Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The 'Zero' Conditional
Uploaded by
Montse Álamo MoyaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The 'Zero' Conditional
Uploaded by
Montse Álamo MoyaCopyright:
Available Formats
'IF' SENTENCES AND THE 'UNREAL' PAST In this section you will find information on sentences containing the
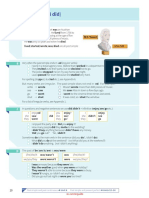
word 'if', the use of conditional tenses, and the 'unreal past', that is, when we use a past tense but we are not actually referring to past time. IF AND THE CONDITIONAL There are four main types of 'if' sentences in English: 1. The 'zero' conditional, where the tense in both parts of the sentence is the simple present: 'IF' CLAUSE If + simple present If you heat ice If it rains MAIN CLAUSE simple present it melts. you get wet
In these sentences, the time is now or always and the situation is real and possible. They are often used to refer to general truths. 2. The Type 1 conditional, where the tense in the 'if clause is the simple present, and the tense in the main clause is the simple future 'IF' CLAUSE If + simple present If it rains If you don't hurry MAIN CLAUSE Simple future you will get wet we will miss the train.
In these sentences, the time is the present or future and the situation is real. They refer to a possible condition and its probable result. 3. The Type 2 conditional, where the tense in the 'if' clause is the simple past, and the tense in the main clause is the present conditional: 'IF' CLAUSE If + simple past If it rained If you went to bed earlier MAIN CLAUSE Present conditional you would get wet you wouldn't be so tired.
In these sentences, the time is now or any time, and the situation is unreal. They are not based on fact, and they refer to an unlikely or hypothetical condition and its probable result. 4. The Type 3 conditional, where the tense in the 'if' clause is the past perfect, and the tense in the main clause is the perfect conditional: 'IF' CLAUSE If + past perfect If it had rained If you had worked harder MAIN CLAUSE Perfect conditional you would have got wet you would have passed the exam.
In these sentences, the time is past, and the situation is contrary to reality. The facts they are based on are the opposite of what is expressed, and they refer to an unreal past condition and its probable past result.
A further type if 'if' sentence exists, where Type 2 and Type 3 are mixed. The tense in the 'if' clause is the past perfect, and the tense in the main clause is the present conditional: 'IF' CLAUSE If + past perfect If I had worked harder at school If we had looked at the map MAIN CLAUSE Present conditional I would have a better job now. we wouldn't be lost.
In these sentences, the time is past in the 'if' clause, and present in the main clause. They refer to an unreal past condition and its probable result in the present.
You might also like
- IF SENTENCES AND THE UNREAL PASTDocument2 pagesIF SENTENCES AND THE UNREAL PASTedu_ejeaNo ratings yet
- The 'Zero' Conditional: 1. FormDocument14 pagesThe 'Zero' Conditional: 1. Formhima67No ratings yet
- Learn the 5 Types of Conditional SentencesDocument2 pagesLearn the 5 Types of Conditional SentencesKahnMéndezNo ratings yet
- IF - Conditional SentencesDocument4 pagesIF - Conditional SentencesChirine AyoubNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument4 pagesEnglishapi-278092100No ratings yet
- G5+8 - Ms. Amara - Conditional SentencesDocument10 pagesG5+8 - Ms. Amara - Conditional SentencesHadjab LyesNo ratings yet
- Conditionalsclass MethodDocument11 pagesConditionalsclass MethodAlejandro J Oquendo MNo ratings yet
- Aptis DocumentsDocument31 pagesAptis DocumentsElenaNo ratings yet
- СONDITIONALS AND WISHESDocument9 pagesСONDITIONALS AND WISHESНастя ШепелеваNo ratings yet
- Conditional If Type 0, 1 & 2Document3 pagesConditional If Type 0, 1 & 2obengNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences TheoryDocument2 pagesConditional Sentences TheorymariecbaNo ratings yet
