Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CCNA3 Lab 5 5 3 ANSWERS
Uploaded by
Maher ChtourouOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CCNA3 Lab 5 5 3 ANSWERS
Uploaded by
Maher ChtourouCopyright:
Available Formats
PT Activity 5.5.
3: Troubleshooting Spanning Tree Protocol (Instructor Version)
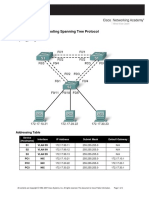
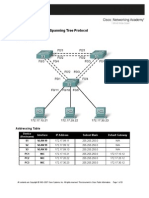
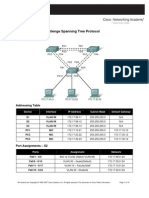
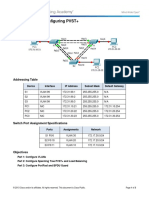
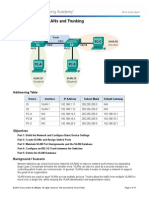
Topology Diagram
Addressing Table
Device S1 S2 S3 PC1 PC2 PC3 Interface VLAN 99 VLAN 99 VLAN 99 NIC NIC NIC IP Address 172.17.99.11 172.17.99.12 172.17.99.13 172.17.10.21 172.17.20.22 172.17.30.23 Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0 Default Gateway N/A N/A N/A 172.17.10.1 172.17.20.1 172.17.30.1
Port Assignments S2
Ports Fa0/1 - 0/5 Fa0/6 - 0/10 Fa0/11 - 0/17 Fa0/18 - 0/24 Assignment 802.1q Trunks (Native VLAN 99) VLAN 30 Guests(Default) VLAN 10 Faculty/Staff VLAN 20 - Students Network 172.17.99.0 /24 172.17.30.0 /24 172.17.10.0 /24 172.17.20.0 /24
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 1 of 2
CCNA Exploration LAN Switching and Wireless: STP
PT Activity 5.5.3: Troubleshooting Spanning Tree Protocol
Learning Objectives
Identify the initial state of all trunks Correct the source of the problem Document the switch configuration
Scenario
You are responsible for the operation of the redundant switched LAN shown in the topology diagram. You and your users have been observing increased latency during peak usage times, and your analysis points to congested trunks. You recognize that of the six trunks configured, only two are forwarding packets in the default STP configuration currently running. The solution to this problem requires more effective use of the available trunks. This activity is complete when all wired trunks are carrying traffic, and all three switches are participating in per-VLAN load balancing for the three user VLANs.
Task 1: Identify the Initial State of All Trunks
On each of the switches, display the spanning tree table with the show spanning-tree command. Note which ports are forwarding on each switch, and identify which trunks are not being used in the default configuration. You can use your network topology drawing to document the initial state of all trunk ports.
Task 2: Correct the Source of the Problem
Modify the spanning tree configuration so that all three trunks are in use. Assume that the three user LANs (10, 20, and 30) carry an equal amount of traffic. Aim for a solution that will have a different set of ports forwarding for each of the three user VLANs. In order for the activity to be correctly graded, you must meet the following guidelines: S1 is root for VLAN 10 (priority 4096) and backup root for VLAN 20 (priority 16384) S2 is root for VLAN 20 (priority 4096) and backup root for VLAN 30 (priority 16384) S3 is root for VLAN 30 (priority 4096) and backup root for VLAN 10 (priority 16384)
Task 3: Document the Switch Configuration
When you have completed your solution, capture the output of the show run command and save it to a text file for each switch.
