Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1MRK502045-BEN - en Product Guide Generator Protection REG650 1.2 IEC
Uploaded by
thomaswangkoroOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1MRK502045-BEN - en Product Guide Generator Protection REG650 1.2 IEC
Uploaded by
thomaswangkoroCopyright:
Available Formats
Relion 650 series
Generator protection REG650 Product Guide
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Contents
1. 650 series overview........................................................3 2. Application.....................................................................3 3. Available functions..........................................................6 4. Differential protection....................................................14 5. Impedance protection..................................................15 6. Current protection........................................................16 7. Voltage protection........................................................18 8. Frequency protection....................................................20 9. Secondary system supervision.....................................20 10. Control........................................................................21 11. Logic...........................................................................22 12. Monitoring...................................................................23 13. Metering......................................................................25 14. Human Machine interface............................................26 15. Basic IED functions.....................................................26 16. Station communication................................................27 17. Hardware description..................................................28 18. Connection diagrams Customized...............................30 19. Connection diagrams Configured................................35 20. Technical data.............................................................48 21. Ordering for Customized IED.......................................82 22. Ordering for Configured IED........................................86 23. Ordering for Accessories.............................................89
Disclaimer The information in this document is subject to change without notice and should not be construed as a commitment by ABB. ABB assumes no responsibility for any errors that may appear in this document. Copyright 2012 ABB. All rights reserved. Trademarks ABB and Relion are registered trademarks of the ABB Group. All other brand or product names mentioned in this document may be trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
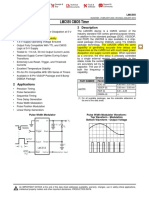
1MRK 502 045-BEN Issued: June 2012 Revision: mainly for small and medium size generation stations. REG670 may be used when more extensive protection systems are required or in combination with REG650 to provide redundant schemes. A wide range of protection functions is available to achieve full and reliable protection for different types of generating plants, for example hydro power plants and thermal power plants. This enables adaptation to the protection requirements of most generating plants. Protection functions are available for detecting and clearing internal faults, such as generator stator short circuits and earth faults, generator rotor earth faults, unit transformer short circuits and earth faults and faults in the external power system, fed from the generating plant. Two packages have been defined for the following applications: Generator protection IED including generator differential protection (B01) Generator-transformer unit protection IED including transformer differential protection (B05) In many generating plants, the protection system can be designed with a combination of the two packages, that is, two IEDs of either same type or different types, will give redundant protection for a generating unit (generator and unit transformer) depending on the requirements for the plant design. The packages are configured and ready for use. Analogue inputs and binary input/output circuits are pre-defined. The pre-configured IED can be changed and adapted with the graphical configuration tool.
1. 650 series overview The 650 series IEDs provide both customized and configured solutions. With the customized IEDs you have the freedom to completely adapt the functionality according to your needs. The 650 series IEDs provide optimum 'off-theshelf', ready-to-use solutions. It is configured with complete protection functionality and default parameters to meet the needs of a wide range of applications for generation, transmission and subtransmission grids. The 650 series IEDs include: Customized versions providing the possibility to adapt the functionality to the application needs. Configured solutions are completely ready to use solutions optimized for a wide range of applications for generation, transmission and sub-transmission grids. Support for user-defined names in the local language for signal and function engineering. Minimized parameter settings based on default values and ABB's new global base value concept. You only need to set those parameters specific to your own application, such as the line data. GOOSE messaging for horizontal communication. Extended HMI functionality with 15 dynamic three-color-indication LEDs per page, on up to three pages, and configurable push-button shortcuts for different actions. Programmable LED text-based labels. Settable 1A/5A -rated current inputs.
2. Application REG650 is used for the protection and monitoring of generating plants. The IED is especially suitable for applications in distributed control systems with high demands on reliability. It is intended
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
110kV HV Substation
HV CB A
200/1
Unit Transformer 29MVA 121/11kV YNd5
Y
11
200/1 J
0.11 0.11 / / kV 3 3 3
Y
TRM module with 4I+1I*+5U AIM module with 6I+4U
Auxiliary Transformer 2500/5 C
59N 100/5 B A, B, C or D
1)
3Uo>
Meter. C MSQI
ROV2 PTOV 51 3I> 49 Ith
Meter. CV MMXN
25
SC
1.6MVA 11/0.4kV
OC4 PTOC
TR PTTR
SES RSYN
Generator CB Excitation Transformer
11 /
Y
32Q 47 59N 3Uo> U2> 32
81R
df/dt
GUP PDOP
3 0.11 0.11 / kV 3 3
Y
SA PFRC
V MSQI P 81O f> ROV2 PTOV 52PD PD 51 3I> GUP PDOP 37 P< SA PTOF 81U f<
50/5
390kVA D 11/0.37kV Dyn11 1600/5
3)
RXTTE4
CC RPLD
OC4 PTOC 50BF 3I> BF
GOP PDUP 50AE
U</I>
SA PTUF 27 3U<
Field CB
~
1600/5 29MVA 11kV 150rpm
U I
Rotor EF protection 64R
67N IN> 67N IN> SDE PSDE EF4 PTOC
CC RBRF
AEG GAPC 40 <
UV2 PTUV 59 3U>
87G
3Id/I
LEX PDIS 78 Ucos
OV2 PTOV 24 U/f>
GEN PDIF
OOS PPAM 46 I2> 49 Ith 21 Z<
OEX PVPH 51V I>/U< 60FL SDD RFUF
NS2 PTOC 200/5 G
11 3 / 0.11 kV
TR PTTR
ZGCPDIS
VR2 PVOC
59THD U3d/N ) IdN STEF PHIZ 59N UN>
1000 10/1 H J, G or H 51N IN> 87N
EF4 PTOC
HZ PDIF REG650-B01
2)
) Requires dedicated CT cores, external resistor and metrosil for correct operation
Note:
1) Input for independent non-directional OC and overload functions. It can be used for different purposes (e.g. OC protection for either Auxiliary trafo or Excitation trafo or Step-up transformer HV side) 2) Input for independent non-directional EF function. It can be used for different purposes (e.g. as stator EF protection or turn-to-turn protection for generators with split winding or even HV side EF protection). Alternatively it can be used for High-Impedance REF protection. 3) Input for independent directional (sensitive) EF function. It can be used for different purposes. (e.g. as rotor EF with RXTTE4 or stator EF for generators operating in parallel)
Function Enabled in Settings
ANSI
Function Disabled in Settings
ANSI IEC
IEC10000299-2-en.vsd
IEC61850
IEC10000299 V2 EN
IEC 61850
IEC
IEC61850
Figure 1.
Generator protection IED including generator differential protection (B01)
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
110kV HV Substation
HV CB 52PD 200/1
110 3 / 0.11 0.11 / kV 3 3
Y Y
PD
51
3I>
50BF 3I> BF CC RBRF
Meter. CV MMXN
TRM module with 4I+1I*+5U AIM module with 6I+4U
CC RPLD
OC4 PTOC
Unit Transformer 29MVA 121/11kV YNd5
200/1 J 25 SC
SES RSYN 87T 59N 3Uo> Meter. C MSQI 49 Ith Meter. CV MMXN GT01 Generator CB 3Id/I
T3D PDIF ROV2 PTOV
3)
Auxiliary Transformer 2500/5
100/5 D or E
51
3I>
1.6MVA 11/0.4kV
OC4 PTOC
TR PTTR
32Q
81R
df/dt
GOP PDOP Excitation Transformer
11 3 /
Y
SA PFRC
50/5
0.11 0.11 / kV 3 3
Y
47
U2> 32 P 81O f>
V MSQI 59N 3Uo> GUP PDOP 37 P< SA PTOF 81U f<
390kVA C 11/0.37kV Dyn11 1600/5
ROV2 PTOV
B
1)
GOP PDUP 50AE
U</I>
SA PTUF 27 3U<
Field CB
RXTTE4
~
1600/5 A 200/5
11
U I
Rotor EF protection 64R
67N IN> 67N IN> SDE PSDE EF4 PTOC
AEG GAPC 40 <
UV2 PTUV 59 3U>
LEX PDIS 78 Ucos
OV2 PTOV 24 U/f>
29MVA 11kV 150rpm A or B 46 I2> 49 Ith NS2 PTOC TR PTTR
OOS PPAM 21 Z<
OEX PVPH 51V I>/U< 60FL SDD RFUF
ZGCPDIS
VR2 PVOC
G 1000
/ 0.11 kV
59THD U3d/N ) STEF PHIZ 59N UN>
10/1
J, G or H
2)
51N
IN>
87N
IdN
EF4 PTOC
HZ PDIF REG650-B05
) Requires dedicated CT cores, external resistor and metrosil for correct operation
Note:
1) Inputs for independent directional (sensitive) EF function. It can be used for different purposes (e.g. as rotor EF with RXTTE4 or stator EF for generators running in parallel) 2) Input for independent non-directional EF function. It can be used for different purposes (e.g. as stator EF protection or turn-to-turn protection for generators with split winding or even HV side EF protection). Alternatively it can be used for High-Impedance REF protection. 3) Alternatively step-up transformer HV side open delta VT can be connected here
Function Enabled in Settings
ANSI
Function Disabled in Settings
ANSI IEC
IEC10000300-2-en.vsd
IEC61850
IEC10000300 V2 EN
IEC 61850
IEC
IEC61850
Figure 2.
Generator-transformer unit protection IED including transformer differential protection (B05)
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
3. Available functions Main protection functions
IEC 61850/ Function block name ANSI Function description Generator
Differential protection T3WPDIF HZPDIF GENPDIF 87T 87 87G Transformer differential protection, three winding 1Ph High impedance differential protection Generator differential protection 01 1 01 1 1 1 1
Impedance protection ZGCPDIS LEXPDIS OOSPPAM LEPDIS 21G 40 78 Underimpedance protection for generators and transformers Loss of excitation Out-of-step protection Load encroachment 01 01 01 01 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
REG650 (B05) Gen+Trafo diff
REG650 (B01) Gen diff
REG650
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Back-up protection functions
IEC 61850/ Function block name ANSI Function description Generator
Current protection OC4PTOC EF4PTOC SDEPSDE TRPTTR CCRBRF CCRPLD GUPPDUP GOPPDOP AEGGAPC NS2PTOC VR2PVOC 51 51N/67N 67N 49 50BF 52PD 37 32 50AE 46I2 51V Four step phase overcurrent protection, 3phase output Four step residual overcurrent protection, zero/ negative sequence direction Sensitive directional residual overcurrent and power protection Thermal overload protection, two time constants Breaker failure protection, 3phase activation and output Pole discordance protection Directional underpower protection Directional overpower protection Accidental energizing protection for synchronous generator Negative-sequence time overcurrent protection for machines Voltage-restrained time overcurrent protection 02 02 01 02 01 01 01 02 01 01 01 2 2 1 2 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 2 2 1 2 1 1 1 2 1 1 1
Voltage protection UV2PTUV OV2PTOV ROV2PTOV OEXPVPH STEFPHIZ 27 59 59N 24 59THD 64R Two step undervoltage protection Two step overvoltage protection Two step residual overvoltage protection Overexcitation protection 100% Stator earth fault protection, 3rd harmonic based Rotor earth protection with RXTTE4 injection unit 01 01 02 01 01 01 1 1 2 1 1 01 1 1 2 1 1 01
Frequency protection SAPTUF SAPTOF SAPFRC 81 81 81 Underfrequency function Overfrequency function Rate-of-change frequency protection 04 04 02 4 4 2 4 4 2
ABB
REG650 (B05) Gen+Trafo diff 7
REG650 (B01) Gen diff
REG650
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Control and monitoring functions
IEC 61850/Function block name ANSI Function description Generator REG650 (B05) Gen+Trafo diff 1 1 1 1 1 15 20 16 5 3 1 1 4 50 50 15 20 16 5 3 1 1 4 50 50 1 3 6 12 283 140 REG650 (B01) Gen diff 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 6 12 283 140
Control SESRSYN QCBAY LOCREM LOCREMCTRL CBC1 CBC2 SLGGIO VSGGIO DPGGIO SPC8GGIO AUTOBITS I103CMD I103IEDCMD I103USRCMD I103GENCMD I103POSCMD Secondary system supervision SDDRFUF TCSSCBR Logic SMPPTRC TMAGGIO OR INVERTER 94 Tripping logic, common 3phase output Trip matrix logic Configurable logic blocks, OR gate Configurable logic blocks, Inverter gate 16 12 283 140 Fuse failure supervision Breaker close/trip circuit monitoring 01 3 25 Synchrocheck, energizing check, and synchronizing Bay control Handling of LR-switch positions LHMI control of Permitted Source To Operate (PSTO) Circuit breaker for 1CB Circuit breaker for 2CB Logic Rotating Switch for function selection and LHMI presentation Selector mini switch extension IEC 61850 generic communication I/O functions double point Single point generic control 8 signals AutomationBits, command function for DNP3.0 Function commands for IEC60870-5-103 IED commands for IEC60870-5-103 Function commands user defined for IEC60870-5-103 Function commands generic for IEC60870-5-103 IED commands with position and select for IEC60870-5-103 01 1 1 1 01 01 15 20 16 5 3 1 1 4 50 50
REG650
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
IEC 61850/Function block name
ANSI
Function description
Generator REG650 (B05) Gen+Trafo diff 40 40 40 40 40 280 40 40 1 16 16 16 16 6 10 6 6 6 6 1 1 1 1 1 9 REG650 (B01) Gen diff 40 40 40 40 40 280 40 40 1 16 16 16 16 6 10 6 6 6 6 1 1 1 1 1
PULSETIMER GATE XOR LOOPDELAY TIMERSET AND SRMEMORY RSMEMORY FXDSIGN B16I B16IFCVI IB16A IB16FCVB Monitoring CVMMXN CMMXU VMMXU CMSQI VMSQI VNMMXU AISVBAS TM_P_P2 AM_P_P4 TM_S_P2 AM_S_P4
Configurable logic blocks, Pulse timer Configurable logic blocks, Controllable gate Configurable logic blocks, exclusive OR gate Configurable logic blocks, loop delay Configurable logic blocks, timer function block Configurable logic blocks, AND gate Configurable logic blocks, set-reset memory flip-flop gate Configurable logic blocks, reset-set memory flip-flop gate Fixed signal function block Boolean 16 to Integer conversion Boolean 16 to Integer conversion with logic node representation Integer to Boolean 16 conversion Integer to Boolean 16 conversion with logic node representation
280 40 40 1 16 16 16 16
Measurements Phase current measurement Phase-phase voltage measurement Current sequence component measurement Voltage sequence measurement Phase-neutral voltage measurement Function block for service values presentation of the analog inputs Function block for service values presentation of primary analog inputs 600TRM Function block for service values presentation of primary analog inputs 600AIM Function block for service values presentation of secondary analog inputs 600TRM Function block for service values presentation of secondary analog inputs 600AIM
ABB
REG650 40 40 40 40 40 6 10 6 6 6 6 1 1 1 1 1
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
IEC 61850/Function block name
ANSI
Function description
Generator REG650 (B05) Gen+Trafo diff 5 1 4 6 64 16 16 66 1 2 2 1 1 3 1 1 1 1 1 20 16 3 REG650 (B01) Gen diff 5 1 4 6 64 16 16 66 1 2 2 1 1 3 1 1 1 1 1 20 16 3
CNTGGIO DRPRDRE AxRADR BxRBDR SPGGIO SP16GGIO MVGGIO MVEXP SPVNZBAT SSIMG SSIML SSCBR I103MEAS I103MEASUSR I103AR I103EF I103FLTPROT I103IED I103SUPERV I103USRDEF Metering PCGGIO ETPMMTR 63 71
Event counter Disturbance report Analog input signals Binary input signals IEC 61850 generic communication I/O functions IEC 61850 generic communication I/O functions 16 inputs IEC 61850 generic communication I/O functions Measured value expander block Station battery supervision Insulation gas monitoring function Insulation liquid monitoring function Circuit breaker condition monitoring Measurands for IEC60870-5-103 Measurands user defined signals for IEC60870-5-103 Function status auto-recloser for IEC60870-5-103 Function status earth-fault for IEC60870-5-103 Function status fault protection for IEC60870-5-103 IED status for IEC60870-5-103 Supervison status for IEC60870-5-103 Status for user defined signals for IEC60870-5-103
01 02 02 01 1 3 1 1 1 1 1 20
Pulse counter logic Function for energy calculation and demand handling
10
REG650 5 1 4 6 64 16 16 66 16 3
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Communication
IEC 61850/Function block name ANSI Function description Generator REG650 (B05) Gen+Trafo diff 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 59 4 1 32 11 REG650 (B01) Gen diff 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 59 4 1 32
Station communication IEC61850-8-1 DNPGEN RS485DNP CH1TCP CH2TCP CH3TCP CH4TCP OPTICALDNP MSTSERIAL MST1TCP MST2TCP MST3TCP MST4TCP RS485GEN OPTICALPROT RS485PROT DNPFREC OPTICAL103 RS485103 GOOSEINTLKRCV GOOSEBINRCV ETHFRNT ETHLAN1 GATEWAY GOOSEDPRCV IEC 61850 communication protocol DNP3.0 for TCP/IP communication protocol DNP3.0 for EIA-485 communication protocol DNP3.0 for TCP/IP communication protocol DNP3.0 for TCP/IP communication protocol DNP3.0 for TCP/IP communication protocol DNP3.0 for TCP/IP communication protocol DNP3.0 for optical serial communication DNP3.0 for serial communication protocol DNP3.0 for TCP/IP communication protocol DNP3.0 for TCP/IP communication protocol DNP3.0 for TCP/IP communication protocol DNP3.0 for TCP/IP communication protocol RS485 Operation selection for optical serial Operation selection for RS485 DNP3.0 fault records for TCP/IP communication protocol IEC60870-5-103 Optical serial communication IEC60870-5-103 serial communication for RS485 Horizontal communication via GOOSE for interlocking GOOSE binary receive Ethernet configuration of front port, LAN1 port and gateway GOOSE function block to receive a double point value 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 59 4 1
ABB
REG650 32
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
IEC 61850/Function block name
ANSI
Function description
Generator REG650 (B05) Gen+Trafo diff 32 16 64 REG650 (B01) Gen diff 32 16 64
GOOSEINTRCV GOOSEMVRCV GOOSESPRCV
GOOSE function block to receive an integer value GOOSE function block to receive a measurand value GOOSE function block to receive a single point value
12
REG650 32 16 64
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Basic IED functions
IEC 61850/Function block name Function description
Basic functions included in all products INTERRSIG SELFSUPEVLST TIMESYNCHGEN SNTP DTSBEGIN, DTSEND, TIMEZONE IRIG-B SETGRPS ACTVGRP TESTMODE CHNGLCK TERMINALID PRODINF SYSTEMTIME RUNTIME PRIMVAL SMAI_20_1 SMAI_20_12 3PHSUM GBASVAL ATHSTAT ATHCHCK SPACOMMMAP FTPACCS DOSFRNT DOSLAN1 DOSSCKT SAFEFILECOPY SPATD BCSCONF Self supervision with internal event list Self supervision with internal event list Time synchronization Time synchronization Time synchronization, daylight saving Time synchronization Setting group handling Parameter setting groups Test mode functionality Change lock function IED identifiers Product information System time IED Runtime comp Primary system values Signal matrix for analog inputs Summation block 3 phase Global base values for settings Authority status Authority check SPA communication mapping FTP access with password Denial of service, frame rate control for front port Denial of service, frame rate control for LAN1 Denial of service, socket flow control Safe file copy function Date and time via SPA protocol Basic communication system 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 12 6 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
ABB
13
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
4. Differential protection Transformer differential protection T3WPDIF Transformer differential protection, three-winding (T3WPDIF) is provided with internal CT ratio matching and vector group compensation and settable zero sequence current elimination. The function can be provided with -phase sets of current inputs. All current inputs are provided with percentage bias restraint features, making the IED suitable for two- or three-winding transformer arrangements.