- Learn about the 3 types of conditional sentencesDocument3 pagesLearn about the 3 types of conditional sentencesDian daniNo ratings yet
- Conditionals ExplainedDocument2 pagesConditionals ExplainedFlorencia Custo BlanchNo ratings yet
- coditionnalsDocument1 pagecoditionnalsfaridahalh20No ratings yet
- Kel. 11 Conditonal SentenceDocument15 pagesKel. 11 Conditonal SentenceNu FaNo ratings yet
- ConditionalDocument3 pagesConditionalSalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Voice, Conditional Sentence & Reported SpeechDocument22 pagesActive and Passive Voice, Conditional Sentence & Reported SpeechTrịnh Quốc HiếuNo ratings yet
- Tên đề tài:: Trường Đại Học Hải Phòng Khoa Ngoại NgữDocument13 pagesTên đề tài:: Trường Đại Học Hải Phòng Khoa Ngoại Ngữmicheal longdikNo ratings yet
- Conditionals: Learn types and uses in argumentsDocument7 pagesConditionals: Learn types and uses in argumentsRoxan Pascua GanadoNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument6 pagesConditional SentencesRachit VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Type 2 Conditional: If + Simple Present Simple FutureDocument7 pagesType 2 Conditional: If + Simple Present Simple FutureJohn PalutlaNo ratings yet
- If Conditional, Noun Phrase, and Relative PronounsDocument15 pagesIf Conditional, Noun Phrase, and Relative PronounsRisa Nanda Yusar100% (2)
- Conditional Sentence Type Usage If Clause Verb Tense Main Clause Verb TenseDocument4 pagesConditional Sentence Type Usage If Clause Verb Tense Main Clause Verb TenseStancu AlinNo ratings yet
- Conditionals SpeechDocument10 pagesConditionals SpeechАнастасия БелокобыльскаяNo ratings yet
- S6 ConditionalsDocument20 pagesS6 ConditionalsPedro FERREIRANo ratings yet
- Ingles Técnico Empresarial Con Énfasis en Negocios: Mauricio JohnstonDocument5 pagesIngles Técnico Empresarial Con Énfasis en Negocios: Mauricio JohnstonAndres OnfireNo ratings yet
- "The Unreal Past": ConditionalsDocument3 pages"The Unreal Past": ConditionalsLuisa Fernanda Orozco LópezNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument4 pagesConditionalspmpl2009No ratings yet
- Eng 2 Live Session 9Document8 pagesEng 2 Live Session 9carlos reynaNo ratings yet
- The Zero ConditionalDocument5 pagesThe Zero ConditionalEduard Hernan Cardona VillamilNo ratings yet
- First Conditional Sentences ExplainedDocument2 pagesFirst Conditional Sentences ExplainedRomina BravoNo ratings yet
- Name:Hosea Roinaldo Class:XII MIPA 2/19 Conditional SentencesDocument4 pagesName:Hosea Roinaldo Class:XII MIPA 2/19 Conditional SentenceshosearoinaldoNo ratings yet
- Form and Meaning: Zero ConditionalDocument2 pagesForm and Meaning: Zero ConditionalHampnie HambertNo ratings yet
- Conditional Theory N Exercise For Class PDFDocument15 pagesConditional Theory N Exercise For Class PDFUmu NeroNo ratings yet
- IF-SENTENCES: ZERO TO THIRD CONDITIONALSDocument7 pagesIF-SENTENCES: ZERO TO THIRD CONDITIONALSarmindoNo ratings yet
- Amanda. T Xii A 2: ConditionalDocument4 pagesAmanda. T Xii A 2: ConditionalGeraldine SitanggangNo ratings yet
- First Conditional: Dina Elizabeth Cortez CossDocument6 pagesFirst Conditional: Dina Elizabeth Cortez CossMonse TrujilloNo ratings yet
- Conditionals Guide: If Clauses and TypesDocument4 pagesConditionals Guide: If Clauses and TypesAhmed RubelNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument6 pagesConditional Sentencesmigue714100% (1)
- MaribelDocument24 pagesMaribelmdiazb01No ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument13 pagesConditional SentencesDiana DandiNo ratings yet
- CONDITIONAL SENTENCES EXPLAINEDDocument3 pagesCONDITIONAL SENTENCES EXPLAINEDMaría Martínez EstebanNo ratings yet
- If + Present Simple, + Present SimpleDocument3 pagesIf + Present Simple, + Present SimpleokecaloNo ratings yet
- Summary 1 Topic: Review Conditional Zero, First and Second: General ExplanationDocument6 pagesSummary 1 Topic: Review Conditional Zero, First and Second: General ExplanationJaime G. MendozaNo ratings yet