Solution
There are a number of different ways that load balancing can be accomplished. One of the most direct is the following: S1(config)#spanning-tree vlan 10 priority 4096 S1(config)#spanning-tree vlan 20 priority 16384 S2(config)#spanning-tree vlan 20 priority 4096 S2(config)#spanning-tree vlan 30 priority 16384 S3(config)#spanning-tree vlan 30 priority 4096 S3(config)#spanning-tree vlan 10 priority 16384
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 2 of 2
You might also like
- E3 - 5.5.3 - PTAct Troubleshooting Spanning Tree ProtocolDocument2 pagesE3 - 5.5.3 - PTAct Troubleshooting Spanning Tree ProtocolIvandiNo ratings yet
- Lab 5.5.3: Troubleshooting Spanning Tree Protocol: Topology DiagramDocument6 pagesLab 5.5.3: Troubleshooting Spanning Tree Protocol: Topology DiagrammedamineNo ratings yet
- ESwitching Lab 5 5 2Document20 pagesESwitching Lab 5 5 2Ninja NuggetNo ratings yet
- Cisco Lab AnswersDocument20 pagesCisco Lab AnswersNada Nader El-ibiary100% (1)
- Lab 6.4.1Document14 pagesLab 6.4.1Janeza JangNo ratings yet
- 2.3.1.5 Packet Tracer - Configuring PVST+ Instructions IGDocument5 pages2.3.1.5 Packet Tracer - Configuring PVST+ Instructions IGJose Affleck100% (1)
- Lab 3.5.1: Basic VLAN Configuration: Topology DiagramDocument6 pagesLab 3.5.1: Basic VLAN Configuration: Topology DiagramIvan Esmit MayhuaNo ratings yet
- Configure DTPDocument5 pagesConfigure DTPAlex MachadoNo ratings yet
- 5 5 2Document20 pages5 5 2Amr Mohamed RedaNo ratings yet
- ESwitching Lab 3 5 1Document7 pagesESwitching Lab 3 5 1Ninja NuggetNo ratings yet
- 2.3.2.3 Lab - Configuring Rapid PVST+, PortFast, and BPDU GuardDocument9 pages2.3.2.3 Lab - Configuring Rapid PVST+, PortFast, and BPDU GuardcoleparksNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 - Creating VLAN - Activity - DocumentDocument7 pagesLab 5 - Creating VLAN - Activity - DocumentSylgon jay SanoyNo ratings yet
- Lab 3.3.2.3 Ccnna EspañolDocument9 pagesLab 3.3.2.3 Ccnna EspañolDylan RomeroNo ratings yet
- Lab03 STP Res PDFDocument11 pagesLab03 STP Res PDFFábio SantosNo ratings yet
- Lab 4.4.2: VTP Configuration Challenge: TopologyDocument3 pagesLab 4.4.2: VTP Configuration Challenge: TopologyJohnny OjohnnyNo ratings yet
- ESwitching Student Lab Skills Based Assessment Answer KeyDocument18 pagesESwitching Student Lab Skills Based Assessment Answer KeyzfanaNo ratings yet
- CCNA Lab 3.3.2.3Document9 pagesCCNA Lab 3.3.2.3Kieran Connolly100% (1)
- ESwitching Student Lab Skills Based AssessmentDocument4 pagesESwitching Student Lab Skills Based AssessmentJessica Carol OwensNo ratings yet
- Task 1: Prepare The Network: System and Network Admin Lab 2Document8 pagesTask 1: Prepare The Network: System and Network Admin Lab 2Bethelhem YetwaleNo ratings yet
- Configuring Trunks Between Switches to Extend VLANsDocument2 pagesConfiguring Trunks Between Switches to Extend VLANsBertNo ratings yet
- E3 PTAct 3 5 1Document6 pagesE3 PTAct 3 5 1Beqa Greg LagidzeNo ratings yet
- Configuring Trunks InstructionsDocument3 pagesConfiguring Trunks Instructionsjose merlanoNo ratings yet
- 2.3.1.5 Packet Tracer - Configuring PVST+ Instructions IG MarioDocument18 pages2.3.1.5 Packet Tracer - Configuring PVST+ Instructions IG MarioARNo ratings yet
- 2.3.2.2 Packet Tracer - Configuring Rapid PVST+ Instructions IGDocument4 pages2.3.2.2 Packet Tracer - Configuring Rapid PVST+ Instructions IGJose AffleckNo ratings yet
- Escuela de Ciencias Básicas, Tecnología e Ingeniería: Universidad Nacional Abierta Y A DistanciaDocument36 pagesEscuela de Ciencias Básicas, Tecnología e Ingeniería: Universidad Nacional Abierta Y A DistancialeoNo ratings yet
- 14-Troubleshooting Spanning TreeDocument13 pages14-Troubleshooting Spanning Treemansoorali_afNo ratings yet