Three-winding applications three-winding power transformer with all three windings connected
1Ph High impedance differential protection HZPDIF The 1Ph High impedance differential protection (HZPDIF) function can be used when the involved CT cores have the same turns ratio and similar magnetizing characteristics. It utilizes an external summation of the currents in the interconnected CTs, a series resistor, and a voltage dependent resistor which are mounted externally connected to the IED. HZPDIF can be used as high impedance REF protection. Generator differential protection GENPDIF The task of Generator differential protection GENPDIF is to determine whether a fault is within the protected zone, or outside the protected zone. If the fault is internal, the faulty generator must be quickly tripped, that is, disconnected from the network, the field breaker tripped and the power to the prime mover interrupted. To limit the damage due to stator winding short circuits, the fault clearance must be as fast as possible (instantaneous). If the generator block is connected to the power system close to other generating blocks, the fast fault clearance is essential to maintain the transient stability of the non-faulted generators. Normally, the short circuit fault current is very large, that is, significantly larger than the generator rated current. There is a risk that a short circuit can occur between phases close to the neutral point of the generator, thus causing a relatively small fault current. The fault current can also be limited due to low excitation of the generator. Therefore, it is desired that the detection of generator phase-to-phase short circuits shall be relatively sensitive, detecting small fault currents. It is also of great importance that the generator differential protection does not trip for external faults, with large fault currents flowing from the generator. To combine fast fault clearance, as well as sensitivity and selectivity, the generator differential protection is normally the best choice for phase-to-phase generator short circuits. A negative-sequence-current-based internalexternal fault discriminator can also be used to
xx05000052.vsd
IEC05000052 V1 EN
xx05000049.vsd
IEC05000049 V1 EN
three-winding power transformer with unconnected delta tertiary winding
Figure 3.
CT group arrangement for differential protection and other protections
The setting facilities cover the applications of the differential protection to all types of power transformers and auto-transformers with or without load tap changer as well as for shunt reactors and local feeders within the station. An adaptive stabilizing feature is included for heavy through-faults. Stabilization is included for inrush currents as well as for overexcitation conditions. Adaptive stabilization is also included for system recovery inrush and CT saturation for external faults. A high set unrestrained differential current protection is included for a very high speed tripping at a high internal fault currents. An innovative sensitive differential protection feature, based on the theory of symmetrical components, offers the best possible coverage for power transformer winding turn-to-turn faults.
14
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
determine whether a fault is internal or external. The internal-external fault discriminator not only positively discriminates between internal and external faults, but can independently detect minor faults which may not be felt (until they develop into more serious faults) by the "usual" differential protection based on operate-restrain characteristic. An open CT circuit condition creates unexpected operations for Generator differential protection under the normal load conditions. It is also possible to damage secondary equipment due to high voltage produced from open CT circuit outputs. Therefore, it may be a requirement from security and reliability points of view to have open CT detection function to block Generator differential protection function in case of open CT conditions and at the same time produce the alarm signal to the operational personal to make quick remedy actions to correct the open CT condition. Generator differential protection GENPDIF is also well suited to generate fast, sensitive and selective fault clearance, if used to protect shunt reactors or small busduct. 5. Impedance protection Underimpedance protection for generators and transformers ZGCPDIS The underimpedance protection for generators and transformers ZGCPDIS, has the offset mho characteristic as a three zone back-up protection for detection of phase-to-phase short circuits in transformers and generators. The three zones have independent measuring and settings that gives high flexibility for all types of applications. A load encroachment characteristic is available for the third zone as shown in figure 4.
jX
Operation area
Operation area
Operation area
No operation area
No operation area
en07000117.vsd
IEC07000117 V1 EN
Figure 4.
Load encroachment influence on the offset mho Z3 characteristic
Loss of excitation LEXPDIS There are limits for the low excitation of a synchronous machine. A reduction of the excitation current weakens the coupling between the rotor and the stator. The machine may lose the synchronism and start to operate like an induction machine. Then, the reactive power consumption will increase. Even if the machine does not loose synchronism it may not be acceptable to operate in this state for a long time. Reduction of excitation increases the generation of heat in the end region of the synchronous machine. The local heating may damage the insulation of the stator winding and the iron core. To prevent damages to the generator it should be tripped when excitation becomes too low. The impedance measurement is used for LEXPDIS function. Its operating characteristic is designed as two zone, offset mho circles and a directional element restrain line. Out-of-step protection OOSPPAM Out-of-step protection (OOSPPAM) function in the IED can be used both for generator protection application as well as, line protection applications. The main purpose of the OOSPPAM function is to detect, evaluate, and take the required action during pole slipping occurrences in the power system.
ABB
15
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
The OOSPPAM function detects pole slip conditions and trips the generator as fast as possible, after the first pole-slip if the center of oscillation is found to be in zone 1, which normally includes the generator and its step-up power transformer. If the center of oscillation is found to be further out in the power system, in zone 2, more than one pole-slip is usually allowed before the generator-transformer unit is disconnected. If there are several out-of-step relays in the power system, then the one which finds the center of oscillation in its zone 1 should operate first. Load encroachment LEPDIS Heavy load transfer is common in many power networks and may make fault resistance coverage difficult to achieve. In such a case, Load encroachment (LEPDIS) function can be used to enlarge the resistive setting of the underimpedance measuring zones without interfering with the load. 6. Current protection Four step phase overcurrent protection, 3-phase output OC4PTOC The four step phase overcurrent protection function OC4PTOC has an inverse or definite time delay independent for step 1 and 4 separately. Step 2 and 3 are always definite time delayed. All IEC and ANSI inverse time characteristics are available. The directional function is voltage polarized with memory. The function can be set to be directional or non-directional independently for each of the steps. A 2nd harmonic blocking can be set individually for each step. Four step residual overcurrent protection, zero sequence and negative sequence direction EF4PTOC The four step residual overcurrent protection, zero or negative sequence direction (EF4PTOC) has a settable inverse or definite time delay independent for step 1 and 4 separately. Step 2 and 3 are always definite time delayed. All IEC and ANSI inverse time characteristics are available.
16
EF4PTOC can be set directional or nondirectional independently for each of the steps. The directional part of the function can be set to operate on following combinations: Directional current (I3PDir) versus Polarizing voltage (U3PPol) Directional current (I3PDir) versus Polarizing current (I3PPol) Directional current (I3PDir) versus Dual polarizing (UPol+ZPol x IPol) where ZPol = RPol + jXPol IDir, UPol and IPol can be independently selected to be either zero sequence or negative sequence. Second harmonic blocking restraint level can be set for the function and can be used to block each step individually. Sensitive directional residual overcurrent and power protection SDEPSDE In isolated networks or in networks with high impedance earthing, the earth fault current is significantly smaller than the short circuit currents. In addition to this, the magnitude of the fault current is almost independent on the fault location in the network. The protection can be selected to use either the residual current or residual power component 3U 03I 0 cos j , for operating quantity. There is also available one non-directional 3I 0 step and one non-directional 3U 0 overvoltage tripping step. Thermal overload protection, two time constant TRPTTR If a power transformer or generator reaches very high temperatures the equipment might be damaged. The insulation within the transformer/ generator will have forced ageing. As a consequence of this the risk of internal phase-tophase or phase-to-earth faults will increase. High temperature will degrade the quality of the transformer/generator insulation. The thermal overload protection estimates the internal heat content of the transformer/generator (temperature) continuously. This estimation is made by using a thermal model of the transformer/ generator with two time constants, which is based on current measurement.
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Two warning levels are available. This enables actions in the power system to be done before dangerous temperatures are reached. If the temperature continues to increase to the trip value, the protection initiates a trip of the protected transformer/generator. Breaker failure protection, 3-phase activation and output CCRBRF can be current based, contact based, or an adaptive combination of these two conditions. Breaker failure protection, 3-phase activation and output (CCRBRF) ensures fast back-up tripping of surrounding breakers in case the own breaker fails to open. CCRBRF can be current based, contact based, or an adaptive combination of these two conditions. Current check with extremely short reset time is used as check criterion to achieve high security against unnecessary operation. Contact check criteria can be used where the fault current through the breaker is small. Breaker failure protection, 3-phase activation and output (CCRBRF) current criteria can be fulfilled by one or two phase currents the residual current, or one phase current plus residual current. When those currents exceed the user defined settings, the function is triggered. These conditions increase the security of the back-up trip command. CCRBRF function can be programmed to give a three-phase re-trip of the own breaker to avoid unnecessary tripping of surrounding breakers. Pole discordance protection CCRPLD Circuit breakers and disconnectors can end up with thes in different positions (close-open), due to electrical or mechanical failures. An open phase can cause negative and zero sequence currents which cause thermal stress on rotating machines and can cause unwanted operation of zero sequence or negative sequence current functions. Normally the own breaker is tripped to correct such a situation. If the situation persists the surrounding breakers should be tripped to clear the unsymmetrical load situation.
The pole discordance function operates based on information from the circuit breaker logic with additional criteria from unsymmetrical phase currents when required. Directional over/underpower protection GOPPDOP/GUPPDUP The directional over-/under-power protection GOPPDOP/GUPPDUP can be used wherever a high/low active, reactive or apparent power protection or alarming is required. The functions can alternatively be used to check the direction of active or reactive power flow in the power system. There are a number of applications where such functionality is needed. Some of them are: detection of reversed active power flow detection of high reactive power flow Each function has two steps with definite time delay. Reset times for both steps can be set as well. Accidental energizing protection for synchronous generator AEGGAPC Inadvertent or accidental energizing of off-line generators has occurred often enough due to operating errors, breaker head flashovers, control circuit malfunctions, or a combination of these causes. Inadvertently energized generator operates as induction motor drawing a large current from the system. The voltage supervised overcurrent protection is used to protect the inadvertently energized generator. Accidental energizing protection for synchronous generator (AEGGAPC) takes the maximum phase current input from the generator terminal side or from generator neutral side and maximum phase to phase voltage inputs from the terminal side. AEGGAPC is enabled when the terminal voltage drops below the specified voltage level for the preset time. Negative sequence time overcurrent protection for machines NS2PTOC Negative-sequence time overcurrent protection for machines NS2PTOC is intended primarily for the protection of generators against possible overheating of the rotor caused by negative sequence current in the stator current. The negative sequence currents in a generator may, among others, be caused by:
ABB
17
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Unbalanced loads Line to line faults Line to earth faults Broken conductors Malfunction of one or more poles of a circuit breaker or a disconnector
NS2PTOC can also be used as a backup protection, that is, to protect the generator in case line protections or circuit breakers fail to clear unbalanced system faults. To provide an effective protection for the generator for external unbalanced conditions, NS2PTOC is able to directly measure the negative sequence current. NS2PTOC also has a time delay characteristic which matches the heating
2 characteristic of the generator I 2 t = K as
Rotor earth fault protection Generator rotor winding and its associated dc supply electric circuit is typically fully insulated from the earth. Therefore single connection of this circuit to earth will not cause flow of any substantial current. However, if second earth-fault appears in this circuit circumstances can be quit serious. Depending on the location of these two faults such operating condition may cause: Partial or total generator loss of field Large dc current flow through rotor magnetic circuit Rotor vibration Rotor displacement sufficient to cause stator mechanical damage Therefore practically all bigger generators have some dedicated protection which is capable to detect the first earth-fault in the rotor circuit and then, depending on the fault resistance, either just to give an alarm to the operating personnel or actually to give stop command to the machine. An injection unit is required for rotor earth fault protection (RXTTE4) and a protective resistor on plate for correct operation. Either SDEPSDE or EF4PTOC function can be used in conjunction with RXTTE4 as rotor earth-fault protection.
defined in standard IEEE C50.13.
where: I2 is negative sequence current expressed in per unit of the rated generator current is operating time in seconds is a constant which depends of the generators size and design
t K
NS2PTOC has a wide range of K settings and the sensitivity and capability of detecting and tripping for negative sequence currents down to the continuous capability of a generator. A separate output is available as an alarm feature to warn the operator of a potentially dangerous situation. Voltage-restrained time overcurrent protection VR2PVOC Voltage-restrained time overcurrent protection (VR2PVOC) function is recommended as a backup protection for generators. The overcurrent protection feature has a settable current level that can be used either with definite time or inverse time characteristic. Additionally, it can be voltage controlled/restrained. One undervoltage step with definite time characteristic is also available with the function in order to provide funcionality for overcurrent protection with undervoltage seal-in.
7. Voltage protection Two step undervoltage protection UV2PTUV Undervoltages can occur in the power system during faults or abnormal conditions. Two step undervoltage protection (UV2PTUV) function can be used to open circuit breakers to prepare for system restoration at power outages or as longtime delayed back-up to primary protection. UV2PTUV has two voltage steps, where step 1 is settable as inverse or definite time delayed. Step 2 is always definite time delayed. Two step overvoltage protection OV2PTOV Overvoltages may occur in the power system during abnormal conditions such as sudden power loss, tap changer regulating failures, open line ends on long lines etc. OV2PTOV has two voltage steps, where step 1 can be set as inverse or definite time delayed. Step 2 is always definite time delayed.
