Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3 Engine System
Uploaded by
Chabou RafikCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3 Engine System
Uploaded by
Chabou RafikCopyright:
Available Formats
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
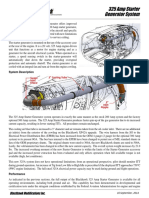
3-E ng i ne Syst em s
Objectives
Fuel System
Given an objective exercise, you will be able to: Identify the location of the components of the fuel system Identify the components of the fuel system Identify the purpose of the components of the fuel system Identify the purpose of the fuel system Identify the operation of the fuel system
Overview
The fuel system consists of different components that function together to distribute fuel to different engine systems and components. The fuel system consists of the following components:
Fuel pump Fuel/oil heat exchanger Fuel filter Servo fuel heater Hydromechanical unit (HMU) IDG fuel/oil heat exchanger Fuel flow transmitter Fuel manifolds Fuel nozzles Combustor drain valve
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
In this lesson, you will learn about the location, identification, and purpose of the components, and the operation of the fuel system.
Location Left Side View
The fuel system consists of components that are listed below. The fuel manifolds are mounted around the circumference of the CRF. The fuel nozzles are mounted around the circumference of the CRF.
Location Right Side View
The fuel system consists of components that are listed below. The fuel pump is installed on the right side of the aft face of the AGB. The fuel/oil heat exchanger is installed directly on the fuel pump on the inboard side.
The fuel filter is installed on the outboard side of the fuel pump.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
The servo fuel heater is installed on the right side of the accessory gearbox, just below the heat shield.
The hydromechanical unit (HMU) is bolted to the front face of the AGB, just below the IDG air/oil cooler.
The IDG fuel/oil heat exchanger is on the right side of the AGB, just below the servo fuel heater.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
The fuel flow transmitter is on the right side of the AGB, just aft of the HMU.
The combustor drain valve is installed on the seventh stage LPT cooling manifold at the 5:30 position.
Purpose
The fuel system receives fuel from the aircraft fuel tank. The fuel system then pressurizes and filters the fuel before supplying the correct quantity of fuel at the required pressure to the combustor for burning.
Operation
Fuel from the aircraft fuel tank enters the centrifugal boost stage of the fuel pump. The fuel then flows to the high pressure stage after passing
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
through the strainer. From here, the fuel flows to the fuel/oil heat exchanger and the fuel filter. The fuel filter removes impurities from the fuel. The clean fuel then enters the HMU. A portion of the fuel also enters the servo fuel heater, where the fuel gets heated before flowing into the HMU. The fuel metering valve in the HMU supplies the correct quantity of fuel to the fuel manifold through the fuel flow transmitter. From the fuel manifold, the fuel is distributed equally to 30 nozzles. The HMU ensures that excess fuel inside it is routed back to the fuel pump through the IDG fuel/oil heat exchanger. In case of an engine no-start, leaking fuel from the combustion chamber drains overboard through the combustor drain valve.
Fuel Pump
Location: The fuel pump is mounted on the right side of the aft face of the accessory gearbox. Identification: The fuel pump is driven directly by the AGB. The fuel pump consists of the following components:
Centrifugal boost stage High pressure stage Relief valve Drive shaft Interstage strainer
The fuel pump also has mounting surfaces for the fuel filter and the fuel/oil heat exchanger. Purpose: The fuel pump is
designed to provide sufficient fuel flow and pressure to meet engine burn flow requirements. The fuel
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
pump is also designed to supply servo fuel flow to all fuel-powered servo controls on the engine.
Fuel/Oil Heat Exchanger
Location: The fuel/oil heat exchanger is mounted directly on the fuel pump on the inboard side. Identification: The fuel/oil heat
exchanger is made up of a number of chambers containing tubes and baffles. The fuel/oil heat exchanger also has an oil bypass valve. Purpose: The function of the fuel/oil heat exchanger is to cool the engine oil and to heat the engine fuel. Cooling of the oil helps in maintaining the oil viscosity, and heating of the fuel prevents icing and improves fuel atomization.