- PT Activity 5.5.2: Challenge Spanning Tree Protocol: Topology DiagramDocument10 pagesPT Activity 5.5.2: Challenge Spanning Tree Protocol: Topology DiagramRidho Ariefalda YansyarNo ratings yet
- 2.3.1.5 Packet Tracer - Configuring PVST Instructions PDFDocument3 pages2.3.1.5 Packet Tracer - Configuring PVST Instructions PDFvannyNo ratings yet
- CCNP3V30 Lab CorrectionDocument16 pagesCCNP3V30 Lab CorrectionveeramachanenipurnaprasadNo ratings yet
- Lab 5: Basic VLAN Configuration: Topology DiagramDocument11 pagesLab 5: Basic VLAN Configuration: Topology DiagramWalid Mazari100% (1)
- Lab - Configuring Rapid PVST+, Portfast, and Bpdu Guard: TopologyDocument11 pagesLab - Configuring Rapid PVST+, Portfast, and Bpdu Guard: TopologyYossi Lara GuardaminoNo ratings yet
- Activity 3.5.1: Basic VLAN Configuration NOTE TO USER: This Activity Is A Variation of Lab 3.5.1. Packet Tracer May NotDocument6 pagesActivity 3.5.1: Basic VLAN Configuration NOTE TO USER: This Activity Is A Variation of Lab 3.5.1. Packet Tracer May NotmedrekNo ratings yet
- 2.3.1.5 Packet Tracer - Configuring Rapid PVST+ ANSWERDocument7 pages2.3.1.5 Packet Tracer - Configuring Rapid PVST+ ANSWERNarayanaSamy67% (3)
- 3.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Trunks InstructionsDocument2 pages3.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Trunks InstructionsJosé AntonioNo ratings yet
- ESwitching Lab 4 4 3Document6 pagesESwitching Lab 4 4 3martyr1107No ratings yet
- Lab 1Document6 pagesLab 1दिब्यम प्रभात्No ratings yet
- 3.4.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Trunks PDFDocument3 pages3.4.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Trunks PDFRichard VahesaluNo ratings yet
- SWITCH-EnterpriseNets and VLANs PDFDocument118 pagesSWITCH-EnterpriseNets and VLANs PDFSabri BalafifNo ratings yet
- Challenge Inter-Vlan RoutingDocument4 pagesChallenge Inter-Vlan RoutingTracey TaylorNo ratings yet
- Observe STP Topology Changes and Implement RSTPDocument14 pagesObserve STP Topology Changes and Implement RSTPcciersmanNo ratings yet
- PT Activity 3.5.1: Basic VLAN Configuration: Topology DiagramDocument6 pagesPT Activity 3.5.1: Basic VLAN Configuration: Topology DiagramKonrad KontekNo ratings yet
- ESwitching Lab 6 4 1 InsDocument14 pagesESwitching Lab 6 4 1 InsciscoscribNo ratings yet
- Take Assessment CCNP BCMSN Final 3: (Version 5.0)Document14 pagesTake Assessment CCNP BCMSN Final 3: (Version 5.0)Manuel Valdés100% (2)
- 2.10-InterVLAN Routing PDFDocument14 pages2.10-InterVLAN Routing PDFYureka MindsetNo ratings yet
- 3.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring VLANs and TrunkingDocument11 pages3.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring VLANs and TrunkingLove BearNo ratings yet
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksFrom EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNo ratings yet
- Next-Generation switching OS configuration and management: Troubleshooting NX-OS in Enterprise EnvironmentsFrom EverandNext-Generation switching OS configuration and management: Troubleshooting NX-OS in Enterprise EnvironmentsNo ratings yet
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationFrom EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNo ratings yet
- Exploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxFrom EverandExploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-A: A Beginner's Guide to Next Level of NetworkingFrom EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-A: A Beginner's Guide to Next Level of NetworkingNo ratings yet
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingFrom EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingNo ratings yet