ABB
18
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
OV2PTOV has an extremely high reset ratio to allow settings close to system service voltage. Two step residual overvoltage protection ROV2PTOV Residual voltages may occur in the power system during earth faults. Two step residual overvoltage protection ROV2PTOV function calculates the residual voltage from the three-phase voltage input transformers or measures it from a single voltage input transformer fed from an open delta or neutral point voltage transformer. ROV2PTOV has two voltage steps, where step 1 can be set as inverse or definite time delayed. Step 2 is always definite time delayed. Overexcitation protection OEXPVPH When the laminated core of a power transformer or generator is subjected to a magnetic flux density beyond its design limits, stray flux will flow into non-laminated components not designed to carry flux and cause eddy currents to flow. The eddy currents can cause excessive heating and severe damage to insulation and adjacent parts in a relatively short time. The function has settable inverse operating curves and independent alarm stages. 95% and 100% Stator earth fault protection based on 3rd harmonic STEFPHIZ Stator earth fault is a fault type having relatively high fault rate. The generator systems normally have high impedance earthing, that is, earthing via a neutral point resistor. This resistor is normally dimensioned to give an earth fault current in the range 3 15 A at a solid earth-fault directly at the generator high voltage terminal. The relatively small earth fault currents give much less thermal and mechanical stress on the generator, compared to the short circuit case, which is between conductors of two phases.
Anyhow, the earth faults in the generator have to be detected and the generator has to be tripped, even if longer fault time compared to internal short circuits, can be allowed. In normal non-faulted operation of the generating unit the neutral point voltage is close to zero, and there is no zero sequence current flow in the generator. When a phase-to-earth fault occurs the neutral point voltage will increase and there will be a current flow through the neutral point resistor. To detect an earth fault on the windings of a generating unit one may use a neutral point overvoltage protection, a neutral point overcurrent protection, a zero sequence overvoltage protection or a residual differential protection. These protections are simple and have served well during many years. However, at best these simple schemes protect only 95% of the stator winding. They leave 5% close to the neutral end unprotected. Under unfavorable conditions the blind zone may extend up to 20% from the neutral. The 95% stator earth fault protection measures the fundamental frequency voltage component in the generator star point and it operates when it exceeds the preset value. By applying this principle approximately 95% of the stator winding can be protected. In order to protect the last 5% of the stator winding close to the neutral end the 3rd harmonic voltage measurement can be performed. In 100% Stator E/F 3rd harmonic protection either the 3rd harmonic voltage differential principle, the neutral point 3rd harmonic undervoltage principle or the terminal side 3rd harmonic overvoltage principle can be applied. However, differential principle is strongly recommended. Combination of these two measuring principles provides coverage for entire stator winding against earth faults.
ABB
19
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
stator winding N x E3 (1- x) E3
CB 1 may not exist T CB 1 CB 2
RN
Rf
Transformer
uN
Samples of the neutral voltage from which the fundamental and 3rd harmonic voltages are filtered out
1- x 1 or 100 %
Neutral point fundamental frequency over-voltage protection 5% - 100%
uT
Samples of the terminal voltage from which the 3rd harmonic voltage is filtered out
over- voltage protection 10% 100%
3rd harmonic Differential differential 0% 30% 0% - 30%
IEC10000202-1-en.vsd
IEC10000202 V1 EN
Figure 5.
Protection principles for STEFPHIZ function
8. Frequency protection Underfrequency protection SAPTUF Underfrequency occurs as a result of a lack of sufficient generation in the network. Underfrequency protection SAPTUF is used for load shedding systems, remedial action schemes, gas turbine startup and so on. SAPTUF is also provided with undervoltage blocking. Overfrequency protection SAPTOF Overfrequency protection function SAPTOF is applicable in all situations, where reliable detection of high fundamental power system frequency is needed. Overfrequency occurs because of sudden load drops or shunt faults in the power network. Close to the generating plant, generator governor problems can also cause over frequency.
SAPTOF is used mainly for generation shedding and remedial action schemes. It is also used as a frequency stage initiating load restoring. SAPTOF is provided with an undervoltage blocking. Rate-of-change frequency protection SAPFRC Rate-of-change frequency protection function (SAPFRC) gives an early indication of a main disturbance in the system. SAPFRC can be used for generation shedding, load shedding and remedial action schemes. SAPFRC can discriminate between positive or negative change of frequency. SAPFRC is provided with an undervoltage blocking. 9. Secondary system supervision Fuse failure supervision SDDRFUF The aim of the fuse failure supervision function (SDDRFUF) is to block voltage measuring functions at failures in the secondary circuits
ABB
20
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
between the voltage transformer and the IED in order to avoid unwanted operations that otherwise might occur. The fuse failure supervision function basically has three different algorithms, negative sequence and zero sequence based algorithms and an additional delta voltage and delta current algorithm. The negative sequence detection algorithm is recommended for IEDs used in isolated or highimpedance earthed networks. It is based on the negative-sequence measuring quantities, a high value of negative sequence voltage 3U 2 without the presence of the negative-sequence current 3I 2 . The zero sequence detection algorithm is recommended for IEDs used in directly or low impedance earthed networks. It is based on the zero sequence measuring quantities, a high value of zero sequence voltage 3U 0 without the presence of the zero sequence current 3I 0. For better adaptation to system requirements, an operation mode setting has been introduced which makes it possible to select the operating conditions for negative sequence and zero sequence based function. The selection of different operation modes makes it possible to choose different interaction possibilities between the negative sequence and zero sequence based algorithm. A criterion based on delta current and delta voltage measurements can be added to the fuse failure supervision function in order to detect a three phase fuse failure, which in practice is more associated with voltage transformer switching during station operations. Breaker close/trip circuit monitoring TCSSCBR The trip circuit supervision function TCSSCBR is designed to supervise the control circuit of the circuit breaker. The invalidity of a control circuit is detected by using a dedicated output contact that contains the supervision functionality. The function operates after a predefined operating time and resets when the fault disappears.
10. Control Synchrocheck, energizing check, and synchronizing SESRSYN The Synchronizing function allows closing of asynchronous networks at the correct moment including the breaker closing time, which improves the network stability. Synchrocheck, energizing check, and synchronizing (SESRSYN) function checks that the voltages on both sides of the circuit breaker are in synchronism, or with at least one side dead to ensure that closing can be done safely. SESRSYN function includes a built-in voltage selection scheme for double bus and 1 breaker or ring busbar arrangements. Manual closing as well as automatic reclosing can be checked by the function and can have different settings. For systems which are running asynchronous a synchronizing function is provided. The main purpose of the synchronizing function is to provide controlled closing of circuit breakers when two asynchronous systems are going to be connected. It is used for slip frequencies that are larger than those for synchrocheck and lower than a set maximum level for the synchronizing function. However this function can not be used to automatically synchronize the generator to the network. Bay control QCBAY The Bay control QCBAY function is used together with Local remote and local remote control functions to handle the selection of the operator place per bay. QCBAY also provides blocking functions that can be distributed to different apparatuses within the bay. Local remote LOCREM /Local remote control LOCREMCTRL The signals from the local HMI or from an external local/remote switch are applied via the function blocks LOCREM and LOCREMCTRL to the Bay control (QCBAY) function block. A parameter in function block LOCREM is set to choose if the switch signals are coming from the local HMI or
ABB
21
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
from an external hardware switch connected via binary inputs. Circuit breaker control for circuit breakers, CBC1 and CBC2 The CBC1 and CBC2 consists of 3 functions each: SCILO - The Logical node for interlocking. SCILO function is used to enable a switching operation if the interlocking conditions permit. SCILO function itself does not provide any interlocking functionality. The interlocking conditions are generated in separate function blocks containing the interlocking logic. SCSWI - The Switch controller initializes and supervises all functions to properly select and operate switching primary apparatuses. The Switch controller may handle and operate on one three-phase device. SXCBR - The purpose of SXCBR is to provide the actual status of positions and to perform the control operations, that is, pass all the commands to primary apparatuses in the form of circuit breakers via output boards and to supervise the switching operation and position. Logic rotating switch for function selection and LHMI presentation SLGGIO The logic rotating switch for function selection and LHMI presentation (SLGGIO) (or the selector switch function block) is used to get a selector switch functionality similar to the one provided by a hardware selector switch. Hardware selector switches are used extensively by utilities, in order to have different functions operating on pre-set values. Hardware switches are however sources for maintenance issues, lower system reliability and an extended purchase portfolio. The logic selector switches eliminate all these problems. Selector mini switch VSGGIO The Selector mini switch VSGGIO function block is a multipurpose function used for a variety of applications, as a general purpose switch. VSGGIO can be controlled from the menu or from a symbol on the single line diagram (SLD) on the local HMI.
IEC 61850 generic communication I/O functions DPGGIO The IEC 61850 generic communication I/O functions (DPGGIO) function block is used to send double indications to other systems or equipment in the substation. It is especially used in the interlocking and reservation station-wide logics. Single point generic control 8 signals SPC8GGIO The Single point generic control 8 signals (SPC8GGIO) function block is a collection of 8 single point commands, designed to bring in commands from REMOTE (SCADA) to those parts of the logic configuration that do not need extensive command receiving functionality (for example, SCSWI). In this way, simple commands can be sent directly to the IED outputs, without confirmation. Confirmation (status) of the result of the commands is supposed to be achieved by other means, such as binary inputs and SPGGIO function blocks. The commands can be pulsed or steady. AutomationBits AUTOBITS The Automation bits function (AUTOBITS) is used to configure the DNP3 protocol command handling. 11. Logic Tripping logic common 3-phase output SMPPTRC A function block for protection tripping is provided for each circuit breaker involved in the tripping of the fault. It provides pulse prolongation to ensure a three-phase trip pulse of sufficient length, as well as all functionality necessary for correct co-operation with autoreclosing functions. The trip function block also includes functionality for breaker lock-out. Trip matrix logic TMAGGIO The Trip matrix logic TMAGGIO function is used to route trip signals and other logical output signals to the tripping logics SMPPTRC and SPTPTRC or to different output contacts on the IED. TMAGGIO output signals and the physical outputs allows the user to adapt the signals to the physical tripping outputs according to the specific application needs.
ABB
22
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Configurable logic blocks A number of logic blocks and timers are available for the user to adapt the configuration to the specific application needs. OR function block. INVERTER function blocks that inverts the input signal. PULSETIMER function block can be used, for example, for pulse extensions or limiting of operation of outputs, settable pulse time. GATE function block is used for whether or not a signal should be able to pass from the input to the output. XOR function block. LOOPDELAY function block used to delay the output signal one execution cycle. TIMERSET function has pick-up and drop-out delayed outputs related to the input signal. The timer has a settable time delay and must be On for the input signal to activate the output with the appropriate time delay. AND function block. SRMEMORY function block is a flip-flop that can set or reset an output from two inputs respectively. Each block has two outputs where one is inverted. The memory setting controls if the block's output should reset or return to the state it was, after a power interruption. The SET input has priority if both SET and RESET inputs are operated simultaneously. RSMEMORY function block is a flip-flop that can reset or set an output from two inputs respectively. Each block has two outputs where one is inverted. The memory setting controls if the block's output should reset or return to the state it was, after a power interruption. The RESET input has priority if both SET and RESET are operated simultaneously. Boolean 16 to Integer conversion B16I Boolean 16 to integer conversion function (B16I) is used to transform a set of 16 binary (logical) signals into an integer.
Boolean 16 to Integer conversion with logic node representation B16IFCVI Boolean 16 to integer conversion with logic node representation function (B16IFCVI) is used to transform a set of 16 binary (logical) signals into an integer. Integer to Boolean 16 conversion IB16A Integer to boolean 16 conversion function (IB16A) is used to transform an integer into a set of 16 binary (logical) signals. Integer to Boolean 16 conversion with logic node representation IB16FCVB Integer to boolean conversion with logic node representation function (IB16FCVB) is used to transform an integer to 16 binary (logic) signals. IB16FCVB function can receive remote values over IEC61850 depending on the operator position input (PSTO). 12. Monitoring IEC61850 generic communication I/O function SPGGIO IEC61850 generic communication I/O functions (SPGGIO) is used to send one single logical signal to other systems or equipment in the substation. IEC61850 generic communication 1/O function 16 inputs IEC 61850 generic communication I/O functions 16 inputs (SP16GGIO) function is used to send up to 16 logical signals to other systems or equipment in the substation. Measurements CVMMXN, CMMXU, VNMMXU, VMMXU, CMSQI, VMSQI The measurement functions are used to get online information from the IED. These service values make it possible to display on-line information on the local HMI and on the Substation automation system about: measured voltages, currents, frequency, active, reactive and apparent power and power factor primary and secondary phasors current sequence components voltage sequence components
ABB
23
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Event counter CNTGGIO Event counter (CNTGGIO) has six counters which are used for storing the number of times each counter input has been activated. Disturbance report DRPRDRE Complete and reliable information about disturbances in the primary and/or in the secondary system together with continuous eventlogging is accomplished by the disturbance report functionality. Disturbance report DRPRDRE, always included in the IED, acquires sampled data of all selected analog input and binary signals connected to the function block with a, maximum of 40 analog and 96 binary signals. The Disturbance report functionality is a common name for several functions: Event list Indications Event recorder Trip value recorder Disturbance recorder
The event list logs all binary input signals connected to the Disturbance report function. The list may contain up to 1000 time-tagged events stored in a ring-buffer. Indications DRPRDRE To get fast, condensed and reliable information about disturbances in the primary and/or in the secondary system it is important to know, for example binary signals that have changed status during a disturbance. This information is used in the short perspective to get information via the local HMI in a straightforward way. There are three LEDs on the local HMI (green, yellow and red), which will display status information about the IED and the Disturbance report function (triggered). The Indication list function shows all selected binary input signals connected to the Disturbance report function that have changed status during a disturbance. Event recorder DRPRDRE Quick, complete and reliable information about disturbances in the primary and/or in the secondary system is vital, for example, timetagged events logged during disturbances. This information is used for different purposes in the short term (for example corrective actions) and in the long term (for example functional analysis). The event recorder logs all selected binary input signals connected to the Disturbance report function. Each recording can contain up to 150 time-tagged events. The event recorder information is available for the disturbances locally in the IED. The event recording information is an integrated part of the disturbance record (Comtrade file). Trip value recorder DRPRDRE Information about the pre-fault and fault values for currents and voltages are vital for the disturbance evaluation. The Trip value recorder calculates the values of all selected analog input signals connected to the Disturbance report function. The result is magnitude and phase angle before and during the fault for each analog input signal.
The Disturbance report function is characterized by great flexibility regarding configuration, starting conditions, recording times, and large storage capacity. A disturbance is defined as an activation of an input to the AxRADR or BxRBDR function blocks, which are set to trigger the disturbance recorder. All signals from start of pre-fault time to the end of post-fault time will be included in the recording. Every disturbance report recording is saved in the IED in the standard Comtrade format. The same applies to all events, which are continuously saved in a ring-buffer. The local HMI is used to get information about the recordings. The disturbance report files may be uploaded to PCM600 for further analysis using the disturbance handling tool. Event list DRPRDRE Continuous event-logging is useful for monitoring the system from an overview perspective and is a complement to specific disturbance recorder functions.
24
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
The trip value recorder information is available for the disturbances locally in the IED. The trip value recorder information is an integrated part of the disturbance record (Comtrade file). Disturbance recorder DRPRDRE The Disturbance recorder function supplies fast, complete and reliable information about disturbances in the power system. It facilitates understanding system behavior and related primary and secondary equipment during and after a disturbance. Recorded information is used for different purposes in the short perspective (for example corrective actions) and long perspective (for example functional analysis). The Disturbance recorder acquires sampled data from selected analog- and binary signals connected to the Disturbance report function (maximum 40 analog and 96 binary signals). The binary signals available are the same as for the event recorder function. The function is characterized by great flexibility and is not dependent on the operation of protection functions. It can record disturbances not detected by protection functions. Up to three seconds of data before the trigger instant can be saved in the disturbance file. The disturbance recorder information for up to 100 disturbances are saved in the IED and the local HMI is used to view the list of recordings. Measured value expander block MVEXP The current and voltage measurements functions (CVMMXN, CMMXU, VMMXU and VNMMXU), current and voltage sequence measurement functions (CMSQI and VMSQI) and IEC 61850 generic communication I/O functions (MVGGIO) are provided with measurement supervision functionality. All measured values can be supervised with four settable limits: low-low limit, low limit, high limit and high-high limit. The measure value expander block has been introduced to enable translating the integer output signal from the measuring functions to 5 binary signals: below low-low limit, below low limit, normal, above high-high limit or above high limit. The output signals can be used as conditions in the configurable logic or for alarming purpose.