- MaturskiDocument14 pagesMaturskiОгњен ШиљеговићNo ratings yet
- Osorio WorkDocument10 pagesOsorio WorkBeres SangeNo ratings yet
- 1st and Zero - ConditionalsDocument3 pages1st and Zero - ConditionalsDarkCreeper13No ratings yet
- If clause determines main clause outcomeDocument95 pagesIf clause determines main clause outcomemmmmmNo ratings yet
- Understanding Conditional SentencesDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Conditional SentencesNhật ChungNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences Modul 8Document3 pagesConditional Sentences Modul 8aben djamien prodoNo ratings yet
- English 9 Q1 WK2Document113 pagesEnglish 9 Q1 WK2Precious Kim AmancaNo ratings yet
- Conditional: Group: - Irene - Lie An - Ivan - Marvin - Jason - Marcella - Joe - MariaDocument10 pagesConditional: Group: - Irene - Lie An - Ivan - Marvin - Jason - Marcella - Joe - MariaMarvin WijayaNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument2 pagesConditional SentenceFitri HanidaNo ratings yet
- Mixed ConditionalsDocument3 pagesMixed ConditionalsRodriguez Banda Guillermo A0% (1)
- ConditionalsDocument2 pagesConditionalsyolandagarciamorenoNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument14 pagesConditional SentencesShabira NadaNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument7 pagesConditional SentenceAbhieey Choi Soo Hyun100% (1)
- Conditianal - If ClausesDocument15 pagesConditianal - If ClausesJbour LaithNo ratings yet
- Use of English XMAS HOMEWORKDocument3 pagesUse of English XMAS HOMEWORKMontse Álamo MoyaNo ratings yet
- Readings Present Perfect 2Document1 pageReadings Present Perfect 2Montse Álamo MoyaNo ratings yet
- Correct Verb FormsDocument2 pagesCorrect Verb FormsanushhhkaNo ratings yet
- Oraciones InglésDocument2 pagesOraciones InglésMontse Álamo MoyaNo ratings yet
- Reading 2ESO SeptemberDocument1 pageReading 2ESO SeptemberMontse Álamo MoyaNo ratings yet
- Tense Rephrasing 3Document2 pagesTense Rephrasing 3Angeles Arjona Serrano100% (1)
- Writing 1º EsoDocument1 pageWriting 1º EsoMontse Álamo MoyaNo ratings yet
- Writing 1º EsoDocument1 pageWriting 1º EsoMontse Álamo MoyaNo ratings yet
- EXERCISE RelativesDocument1 pageEXERCISE RelativesMontse Álamo MoyaNo ratings yet
- Correct Verb FormsDocument2 pagesCorrect Verb FormsanushhhkaNo ratings yet
- An Informal Email To A Friend 4º EsoDocument2 pagesAn Informal Email To A Friend 4º EsoMontse Álamo MoyaNo ratings yet
- Writing 1º EsoDocument1 pageWriting 1º EsoMontse Álamo MoyaNo ratings yet
- Oraciones InglésDocument2 pagesOraciones InglésMontse Álamo MoyaNo ratings yet
- Writing-1º EsoDocument1 pageWriting-1º EsoMontse Álamo MoyaNo ratings yet
- Relative ClausesDocument11 pagesRelative ClausesSteve Cali100% (1)
- Writing-1º EsoDocument1 pageWriting-1º EsoMontse Álamo MoyaNo ratings yet
- Prepositions and MoreDocument11 pagesPrepositions and MoreMontse Álamo MoyaNo ratings yet
- Writing 1º EsoDocument1 pageWriting 1º EsoMontse Álamo MoyaNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1Montse Álamo MoyaNo ratings yet
- Word Formation - Noun and Adjective Suffixes PDFDocument6 pagesWord Formation - Noun and Adjective Suffixes PDFMontse Álamo MoyaNo ratings yet
- 3 ExercicesDocument3 pages3 Exercicesisabelle gorgeuNo ratings yet
- Writing-1º EsoDocument1 pageWriting-1º EsoMontse Álamo MoyaNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 Subj Obj QuestionsDocument2 pagesActivity 2 Subj Obj QuestionsYolanda CondoriNo ratings yet
- Writing-1º EsoDocument1 pageWriting-1º EsoMontse Álamo MoyaNo ratings yet
- Modal SentencesDocument2 pagesModal SentencesMontse Álamo MoyaNo ratings yet
- G - Supplemental - Relative ClausesDocument10 pagesG - Supplemental - Relative ClausesKen Hung Wing KitNo ratings yet
- Word Formation - Noun and Adjective SuffixesDocument6 pagesWord Formation - Noun and Adjective SuffixesMontse Álamo MoyaNo ratings yet