- Automated Broad and Narrow Band Impedance Matching for RF and Microwave CircuitsFrom EverandAutomated Broad and Narrow Band Impedance Matching for RF and Microwave CircuitsNo ratings yet
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3From EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3No ratings yet
- Kathleen Langreo Notes FB (Feb6)Document27 pagesKathleen Langreo Notes FB (Feb6)Kaycee Ayo100% (4)
- DUB01CB Eng PDFDocument4 pagesDUB01CB Eng PDFAnonymous hj273CMNo ratings yet
- AAA Variable Spring Hangers CatalogDocument31 pagesAAA Variable Spring Hangers CatalogNopparut0% (1)
- The Karnataka Maternity Benefit (Amendment) Rules 2019Document30 pagesThe Karnataka Maternity Benefit (Amendment) Rules 2019Manisha SNo ratings yet
- Shop Math PDFDocument29 pagesShop Math PDFKen LeeNo ratings yet
- Difference Between AerospaceDocument2 pagesDifference Between AerospaceSyawalMaulanaNo ratings yet
- Steel PropertiesDocument26 pagesSteel PropertiesLutfy AzanNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech 15Document16 pagesParts of Speech 15lost finNo ratings yet
- LirikDocument537 pagesLirikMuhamad Iqbal FahmiNo ratings yet
- Site Master FileDocument51 pagesSite Master FileMilonhg100% (2)
- Dell Precision Workstations: The #1 Workstations in The WorldDocument7 pagesDell Precision Workstations: The #1 Workstations in The WorldDiego RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet - MSDS: Section 1. Chemical Product and Company IdentificationDocument5 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet - MSDS: Section 1. Chemical Product and Company IdentificationPubcrawlNo ratings yet
- Hyundai Elevator Manual Helmon 2000 InstructionDocument27 pagesHyundai Elevator Manual Helmon 2000 InstructionReynold Suarez100% (1)
- Unit 3 Assignment - CompletedDocument7 pagesUnit 3 Assignment - CompletedSu GarrawayNo ratings yet
- Overview of Pathophysiology of Hypoxemia and HypoxiaDocument15 pagesOverview of Pathophysiology of Hypoxemia and HypoxiaMARY ANN CAGATANNo ratings yet
- Borneo SporenburgDocument2 pagesBorneo SporenburgDorin TecuceanuNo ratings yet
- Data Biostataplus Sbi2014-EDocument4 pagesData Biostataplus Sbi2014-ELucila Milagros PinillosNo ratings yet
- Quant One Analyser – endless possibilitiesDocument6 pagesQuant One Analyser – endless possibilitiesSamuel SuNo ratings yet
- Procedure - AC Circuits and Signal Modulation - W20Document6 pagesProcedure - AC Circuits and Signal Modulation - W20ChocoNo ratings yet
- Customer Part Exchange Program: Product InformationDocument8 pagesCustomer Part Exchange Program: Product InformationAdrian GarciaNo ratings yet
- INChO 2008 Question PaperDocument23 pagesINChO 2008 Question PaperChaitanya GaurNo ratings yet
- Syllabi - EE 5004 - Power ElectronicsDocument2 pagesSyllabi - EE 5004 - Power ElectronicsKalum ChandraNo ratings yet
- January 2010 QP - Unit 1 Edexcel Physics A-LevelDocument23 pagesJanuary 2010 QP - Unit 1 Edexcel Physics A-Levelpraveen alwisNo ratings yet
- Modicon TM172PDG42R DatasheetDocument14 pagesModicon TM172PDG42R DatasheetRonnie SolomonNo ratings yet
- Coley A4Document49 pagesColey A4mfiarkeeaNo ratings yet
- TICSA - Diesel Uno Petroleos Guatemala (13.01.23)Document1 pageTICSA - Diesel Uno Petroleos Guatemala (13.01.23)Luis M LópezNo ratings yet
- Approach To Malabsorption (SANJAY)Document58 pagesApproach To Malabsorption (SANJAY)Sanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine Performance Enhancement Update: GE Energy ServicesDocument45 pagesGas Turbine Performance Enhancement Update: GE Energy Servicesesteban100% (1)
- 1B Cosmos-Standard - Technical - Guide - v40Document45 pages1B Cosmos-Standard - Technical - Guide - v40carla deiddaNo ratings yet
- Terminal BlockDocument12 pagesTerminal BlockAlmaforNo ratings yet