Station battery supervision SPVNZBAT The station battery supervision function SPVNZBAT is used for monitoring battery terminal voltage. SPVNZBAT activates the start and alarm outputs when the battery terminal voltage exceeds the set upper limit or drops below the set lower limit. A time delay for the overvoltage and undervoltage alarms can be set according to definite time characteristics. In the definite time (DT) mode, SPVNZBAT operates after a predefined operate time and resets when the battery undervoltage or overvoltage condition disappears after reset time. Insulation gas monitoring function SSIMG Insulation gas monitoring function SSIMG is used for monitoring the circuit breaker condition. Binary information based on the gas pressure in the circuit breaker is used as input signals to the function. In addition, the function generates alarms based on received information. Insulation liquid monitoring function SSIML Insulation liquid monitoring function SSIML is used for monitoring the circuit breaker condition. Binary information based on the oil level in the circuit breaker is used as input signals to the function. In addition, the function generates alarms based on received information. Circuit breaker monitoring SSCBR The circuit breaker condition monitoring function SSCBR is used to monitor different parameters of the circuit breaker. The breaker requires maintenance when the number of operations has reached a predefined value. The energy is calculated from the measured input currents as a sum of I yt values. Alarms are generated when the calculated values exceed the threshold settings. The function contains a blocking functionality. It is possible to block the function outputs, if desired.
13. Metering Pulse counter logic PCGGIO Pulse counter (PCGGIO) function counts externally generated binary pulses, for instance
ABB
25
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
pulses coming from an external energy meter, for calculation of energy consumption values. The pulses are captured by the BIO (binary input/ output) module and then read by the PCGGIO function. A scaled service value is available over the station bus. Function for energy calculation and demand handling ETPMMTR Outputs from the Measurements (CVMMXN) function can be used to calculate energy consumption. Active as well as reactive values are calculated in import and export direction. Values can be read or generated as pulses. Maximum demand power values are also calculated by the function. 14. Human Machine interface Local HMI
Status indication LEDs Alarm indication LEDs which can indicate three states with the colors green, yellow and red, with user printable label. All LEDs are configurable from the PCM600 tool Liquid crystal display (LCD) Keypad with push buttons for control and navigation purposes, switch for selection between local and remote control and reset Five user programmable function buttons An isolated RJ45 communication port for PCM600
15. Basic IED functions Self supervision with internal event list The Self supervision with internal event list (INTERRSIG and SELFSUPEVLST) function reacts to internal system events generated by the different built-in self-supervision elements. The internal events are saved in an internal event list. Time synchronization Use a common global source for example GPS time synchronization inside each substation as well as inside the area of the utility responsibility to achieve a common time base for the IEDs in a protection and control system. This makes comparison and analysis of events and disturbance data between all IEDs in the power system possible. Time-tagging of internal events and disturbances are an excellent help when evaluating faults. Without time synchronization, only the events within the IED can be compared to one another. With time synchronization, events and disturbances within the entire station, and even between line ends, can be compared during evaluation. In the IED, the internal time can be synchronized from a number of sources: SNTP IRIG-B DNP IEC60870-5-103
IEC12000175 V1 EN
Figure 6.
Local human-machine interface
The LHMI of the IED contains the following elements: Display (LCD) Buttons LED indicators Communication port The LHMI is used for setting, monitoring and controlling. The Local human machine interface, LHMI includes a graphical monochrome LCD with a resolution of 320x240 pixels. The character size may vary depending on selected language. The amount of characters and rows fitting the view depends on the character size and the view that is shown. The LHMI is simple and easy to understand. The whole front plate is divided into zones, each with a well-defined functionality:
Parameter setting groups ACTVGRP Use the four different groups of settings to optimize the IED operation for different power
ABB
26
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
system conditions. Creating and switching between fine-tuned setting sets, either from the local HMI or configurable binary inputs, results in a highly adaptable IED that can cope with a variety of power system scenarios. Test mode functionality TESTMODE The protection and control IEDs may have many included functions. To make the testing procedure easier, the IEDs include the feature that allows individual blocking of all functions except the function(s) the shall be tested. There are two ways of entering the test mode: By configuration, activating an input signal of the function block TESTMODE By setting the IED in test mode in the local HMI While the IED is in test mode, all protection functions are blocked. Any function can be unblocked individually regarding functionality and event signaling. This enables the user to follow the operation of one or several related functions to check functionality and to check parts of the configuration, and so on. Change lock function CHNGLCK Change lock function (CHNGLCK) is used to block further changes to the IED configuration and settings once the commissioning is complete. The purpose is to block inadvertent IED configuration changes beyond a certain point in time. Authority status ATHSTAT Authority status (ATHSTAT) function is an indication function block for user log-on activity. Authority check ATHCHCK To safeguard the interests of our customers, both the IED and the tools that are accessing the IED are protected, by means of authorization handling. The authorization handling of the IED and the PCM600 is implemented at both access points to the IED: local, through the local HMI remote, through the communication ports
16. Station communication IEC 61850-8-1 communication protocol The IED supports the communication protocols IEC 61850-8-1 and DNP3 over TCP/IP. All operational information and controls are available through these protocols. However, some communication functions, for example, horizontal communication (GOOSE) between the IEDs, is only enabled by the IEC 61850-8-1 communication protocol. The IED is equipped with an optical Ethernet rear port for the substation communication standard IEC 61850-8-1. IEC 61850-8-1 protocol allows intelligent electrical devices (IEDs) from different vendors to exchange information and simplifies system engineering. Peer-to-peer communication according to GOOSE is part of the standard. Disturbance files uploading is provided. Disturbance files are accessed using the IEC 61850-8-1 protocol. Disturbance files are available to any Ethernet based application via FTP in the standard Comtrade format. Further, the IED can send and receive binary values, double point values and measured values (for example from MMXU functions), together with their quality bit, using the IEC 61850-8-1 GOOSE profile. The IED meets the GOOSE performance requirements for tripping applications in substations, as defined by the IEC 61850 standard. The IED interoperates with other IEC 61850-compliant IEDs, tools, and systems and simultaneously reports events to five different clients on the IEC 61850 station bus. The event system has a rate limiter to reduce CPU load. The event channel has a quota of 10 events/second. If the quota is exceeded the event channel transmission is blocked until the event changes is below the quota, no event is lost. All communication connectors, except for the front port connector, are placed on integrated communication modules. The IED is connected to Ethernet-based communication systems via the fibre-optic multimode LC connector (100BASEFX). The IED supports SNTP and IRIG-B time synchronization methods with a time-stamping resolution of 1 ms.
ABB
27
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Ethernet based: SNTP and DNP3 With time synchronization wiring: IRIG-B
The IED supports IEC 60870-5-103 time synchronization methods with a time stamping resolution of 5 ms.
Table 1. Supported station communication interfaces and protocols Protocol Ethernet 100BASE-FX LC IEC 6185081 DNP3 IEC 60870-5-103 = Supported Serial Glass fibre (ST connector) EIA-485
Horizontal communication via GOOSE for interlocking GOOSE communication can be used for exchanging information between IEDs via the IEC 61850-8-1 station communication bus. This is typically used for sending apparatus position indications for interlocking or reservation signals for 1-of-n control. GOOSE can also be used to exchange any boolean, integer, double point and analog measured values between IEDs. DNP3 protocol DNP3 (Distributed Network Protocol) is a set of communications protocols used to communicate data between components in process automation systems. For a detailed description of the DNP3 protocol, see the DNP3 Communication protocol manual. IEC 60870-5-103 communication protocol IEC 60870-5-103 is an unbalanced (master-slave) protocol for coded-bit serial communication exchanging information with a control system,
and with a data transfer rate up to 19200 bit/s. In IEC terminology, a primary station is a master and a secondary station is a slave. The communication is based on a point-to-point principle. The master must have software that can interpret IEC 60870-5-103 communication messages. IEC 60870-5-103 protocol can be configured to use either the optical serial or RS485 serial communication interface on the COM05 communication module. The functions Operation selection for optical serial (OPTICALPROT) and Operation selection for RS485 (RS485PROT) are used to select the communication interface. The functions IEC60870-5-103 Optical serial communication (OPTICAL103) and IEC60870-5-103 serial communication for RS485 (RS485103) are used to configure the communication parameters for either the optical serial or RS485 serial communication interfaces.
17. Hardware description Layout and dimensions Mounting alternatives The following mounting alternatives are available (IP40 protection from the front): 19 rack mounting kit
See ordering for details about available mounting alternatives.
28
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Rack mounting a single 3U IED
A
B
IEC11000248 V1 EN
Figure 7.
Rack mounted 3U IED
A B
224 mm + 12 mm with ring-lug connectors 22.5 mm
C 482 mm D 132 mm, 3U
ABB
29
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
18. Connection diagrams Customized Connection diagrams for 650 series
IEC12000593 V1 EN
Figure 8.
Designation for 3U, 1/1x19" casing with 1 TRM
IEC12000594 V1 EN
Figure 9.
Designation for 3U, 1/1x19" casing with 1 TRM and 1 AIM
30
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
IEC12000595 V1 EN
Figure 10.
Communication module (COM)
ABB
31
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
IEC12000596 V1 EN
Figure 11.
Power supply module (PSM) 48-125V DC
32
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
IEC12000597 V1 EN
Figure 12.
Power supply module (PSM) 110-250V DC, 100240V AC
IEC12000598 V1 EN
Figure 13.
Transformer module (TRM)
ABB
33
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
IEC12000599 V1 EN
Figure 14.
Analog input (AIM)
IEC12000600 V1 EN
Figure 15.
Binary input/output (BIO) option
34
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
19. Connection diagrams Configured
IEC12000497 V1 EN
Figure 16.
Designation for 3U, 1/1x19" casing with 1 TRM and 1 AIM
ABB
35
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Connection diagrams for REG650 B01
IEC12000498 V1 EN
Figure 17.
Communication module (COM)
36
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
IEC12000499 V1 EN
Figure 18.
Power supply module (PSM) 48-125V DC
ABB
37
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
IEC12000500 V1 EN
Figure 19.
Power supply module (PSM), 110-250V DC, 100240V AC
38
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
IEC12000501 V1 EN
Figure 20.
Transformer module (TRM)
ABB
39
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
IEC12000502 V1 EN
Figure 21.
Analog input module (AIM)
40
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
IEC12000503 V1 EN
Figure 22.
Binary input/output (BIO) option
ABB
41
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Connection diagrams for REG650 B05
IEC12000505 V1 EN
Figure 23.
Communication module (COM)
42
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
IEC12000506 V1 EN
Figure 24.
Power supply module (PSM) 48-125V DC
ABB
43
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
IEC12000507 V1 EN
Figure 25.
Power supply module (PSM), 110-250V DC, 100240V AC
44
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
IEC12000508 V1 EN
Figure 26.
Transformer module (TRM)
ABB
45
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
IEC12000509 V1 EN
Figure 27.
Analog input module (AIM)
46
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
IEC12000510 V1 EN
Figure 28.
Binary input/output (BIO) option
ABB
47
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
20. Technical data General
Definitions Reference value Nominal range Operative range The specified value of an influencing factor to which are referred the characteristics of the equipment The range of values of an influencing quantity (factor) within which, under specified conditions, the equipment meets the specified requirements The range of values of a given energizing quantity for which the equipment, under specified conditions, is able to perform its intended functions according to the specified requirements
Energizing quantities, rated values and limits Analog inputs
Table 2. Energizing inputs Description Rated frequency Operating range Current inputs Rated current, In Thermal withstand capability: Continuously For 1 s For 10 s Dynamic current withstand: Half-wave value Input impedance Voltage inputs Rated voltage, Un Voltage withstand: Continuous For 10 s Burden at rated voltage 420 V rms 450 V rms <0.05 VA 250 A <100 m 1250 A <20 m 4A 100 A 20 A 20 A 500 A *) 100 A Value 50/60 Hz Rated frequency 5 Hz 0.1/0.5 A1) 1/5 A2)
100 V AC/ 110 V AC/ 115 V AC/ 120 V AC
*) max. 350 A for 1 s when COMBITEST test switch is included.