- Past Simple-Past ContinuousDocument4 pagesPast Simple-Past ContinuousAnonymous TswlBzNo ratings yet
- Examen de InglésDocument2 pagesExamen de InglésMontse Álamo MoyaNo ratings yet
- How To Write...Document5 pagesHow To Write...Montse Álamo MoyaNo ratings yet
- LND EngDocument3 pagesLND EngNasir AbbasNo ratings yet
- The Passive Voice WorksheetsDocument7 pagesThe Passive Voice WorksheetsAzra IlyasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 01 - Errors With Countable and Uncountable Nouns PDFDocument6 pagesLesson 01 - Errors With Countable and Uncountable Nouns PDFRao ShahgeerNo ratings yet
- English For Civil Engineering Students (ESP Module)Document16 pagesEnglish For Civil Engineering Students (ESP Module)joyce100% (1)
- Compact Keys For School Student BookDocument127 pagesCompact Keys For School Student BookTHUNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 10 PronounsDocument19 pagesKelompok 10 PronounssariNo ratings yet
- Writing 3 Long Functional TextDocument14 pagesWriting 3 Long Functional TextSumut RekNo ratings yet
- Material Curso British CouncilDocument13 pagesMaterial Curso British CouncilAbel AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Verb Patterns: Verb + Infinitive or Verb + - Ing ? - English Grammar Today - Cambridge DictionaryDocument12 pagesVerb Patterns: Verb + Infinitive or Verb + - Ing ? - English Grammar Today - Cambridge DictionaryPato HerediaNo ratings yet
- REVIEW UNITS 1-10 BACCALAUREATE YEARDocument30 pagesREVIEW UNITS 1-10 BACCALAUREATE YEARsaid sibouihNo ratings yet
- Latest News in BriefDocument14 pagesLatest News in Brieffikri akbarNo ratings yet
- Outlook and BehaviorDocument12 pagesOutlook and BehaviorMAYENo ratings yet
- Auxilary VerbsDocument13 pagesAuxilary Verbsakmal sajaNo ratings yet
- (Mouton Grammar Library 37) Knut J. Olawsky - A Grammar of Urarina-Mouton de Gruyter (2006)Document964 pages(Mouton Grammar Library 37) Knut J. Olawsky - A Grammar of Urarina-Mouton de Gruyter (2006)ST100% (1)
- El Verbo "GustarDocument16 pagesEl Verbo "GustarMallory CaudleNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous Tense for Actions Happening NowDocument6 pagesPresent Continuous Tense for Actions Happening NowAri WahyuNo ratings yet
- Grammar, Punctuation and Spelling Mark Schemes: English TestsDocument24 pagesGrammar, Punctuation and Spelling Mark Schemes: English TestsSahar SayedNo ratings yet
- If we come to the party, you will have funDocument3 pagesIf we come to the party, you will have funEva NazarenkoNo ratings yet
- Diagonistic Oxford - Practice - Grammar - Bas1Document5 pagesDiagonistic Oxford - Practice - Grammar - Bas1Dipendra SilwalNo ratings yet
- WorksheetWorks Possessive Noun Phrases 1Document2 pagesWorksheetWorks Possessive Noun Phrases 1kaitlynngeeNo ratings yet
- Past Simple (I Did) : Past Simple and Past Continuous Unit 6 Past Simple and Present Perfect Units 12-14Document1 pagePast Simple (I Did) : Past Simple and Past Continuous Unit 6 Past Simple and Present Perfect Units 12-14Chan Myae KoNo ratings yet
- GCSE French Verbs GuideDocument13 pagesGCSE French Verbs GuidePJ0% (1)
- Describing Graphs - Prepositions - Great!!!Document2 pagesDescribing Graphs - Prepositions - Great!!!Miodrag UroševićNo ratings yet
- The Development of Speech ProductionDocument24 pagesThe Development of Speech ProductionNadia TurRahmiNo ratings yet
- HAKISANDocument11 pagesHAKISANnairaNo ratings yet
- Inglês 10ano Reported Speech Exerc 20121129Document6 pagesInglês 10ano Reported Speech Exerc 20121129MeninaDuMarNo ratings yet
- Prepositions in On 00 Be LD RichDocument98 pagesPrepositions in On 00 Be LD RichKristina LaovaNo ratings yet
- Intensifiers Too Much, Too Many, EnoughDocument3 pagesIntensifiers Too Much, Too Many, EnoughRobert SalgadoNo ratings yet
- The Aims and Objectives of PETDocument8 pagesThe Aims and Objectives of PETa_tomsa100% (1)
- NominalisationsDocument11 pagesNominalisationsKevin NguyenNo ratings yet