Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Common Mistakes in English
Uploaded by
Hasen BebbaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Common Mistakes in English
Uploaded by
Hasen BebbaCopyright:
Available Formats
Common Mistakes in English
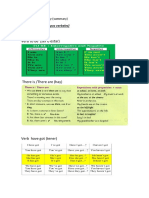
There are a number of common mistakes in English that learners face. This page provides links to these common mistakes. Each page has a clear explanation with example sentences. Each common mistake page is .followed by a quiz to help you check your understanding
Good or Well Good is an adjective and well is an adverb. Many people, including many native speakers, incorrectly use the adjective form good, rather than the adverb well. Examples: I did good on the test. INCORRECT! - Correct form: I did well on the test. She played the game good. INCORRECT! - Correct form: She played the game well. Use the adjective form good when describing something or someone. In other words, use good when stating how something or someone is. Examples: She is a good tennis player. Tom thinks he is a good listener. Use the adverb form well when describing how something or someone does something. Examples: She did extremely well on the exam. Our parents think we speak English well. Do you understand the rules? Test your knowledge with this good vs. well quiz. Good vs. Well Quiz Choose whether good or well is correct. Each question has only one correct answer. When you are finished click on the "Next Question" button. There are 10 questions to this quiz. Try to use only 30 seconds per question. At the end of the quiz, your score.
1. I think he is a _____ polo player. good well 2. She played the piece very _____. good well
3. They think he is quite a _____ speaker. good well 4. Janice was quite _____ at the flute. good well 5. She played the instrument _____. good well 6. Our neighbors' child speaks French _____. good well 7. Their interest in _____ wine is quite evident. good well 8. Her knowledge of the subject allowed her to do _____ in debates. good well 9. Peter's a _____ clarinet player. good well 10. Our soccer team did very _____ last year. good well Bring Take Fetch/Get The use of bring and take is confusing for many students. The choice between bring or take depends on the location of the speaker. If the speaker refers to something that is at her current location, she uses bring. Generally, use bring when something moves from there to here. Examples: I'm glad you brought me to this shop. It's great! I'll bring the map with me on the trip. If the speaker refers to something that has been moved to a different location, she uses take. Generally, use take when something moves from here to there. Examples: The coach took the boys to football field. Jack took his laptop with him on his trip. Fetch/Get When speaking about going somewhere and getting something and then bringing it back, use get (American English) or fetch (British English).
Examples: Could you get the newspaper? She fetched her diary and showed him the entry. Do you understand the rules? Test your knowledge with this bring, take, fetch, get quiz. 1. Could you _____ the TV guide and show me? bring take get 2. She _____ her children to the theater. brought took fetched 3. Susan thanked me for _____ her to this restaurant. bringing taking fetching 4. I've _____ my calender with me. brought took fetched 5. Let's _____ some food to the park. bring take get 6. The dog _____ the slippers for his master. brought took fetched 7. Should we ______ some newspapers with us today? bring take fetch 8. The children _____ along some extra clothes on the camping trip. took brought fetched 9. His friend went over to the table, _____ the book and showed him the evidence. took brought got 10. Our friends are _____ a cake with them when they visit us this afternoon. bringing taking getting
Common Mistakes in English Everyone and Every One
Everyone Use everyone as a pronoun to mean all the people in a group. Examples: Do you think everyone will want to come to the party? She wants everyone to leave comments on her blog. Every one Use every one as a noun to indicate each person. Examples: Every one of the students has a question about the grammar. My boss told every one of the employees himself.
Do you understand the rules? Test your knowledge with this Everyone vs .Every one quiz
Everyone vs Every One Quiz Choose whether everyone or every one is correct. Each question has only one correct answer. When you are finished click on the "Next Question" button. There are 10 questions to this quiz. Try to use only 30 seconds per question. At the end of the quiz, your score. 1. _____ wants to have some fun some of the time! Everyone Every one 2. I'll hand out the sheet to _____. everyone every one 3. I'm sure that ______ of the students understands the problem. everyone every one 4. She's asking _______ for their opinion. everyone every one 5. ______ in that group of people has a different responsibility. Everyone Every one 6. I saw _______ at the party. everyone
every one 7. I wish _______ of those employees could take the course. everyone every one 8. Does _______ understand? everyone every one 9. Jack handed out a sheet to _____ of those who had expressed interest. everyone every one 10. Here's free candy for _____! everyone every one Note : the answers are 60 % correct!.