1) 2) Residual current Phase currents or residual current
48
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Auxiliary AC and DC voltage
Table 3. Power supply Description Uauxnominal 600PSM02 48, 60, 110, 125 V DC 600PSM03 100, 110, 120, 220, 240 V AC, 50 and 60 Hz 110, 125, 220, 250 V DC Uauxvariation 80...120% of Un (38.4...150 V DC) 85...110% of Un (85...264 V AC) 80...120% of Un (88...300 V DC) Maximum load of auxiliary voltage supply Ripple in the DC auxiliary voltage Maximum interruption time in the auxiliary DC voltage without resetting the IED 35 W for DC 40 W for AC Max 15% of the DC value (at frequency of 100 and 120 Hz) 50 ms at Uaux
Binary inputs and outputs
Table 4. Binary inputs Description Operating range Rated voltage Current drain Power consumption/input Threshold voltage Value Maximum input voltage 300 V DC 24...250 V DC 1.6...1.8 mA <0.38 W 15...221 V DC (parametrizable in the range in steps of 1% of the rated voltage)
Table 5. Signal output and IRF output IRF relay change over - type signal output relay Description Rated voltage Continuous contact carry Make and carry for 3.0 s Make and carry 0.5 s Breaking capacity when the control-circuit time constant L/ R<40 ms, at U< 48/110/220 V DC Value 250 V AC/DC 5A 10 A 30 A 0.5 A/0.1 A/0.04 A
ABB
49
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Table 6. Power output relays without TCS function Description Rated voltage Continuous contact carry Make and carry for 3.0 s Make and carry for 0.5 s Breaking capacity when the control-circuit time constant L/ R<40 ms, at U< 48/110/220 V DC Table 7. Power output relays with TCS function Description Rated voltage Continuous contact carry Make and carry for 3.0 s Make and carry for 0.5 s Breaking capacity when the control-circuit time constant L/ R<40 ms, at U< 48/110/220 V DC Control voltage range Current drain through the supervision circuit Minimum voltage over the TCS contact Table 8. Ethernet interfaces Ethernet interface 100BASE-TX 100BASE-FX Protocol TCP/IP protocol Cable CAT 6 S/FTP or better Fibre-optic cable with LC connector Data transfer rate 100 MBits/s 100 MBits/s Value 250 V DC 8A 15 A 30 A 1 A/0.3 A/0.1 A 20...250 V DC ~1.0 mA 20 V DC Value 250 V AC/DC 8A 15 A 30 A 1 A/0.3 A/0.1 A
Table 9. Fibre-optic communication link Wave length 1300 nm Fibre type MM 62.5/125 m glass fibre core Connector LC Permitted path attenuation1) <8 dB Distance 2 km
1)
Maximum allowed attenuation caused by connectors and cable together
50
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Table 10. X8/IRIG-B and EIA-485 interface Type Screw terminal, pin row header Screw terminal, pin row header Protocol IRIG-B Cable Shielded twisted pair cable Recommended: CAT 5, Belden RS-485 (9841- 9844) or Alpha Wire (Alpha 6222-6230) Shielded twisted pair cable Recommended: DESCAFLEX RD-H(ST)H-2x2x0.22mm2, Belden 9729, Belden 9829
Table 11. IRIG-B Type Input impedance Minimum input voltage HIGH Maximum input voltage LOW Table 12. EIA-485 interface Type Minimum differential driver output voltage Maximum output current Minimum differential receiver input voltage Supported bit rates Value 1.5 V 60 mA 0.2 V 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200 32 Conditions Value 430 Ohm 4.3 V 0.8 V Accuracy
Maximum number of 650 IEDs supported on the same bus Max. cable length Table 13. Serial rear interface Type Serial port (X9)
925 m (3000 ft)
Cable: AWG24 or better, stub lines shall be avoided
Counter connector Optical serial port, type ST for IEC 60870-5-103 and DNP serial
ABB
51
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Table 14. Optical serial port (X9) Wave length 820 nm 820 nm Fibre type MM 62,5/125 m glass fibre core MM 50/125 m glass fibre core Connector ST ST Permitted path attenuation1) 6.8 dB (approx. 1700m length with 4 db / km fibre attenuation) 2.4 dB (approx. 600m length with 4 db / km fibre attenuation)
1)
Maximum allowed attenuation caused by fibre
Influencing factors
Table 15. Degree of protection of rack-mounted IED Description Front side Rear side, connection terminals Table 16. Degree of protection of the LHMI Description Front and side Table 17. Environmental conditions Description Operating temperature range Short-time service temperature range Value -25...+55C (continuous) -40...+70C (<16h) Note: Degradation in MTBF and HMI performance outside the temperature range of -25...+55C <93%, non-condensing 86...106 kPa up to 2000 m -40...+85C Value IP40 Value IP 40 IP 20
Relative humidity Atmospheric pressure Altitude Transport and storage temperature range
52
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Table 18. Environmental tests Description Cold tests operation Type test value 96 h at -25C 16 h at -40C 96 h at -40C 16 h at +70C IEC 60068-2-2/ANSI C37.90-2005 (chapter 4) Reference IEC 60068-2-1/ANSI C37.90-2005 (chapter 4)
storage Dry heat tests operation
storage Damp heat tests steady state
96 h at +85C 240 h at +40C humidity 93% 6 cycles at +25 to +55C humidity 93...95% IEC 60068-2-78
cyclic
IEC 60068-2-30
ABB
53
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Type tests according to standards
Table 19. Electromagnetic compatibility tests Description 100 kHz and 1 MHz burst disturbance test Common mode Differential mode Electrostatic discharge test 2.5 kV 2.5 kV IEC 61000-4-2, level 4 IEC 60255-22-2 ANSI C37.90.3-2001 8 kV 15 kV Type test value Reference IEC 61000-4-18, level 3 IEC 60255-22-1 ANSI C37.90.1-2002
Contact discharge Air discharge Radio frequency interference tests Conducted, common mode Radiated, amplitude-modulated
10 V (emf), f=150 kHz...80 MHz 20 V/m (rms), f=80...1000 MHz and f=1.4...2.7 GHz
IEC 61000-4-6 , level 3 IEC 60255-22-6 IEC 61000-4-3, level 3 IEC 60255-22-3 ANSI C37.90.2-2004 IEC 61000-4-4 IEC 60255-22-4, class A ANSI C37.90.1-2002
Fast transient disturbance tests
Communication ports Other ports Surge immunity test Communication Other ports Power frequency (50 Hz) magnetic field 3s Continuous Pulse magnetic field immunity test Power frequency immunity test Common mode Differential mode
4 kV 4 kV IEC 61000-4-5, level 3/2 IEC 60255-22-5 1 kV line-to-earth 2 kV line-to-earth, 1 kV line-to-line IEC 61000-4-8, level 5 1000 A/m 100 A/m 1000A/m IEC 6100049, level 5 IEC 60255-22-7, class A IEC 61000-4-16 300 V rms 150 V rms
54
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Table 19. Electromagnetic compatibility tests, continued Description Voltage dips and short interruptionsc on DC power supply Type test value Dips: 40%/200 ms 70%/500 ms Interruptions: 0-50 ms: No restart 0... s : Correct behaviour at power down Dips: 40% 10/12 cycles at 50/60 Hz 70% 25/30 cycles at 50/60 Hz Interruptions: 050 ms: No restart 0... s: Correct behaviour at power down Reference IEC 60255-11 IEC 61000-4-11
Voltage dips and interruptions on AC power supply
IEC 6025511 IEC 61000411
Electromagnetic emission tests Conducted, RF-emission (mains terminal) 0.15...0.50 MHz 0.5...30 MHz Radiated RF-emission 30...230 MHz 230...1000 MHz < 40 dB(V/m) quasi peak, measured at 10 m distance < 47 dB(V/m) quasi peak, measured at 10 m distance < 79 dB(V) quasi peak < 66 dB(V) average < 73 dB(V) quasi peak < 60 dB(V) average
EN 55011, class A IEC 60255-25
ABB
55
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Table 20. Insulation tests Description Dielectric tests: Test voltage Impulse voltage test: Test voltage 5 kV, unipolar impulses, waveform 1.2/50 s, source energy 0.5 J 1 kV, unipolar impulses, waveform 1.2/50 s, source energy 0.5 J, communication IEC 60255-5 ANSI C37.90-2005 >100 M, 500 V DC IEC 60255-27 <0.1 (60 s) 2 kV, 50 Hz, 1 min 1 kV, 50 Hz, 1 min, communication IEC 60255-5 ANSI C37.90-2005 Type test value Reference IEC 60255-5 ANSI C37.90-2005
Insulation resistance measurements Isolation resistance Protective bonding resistance Resistance Table 21. Mechanical tests Description Vibration response tests (sinusoidal) Vibration endurance test Shock response test Shock withstand test Bump test Seismic test Reference IEC 60255-21-1 IEC60255-21-1 IEC 60255-21-2 IEC 60255-21-2 IEC 60255-21-2 IEC 60255-21-3
Requirement Class 2 Class 1 Class 1 Class 1 Class 1 Class 2
Product safety
Table 22. Product safety Description LV directive Standard Reference 2006/95/EC EN 60255-27 (2005)
56
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
EMC compliance
Table 23. EMC compliance Description EMC directive Standard Reference 2004/108/EC EN 50263 (2000) EN 60255-26 (2007)
ABB
57
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Differential protection
Table 24. Transformer differential protection T2WPDIF, T3WPDIF Function Operating characteristic Reset ratio Unrestrained differential current limit Base sensitivity function Minimum negative sequence current Operate angle, negative sequence Second harmonic blocking Range or value Adaptable >94% (1.00-50.00)xIBase on high voltage winding (0.05 - 0.60) x IBase (0.02 - 0.20) x IBase (30.0 - 90.0) degrees (5.0-100.0)% of fundamental differential current (5.0-100.0)% of fundamental differential current Y or D 011 Accuracy 1.0% of Ir for I < Ir 1.0% of I for I > Ir 1.0% of set value 1.0% of Ir 1.0% of Ir 1.0 degrees 2.0% of applied harmonic magnitude
Fifth harmonic blocking
12.0% of applied harmonic magnitude
Connection type for each of the windings Phase displacement between high voltage winding, W1 and each of the windings, W2 and W3. Hour notation Operate time, restrained function Reset time, restrained function Operate time, unrestrained function Reset time, unrestrained function
25 ms typically at 0 to 5 x set level 25 ms typically at 5 to 0 x set level 20 ms typically at 0 to 5 x set level 25 ms typically at 5 to 0 x set level
Table 25. 1Ph High impedance differential protection HZPDIF Function Operate voltage Reset ratio Maximum continuous power Operate time Reset time Critical impulse time Range or value (20-400) V I=U/R >95% U>Trip2/SeriesResistor 200 W 10 ms typically at 0 to 10 x Ud 105 ms typically at 10 to 0 x Ud 2 ms typically at 0 to 10 x Ud Accuracy 1.0% of Ir -
58
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Table 26. Generator differential protection GENPDIF Function Unrestrained differential current limit Reset ratio Base sensitivity function Negative sequence current level Operate time, restrained function Reset time, restrained function Operate time, unrestrained function Reset time, unrestrained function Operate time, negative sequence unrestrained function Critical impulse time, unrestrained function Range or value (1-50)p.u. of IBase > 90% (0.051.00)p.u. of IBase (0.020.2)p.u. of IBase 40 ms typically at 0 to 2 x set level 40 ms typically at 2 to 0 x set level 20 ms typically at 0 to 5 x set level 40 ms typically at 5 to 0 x set level 15 ms typically at 0 to 5 x set level 3 ms typically at 0 to 5 x set level Accuracy 1.0% of set value 1.0% of Ir 1.0% of Ir -
ABB
59
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Impedance protection
Table 27. Underimpedance protection for generators and transformers ZGCPDIS Function Number of zones Forward positive sequence impedance Range or value 3 (0.005-3000.000) / phase Accuracy 2.0% static accuracy Conditions: Voltage range: (0.1-1.1) x Ur Current range: (0.5-30) x Ir Angle: at 85 degrees Reverse positive sequence impedance Angle for positive sequence impedance, Timers Operate time Reset ratio Table 28. Loss of excitation LEXPDIS Function X offset of Mho top point Diameter of Mho circle Timers Operate time Reset ratio Range or value (1000.001000.00)% of ZBase (0.003000.00)% of ZBase (0.006000.00) s 55 ms typically 105% typically Accuracy 2.0% of Ur/Ir 2.0% of Ur/Ir 0.5% 25 ms (0.005-3000.000) / phase (10-90) degrees (0.000-60.000) s 25 ms typically 105% typically 0.5% 10 ms -
Table 29. Out-of-step protection OOSPPAM Function Impedance reach Characteristic angle Start and trip angles Zone 1 and Zone 2 trip counters Range or value (0.001000.00)% of Zbase (72.0090.00) degrees (0.0180.0) degrees (1-20) Accuracy 2.0% of Ur/Ir 5.0 degrees 5.0 degrees -
Table 30. Load enchroachment LEPDIS Function Load encroachment criteria: Load resistance, forward and reverse Safety load impedance angle Range or value (1.003000.00) /phase (5-85) degrees Accuracy 5.0% static accuracy 2.0 degrees static angular accuracy Conditions: Voltage range: (0.1-1.1) x Ur Current range: (0.5-30) x Ir Reset ratio 105% typically -
60
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Current protection
Table 31. Four step phase overcurrent protection, 3-phase output OC4PTOC Function Operate current Setting range (5-2500)% of lBase Accuracy 1.0% of Ir at I Ir 1.0% of I at I > Ir Reset ratio Min. operating current > 95% (1-10000)% of lBase 1.0% of Ir at I Ir 1.0% of I at I > Ir 2nd harmonic blocking Independent time delay Minimum operate time for inverse characteristics Inverse characteristics, see table 72, table 73 and table 74 (5100)% of fundamental (0.000-60.000) s (0.000-60.000) s 17 curve types 2.0% of Ir 0.5% 25 ms 0.5% 25 ms
1)
ANSI/IEEE C37.112 IEC 60255151 3% or 40 ms 0.10 k 3.00 1.5 x Iset I 20 x Iset -
Operate time, nondirectional start function Reset time, nondirectional start function Operate time, directional start function Reset time, directional start function Critical impulse time Impulse margin time
1) Note:
25 ms typically at 0 to 2 x Iset 30 ms typically at 2 to 0 x Iset 50 ms typically at 0 to 2 x Iset 35 ms typically at 2 to 0 x Iset 10 ms typically at 0 to 2 x Iset 15 ms typically
Timing accuracy only valid when 2nd harmonic blocking is turned off
ABB
61
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Table 32. Four step residual overcurrent protection EF4PTOC Function Operate current Range or value (1-2500)% of lBase Accuracy 1.0% of Ir at I < Ir 1.0% of I at I > Ir Reset ratio Operate current for directional comparison, Zero sequence Operate current for directional comparison, Negative sequence Min. operating current > 95% (1100)% of lBase (1100)% of lBase (1-10000)% of lBase 2.0% of Ir 2.0% of Ir 1.0% of Ir at I < Ir 1.0% of I at I >Ir Minimum operate time for inverse characteristics Timers Inverse characteristics, see table 72, table 73 and table 74 (0.000-60.000) s (0.000-60.000) s 17 curve types 0.5% 25 ms 0.5% 25 ms
1)
ANSI/IEEE C37.112 IEC 60255151 3% or 40 ms 0.10 k 3.00 1.5 x Iset I 20 x Iset 0.5% of Ur 0.5% of Ur 1.0% of Ir 1.0% of Ir -
Minimum polarizing voltage, Zero sequence Minimum polarizing voltage, Negative sequence Minimum polarizing current, Zero sequence Minimum polarizing current, Negative sequence Real part of source Z used for current polarization Imaginary part of source Z used for current polarization Operate time, non-directional start function Reset time, non-directional start function Operate time, directional start function Reset time, directional start function
1) Note:
(1100)% of UBase (1100)% of UBase (2100)% of IBase (2100)% of IBase (0.50-1000.00) W/phase (0.503000.00) W/phase 30 ms typically at 0.5 to 2 x Iset 30 ms typically at 2 to 0.5 x Iset 30 ms typically at 0,5 to 2 x IN 30 ms typically at 2 to 0,5 x IN
Timing accuracy only valid when 2nd harmonic blocking is turned off.
