Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Final 2010
Uploaded by
Hakkı ÇelimliOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Final 2010
Uploaded by
Hakkı ÇelimliCopyright:
Available Formats
ENS 205 Materials Science, Final Exam
19/01/2011
Name: __________________________________________________________________________
You have a total of 180 minutes. The exam is 8 pages long. Make sure you have all pages. Do not separate pages of the exam; exams with missing pages will not be marked. You may use scientific calculators. You may not use phones or any other gadgets; your phones should not be visible, or we will collect them. Even the slightest attempt at copying will be reported to the Deans office. Answer all questions in English! total points 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 20 120 your points
Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q5 Q6 Q7 Q8 Q9 Q10 Bonus Total
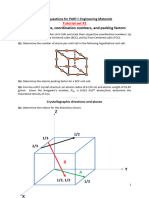
1. (a) One crystalline form of silica (SiO2) has a cubic unit cell, and from x-ray diffraction data, it is known that the cell edge is 0.700 nm. If the measured density is 2.32 g/cm3, how many Si4+ and O2- ions are there per unit cell?
(b) What are the indices for the directions indicated by the vector in the sketch below?
(c) Determine the Miller indices for the planes shown in the following unit cell:
ENS 205 Materials Science, Final Exam
19/01/2011
Name: __________________________________________________________________________
2. Figure shows the first five peaks of the x-ray diffraction pattern for tungsten, which has a BCC crystal structure; radiation having a wavelength of 0.1542 nm was used. (a) Give h,k,l indices for each of these peaks (b) Determine the interplanar spacing for each of the peaks (c) For each peak, determine the atomic radius for tungsten and give reasons as to why the values are different, if they are. Reminder: in BCC crystals, diffraction only occurs for h+k+l = even number
ENS 205 Materials Science, Final Exam
19/01/2011
Name: __________________________________________________________________________
3. Atomic radius, crystal structure, electronegativity, and the most common valence are given in the table for several elements; for those that are nonmetals, only atomic radii are indicated. Give one example of an element you would expect to form the following with nickel: (a) A substitutional solid solution having complete solubility (b) A substitutional solid solution of incomplete solubility (c) An interstitial solid solution Give your reason!
4. A sheet of BCC iron 2 mm thick was exposed to a carburizing gas atmosphere on one side and a decarburizing atmosphere on the other side at 725C. After having reached steady state, the iron was quickly cooled to room temperature. The carbon concentrations at the two surfaces of the sheet were determined to be 0.012 and 0.0075 weight%. Compute the diffusion coefficient if the diffusion flux is 1.6 10 8 kg/m2-s. Hint: First convert the concentrations from weight percent to kilograms of carbon per cubic meter of iron. Data: density of carbon 2.25 g/cm3; density of iron 7.87 g/cm3
ENS 205 Materials Science, Final Exam
19/01/2011
Name: __________________________________________________________________________
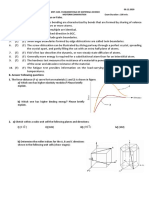
5. A cylindrical specimen of stainless steel having a diameter of 12.8 mm and a gauge length of 50.800 mm is pulled in tension. The true stress-strain data for the specimen is shown. (a) Compute the modulus of elasticity. (b) Determine the yield strength. (c) Determine the tensile strength of this alloy. (d) What is the approximate ductility, in percent elongation? (e) What is the resilience (elastic energy stored)?
6. Consider a metal single crystal oriented such that the normal to the slip plane and the slip direction are at angles of 60 and 35, respectively, with the tensile axis. (a) Sketch the test situation, showing the sample and pulling direction. Label the two angles mentioned above. (b) If the critical resolved shear stress is 6.2 MPa, will an applied stress of 12 MPa cause the single crystal to yield? If not, what stress will be necessary?
7. (a) The room-temperature electrical conductivity of a semiconductor specimen is 1.2 10 -3 (-m)1. The hole concentration is known to be 1.0 1023 m3. The electron and hole mobilities for this material are 0.14 and 0.05 m2/V-s, respectively. Compute the electron concentration. (b) On the basis of the result in part (a), is the specimen intrinsic, n-type extrinsic, or p-type extrinsic.