Common Mistakes in English Everyday vs Every Day
Everyday Use everyday as an adjective to mean 'daily'. ( Adj.) Examples: Peter has an everyday appointment with his boss for briefings. Susan has an everyday yoga class at five pm. Every day Use every day as a time expression to mean 'each day'. (Adv.) Examples: Peter studies Russian every day. She pratices the piano three hours every day. Do you understand the rules? Test your knowledge with this Everyday vs Every day quiz. Everyday vs Every Day Quiz Choose whether everyday or every day is correct. Each question has only one correct answer. When you are finished click on the "Next Question" button. There are 10 questions to this quiz. Try to use only 30 seconds per question. At the end of the quiz, your score.
1. She goes to school _____. every day c everyday 2. Peter has an ______ meeting at ten. everyday c every day 3. They'd like to eat popcorn _____. everyday every day c 4. How often have you had an _______ class? everyday c every day 5. Jack gets up at six in the morning _____. everyday every day c 6. Our friends like to have an _____ get together to talk about neighborhood gossip. everyday c every day 7. She likes having an ______ swim. everyday c every day 8. I'd love to have an _____ massage! everyday c every day 9. Will you be able to pick him up ____? everyday every day c 10. They eventually decided to meet _______ until the problem was solved. everyday every day c
Common Mistakes in English - Whether / If
Whether / If Both whether and if are used to introduce a yes/no question: Examples: He asked me whether I felt well. We're not sure if they have decided. The verb discuss generally takes whether rather than if. Examples:
We discussed whether he should be hired. They discussed whether to invest in the new idea. After Prepositions Use only whether after prepositions: Examples: We talked about whether we should go or not. I looked into whether he should stay. Infinitives Use only whether before infinitives: Examples: She can't decide whether to buy the house or wait. He considered whether to give up the position or quit next year. Formal / Informal Generally, whether is considered more formal than if. Examples: Let me know whether you will be able to attend the conference. The CEO will decide whether this is a risk worth taking. Do you understand the rules? Test your knowledge with this Whether / If quiz. Whether or If Quiz Choose whether whether or if is correct. Each question has only one correct answer. When you are finished click on the "Next Question" button. There are 10 questions to this quiz. Try to use only 30 seconds per question. At the end of the quiz, your score.
1. Let's discuss ______ we should go or not. whether c if 2. They were wondering ______ to come or not. whether c if 3. (Formal) Let me know ______ you will be able to attend the conference. whether c if 4. (Informal) Tell me ______ you can come to the party or not.