62
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Table 33. Sensitive directional residual overcurrent and power protection SDEPSDE Function Operate level for 3I0cosj directional residual overcurrent Range or value (0.25-200.00)% of lBase At low setting: (2.5-10) mA (10-50) mA (0.25-200.00)% of SBase At low setting: (0.25-5.00)% of SBase (0.25-200.00)% of lBase At low setting: (2.5-10) mA (10-50) mA (1.00-400.00)% of lBase At low setting: (10-50) mA Operate level for nondirectional residual overvoltage Residual release current for all directional modes (1.00-200.00)% of UBase Accuracy 1.0% of Ir at I Ir 1.0% of I at I > Ir 0.5 mA 1.0 mA 2.0% of Sr at S Sr 2.0% of S at S > Sr 10% of set value 1.0% of Ir at Ir 1.0% of I at I > Ir 0.5 mA 1.0 mA 1.0% of Ir at I Ir 1.0% of I at I > Ir 1.0 mA 0.5% of Ur at UUr 0.5% of U at U > Ur (0.25-200.00)% of lBase At low setting: (2.5-10) mA (10-50) mA Residual release voltage for all directional modes Reset ratio Timers Inverse characteristics, see table 72, table 73 and table 74 (1.00 - 300.00)% of UBase 1.0% of Ir at I Ir 1.0% of I at I > Ir 0.5 mA 1.0 mA 0.5% of Ur at UUr 0.5% of U at U > Ur > 95% (0.000-60.000) s 17 curve types 0.5% 25 ms ANSI/IEEE C37.112 IEC 60255151 +100 ms(3% or 90 ms) 0.10 k 3.00 1.5 x Iset I 20 x Iset 2.0 degrees 2.0 degrees -
Operate level for 3I03U0 cosj directional residual power Operate level for 3I0 and j residual overcurrent
Operate level for nondirectional overcurrent
Relay characteristic angle RCA Relay open angle ROA Operate time, non-directional residual over current Reset time, non-directional residual over current Operate time, non-directional residual overvoltage
(-179 to 180) degrees (0-90) degrees 80 ms typically at 0.5 to 2 x Iset 90 ms typically at 1.2 to 0.5 x Iset 70 ms typically at 0.8 to 1.5 x Uset
ABB
63
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Table 33. Sensitive directional residual overcurrent and power protection SDEPSDE, continued Function Reset time, non-directional residual overvoltage Operate time, directional residual over current Reset time, directional residual over current Critical impulse time nondirectional residual over current Impulse margin time nondirectional residual over current Range or value 120 ms typically at 1.2 to 0.8 x Uset 260 ms typically at 0.5 to 2 x Iset 170 ms typically at 2 to 0.5 x Iset 100 ms typically at 0 to 2 x Iset 20 ms typically at 0 to 10 x Iset 25 ms typically Accuracy -
Table 34. Thermal overload protection, two time constants TRPTTR Function Base current 1 and 2 Operate time: Range or value (30250)% of IBase Ip = load current before overload Accuracy 1.0% of Ir IEC 602558, 5% + 200 ms
I 2 - I p2 t = t ln 2 I - Ib 2
EQUATION1356 V1 EN
(Equation 1)
occurs Time constant = (1500) minutes
I = Imeasured Alarm level 1 and 2 Operate current Reset level temperature (5099)% of heat content trip value (50250)% of IBase (1095)% of heat content trip 2.0% of heat content trip 1.0% of Ir 2.0% of heat content trip
64
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Table 35. Breaker failure protection, 3-phase activation and output CCRBRF Function Operate phase current Range or value (5-200)% of lBase Accuracy 1.0% of Ir at I Ir 1.0% of I at I > Ir Reset ratio, phase current Operate residual current > 95% (2-200)% of lBase 1.0% of Ir at I Ir 1.0% of I at I > Ir Reset ratio, residual current Phase current level for blocking of contact function Reset ratio Timers Operate time for current detection Reset time for current detection > 95% (5-200)% of lBase 1.0% of Ir at I Ir 1.0% of I at I > Ir > 95% (0.000-60.000) s 35 ms typically 10 ms maximum 0.5% 10 ms -
Table 36. Pole discordance protection CCRPLD Function Operate value, current asymmetry level Reset ratio Time delay Range or value (0-100) % >95% (0.000-60.000) s Accuracy 1.0% of Ir 0.5% 25 ms
Table 37. Directional over/underpower protection GOPPDOP, GUPPDUP Function Power level Range or value (0.0500.0)% of SBase (1.0-2.0)% of SBase (2.0-10)% of SBase Characteristic angle Timers (-180.0180.0) degrees (0.010 - 6000.000) s Accuracy 1.0% of Sr at S < Sr 1.0% of S at S > Sr < 50% of set value < 20% of set value 2 degrees 0.5% 25 ms
ABB
65
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Table 38. Accidental energizing protection for synchronous generator AEGGAPC Function Operate value, overcurrent Range or value (2-900)% of IBase Accuracy 1,0% of Ir at I<Ir 1.0% of I at I>Ir Reset ratio, overcurrent Transient overreach, overcurrent function Critical impulse time, overcurrent Impulse margin time, overcurrent Operate value, undervoltage >95% <20% at = 100 ms 10 ms typically at 0 to 2 x Iset 15 ms typically (2-200)% of UBase 0.5% of Ur at U<Ur 0.5% of U at U>Ur Critical impulse time, undervoltage Impulse margin time, undervoltage Operate value, overvoltage 10 ms typically at 2 to 0 x Uset 15 ms typically (2-200)% of UBase 0.5% of Ur at U<Ur 0.5% of U at U>Ur Timers (0.000-60.000) s 0.5% 25 ms
Table 39. Negative sequence time overcurrent protection for machines NS2PTOC Function Operate value, step 1 and 2, negative sequence overcurrent Reset ratio, step 1 and 2 Operate time, start Range or value (3-500)% of IBase Accuracy 1.0% of Ir at I < Ir 1.0% of I at I > Ir >95% 30 ms typically at 0 to 2 x Iset 20 ms typically at 0 to 10 x Iset Reset time, start Time characteristics Inverse time characteristic step 1, 40 ms typically at 2 to 0 x Iset Definite or Inverse K=1.0-99.0 3% or 40 ms 1 K 20 10% or 50 ms 1 K 20 0.5% 25 ms 0.5% 25 ms 0.5% 25 ms -
I2 t = K
Reset time, inverse characteristic step 1, K=0.01-20.00
I2 t = K
(0.00-6000.00) s (0.000-60.000) s (0.00-6000.00) s
Maximum trip delay, step 1 IDMT Minimum trip delay, step 1 IDMT Timers
66
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Table 40. Voltage-restrained time overcurrent protectionVR2PVOC Function Start overcurrent Range or value (2 - 5000)% of IBase Accuracy 1.0% of Ir at I<Ir 1.0% of I at I>Ir Definite time delay Inverse characteristics, see table 72, table 73 and table 74 (0.00 - 6000.00) s 17 curves type 0.5% 25 ms ANSI/IEEE C37.112 IEC 60255151 3% or 40 ms 0.10 k 3.00 1.5 x Iset I 20 x Iset -
Operate time start overcurrent
30 ms typically at 0 to 2 x Iset 20 ms typically at 0 to 10 x Iset 40 ms typically at 2 to 0 x Iset (2.0 - 100.0)% of UBase 30 ms typically 2 to 0 x Uset 40 ms typically at 0 to 2 x Uset (30 - 100)% of UBase > 95% < 105% 10 ms typically at 0 to 2 x Iset 15 ms typically
Reset time start overcurrent Start undervoltage Operate time start undervoltage Reset time start undervoltage High voltage limit, voltage dependent operation Reset ratio, overcurrent Reset ratio, undervoltage Overcurrent: Critical impulse time Impulse margin time
0.5% of Ur 1.0% of Ur -
Voltage protection
Table 41. Two step undervoltage protection UV2PTUV Function Operate voltage, low and high step Reset ratio Inverse time characteristics for low and high step, see table 76 Definite time delay, step 1 Definite time delays, step 2 Minimum operate time, inverse characteristics Operate time, start function Reset time, start function Critical impulse time Impulse margin time Range or value (1100)% of UBase <105% (0.00 - 6000.00) s (0.000-60.000) s (0.00060.000) s 30 ms typically at 1.2 to 0.5 x Uset 40 ms typically at 0.5 to 1.2 xUset 10 ms typically at 1.2 to 0.8 x Uset 15 ms typically Accuracy 0.5% of Ur See table 76 0.5% 25 ms 0.5% 25 ms 0.5% 25 ms -
ABB
67
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Table 42. Two step overvoltage protection OV2PTOV Function Operate voltage, low and high step Range or value (1-200)% of UBase Accuracy 0.5% of Ur at U < Ur 0.5% of U at U > Ur Reset ratio Inverse time characteristics for low and high step, see table 75 Definite time delay, step 1 Definite time delays, step 2 Minimum operate time, Inverse characteristics Operate time, start function Reset time, start function Critical impulse time Impulse margin time >95% (0.00 - 6000.00) s (0.000-60.000) s (0.000-60.000) s 30 ms typically at 0 to 2 x Uset 40 ms typically at 2 to 0 x Uset 10 ms typically at 0 to 2 x Uset 15 ms typically See table 75 0.5% 25 ms 0.5% 25 ms 0.5% 25 ms -
Table 43. Two step residual overvoltage protection ROV2PTOV Function Operate voltage, step 1 Range or value (1-200)% of UBase (1100)% of UBase Accuracy 0.5% of Ur at U < Ur 0.5% of U at U > Ur Operate voltage, step 2 0.5% of Ur at U < Ur 0.5% of U at U > Ur Reset ratio Inverse time characteristics for low and high step, see table 77 Definite time setting, step 1 Definite time setting, step 2 Minimum operate time for step 1 inverse characteristic Operate time, start function Reset time, start function Critical impulse time Impulse margin time >95% (0.006000.00) s (0.00060.000) s (0.000-60.000) s 30 ms typically at 0 to 2 x Uset 40 ms typically at 2 to 0 x Uset 10 ms typically at 0 to 1.2 xUset 15 ms typically See table 77 0.5% 25 ms 0.5% 25 ms 0.5% 25 ms -
68
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Table 44. Overexcitation protection OEXPVPH Function Operate value, start Operate value, alarm Range or value (100180)% of (UBase/frated) (50120)% of start level Accuracy 0.5% of U 0.5% of Ur at U Ur 0.5% of U at U > Ur Operate value, high level Curve type (100200)% of (UBase/frated) IEEE
IEEE : t = (0.18 k ) ( M - 1) 2
0.5% of U 5% + 40 ms
EQUATION1319 V1 EN
(Equation 2)
where M = (E/f)/(Ur/fr) Minimum time delay for inverse function Alarm time delay (0.00060.000) s (0.00060.000) s 0.5% 25 ms 0.5% 25 ms
Table 45. 100% Stator E/F 3rd harmonic STEFPHIZ Function Fundamental frequency level UN (95% Stator EF) Third harmonic differential level Third harmonic differential block level Timers Filter characteristic: Fundamental Third harmonic Range or value (1.050.0)% of UBase (0.510.0)% of UBase (0.110.0)% of UBase (0.02060.000) s Reject third harmonic by 140 Reject fundamental harmonic by 140 Accuracy 0.5% of Ur 5.0% of Ur 5.0% of Ur 0.5% 25 ms -
ABB
69
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Frequency protection
Table 46. Under frequency protection SAPTUF Function Operate value, start function Operate value, restore frequency Reset ratio Operate time, start function Range or value (35.00-75.00) Hz (45 - 65) Hz <1.001 At 50 Hz: 200 ms typically at fset +0.5 Hz to fset -0.5 Hz At 60 Hz: 170 ms typically at fset +0.5 Hz to fset -0.5 Hz Reset time, start function At 50 Hz: 60 ms typically at fset -0.5 Hz to fset +0.5 Hz At 60 Hz: 50 ms typically at fset -0.5 Hz to fset +0.5 Hz Operate time delay Restore time delay Table 47. Overfrequency protection SAPTOF Function Operate value, start function Range or value (35.00-75.00) Hz Accuracy 2.0 mHz at symmetrical threephase voltage (0.000-60.000)s (0.000-60.000)s <250 ms <150 ms Accuracy 2.0 mHz 2.0 mHz -
Reset ratio Operate time, start function
>0.999 At 50 Hz: 200 ms typically at fset -0.5 Hz to fset +0.5 Hz At 60 Hz: 170 ms typically at fset -0.5 Hz to fset +0.5 Hz
Reset time, start function
At 50 and 60 Hz: 55 ms typically at fset +0.5 Hz to fset-0.5 Hz (0.000-60.000)s
Timer
<250 ms
Table 48. Rate-of-change frequency protection SAPFRC Function Operate value, start function Operate value, restore enable frequency Timers Operate time, start function Range or value (-10.00-10.00) Hz/s (45.00 - 65.00) Hz (0.000 - 60.000) s At 50 Hz: 100 ms typically At 60 Hz: 80 ms typically Accuracy 10.0 mHz/s 2.0 mHz <130 ms -
70
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Secondary system supervision
Table 49. Fuse failure supervision SDDRFUF Function Operate voltage, zero sequence Operate current, zero sequence Operate voltage, negative sequence Operate current, negative sequence Operate voltage change level Operate current change level Operate phase voltage Operate phase current Operate phase dead line voltage Operate phase dead line current Range or value (1-100)% of UBase (1100)% of IBase (1100)% of UBase (1100)% of IBase (1100)% of UBase (1100)% of IBase (1-100)% of UBase (1-100)% of IBase (1-100)% of UBase (1-100)% of IBase Accuracy 1.0% of Ur 1.0% of Ir 0.5% of Ur 1.0% of Ir 5.0% of Ur 5.0% of Ir 0.5% of Ur 1.0% of Ir 0.5% of Ur 1.0% of Ir
Table 50. Breaker close/trip circuit monitoring TCSSCBR Function Operate time delay Range or value (0.020 - 300.000) s Accuracy 0,5% 110 ms
ABB
71
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Control
Table 51. Synchronizing, synchrocheck and energizing check SESRSYN Function Phase shift, jline - jbus Voltage ratio, Ubus/Uline Reset ratio, synchrocheck Frequency difference limit between bus and line for synchrocheck Phase angle difference limit between bus and line for synchrocheck Voltage difference limit between bus and line for synchronizing and synchrocheck Time delay output for synchrocheck Frequency difference minimum limit for synchronizing Frequency difference maximum limit for synchronizing Maximum allowed frequency rate of change Closing time of the breaker Breaker closing pulse duration tMaxSynch, which resets synchronizing function if no close has been made before set time Minimum time to accept synchronizing conditions Frequency difference minimum limit for synchronizing Frequency difference maximum limit for synchronizing Closing time of the breaker Breaker closing time duration tMaxSynch, which resets synchronizing function if no close has been made before set time Time delay output for energizing check Operate time for synchrocheck function Operate time for energizing function Minimum time to accept synchronizing conditions Maximum allowed frequency rate of change Range or value (-180 to 180) degrees 0.500 - 2.000 > 95% (0.003-1.000) Hz (5.0-90.0) degrees 0.03-0.50 p.u (0.000-60.000) s (0.003-0.250) Hz (0.050-0.500) Hz (0.000-0.500) Hz/s (0.000-60.000) s (0.000-60.000) s (0.000-60.000) s Accuracy 2.0 mHz 2.0 degrees 0.5% of Ur 0.5% 25 ms 2.0 mHz 2.0 mHz 10.0 mHz/s 0.5% 10 ms 0.5% 10 ms 0.5% 10 ms
(0.000-60.000) s (0.003-0.250) Hz (0.050-0.500) Hz (0.000-60.000) s (0.050-60.000) s (0.00-6000.00) s
0.5% 10 ms 2.0 mHz 2.0 mHz 0.5% 10 ms 0.5% 10 ms 0.5% 10 ms
(0.000-60.000) s 160 ms typically 80 ms typically (0.000-60.000) s (0.000-0.500) Hz/s
0.5% 10 ms 0.5% 10 ms 10.0 mHz/s
72
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Logic
Table 52. Tripping logic common 3-phase output SMPPTRC Function Trip action Timers Table 53. Configurable logic blocks Logic block Quantity with cycle time 5 ms AND OR XOR INVERTER SRMEMORY RSMEMORY GATE PULSETIMER TIMERSET LOOPDELAY 60 60 10 30 10 10 10 10 10 10 20 ms 60 60 10 30 10 10 10 10 10 10 100 ms 160 160 20 80 20 20 20 20 20 20 (0.00090000.000) s (0.00090000.000) s 0.5% 25 ms for 20 ms cycle time 0.5% 25 ms for 20 ms cycle time Range or value Accuracy Range or value 3-ph (0.000-60.000) s Accuracy 0.5% 10 ms
ABB
73
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Monitoring
Table 54. Technical datacovering measurement functions:CVMMXN, CMMXU, VMMXU, CMSQI, VMSQI, VNMMXU Function Voltage Range or value (0.1-1.5) Ur (0.2-4.0) Ir 0.1 x Ur< U < 1.5 x Ur 0.2 x Ir < I < 4.0 x Ir Reactive power, Q 0.1 x Ur< U < 1.5 x Ur 0.2 x Ir < I < 4.0 x Ir Apparent power, S 0.1 x Ur < U < 1.5 x Ur 0.2 x Ir< I < 4.0 x Ir Apparent power, S Three phase settings Power factor, cos () cos phi = 1 Accuracy 0.5% of Ur at UUr 0.5% of U at U > Ur Connected current 0.5% of Ir at I Ir 0.5% of I at I > Ir Active power, P 1.0% of Sr at S Sr 1.0% of S at S > Sr 1.0% of Sr at S Sr 1.0% of S at S > Sr 1.0% of Sr at S Sr 1.0% of S at S > Sr 0.5% of S at S > Sr 0.5% of Sr at S Sr 0.1 x Ur < U < 1.5 x Ur 0.2 x Ir< I < 4.0 x Ir Table 55. Event counter CNTGGIO Function Counter value Max. count up speed Range or value 0-10000 10 pulses/s Accuracy < 0.02
