largest Ammonia PlantDocument13 pagesTopsoe Ammonia 4 Start Up Worlds Largest Ammonia Plantpekanselandar0% (1)
- Accounting For ManagersDocument286 pagesAccounting For ManagersSatyam Rastogi100% (1)
- 1716,1734,1751,1769 - Highrise and Earthquake Resistant ConstructionDocument34 pages1716,1734,1751,1769 - Highrise and Earthquake Resistant ConstructionFAB RAHINo ratings yet
- Emtl Qbank 2012-13Document8 pagesEmtl Qbank 2012-13vikramvsuNo ratings yet
- Emtl Question Bank Imp QsDocument9 pagesEmtl Question Bank Imp QsSri MurthyNo ratings yet
- Jntu Kak 2 2 Ece Emtl Set 4Document4 pagesJntu Kak 2 2 Ece Emtl Set 4himeshemraanNo ratings yet
- Jntu Kak 2 2 Ece Emtl Set 2Document8 pagesJntu Kak 2 2 Ece Emtl Set 2himeshemraanNo ratings yet
- Jntu Kak 2 2 Ece Emtl Set 3Document6 pagesJntu Kak 2 2 Ece Emtl Set 3himeshemraanNo ratings yet
- R5211001-Electromagnetic Waves and Transmission LinesDocument4 pagesR5211001-Electromagnetic Waves and Transmission LinessivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- EE2202 QB MCE Edition PDFDocument10 pagesEE2202 QB MCE Edition PDFGanesh KrishnamurthyNo ratings yet
- r050211001 Electromagnetic Waves and Transmission LinesDocument8 pagesr050211001 Electromagnetic Waves and Transmission LinesSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Jntu Kak 2 2 Ece Emtl Set 1Document15 pagesJntu Kak 2 2 Ece Emtl Set 1himeshemraanNo ratings yet
- r05220404 Electromagnetic Waves and Transmission LinesDocument8 pagesr05220404 Electromagnetic Waves and Transmission LinesSrinivasa Rao G100% (1)
- Electromagnetic Waves and Transmission Lines Question PaperDocument8 pagesElectromagnetic Waves and Transmission Lines Question PaperelimelekNo ratings yet
- E 13Document2 pagesE 13ArkadebSenguptaNo ratings yet
- Suggestion em WavesDocument3 pagesSuggestion em Wavesrishavkumarsingh088No ratings yet
- Em Waves and Transmission Lines May 2017Document5 pagesEm Waves and Transmission Lines May 2017Veerayya JavvajiNo ratings yet
- rr220403 e M Waves and Transmission LinesDocument8 pagesrr220403 e M Waves and Transmission LinesSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Emf 3Document6 pagesEmf 329viswa12No ratings yet
- Ra 07a31001 Electromagnetic Waves and Transmission LinesDocument1 pageRa 07a31001 Electromagnetic Waves and Transmission LinessivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Emf 7Document8 pagesEmf 729viswa12No ratings yet
- EC 232 Tutorial 2Document3 pagesEC 232 Tutorial 2RUSHIL MOTWANINo ratings yet
- EMTL 4 Units Important QuestionsDocument27 pagesEMTL 4 Units Important Questionsganesh4u_p71% (7)
- Electromagnetic FieldsDocument4 pagesElectromagnetic FieldsKrishna Reddy SvvsNo ratings yet
- 07a31001 Electromagnetic Waves and Transmission LinesDocument6 pages07a31001 Electromagnetic Waves and Transmission LinesvengalamahenderNo ratings yet
- Emf Question PaperDocument3 pagesEmf Question PaperRamadhuraiNo ratings yet
- Fke May 2011Document522 pagesFke May 2011Nur Ezzaty Binti AsmaraniNo ratings yet
- R5210205-Electromagnetic FieldsDocument4 pagesR5210205-Electromagnetic FieldssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Em Waves and Transmission Lines - June-2015Document4 pagesEm Waves and Transmission Lines - June-2015Veerayya JavvajiNo ratings yet
- Rr211002 Electromagnetic TheoryDocument8 pagesRr211002 Electromagnetic TheorySrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Final Mock 2Document3 pagesFinal Mock 2Subho SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Assign N LabDocument4 pagesAssign N LabMtende MosesNo ratings yet
- EET416 Problem Set 2 SolutionDocument8 pagesEET416 Problem Set 2 SolutionAbdallah E. Abdallah100% (1)
- Field and Wave Sample Paper97-2003Document6 pagesField and Wave Sample Paper97-2003Abhimanyu NainNo ratings yet
- Set PaperDocument4 pagesSet PaperSagar AyushNo ratings yet
- QP GeolM 23 GEO PHYSICS PAPER III 250623Document8 pagesQP GeolM 23 GEO PHYSICS PAPER III 250623Arvind sharmaNo ratings yet
- 2b365ant TuteDocument13 pages2b365ant TuteSakshi ChhabraNo ratings yet