if c when 5. We talked about ______ we should go or not. whether c if 6. We're not sure ______ they have decided. if c who 7. She's the one _____ telephoned last night. if who c 8. I looked into ______ he should stay. whether c if 9. (Formal) The CEO will decide _____ this is a risk worth taking. whether c if 10. (Informal) He asked ______ I could help him with his math homework. whether if c
Common Mistakes in English - Enough
Enough Adjective / Adverb + Enough When enough modifies an adjective or an adverb place enough after the adjective / adverb: Examples: Do you think he is strong enough to lift that weight? I think it's warm enough to take a walk without my jacket. Enough + Noun When enough modifies a noun, place enough before the noun: Examples: He has enough money to buy a ticket. She said there were enough participants to begin the study. Do you understand the rules? Test your knowledge with this Enough quiz. 1. Do you have ______ to help me? time enough enough time c
2. I don't think she's _____ to pass that test. smart enough c enough smart 3. She said their were ______ to begin the study. participants enough enough participants c 4. She says it's ______ to go outside without a jacket. enough sunny sunny enough c 5. I brought along ______ to buy lunch. enough money c money enough 6. Do you think the test is ______ for the advanced level? enough difficult difficult enough c 7. There are _______ here to begin the lesson. enough people c people enough 8. I'm not ______ to cry. enough sad sad enough c 9. Her opinion isn't ______ to change mine. strong enough c enough strong 10. There are ______ to win the election. enough votes c votes enough
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Parts of Speech - Trainer's ManualDocument5 pagesParts of Speech - Trainer's ManualDivyaNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- English VocabDocument11 pagesEnglish VocabArvindKumarNo ratings yet
- DCVG Surveys Training Manual - GX Version PDFDocument73 pagesDCVG Surveys Training Manual - GX Version PDFlaz_kNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Structural MechanicsDocument111 pagesStructural MechanicsDirkPons100% (5)
- English Grammar ExercisesDocument374 pagesEnglish Grammar ExercisesEmese Boda96% (28)
- Get Ready For IELTS SBDocument162 pagesGet Ready For IELTS SBDuc Dao80% (5)
- Cathodic Protection ReportDocument32 pagesCathodic Protection ReportMuhammad Ibad Alam100% (1)
- Control Valve CharacteristicsDocument65 pagesControl Valve CharacteristicsAzar DeenNo ratings yet
- Grammar - The Essential GuideDocument75 pagesGrammar - The Essential GuideMateus Scherer Cardoso0% (1)
- KBR Standard Report Template Rev 9.01Document268 pagesKBR Standard Report Template Rev 9.01Hasen BebbaNo ratings yet
- DCVG Coating Survey Data SheetDocument8 pagesDCVG Coating Survey Data SheetMihail BusuiocNo ratings yet
- Grease ProcessingDocument110 pagesGrease ProcessingRishikesh Awale60% (5)
- ABB Control ValveDocument30 pagesABB Control ValveHafzi88% (8)
- Design Manual Pump StationDocument127 pagesDesign Manual Pump Stationtsraj10100% (3)
- Using An IonX Electrode To Check RE 5Document2 pagesUsing An IonX Electrode To Check RE 5Jaya DiNo ratings yet
- Compatibility of Paints PDFDocument1 pageCompatibility of Paints PDFAhmed FodaNo ratings yet
- CS 51 IDocument1 pageCS 51 IHasen BebbaNo ratings yet
- Mva RitecDocument1 pageMva RitecHasen BebbaNo ratings yet
- What Plumbing Designers Need To Know About Valves, Part 2 PDFDocument4 pagesWhat Plumbing Designers Need To Know About Valves, Part 2 PDFHasen BebbaNo ratings yet
- General Requirements For Technical Publication Preparation: 1. ScopeDocument15 pagesGeneral Requirements For Technical Publication Preparation: 1. ScopeHasen BebbaNo ratings yet
- Me471s03 Lec11aDocument14 pagesMe471s03 Lec11aHasen BebbaNo ratings yet
- CIPS Training Course PDFDocument11 pagesCIPS Training Course PDFshiviariNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageAn Introduction To Mechanical EngineeringHasen BebbaNo ratings yet