74
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Table 56. Disturbance report DRPRDRE Function Current recording Voltage recording Range or value Accuracy 1,0% of Ir at I Ir 1,0% of I at I > Ir 1,0% of Ur at U Ur 1,0% of U at U > Ur Pre-fault time Post-fault time Limit time Maximum number of recordings Time tagging resolution Maximum number of analog inputs Maximum number of binary inputs Maximum number of phasors in the Trip Value recorder per recording Maximum number of indications in a disturbance report Maximum number of events in the Event recording per recording Maximum number of events in the Event list Maximum total recording time (3.4 s recording time and maximum number of channels, typical value) Sampling rate Recording bandwidth Table 57. Event list DRPRDRE Function Buffer capacity Resolution Accuracy Table 58. Indications DRPRDRE Function Buffer capacity Maximum number of indications presented for single disturbance Maximum number of recorded disturbances Value 96 100 Maximum number of events in the list Value 1000 1 ms Depending on time synchronizing (0.053.00) s (0.110.0) s (0.58.0) s 100, first in - first out 1 ms 30 + 10 (external + internally derived) 96 30 96 150 1000, first in - first out 340 seconds (100 recordings) at 50 Hz, 280 seconds (80 recordings) at 60 Hz 1 kHz at 50 Hz 1.2 kHz at 60 Hz (5-300) Hz See time synchronization technical data -
ABB
75
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Table 59. Event recorder DRPRDRE Function Buffer capacity Maximum number of events in disturbance report Maximum number of disturbance reports Resolution Accuracy Value 150 100 1 ms Depending on time synchronizing
Table 60. Trip value recorder DRPRDRE Function Buffer capacity Maximum number of analog inputs Maximum number of disturbance reports Table 61. Disturbance recorder DRPRDRE Function Buffer capacity Maximum number of analog inputs Maximum number of binary inputs Maximum number of disturbance reports Maximum total recording time (3.4 s recording time and maximum number of channels, typical value) Table 62. Station battery supervision SPVNZBAT Function Lower limit for the battery terminal voltage Reset ratio, lower limit Upper limit for the battery terminal voltage Reset ratio, upper limit Timers Range or value (60-140) % of Ubat <105 % (60-140) % of Ubat >95 % (0.000-60.000) s Accuracy 1.0% of set battery voltage 1.0% of set battery voltage 0.5% 110 ms Value 40 96 100 340 seconds (100 recordings) at 50 Hz 280 seconds (80 recordings) at 60 Hz Value 30 100
Table 63. Insulation gas monitoring function SSIMG Function Pressure alarm Pressure lockout Temperature alarm Temperature lockout Timers Range or value 0.00-25.00 0.00-25.00 -40.00-200.00 -40.00-200.00 (0.000-60.000) s Accuracy 0.5% 110 ms
76
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Table 64. Insulation liquid monitoring function SSIML Function Alarm, oil level Oil level lockout Temperature alarm Temperature lockout Timers Range or value 0.00-25.00 0.00-25.00 -40.00-200.00 -40.00-200.00 (0.000-60.000) s Accuracy 0.5% 110 ms
Table 65. Circuit breaker condition monitoring SSCBR Function Alarm levels for open and close travel time Alarm levels for number of operations Setting of alarm for spring charging time Time delay for gas pressure alarm Time delay for gas pressure lockout Range or value (0-200) ms (0 - 9999) (0.00-60.00) s (0.00-60.00) s (0.00-60.00) s Accuracy 0.5% 25 ms 0.5% 25 ms 0.5% 25 ms 0.5% 25 ms
Metering
Table 66. Pulse counter PCGGIO Function Cycle time for report of counter value Setting range (13600) s Accuracy -
Table 67. Function for energy calculation and demand handling ETPMMTR Function Energy metering Range or value MWh Export/Import, MVArh Export/Import Accuracy Input from MMXU. No extra error at steady load
ABB
77
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Station communication
Table 68. Communication protocol Function Protocol TCP/IP Communication speed for the IEDs Protocol Communication speed for the IEDs Protocol Communication speed for the IEDs Protocol, serial Communication speed for the IEDs Protocol, serial Communication speed for the IEDs Value Ethernet 100 Mbit/s IEC 6185081 100BASE-FX DNP3.0/TCP 100BASE-FX IEC 608705103 9600 or 19200 Bd DNP3.0 30019200 Bd
Hardware IED
Table 69. Degree of protection of rack-mounted IED Description Front side Rear side, connection terminals Table 70. Degree of protection of the LHMI Description Front and side Value IP40 Value IP 40 IP 20
Dimensions
Table 71. Dimensions of the IED - 3U full 19" rack Description Width Height Depth Weight box Weight LHMI Value 442 mm (17.40 inches) 132 mm (5.20 inches), 3U 249.5 mm (9.82 inches) 10 kg (<22.04 lbs) 1.3 kg (2.87 lbs)
78
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Inverse time characteristics
Table 72. ANSI Inverse time characteristics Function Operating characteristic: Range or value k = (0.05-999) in steps of 0.01 Accuracy -
t =
A P ( I - 1)
+ B k
EQUATION1249-SMALL V1 EN
I = Imeasured/Iset ANSI Extremely Inverse ANSI Very inverse ANSI Normal Inverse ANSI Moderately Inverse ANSI Long Time Extremely Inverse ANSI Long Time Very Inverse ANSI Long Time Inverse Table 73. IEC Inverse time characteristics Function Operating characteristic: Range or value k = (0.05-999) in steps of 0.01 Accuracy A=28.2, B=0.1217, P=2.0 A=19.61, B=0.491, P=2.0 A=0.0086, B=0.0185, P=0.02, tr=0.46 A=0.0515, B=0.1140, P=0.02 A=64.07, B=0.250, P=2.0 A=28.55, B=0.712, P=2.0 A=0.086, B=0.185, P=0.02
t =
A P k ( I - 1)
EQUATION1251-SMALL V1 EN
I = Imeasured/Iset IEC Normal Inverse IEC Very inverse IEC Inverse IEC Extremely inverse IEC Short time inverse IEC Long time inverse A=0.14, P=0.02 A=13.5, P=1.0 A=0.14, P=0.02 A=80.0, P=2.0 A=0.05, P=0.04 A=120, P=1.0
ABB
79
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Table 74. RI and RD type inverse time characteristics Function RI type inverse characteristic
1
Range or value k = (0.05-999) in steps of 0.01
Accuracy
t =
0.339 -
0.236 I
EQUATION1137-SMALL V1 EN
I = Imeasured/Iset RD type logarithmic inverse characteristic
t = 5.8 - 1.35 In
EQUATION1138-SMALL V1 EN
k = (0.05-999) in steps of 0.01
I k
I = Imeasured/Iset Table 75. Inverse time characteristics for overvoltage protection Function Type A curve:
t =
Range or value k = (0.05-1.10) in steps of 0.01
Accuracy 5% +60 ms
U -U >
U >
EQUATION1436-SMALL V1 EN
U> = Uset U = Umeasured Type B curve:
t =
k = (0.05-1.10) in steps of 0.01
k 480
32 U - U > - 0.5 U >
2.0
- 0.035
EQUATION1437-SMALL V1 EN
Type C curve:
t =
k = (0.05-1.10) in steps of 0.01
k 480
32 U - U > - 0.5 U >
3.0
- 0.035
EQUATION1438-SMALL V1 EN
80
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Table 76. Inverse time characteristics for undervoltage protection Function Type A curve: Range or value k = (0.05-1.10) in steps of 0.01 Accuracy 5% +60 ms
t =
U < -U
U<
EQUATION1431-SMALL V1 EN
U< = Uset U = UVmeasured Type B curve: k = (0.05-1.10) in steps of 0.01
t =
k 480
32 U < -U - 0.5 U <
2.0
+ 0.055
EQUATION1432-SMALL V1 EN
U< = Uset U = Umeasured Table 77. Inverse time characteristics for residual overvoltage protection Function Type A curve:
t =
Range or value k = (0.05-1.10) in steps of 0.01
Accuracy 5% +70 ms
U -U >
U >
EQUATION1436-SMALL V1 EN
U> = Uset U = Umeasured Type B curve:
t =
k = (0.05-1.10) in steps of 0.01
k 480
2.0
32 U - U > - 0.5 U >
- 0.035
EQUATION1437-SMALL V1 EN
Type C curve:
t =
k = (0.05-1.10) in steps of 0.01
k 480
3.0
32 U - U > - 0.5 U >
- 0.035
EQUATION1438-SMALL V1 EN
ABB
81
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
21. Ordering for Customized IED Guidelines
Carefully read and follow the set of rules to ensure problem-free order management. Be aware that certain functions can only be ordered in combination with other functions and that some functions require specific hardware selections.
Product specification
Basic IED 650 platform and common functions housed in 3U 1/1 sized 19 casing REG650 Quantity: 1MRK 006 526-AC
Option: Customer specific configuration On request
Connection type for Analog modules
Rule: One connection type must be selected
Compression terminals Ring lug terminals 1MRK 002 960-CA 1MRK 002 960-DA
Connection type for Power supply, Input/Output and communication modules
Rule: One connection type must be selected
Compression terminals Ring lug terminals 1MRK 002 960-EA 1MRK 002 960-FA
Power supply module
Rule: One Power supply module must be specified
Power supply module(PSM) 48-125 VDC 110-250 VDC, 100240V AC 1KHL178073R0001 1KHL178082R0001
Differential protection
Rule: One and only one of Transformer differential protection or Generator differential protection must be ordered
Transformer differential protection, three winding (T3WPDIF) Generator differential protection (GENPDIF) Qty: Qty: 1MRK 004 904-BB 1MRK 004 904-EA
Control
Rule: One and only one of Circuit breaker must be ordered
Circuit breaker for 1 CB (CBC1) Circuit breaker for 2 CB (CBC2) Qty: Qty: 1MRK 004 918-AA 1MRK 004 918-BA
82
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Logic
Rule: One Tripping logic must be ordered
Tripping logic, common 3phase output (SMPPTRC) Qty:
1 2 3 4 5 6
1MRK 004 922-AA
Optional functions Impedance protection
Underimpedance protection for generators and transformers (ZGCPDIS ) Loss of excitation (LEXPDIS) Out-of-step protection (OOSPPAM ) Load enchroachment (LEPDIS) Qty: Qty: Qty: Qty: 1MRK 004 906SA 1MRK 004 906-LA 1MRK 004 906-MA 1MRK 004 906-NA
Current protection
1 2
Four step phase overcurrent protection, 3phase output (OC4PTOC) Four step residual overcurrent protection, zero/negative sequence direction (EF4PTOC) Sensitive directional residual overcurrent and power protection (SDEPSDE) Thermal overload protection, two time constants (TRPTTR) Breaker failure protection, 3phase activation and output (CCRBRF) Pole discordance protection (CCRPLD) Directional underpower protection (GUPPDUP) Directional overpower protection (GOPPDUP) Accidental energizing protection for synchronous generator (AEGGAPC) Negative sequence time overcurrent protection for machines (NS2PTOC) Voltage-restrained time overcurrent protection (VR2PVOC)
Qty:
1MRK 004 908-BB
Qty: Qty:
1MRK 004 908-FA 1MRK 004 908-EA
Qty: Qty: Qty: Qty: Qty:
1MRK 004 908-KA 1MRK 004 908-LA 1MRK 004 908-NA 1MRK 004 908-RB
1MRK 004 908-SB
Qty: Qty: Qty:
1MRK 004 908-WA 1MRK 004 908-YA 1MRK 004 908-ZA
ABB
83
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Voltage protection
Two step undervoltage protection (UV2PTUV) Two step overvoltage protection (OV2PTOV) Two step residual overvoltage protection (ROV2PTOV) Overexcitation protection (OEXPVPH) 100% Stator earth faule protection, 3rd harmonic based (STEFPHIZ) Qty: Qty: Qty: Qty: Qty:
1 2
1MRK 004 910-AB 1MRK 004 910-BB 1MRK 004 910-CB 1MRK 004 910-DC 1MRK 004 910-FA
Frequency protection
1 2 3 4
Underfrequency protection (SAPTUF)
Qty:
1MRK 004 912-AA
Overfrequency protection (SAPTOF)
Qty:
1MRK 004 912-BA
Rate-of-change frequency protection (SAPFRC)
Qty:
1MRK 004 912-CA
Secondary system supervision
Fuse failure supervision (SDDRFUF) Qty: 1MRK 004 914-BA
Control
Synchrocheck, energizing check and synchronizing (SESRSYN) Qty: 1MRK 004 917-AC
Monitoring
Station battery supervision (SPVNZBAT) Insulation gas monitoring function (SSIMG) Qty: Qty:
1 2
1MRK 004 925-HB 1MRK 004 925-KA
Insulation liquid monitoring function (SSIML) Circuit breaker condition monitoring (SSCBR)
Qty: Qty:
1MRK 004 925-LA 1MRK 004 925-MA
First local HMI user dialogue language
HMI language, English IEC Always included
Additional local HMI user dialogue language
HMI language, English US 1MRK 002 940-MA
Optional hardware
84
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Human machine interface
Rule: One must be ordered.
Display type Local human machine interface (LHMI) Local human machine interface (LHMI) Keypad symbol IEC ANSI Case size 3U 1/1 19" 3U 1/1 19" 1KHL160055R0001 1KHL160042R0001
Analog system
Rule: One Transformer input module must be ordered
Transformer module (TRM) Transformer module (TRM) Transformer module (TRM) Transformer module (TRM) 6I+4U, 1/5A,100/220V 8I+2U, 1/5A, 100/220V 4I, 1/5A+1I, 0.1/0.5A+5U, 100/220V 4I+6U, 1/5A, 100/220V Qty: Qty: Qty: Qty: 1KHL178083R0001 1KHL178083R0013 1KHL178083R0016 1KHL178083R0003
Rule: Only one Analog input module can be ordered
Analog input module (AIM) Analog input module (AIM) 6I+4U, 1/5A, 100/220V 4I, 1/5A+1I, 0.1/0.5A+5U, 100/220V Qty: Qty: 1KHL178083R5001 1KHL178083R5016
Binary input/output modules
Note: If analog input module (AIM) is ordered only 2 BIO modules can be ordered
Binary input/output module (BIO) Qty:
1 2 3 4
1KHL178074R0001
Rack mounting kit
Rack mounting kit for 3U 1/1 x 19 case Quantity: 1KHL400352R0001
ABB
85
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
22. Ordering for Configured IED
Guidelines Carefully read and follow the set of rules to ensure problem-free order management. Please refer to the available functions table for included application functions. To obtain the complete ordering code, please combine code from the tables, as given in the example below. Exemple code: REG650*1.2-B01X00-X00-B1A5-B-A-SA-AB1-RA3B1-AX-E. Using the code of each position #1-11 specified as REG650*1-2 2-3-4 4-5-6-7 7-8 8-9 9 9-10 10 10 10-11 # REG650* 1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5 6 - 7 - 8 Position - 9 - 10 - 11 -
SOFTWARE Version number Version no Selection for position #1. Configuration alternatives Generator protection Generator-Transformer protection ACT configuration ABB standard configuration Selection for position #2. Software options No option Selection for postition #3 First HMI language English IEC Selection for position #4. Additional HMI language No second HMI language Selection for position #4. Casing Rack casing, 3U 1/1 x 19" Selection for position #5. B1 B1 #4 B01 B05
#1
Notes and Rules
1.2 1.2 Notes and Rules
#2
X00 X00 #3 X00 X00 Notes and Rules Notes and Rules
#4 X0 X0 #5 D D Notes and Rules
86
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Mounting details with IP40 of protection from the front No mounting kit included Rack mounting kit for 3U 1/1 x 19" Selection for position #6. Connection type for Power supply, Input/output and Communication modules Compression terminals Ringlug terminals Power supply S R
#6 X H
Notes and Rules
#7
Notes and Rules
100-240V AC, 110-250V DC, 9BO 48-125V DC, 9BO Selection for position #7. Human machine interface Local human machine interface, OL8000, IEC 3U 1/1 x 19", Basic Detached LHMI No detached mounting of LHMI Selection for position #8. Connection type for Analog modules Compression terminals Ringlug terminals Analog system Slot position: Transformer module, 4I, 1/5A+1I, 0.1/0.5A+5U, 100/220V Slot position: Analog input module, 6I + 4U, 1/5A, 100/220V Selection for position #9. Binary input/output module Slot position (rear view) Available slots in 1/1 case No board in slot Binary input/output module 9 BI, 3 NO Trip, 5 NO Signal, 1 CO Signal Selection for position #10. X A A p5 A3 p2 S R E #9 E #8
pPSM A B Notes and Rules X0 X0 Notes and Rules A3 p4 B1 B1 Notes and Rules #10 p6 X A AIM in p4 p5 basic, p6 optional
Slot position:
ABB
87
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Communication and processing module Slot position (rear view) 12BI, IRIG-B, RS485, Ethernet, LC optical, ST serial Selection for position #11.