ENS 205 Materials Science, Final Exam
19/01/2011
Name: __________________________________________________________________________
8. Is it possible to have a magnesiumlead alloy in which the mass fractions of primary and total are 0.60 and 0.85, respectively, at 460C? Why or why not? The phase diagram is provided.
9. (a) In the solidification process, the first step is the nucleation of grains. For homogeneous nucleation, one must form the initial nucleates, and reinforce them via diffusion of new atoms onto the nucleate. In the figure below, the temperature dependence on nucleation rate is shown for the two processes mentioned above, as well as their net effect. Correctly label in the boxes drawn. (b) Once a stable nucleate is formed, additional atoms must also diffuse towards it to grow the grain. For a system where the activation energy for diffusion of atoms is low, do you expect the temperature at which the maximum rate is observed to be increased or decreased? Explain by sketching on the figure a representative growth rate curve, and the resulting overall transformation rate curve. Label clearly for full marks.
ENS 205 Materials Science, Final Exam
19/01/2011
Name: __________________________________________________________________________
10. Isothermal transformation diagram for a 1.13 weight % C ironshown below (same figure is reproduced four times; the Fe-C phase diagram is shown on the right for your convenience.)
A: austenite; B: bainite; C: proeutectoid cementite; M: martensite; P: pearlite.
carbon alloy is
Sketch and label timetemperature paths to produce the following microstructures: (a) 6.2% proeutectoid cementite and 93.8% coarse pearlite (b) 50% fine pearlite and 50% bainite (c) 100% martensite (d) 100% tempered martensite
ENS 205 Materials Science, Final Exam
19/01/2011
Name: __________________________________________________________________________
Bonus question. The net potential energy between two adjacent ions, UN, may be represented by the sum of repulsive and attractive energies as follows, with possible values of the exponent n in the range 7-9:
(a) Sketch the form of this equation. On your sketch, show the point at which the interionic distance is most likely to occur. (b) Consider a hypothetical Q+P- ion pair for which the constants are A=1.93 eV-nm and B=8.9310-6 eV-nm8. Given that for this ion pair, the exponent n in the equation has a value of 8, find the inter-ionic spacing, and the bonding energy at that value of the distance. (c) The above equation is also valid for the bonding energy between adjacent ions in solid material. As a reminder, the modulus of elasticity, E, is the slope of the force separation curve at the equilibrium inter-ionic separation:
where C is a constant. Also note that the force is the negative derivative of the potential. In the table below, you are given the data for three hypothetical materials X, Y, Z. Rank their magnitudes of the moduli of elasticity from the greatest to the least. Show all your calculations and provide numbers. Material A B n 1.5 eV-nm 7.010-6 eV-nm8 8 X 2.0 eV-nm 1.010-5 eV-nm9 9 Y 3.5 eV-nm 4.010-6 eV-nm7 7 Z
ENS 205 Materials Science, Final Exam
19/01/2011
Name: __________________________________________________________________________ Formula Sheet
D= b/
D D0eQ / RT
Chapter 13 Fermi function: electrical conductivity: in intrinsic semiconductors:
; the value of e is 1.602 10-19 C
You might also like
- Eg2010 2021 SP2Document8 pagesEg2010 2021 SP2Edwin JomonNo ratings yet