- r05220404 Electromagnetic Waves and Transmission LinesDocument8 pagesr05220404 Electromagnetic Waves and Transmission LinesSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3:) 10 8 Cos (20 yDocument2 pagesTutorial 3:) 10 8 Cos (20 yputra azriNo ratings yet
- 17 Ec 362Document2 pages17 Ec 362MATAM VENKATESHANo ratings yet
- Ece 222 Problem Set: AB Carries A Current of 0.2A in TheDocument1 pageEce 222 Problem Set: AB Carries A Current of 0.2A in TheLeilani MaurealNo ratings yet
- FVT 2015Document9 pagesFVT 2015joeNo ratings yet
- R07 Set No. 2: Ii B.Tech Ii Sem-Regular/Supplementary Examinations May - 2010Document5 pagesR07 Set No. 2: Ii B.Tech Ii Sem-Regular/Supplementary Examinations May - 2010Mohan KumarNo ratings yet
- Jack 1971 ADocument38 pagesJack 1971 AdschdeschNo ratings yet
- ICT 9A04406 Electromagnetic Theory and Transmission LinesDocument1 pageICT 9A04406 Electromagnetic Theory and Transmission LinessivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Imp QusDocument17 pagesImp QusBck SreedharNo ratings yet
- EME Tutorial - 2 To 5Document5 pagesEME Tutorial - 2 To 5Aditya Gadgil100% (1)
- Emf 6Document4 pagesEmf 629viswa12No ratings yet
- EM Waves and Transmision Lines - R2015 - 05-11-2019Document2 pagesEM Waves and Transmision Lines - R2015 - 05-11-2019ashokkumarNo ratings yet
- r5210205 Electromagnetic FieldsDocument1 pager5210205 Electromagnetic FieldsMicro EmissionNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions: Second Internal Test - March 2013Document2 pagesAnswer All Questions: Second Internal Test - March 2013BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Cf22 Extra Problems WeakDocument2 pagesCf22 Extra Problems WeakHarikrishna KhariduNo ratings yet
- Field Theory July 2013Document0 pagesField Theory July 2013Prasad C MNo ratings yet
- Main Tutorial EMF B I 2021Document2 pagesMain Tutorial EMF B I 2021Terrero roNo ratings yet
- EMF - 2 Mark & 16 MarksDocument26 pagesEMF - 2 Mark & 16 MarksKALAIMATHINo ratings yet
- PS-1 Question PapersDocument98 pagesPS-1 Question Paperssatyakar_vvkNo ratings yet
- QPEMFDocument2 pagesQPEMFkskumargieNo ratings yet
- X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials SciencesFrom EverandX-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials SciencesNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- AjayDocument1 pageAjayvikramvsuNo ratings yet
- Brand Reinforcement and RevitalizationDocument2 pagesBrand Reinforcement and Revitalizationvikramvsu100% (1)
- Vijaya Lakshmi Arikatla Resume @Document2 pagesVijaya Lakshmi Arikatla Resume @vikramvsuNo ratings yet
- Adil ResumeDocument2 pagesAdil ResumevikramvsuNo ratings yet
- Brand Value ChainDocument1 pageBrand Value ChainvikramvsuNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Branding StrategiesDocument2 pagesDifferent Types of Branding Strategiesvikramvsu100% (1)
- A JyothiDocument35 pagesA JyothivikramvsuNo ratings yet
- Competitive Positioning of BrandsDocument2 pagesCompetitive Positioning of BrandsvikramvsuNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Management: Total No. of Questions 17Document2 pagesAccounting For Management: Total No. of Questions 17vikramvsuNo ratings yet
- I Types of AccountsDocument12 pagesI Types of AccountsvikramvsuNo ratings yet
- Brand Equity ModelsDocument7 pagesBrand Equity ModelsvikramvsuNo ratings yet
- Pondicherry University Adhoc Recruitment NotificationDocument3 pagesPondicherry University Adhoc Recruitment NotificationvikramvsuNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Management: Instruction To CandidatesDocument2 pagesAccounting For Management: Instruction To CandidatesvikramvsuNo ratings yet
- Ug C Revised Pay Scales GoDocument65 pagesUg C Revised Pay Scales GoVenugopal Reddyvari100% (1)
- Academic Consultants2016 17Document5 pagesAcademic Consultants2016 17vikramvsuNo ratings yet
- Advt Appointment For Faculty PositionsDocument1 pageAdvt Appointment For Faculty PositionsvikramvsuNo ratings yet
- Advt Appointment For Faculty PositionsDocument1 pageAdvt Appointment For Faculty PositionsvikramvsuNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology Paper-IDocument2 pagesResearch Methodology Paper-IvikramvsuNo ratings yet