#11 pCOM F F
Notes and Rules
88
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
23. Ordering for Accessories External resistor unit
High impedance resistor unit 1-ph with resistor and voltage dependent resistor for 20-100V operating voltage High impedance resistor unit 1-ph with resistor and voltage dependent resistor for 100-400V operating voltage Quantity: Quantity: RK795101-MA RK795101-CB
Configuration and monitoring tools
Front connection cable between LCD-HMI and PC Quantity: 1MRK 001 665-CA
LED Label special paper A4, 1 pc
Quantity:
1MRK 002 038-CA
LED Label special paper Letter, 1 pc
Quantity:
1MRK 002 038-DA
External interface units for Rotor earth fault protection
Injection unit for Rotor earth fault protection (RXTTE 4) Quantity: 1MRK 002 108-BA
Protective resistor on plate
Quantity:
RK795102-AD
Manuals
Note: One (1) IED Connect DVD containing user documentation Operation manual Technical manual Installation manual Commissioning manual Application manual Communication protocol manual, DNP3 Communication protocol manual, IEC61850-8-1 Communication protocol manual, IEC60870-5-103 Cyber security deployment guidelines Type test certificate Engineering manual Point list manual, DNP3 Connectivity packages and LED label template is always included for each IED
Rule: Specify additional quantity of IED Connect DVD requested
User documentation Quantity: 1MRK 003 500-AA
ABB
89
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Rule: Specify the number of printed manuals requested
Operation manual IEC Quantity: 1MRK 500 095-UEN
Technical manual
IEC
Quantity:
1MRK 502 043-UEN
Commissioning manual
IEC
Quantity:
1MRK 502 044-UEN
Application manual
IEC
Quantity:
1MRK 502 042-UEN
Communication protocol manual, DNP3
IEC
Quantity:
1MRK 511 257-UEN
Communication protocol manual, IEC 61850-8-1
IEC
Quantity:
1MRK 511 258-UEN
Communication protocol manual, IEC 60870-5-103
IEC
Quantity:
1MRK 511 259-UEN
Engineering manual
IEC
Quantity:
1MRK 511 261-UEN
Installation manual
IEC
Quantity:
1MRK 514 015-UEN
Point list manual, DNP3
IEC
Quantity:
1MRK 511 260-UEN
Cyber Security deployment guidelines
IEC
Quantity:
1MRK 511 268-UEN
Reference information
For our reference and statistics we would be pleased to be provided with the following application data: Country: Station name: End user: Voltage level: kV
90
ABB
Generator protection REG650 Product version: 1.2
1MRK 502 045-BEN -
Related documents
Documents related to REG650 Application manual Technical manual Commissioning manual Product Guide Type test certificate Rotor Earth Fault Protection with Injection Unit RXTTE4 and REG670 Application notes for Circuit Breaker Control 650 series manuals Communication protocol manual, DNP3 Communication protocol manual, IEC 6185081 Communication protocol manual, IEC 60870-5-103 Cyber Security deployment guidelines Point list manual, DNP3 Engineering manual Operation manual Installation manual Identity number 1MRK 502 042-UEN 1MRK 502 043-UEN 1MRK 502 044-UEN 1MRK 502 045-BEN 1MRK 502 045-TEN 1MRG001910 1MRG006806 Identity number 1MRK 511 257-UEN 1MRK 511 258-UEN 1MRK 511 259-UEN 1MRK 511 268-UEN 1MRK 511 260-UEN 1MRK 511 261-UEN 1MRK 500 095-UEN 1MRK 514 015-UEN
ABB
91
92
Contact us
ABB AB Substation Automation Products SE-721 59 Vsters, Sweden Phone +46 (0) 21 32 50 00 Fax +46 (0) 21 14 69 18 www.abb.com/substationautomation
1MRK 502 045-BEN - Copyright 2012 ABB. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- 1MRK502031-BEN A en Product Guide REG670 1.2 CustomizedDocument128 pages1MRK502031-BEN A en Product Guide REG670 1.2 CustomizedmarganoNo ratings yet
- Transformer Protection RET650: Product GuideDocument80 pagesTransformer Protection RET650: Product GuideShahir IbrahimiNo ratings yet
- Generator Protection REG650: Product GuideDocument72 pagesGenerator Protection REG650: Product GuideMuhammad NadirNo ratings yet
- 502036-BUS - PG G650A 1p1Document93 pages502036-BUS - PG G650A 1p1Hai PhamNo ratings yet
- ABB RET 670 Product GuideDocument107 pagesABB RET 670 Product Guiderazvan_nNo ratings yet
- 1MRK504141-BEN A en Product Guide Transformer Protection RET670 2.0Document125 pages1MRK504141-BEN A en Product Guide Transformer Protection RET670 2.0Insan AzizNo ratings yet
- 1MRK502031-BUS D en Product Guide REG670 1.2 ANSI Customized-1Document108 pages1MRK502031-BUS D en Product Guide REG670 1.2 ANSI Customized-1Ardi UtamaNo ratings yet
- Hitachi Product OverviewDocument10 pagesHitachi Product Overviewlinhcdt3No ratings yet
- 1MRK511289-BEN A en Product Guide Bay Control REC650 1.3 IECDocument66 pages1MRK511289-BEN A en Product Guide Bay Control REC650 1.3 IECInsan AzizNo ratings yet
- 1MRK502031-BEN D en Product Guide REG670 1.2 CustomizedDocument111 pages1MRK502031-BEN D en Product Guide REG670 1.2 CustomizedSanthosh Reddy BNo ratings yet
- SIP5 APN 002 Breaker and A Half Solutions enDocument11 pagesSIP5 APN 002 Breaker and A Half Solutions enanand.balaNo ratings yet
- 502036-BEN - PG G650I 1p1Document83 pages502036-BEN - PG G650I 1p1Hai PhamNo ratings yet
- Ice3b0565 PDFDocument30 pagesIce3b0565 PDFimperadoreletronNo ratings yet
- 1mrk505228-Ben A en Product Guide Red670 1.2 Pre-ConfiguredDocument116 pages1mrk505228-Ben A en Product Guide Red670 1.2 Pre-Configuredinsan_soft6498No ratings yet
- Generator Protection REG670 Pre-Configured: Product GuideDocument107 pagesGenerator Protection REG670 Pre-Configured: Product GuideTesla EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Lmc555 Cmos TimerDocument25 pagesLmc555 Cmos TimerCataNo ratings yet
- ESDR4Document4 pagesESDR4Eddy Skb0% (1)
- 1MRK502068-BEN F en Product Guide Generator Protection REG670 2.1Document140 pages1MRK502068-BEN F en Product Guide Generator Protection REG670 2.1Alexandre MorenoNo ratings yet
- Moog ServoDrives DS2000 Manual enDocument142 pagesMoog ServoDrives DS2000 Manual enBojan MarkovićNo ratings yet
- Power System LaboratoryDocument20 pagesPower System LaboratoryBahadır Akbal100% (1)
- 1MRK504161-BEN A en Product Guide Transformer Protection RET650 2.1Document68 pages1MRK504161-BEN A en Product Guide Transformer Protection RET650 2.1osmpotNo ratings yet
- 7UM62 Catalog SIP E7 PDFDocument36 pages7UM62 Catalog SIP E7 PDFu_ulloaNo ratings yet
- REL650Document79 pagesREL650denisseNo ratings yet
- SPAD346CDocument36 pagesSPAD346CKo PaukNo ratings yet
- 1MRK504172-BEN - en Product Guide Transformer Protection RET650 Version 2.2Document80 pages1MRK504172-BEN - en Product Guide Transformer Protection RET650 Version 2.2Pavel DobiasNo ratings yet
- Bien Tan Fr-d700 CatalogDocument33 pagesBien Tan Fr-d700 CatalogNguyen DinhNo ratings yet
- DRV10866 5-V, 3-Phase, Sensorless BLDC Motor Driver: 1 Features 3 DescriptionDocument23 pagesDRV10866 5-V, 3-Phase, Sensorless BLDC Motor Driver: 1 Features 3 DescriptionSitt Nyein SoeNo ratings yet
- SIPROTEC Compact 7SK Motor Protection RelayDocument36 pagesSIPROTEC Compact 7SK Motor Protection RelayphkhatriNo ratings yet
- CSC-326 Transformer Protection IED Product Guide - V1.10Document75 pagesCSC-326 Transformer Protection IED Product Guide - V1.10Jaka Sembung GolokNo ratings yet
- 77 Catalog Convertizoare de Frecventa Frenic EcoDocument32 pages77 Catalog Convertizoare de Frecventa Frenic EcoMircea MiNo ratings yet
- EatonDocument89 pagesEatonhernangycNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi D700 Series VFD BrochureDocument33 pagesMitsubishi D700 Series VFD BrochureMROstop.com100% (1)
- Transformer Protection RET650: Product GuideDocument72 pagesTransformer Protection RET650: Product Guidehaichau199No ratings yet
- 1MRK504117-BEN B en Product Guide RET670 1.2 CustomizedDocument125 pages1MRK504117-BEN B en Product Guide RET670 1.2 Customizedyesfriend28No ratings yet
- Transistor Inverter: You Thought They Were All The SameDocument2 pagesTransistor Inverter: You Thought They Were All The SameMaitry ShahNo ratings yet
- 1MRK505265-BEN - en Product Guide Busbar Protection REB650 IECDocument61 pages1MRK505265-BEN - en Product Guide Busbar Protection REB650 IECRobert RocafuerteNo ratings yet
- 1mrk505265-Ben - en Product Guide Busbar Protection Reb650 Iec PDFDocument61 pages1mrk505265-Ben - en Product Guide Busbar Protection Reb650 Iec PDFaashish bissaNo ratings yet
- 7SK80xx Catalog SIP-2008 A3 enDocument36 pages7SK80xx Catalog SIP-2008 A3 enalainNo ratings yet
- Rel670 ManualDocument99 pagesRel670 ManualBelinda WagnerNo ratings yet
- 5-Channel Integrated Power Solution With Quad Buck Regulators and 200 Ma LDO RegulatorDocument40 pages5-Channel Integrated Power Solution With Quad Buck Regulators and 200 Ma LDO RegulatorMichael LeeNo ratings yet
- R448 Manual From Mac Far Lane GeneratorsDocument14 pagesR448 Manual From Mac Far Lane Generatorstocanh1990No ratings yet
- 7SJ80 Pages From SIPROTEC Compact Protection Systems A1 enDocument26 pages7SJ80 Pages From SIPROTEC Compact Protection Systems A1 enAchint KumarNo ratings yet
- Alternator Maintenance ManualDocument24 pagesAlternator Maintenance ManualRashmi Singh100% (3)
- ABB - Generator Protections GuideDocument45 pagesABB - Generator Protections GuideAyesha ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorFrom Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Offshore Wind Energy Generation: Control, Protection, and Integration to Electrical SystemsFrom EverandOffshore Wind Energy Generation: Control, Protection, and Integration to Electrical SystemsNo ratings yet
- 8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionFrom Everand8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- Build Your Own Low-Power Transmitters: Projects for the Electronics ExperimenterFrom EverandBuild Your Own Low-Power Transmitters: Projects for the Electronics ExperimenterRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The IGBT Device: Physics, Design and Applications of the Insulated Gate Bipolar TransistorFrom EverandThe IGBT Device: Physics, Design and Applications of the Insulated Gate Bipolar TransistorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Protection of Substation Critical Equipment Against Intentional Electromagnetic ThreatsFrom EverandProtection of Substation Critical Equipment Against Intentional Electromagnetic ThreatsNo ratings yet
- RI renewable energy study finds installation quality issuesDocument61 pagesRI renewable energy study finds installation quality issuesthomaswangkoroNo ratings yet
- FCR - Integration MP#1 - MP#2 PDFDocument4 pagesFCR - Integration MP#1 - MP#2 PDFthomaswangkoroNo ratings yet
- MV Protection RetrofitDocument8 pagesMV Protection RetrofitthomaswangkoroNo ratings yet
- Bossard CatalogueDocument150 pagesBossard CataloguethomaswangkoroNo ratings yet
- Financial EbookDocument13 pagesFinancial EbookthomaswangkoroNo ratings yet
- LS Inverter Series PDFDocument16 pagesLS Inverter Series PDFQuang Chánh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Multi-Mode Optical FiberDocument24 pagesMulti-Mode Optical FiberthomaswangkoroNo ratings yet
- VMA, Density, and Air Voids in HMA Mix DesignDocument37 pagesVMA, Density, and Air Voids in HMA Mix DesignGerardo Andres Argote ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Branch Listing PDFDocument5 pagesBranch Listing PDFthomaswangkoroNo ratings yet
- SPAU140C Synch Check RelayDocument72 pagesSPAU140C Synch Check RelaymentongNo ratings yet
- HRC Fuses LSISDocument12 pagesHRC Fuses LSISthomaswangkoroNo ratings yet
- SecoGear Cat Final2Document22 pagesSecoGear Cat Final2Eulalio HortaNo ratings yet
- Motor Control CenterDocument8 pagesMotor Control CenterthomaswangkoroNo ratings yet
- HRC Fuses LSISDocument12 pagesHRC Fuses LSISthomaswangkoroNo ratings yet
- 1MRK513003-BEN C en Connection and Installation Components COMBIFLEXDocument30 pages1MRK513003-BEN C en Connection and Installation Components COMBIFLEXthomaswangkoroNo ratings yet
- 1MRK502046-SEN en Generator Protection REG670 650Document10 pages1MRK502046-SEN en Generator Protection REG670 650thomaswangkoroNo ratings yet
- Datasheet G RelaysDocument10 pagesDatasheet G RelaysthomaswangkoroNo ratings yet
- SM6 Catalogo 2011Document120 pagesSM6 Catalogo 2011thomaswangkoroNo ratings yet
- ABB PFC ControlerDocument6 pagesABB PFC ControlermajzdorNo ratings yet
- Formula MCCBDocument104 pagesFormula MCCBthomaswangkoro100% (1)
- LZQJ ManualDocument54 pagesLZQJ Manualthomaswangkoro100% (3)
- NIST Guide To Supervisory and Data Acquisition-SCADA and Industrial Control Systems Security (2007)Document164 pagesNIST Guide To Supervisory and Data Acquisition-SCADA and Industrial Control Systems Security (2007)thomaswangkoroNo ratings yet
- Relay Selection Guide A1 enDocument28 pagesRelay Selection Guide A1 ensatieaplNo ratings yet
- Variomod BrochureDocument2 pagesVariomod BrochurethomaswangkoroNo ratings yet
- Electric Drives and Control LabDocument6 pagesElectric Drives and Control LabParul ChandnaNo ratings yet
- Smart Dustbin System Using IotDocument48 pagesSmart Dustbin System Using Iotsamruddhi100% (1)
- 20KW 96v Front & Rear Drive EV Project ReportDocument6 pages20KW 96v Front & Rear Drive EV Project ReportPutera AlviraNo ratings yet
- Ultra Fast Avalanche Sinterglass Diode Specifications and Data SheetDocument7 pagesUltra Fast Avalanche Sinterglass Diode Specifications and Data SheetRey TiburonNo ratings yet
- 3 Axis TB6560 3.5A Stepper Motor Driver Board Manual PDFDocument10 pages3 Axis TB6560 3.5A Stepper Motor Driver Board Manual PDFNisar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Arc Model PDFDocument67 pagesArc Model PDFdankorankoNo ratings yet
- lg55ld520 SM PDFDocument71 pageslg55ld520 SM PDFDan Prewitt100% (1)
- Sharp Lc-C3242u Supp PDFDocument6 pagesSharp Lc-C3242u Supp PDFHugo Cortés0% (1)
- 1vcp000931 Rev e CA DcbreakDocument26 pages1vcp000931 Rev e CA DcbreakMouth GoonieNo ratings yet
- Diode IntroDocument34 pagesDiode IntroSachin AroraNo ratings yet
- Frenic-Ehvac (F2e) User - S ManualDocument631 pagesFrenic-Ehvac (F2e) User - S ManualkarunNo ratings yet
- FMG31R Thru FMG36R: PB Free Plating ProductDocument3 pagesFMG31R Thru FMG36R: PB Free Plating ProductTspi RitzelNo ratings yet
- Sony dsr-pdx10 Ver-1.8 SMDocument526 pagesSony dsr-pdx10 Ver-1.8 SMSaulvcr64 PorleyNo ratings yet
- High-Voltage Compact Switchgear 3AP1 DTC For 145 KV and 245 KVDocument8 pagesHigh-Voltage Compact Switchgear 3AP1 DTC For 145 KV and 245 KVJunaid LankerNo ratings yet
- The Hubbard Energy Transformer by Gaston BurridgeDocument6 pagesThe Hubbard Energy Transformer by Gaston BurridgepboserupNo ratings yet
- Cavity Magnetron OscillatorDocument3 pagesCavity Magnetron OscillatorsuriyaNo ratings yet
- Markon Generator ManualDocument52 pagesMarkon Generator ManualMd Rodi Bidin67% (3)
- Zener Diode CharaDocument12 pagesZener Diode Charaaleena s lNo ratings yet
- Om On280Document38 pagesOm On280yonasNo ratings yet
- KZN Physical Science Grade 11 Scope 2023Document6 pagesKZN Physical Science Grade 11 Scope 2023fiercestallionofficialNo ratings yet
- Practice 12 Dynamic Logic 2011 12 ADocument5 pagesPractice 12 Dynamic Logic 2011 12 AKamleshNo ratings yet
- Multimeter Tutorial V1.2Document70 pagesMultimeter Tutorial V1.2EDUARDO ALCANTARA JR100% (4)
- Electrical System Design GuidelinesDocument125 pagesElectrical System Design Guidelinescarlosmarciosfreitas100% (1)
- Converting Watts & Amps To 12V Run TimesDocument2 pagesConverting Watts & Amps To 12V Run TimesWaqar AhmedNo ratings yet
- HVAC Start-Up Checklist EssentialsDocument3 pagesHVAC Start-Up Checklist EssentialsNorman CanlasNo ratings yet
- Entrelec 05Document56 pagesEntrelec 05baurzhan.kunkuzhayevNo ratings yet
- Solar Turbines Taurus 65 Data SheetDocument2 pagesSolar Turbines Taurus 65 Data SheetLuis SanguinettiNo ratings yet
- Resin-Impregnated Paper (RIP) Condenser Transformer BushingDocument6 pagesResin-Impregnated Paper (RIP) Condenser Transformer BushingDHANASEKARAN NNo ratings yet
- Smart-UPS SMC2000IDocument3 pagesSmart-UPS SMC2000IMothafukin MorrisseyNo ratings yet
- TSPL - Generator - Protecction.Document8 pagesTSPL - Generator - Protecction.Amaresh NayakNo ratings yet