- ANSWER Final EGMDocument9 pagesANSWER Final EGMAndil MaulanaNo ratings yet
- (2nd Sem) - Engineering-Physics-2-Eas-201-2011-12Document3 pages(2nd Sem) - Engineering-Physics-2-Eas-201-2011-12Mahima FamousNo ratings yet
- 10CV/EV33: Strength of MaterialsDocument2 pages10CV/EV33: Strength of MaterialsnvnrevNo ratings yet
- Lectut-MTN-105-Doc-MT 201A-Tutorial - CH 1 (4 Files Merged)Document9 pagesLectut-MTN-105-Doc-MT 201A-Tutorial - CH 1 (4 Files Merged)Vikhyath KstNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Nanoelectronics FinalDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Nanoelectronics Finalparmis1212No ratings yet
- Assign#1Document2 pagesAssign#1vineet mishraNo ratings yet
- CBSE Annual Examination Question Paper 2013: CSBE Sample Papers, Question, Papers, Notes For Class 6 To 12Document7 pagesCBSE Annual Examination Question Paper 2013: CSBE Sample Papers, Question, Papers, Notes For Class 6 To 12arjunNo ratings yet
- Solid State Physics Midterm ExamDocument3 pagesSolid State Physics Midterm ExamToqa ShweikiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Physics - I - PH6151 Important 2 Marks With AnswersDocument23 pagesEngineering Physics - I - PH6151 Important 2 Marks With AnswersZaffu Zealy100% (4)
- Ece630 ASSN1 SolutionsDocument5 pagesEce630 ASSN1 SolutionsLeticia Dishel VasNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Physics Coursework ExampleDocument5 pagesEdexcel Physics Coursework Exampledthtrtlfg100% (2)
- Cbse Sample Paper: 2010 Class: Xii Subject: Physics: General InstructionsDocument7 pagesCbse Sample Paper: 2010 Class: Xii Subject: Physics: General InstructionsBinu PrasanthNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Atomic StructureDocument9 pagesTopic 1 Atomic StructurearyanNo ratings yet
- SampleTest1 KeyDocument6 pagesSampleTest1 KeyMAJDEJBRNo ratings yet
- ZEBAR SCHOOL PERIODIC TEST-3 SCIENCEDocument4 pagesZEBAR SCHOOL PERIODIC TEST-3 SCIENCERohan VayaNo ratings yet
- MIME262MidtermWinter2018 SolutionsUploadVersionDocument8 pagesMIME262MidtermWinter2018 SolutionsUploadVersionNoor JethaNo ratings yet
- CBSE XII - Physics: Board Paper - 2006Document5 pagesCBSE XII - Physics: Board Paper - 2006venkithebossNo ratings yet
- Chap 7 Electrity & MagnetismDocument5 pagesChap 7 Electrity & Magnetismchristina teoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Questions For Part 1Document5 pagesTutorial Questions For Part 1j8tjb68gm2No ratings yet
- 5116 Prelim P2 BBSS 2009Document10 pages5116 Prelim P2 BBSS 2009topcatNo ratings yet
- MATH 114 Module 10 All AnswersDocument22 pagesMATH 114 Module 10 All AnswersJohn Arvin EscoteNo ratings yet
- 1i' JN ::x. Ii Ii',: Sub: EEE 307 ofDocument23 pages1i' JN ::x. Ii Ii',: Sub: EEE 307 ofTrisha DasNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12 Physics 2015-2016 PDFDocument22 pagesCBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12 Physics 2015-2016 PDFHrithik RajNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam 1Document2 pagesPractice Exam 1jfisher84118No ratings yet
- CHM1011 S1,2011 PDFDocument28 pagesCHM1011 S1,2011 PDFSasuke AhmedNo ratings yet
- Topic Test Oxfordaqa Int As Level Physics ElectricityDocument17 pagesTopic Test Oxfordaqa Int As Level Physics Electricityandhi soesiloNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 E FDocument2 pagesAssignment 1 E FSudhananda MallickNo ratings yet
- Kittel Chapter 1-2 and Ashcroft/Mermin Chapters 4-7 Homework 1Document4 pagesKittel Chapter 1-2 and Ashcroft/Mermin Chapters 4-7 Homework 1Iqra WahidNo ratings yet