- Narendra MurkumbiDocument2 pagesNarendra MurkumbivikramvsuNo ratings yet
- Vspu MBTDocument1 pageVspu MBTvikramvsuNo ratings yet
- I Semester ECDocument1 pageI Semester ECvikramvsuNo ratings yet
- Vspu MbaDocument2 pagesVspu MbavikramvsuNo ratings yet
- AP Polycet 2015 Information BrochureDocument65 pagesAP Polycet 2015 Information BrochureNeepur GargNo ratings yet
- Svuc - S V U College of MNGT and Info Sci, Tirupathi Master of Business Administration Show AllotmentsDocument2 pagesSvuc - S V U College of MNGT and Info Sci, Tirupathi Master of Business Administration Show AllotmentsvikramvsuNo ratings yet
- Vspu McaDocument1 pageVspu McavikramvsuNo ratings yet
- Svuc - S V U College of MNGT and Info Sci, Tirupathi Master of Computer Applications Show AllotmentsDocument1 pageSvuc - S V U College of MNGT and Info Sci, Tirupathi Master of Computer Applications Show AllotmentsvikramvsuNo ratings yet
- Svucsf McaDocument3 pagesSvucsf McavikramvsuNo ratings yet
- Svucsf Mba Joining ListDocument3 pagesSvucsf Mba Joining Listvikramvsu100% (1)
- APICET Detailed NotificationDocument2 pagesAPICET Detailed NotificationvikramvsuNo ratings yet
- R32 Manual Armado de MotorDocument241 pagesR32 Manual Armado de Motor15EPR4680V P265No ratings yet
- Ratio Worksheet AKDocument12 pagesRatio Worksheet AKChika AuliaNo ratings yet
- Vdocuments - MX - Catalogo Maquinas Despiezables de Feedback PDFDocument4 pagesVdocuments - MX - Catalogo Maquinas Despiezables de Feedback PDFHelder NascimentoNo ratings yet
- Hofman NotesDocument114 pagesHofman NotesNoelia PizziNo ratings yet
- 62684en1 PDFDocument447 pages62684en1 PDFsurajNo ratings yet
- Roasting Matte To Nickel Oxide and MetalDocument7 pagesRoasting Matte To Nickel Oxide and MetalDavid SanchezNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - PolyDocument16 pagesQuestion Bank - Polyمحمود صابرNo ratings yet
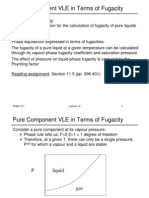
- Pure Component VLE in Terms of Fugacity: CHEE 311 1Document8 pagesPure Component VLE in Terms of Fugacity: CHEE 311 1scienziatoNo ratings yet
- Class Progress Chart Electrical Installation and Maintenance NC Ii (196 HRS)Document2 pagesClass Progress Chart Electrical Installation and Maintenance NC Ii (196 HRS)Shairrah Claire Bañares BatangueNo ratings yet
- White Paper: Professor Dr. Thorsten Hens Msc. Ba Anna MeierDocument29 pagesWhite Paper: Professor Dr. Thorsten Hens Msc. Ba Anna MeierDark11No ratings yet
- CATL 37V 50ah Lithium Ternary Battery Cell - LiFePO4 BatteryDocument4 pagesCATL 37V 50ah Lithium Ternary Battery Cell - LiFePO4 BatterymlutfimaNo ratings yet
- Atmel 0038Document1 pageAtmel 0038namerNo ratings yet
- BioFluid Mechanics 1Document29 pagesBioFluid Mechanics 1roxannedemaeyerNo ratings yet
- HCL McQs SET-3Document8 pagesHCL McQs SET-3ThorNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Instructions - Isolation of Cinnamaldehyde - SP16Document4 pagesLab Report Instructions - Isolation of Cinnamaldehyde - SP16Al SharptonNo ratings yet
- Mv324 Data SheetDocument17 pagesMv324 Data SheetGianmarco CastilloNo ratings yet
- KOPP TransmittersDocument32 pagesKOPP TransmittersMike BrendNo ratings yet
- Product Manual: 1018 - Phidgetinterfacekit 8/8/8Document21 pagesProduct Manual: 1018 - Phidgetinterfacekit 8/8/8Eduardo Piña Martínez100% (1)
- Chameleon ChipDocument2 pagesChameleon ChipChetan KumarNo ratings yet
- About The MS Regression ModelsDocument17 pagesAbout The MS Regression ModelsLars LarsonNo ratings yet
- Competition Systems IGN1A Inductive Smart Coil - IGN1ADocument2 pagesCompetition Systems IGN1A Inductive Smart Coil - IGN1AJoão Lucas ZaionsNo ratings yet
- DSI - MPS® Transfer System Compact Trainer I4.0 - EN - DID1089 (Screen)Document2 pagesDSI - MPS® Transfer System Compact Trainer I4.0 - EN - DID1089 (Screen)mhafizanNo ratings yet
- Smith Meter Microloadnet Operator Reference Manual-A Voir PDFDocument96 pagesSmith Meter Microloadnet Operator Reference Manual-A Voir PDFmehrezNo ratings yet
- Magnetron PDFDocument1 pageMagnetron PDFmytrya debNo ratings yet