- What Plumbing Designers Need To Know About Valves, Part 2 PDFDocument4 pagesWhat Plumbing Designers Need To Know About Valves, Part 2 PDFHasen BebbaNo ratings yet
- Innovation Workshop Brainstorming: Jonathan Weaver & Darrell KleinkeDocument14 pagesInnovation Workshop Brainstorming: Jonathan Weaver & Darrell KleinkeAli M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- CDC UP Project Management Plan TemplateDocument11 pagesCDC UP Project Management Plan TemplateMими Кољушкова100% (1)
- Advantages of Globe ValvesDocument3 pagesAdvantages of Globe ValvesJohn Rey TumalaNo ratings yet
- Me471s03 SyDocument2 pagesMe471s03 SyHasen BebbaNo ratings yet
- Me471s03 q2 AnsDocument12 pagesMe471s03 q2 AnsHasen BebbaNo ratings yet
- Me471s03 q1 AnsDocument5 pagesMe471s03 q1 AnsHasen BebbaNo ratings yet
- Me471s03 Lec09Document12 pagesMe471s03 Lec09Hasen BebbaNo ratings yet
- Me471s03 Lec10Document13 pagesMe471s03 Lec10Hasen BebbaNo ratings yet
- Me471s03 Lec06Document2 pagesMe471s03 Lec06Hasen BebbaNo ratings yet
- Me471s03 Lec08Document7 pagesMe471s03 Lec08Hasen BebbaNo ratings yet
- Me471s03 Lec07Document9 pagesMe471s03 Lec07Hasen BebbaNo ratings yet
- Basic English Grammar Review Material Mr. Amadeo F. NarcaDocument33 pagesBasic English Grammar Review Material Mr. Amadeo F. NarcaRengie GaloNo ratings yet
- 1st Yeaar 2022Document46 pages1st Yeaar 2022Andrea RodriguezNo ratings yet
- PT ENGLISH3 4th-QuarterDocument4 pagesPT ENGLISH3 4th-QuarterJuMeLa SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 - Module 6: Phrases, Clauses, and SentencesDocument66 pagesQuarter 1 - Module 6: Phrases, Clauses, and SentencesJohn Edmark Telesforo0% (1)
- Verb Past Simple Past ParticipleDocument23 pagesVerb Past Simple Past ParticipleEhr WinNo ratings yet
- Q4 WLP WK 3Document36 pagesQ4 WLP WK 3Donna AbenojaNo ratings yet
- Future 4 Main Verbs Used CLT Communicative Language Teaching Resources Gram - 85225Document18 pagesFuture 4 Main Verbs Used CLT Communicative Language Teaching Resources Gram - 85225Karoline LimaNo ratings yet
- Adj Adv With Trans and Intrans Verbs 4Document13 pagesAdj Adv With Trans and Intrans Verbs 4Insaf AliNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 - 1quarter Sample TestDocument3 pagesGrade 8 - 1quarter Sample TestJeremias MartirezNo ratings yet
- Lesson One AS1Document22 pagesLesson One AS1HaDIL Gaidi officielNo ratings yet
- LISTA545Document65 pagesLISTA545monalisa_amaralNo ratings yet
- 02-05 - Adverbs - Forms - English Grammar Today - Cambridge DictionaryDocument7 pages02-05 - Adverbs - Forms - English Grammar Today - Cambridge DictionaryMaja KneževićNo ratings yet
- DAY 5 Analisis Penerapan Materi - Modul 5 - ULLYDocument13 pagesDAY 5 Analisis Penerapan Materi - Modul 5 - ULLYUlly Norprahatini HalyfaNo ratings yet
- Mubarak Use of English GNS 301Document18 pagesMubarak Use of English GNS 301Mubarak AdamuNo ratings yet
- Sentence DiagrammingDocument29 pagesSentence DiagrammingJoshua JethrohNo ratings yet
- How To Master and Earn Toefl Itp Score More Than 600 EasilyDocument31 pagesHow To Master and Earn Toefl Itp Score More Than 600 EasilyDIANNo ratings yet
- Nav BR LP Upp I08 2 VRDocument1 pageNav BR LP Upp I08 2 VRYannina RojasNo ratings yet
- Q3 English 8 Module 6Document29 pagesQ3 English 8 Module 6Laila JulveNo ratings yet
- Prepositions: According To, Due To, Instead of - TheDocument21 pagesPrepositions: According To, Due To, Instead of - TheZUHRANo ratings yet
- Time Is A Great TeacherDocument17 pagesTime Is A Great TeacherMuhammad Hamza HamzaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3, Sem 1Document14 pagesUnit 3, Sem 1Maria AnaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Step ForwardDocument21 pagesUnit 1 - Step ForwardLuan MirandaNo ratings yet
- Engleza 1Document51 pagesEngleza 1Cristian PandeleaNo ratings yet
- Use of Very Too Much EnoughDocument5 pagesUse of Very Too Much EnoughPatricia SandovalNo ratings yet
- Instructional Learning Modules in English PlusDocument23 pagesInstructional Learning Modules in English PlusBenedic BaluyotNo ratings yet