- Summer 2014Document2 pagesSummer 2014babu moshaiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12 Physics 2017-2018 PDFDocument19 pagesCBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12 Physics 2017-2018 PDFHrithik RajNo ratings yet
- FEpapersDocument107 pagesFEpapersChetan BhagatNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Methods AssignmentDocument8 pagesFinite Element Methods AssignmentSanju ReddyNo ratings yet
- Class 12 National Genius Search Examination: Advanced: Test CodeDocument8 pagesClass 12 National Genius Search Examination: Advanced: Test CodePPNo ratings yet
- 2013 PDFDocument7 pages2013 PDFnandagopanNo ratings yet
- Crystal LatticesDocument11 pagesCrystal LatticeschrischeelyNo ratings yet
- 12.1. Turning Points in Physics - Discovery of The Electron QPDocument10 pages12.1. Turning Points in Physics - Discovery of The Electron QPhaseeb3382786No ratings yet
- Theory of Elasticity and StabilityDocument2 pagesTheory of Elasticity and StabilityAmit ThoriyaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For First Year First Sem Question Bank For Physics-I Regulation 20913Document21 pagesQuestion Bank For First Year First Sem Question Bank For Physics-I Regulation 20913PRIYA RAJINo ratings yet
- Model Paper: Government College University, FaisalabadDocument8 pagesModel Paper: Government College University, FaisalabadIce IceNo ratings yet
- USN X, E/ Y: Experim N MechaDocument2 pagesUSN X, E/ Y: Experim N Mechamusic lover oldNo ratings yet
- EAT227 May 2019 ExamDocument5 pagesEAT227 May 2019 ExamΚωνσταντινος ΕυρουNo ratings yet
- Name: - Student IDDocument7 pagesName: - Student IDinrhgoiwnowbNo ratings yet
- 2020-10-30SupplementaryEC203EC203-I - Ktu QbankDocument2 pages2020-10-30SupplementaryEC203EC203-I - Ktu QbankFayaz aliNo ratings yet
- Study SET 1 SimplfiedDocument2 pagesStudy SET 1 SimplfiedTheMasterOf MCNo ratings yet
- Question Paper of Summer Session 2022 23Document31 pagesQuestion Paper of Summer Session 2022 23moresachin7040No ratings yet
- Do Not Detach This Page From Your Test!!!!: Page 1 of 5 Tuesday Quiz InstructorDocument5 pagesDo Not Detach This Page From Your Test!!!!: Page 1 of 5 Tuesday Quiz InstructorDana CapbunNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Questions For Part 1Document5 pagesTutorial Questions For Part 1Ng Yan XiongNo ratings yet
- HomeworkDocument6 pagesHomeworkmyalyaNo ratings yet
- At Least TWO Questions From Each Part.: (06 Marks)Document2 pagesAt Least TWO Questions From Each Part.: (06 Marks)nvnrevNo ratings yet
- Report2003 9Document4 pagesReport2003 9GaetanoLNo ratings yet
- 6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Quiz #1 SolutionsDocument10 pages6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Quiz #1 Solutionsdan gNo ratings yet
- Ceeb Mock 2019 Al Phy 2Document6 pagesCeeb Mock 2019 Al Phy 2tech boyNo ratings yet
- Materials Engineering Final Exam ReviewDocument6 pagesMaterials Engineering Final Exam ReviewFaisal AbdulazizNo ratings yet
- ImpDocument11 pagesImpDhvani PatelNo ratings yet
- S20 Homework 2Document2 pagesS20 Homework 2carlosNo ratings yet
- Problemario1-Diseã o Mecanico1Document4 pagesProblemario1-Diseã o Mecanico1Gerardo BocanegraNo ratings yet
- 322 F22 PS9 - UpdatedDocument4 pages322 F22 PS9 - UpdatedlokeshNo ratings yet
- MET213E-midterm 2020-2021Document4 pagesMET213E-midterm 2020-2021Barış UlukanNo ratings yet
- Directed Energy WeaponsDocument5 pagesDirected Energy WeaponsRichard BachmanNo ratings yet
- TEM - Electron Microscopy and DiffractionDocument57 pagesTEM - Electron Microscopy and DiffractionHoang LamNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Devices Physics PN Junction Diode CharacteristicsDocument17 pagesSemiconductor Devices Physics PN Junction Diode Characteristicsg_groupNo ratings yet
- Dioun Light Metal Alloys Applications Ed by Waldemar A Monteiro PDFDocument245 pagesDioun Light Metal Alloys Applications Ed by Waldemar A Monteiro PDFelmardaNo ratings yet
- Modern Electronic Communication 7th Edition by Beasley Miller MCQDocument38 pagesModern Electronic Communication 7th Edition by Beasley Miller MCQFranch Maverick Arellano LorillaNo ratings yet
- Wireless Landmine Detection Robot: A ReviewDocument3 pagesWireless Landmine Detection Robot: A ReviewIJRASETPublications100% (1)
- bizurado-silvaco-PIN Detector Thesis PDFDocument143 pagesbizurado-silvaco-PIN Detector Thesis PDFombraga1896No ratings yet
- Tunable Diode Laser Analyzer: Bild Durch Klicken Auf Symbol HinzufügenDocument16 pagesTunable Diode Laser Analyzer: Bild Durch Klicken Auf Symbol Hinzufügenadity_saxenaaNo ratings yet
- EE 303 Tutorial 1Document19 pagesEE 303 Tutorial 1Syama SameekshaNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi RENO D50Document1 pageSpesifikasi RENO D50Anonymous tbJ24554No ratings yet
- Beam Analyzer 05Document4 pagesBeam Analyzer 05Israel ExporterNo ratings yet
- APX HF3 Technical ManualDocument84 pagesAPX HF3 Technical ManualAlexander Grau100% (4)
- Carbon Dioxide Permeability DIN 53380-4 DIN 53380-IDocument2 pagesCarbon Dioxide Permeability DIN 53380-4 DIN 53380-IJOSENo ratings yet
- Lightolier Execuline Lighting System Brochure 1969Document8 pagesLightolier Execuline Lighting System Brochure 1969Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- Kodak Intermediet 5242Document6 pagesKodak Intermediet 5242feybrian thomasNo ratings yet
- Termometro IR LUTRON-TM-969-BROCHUREDocument2 pagesTermometro IR LUTRON-TM-969-BROCHUREKevin HuarachaNo ratings yet
- WDM Commissioning Guide: Optical Amplifier Commissioning RequirementsDocument107 pagesWDM Commissioning Guide: Optical Amplifier Commissioning RequirementsThiago Andrade RangelNo ratings yet
- Irda-Welder User Manual T-862Document14 pagesIrda-Welder User Manual T-862Alan CukojevicNo ratings yet
- QSG Tksa 20 - MP5370 PDFDocument24 pagesQSG Tksa 20 - MP5370 PDFjairoNo ratings yet
- ScienceBlissCourse PDFDocument34 pagesScienceBlissCourse PDFAngie MistrettaNo ratings yet
- Beam Quality Tutorial OsaDocument18 pagesBeam Quality Tutorial OsaravindrannnnNo ratings yet
- Inspection Checklist OTDR Test For Fiber Optic CablesDocument2 pagesInspection Checklist OTDR Test For Fiber Optic Cablesamir11601100% (19)
- Xerox Phaser 6500Document162 pagesXerox Phaser 6500dinkeyNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Microscope - 2016Document2 pagesCalibration of Microscope - 2016Amanda Sturridge100% (1)
- S355 Grade Structural Steel PropertiesDocument2 pagesS355 Grade Structural Steel PropertiesAlmir Pendek100% (1)
- Plough Shear MixerDocument2 pagesPlough Shear MixerdeepeshNo ratings yet
- Metal Forming OverviewDocument120 pagesMetal Forming OverviewSang Ka KalaNo ratings yet
- LR-Z C 613232 Us 1033-1Document18 pagesLR-Z C 613232 Us 1033-1Eng Castaneda100% (1)
- Waffle StructureDocument4 pagesWaffle StructureRitika GandhiNo ratings yet
- SICK Foto-Elektriniai SensoriaiDocument96 pagesSICK Foto-Elektriniai SensoriaietecsantoNo ratings yet