Fuel Filter
Location: The fuel filter is installed on the outboard side of the fuel pump. Identification: The fuel filter contains a removable filter bowl with a disposable filter element. The bowl contains an inlet for fuel from the fuel pump, and an outlet for fuel to the HMU. The fuel filter also has a servo outlet port for sending a small quantity of fuel to the servo fuel heater. Purpose: The fuel filter is used to remove impurities from the fuel before the fuel flows to the HMU.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Servo Fuel Heater
Location: The servo fuel heater is mounted on the right side of the accessory gearbox, just below the heat shield. Identification: The servo fuel heater is a fuel/oil heat exchanger containing chambers with tubes and baffles. The servo fuel
heater also contains a delta pressure oil bypass valve and a thermal bypass valve. Purpose: flows servo fuel heater providesHMU. before it The to the servo section of the additional heating of the fuel
Hydromechanical Unit (HMU)
Location: The hydromechanical unit (HMU) is bolted to the front face of the AGB, just below the IDG air/oil cooler. Identification: The HMU contains the following valves:
Fuel metering valve (FMV) Pressurizing and shutoff valve (PSOV)
In addition, the HMU contains ports for providing interfaces with fuel inlets and outlets to and from different engine components. The HMU also contains connections for the ECU channel A and channel B connectors.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Purpose:
Meters and distributes the correct amount of fuel for combustion under all operating conditions Provides servo fuel pressure for the positioning of actuators and valves of the engine systems
IDG Fuel/Oil Heat Exchanger
Location: The IDG fuel/oil heat exchanger is on the right side of the AGB, just below the servo fuel heater. Identification: The IDG fuel/oil heat exchanger consists of a rectangular metal box with inlet and outlet connections for fuel. The inside of the box contains a number of chambers, baffles, and hollow tubes. The IDG fuel/oil heat exchanger also contains a bypass valve. Purpose: The IDG fuel/oil heat exchanger helps to cool the IDG oil.
Fuel Flow Transmitter
Location: The fuel flow transmitter is on the right side of the AGB, just aft of the HMU. Identification: The fuel flow
transmitter is an electro-mechanical component that consists of a rotor and a set of magnets with electrical coils. An electrical connector sends signals from the transmitter to the ECU.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Purpose: The fuel flow transmitter measures the total mass of fuel flow to the engine combustor. The fuel filter transmitter sends this information to the ECU as an electrical signal.
Fuel Manifolds
Location: The fuel manifolds are mounted around the circumference of the CRF. Identification: The engine contains a set of three fuel manifolds. Of these, two are fuel-feed manifolds and the third is the drain manifold. Each of the three manifolds is divided into two halves, one for each side of the engine. Purpose: The two fuel feed manifolds distribute metered fuel from the HMU to the 30 fuel nozzles. The drain manifold collects leaking fuel that may leak from the nozzle connections.
Fuel Nozzles
Location: The fuel nozzles are located around the circumference of the CRF. Identification: The engine contains 30 fuel nozzles. Each nozzle contains a check valve, primary, and secondary fuel flow circuits, and a fuel divider valve. Purpose: The fuel nozzles distribute atomized fuel to the combustor for combustion during starting, and for low and high power engine operations.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Combustor Drain Valve
Location: The combustor drain valve is mounted on the seventh stage LPT cooling manifold at the 5:30 position. Identification: The combustor drain valve is a spring-loaded drain valve with inlet and outlet fittings. Purpose: The combustor drain valve allows fuel and other liquids to drain overboard out of the rear of the engine nacelle.
Objectives
Control System
Given an objective exercise, you will be able to: Identify Identify Identify Identify Identify the the the the the location of the components of the control system components of the control system purpose of the components of the control system purpose of the control system operation of the control system
Overview
The control system consists of the following components that provide engine control under all operating conditions:
Electronic control unit (ECU) Permanent magnet alternator (PMA) Engine rating/identification plug N1 sensor N2 sensor T4.9 (EGT) sensors Ps3 sensor PO sensor T12 sensor Ps12 sensor
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
T2.5 sensor T3 sensor Fuel temperature sensor Thrust reverser position feedback RVDT sensor Optional sensors (T5 /Ps14 /P2.5 /P4.9)
In this lesson, you will learn about the location, identification, and purpose of the components, and the operation of the control system.
Location Left Side View
The components of the control system are listed below. The electronic control unit (ECU) is on the fan case at the 8:30 position. The permanent magnet alternator (PMA) is mounted to the left of the lube and scavenge pump on the forward side of the AGB.
The T4.9 exhaust gas temperature (EGT) sensors are installed around the circumference of the low pressure turbine (LPT) case.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
The T12 sensor is installed on the forward fan case at the 12 o'clock position.
The T3 sensor is installed on the CRF at the 11:30 position.
The T5 sensor is an optional control system component that is installed on the turbine rear frame (TRF) at the 9:30 position. The engine rating/identification plug is connected to the J11 connector on the ECU and is also attached to the fan case.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
The T2.5 sensor is installed on the aft side of the fan frame at the 7:30 position.
The Ps12 sensors are installed at approximately 10:30 and 1:30 positions on the forward fan case.
The PO sensor is at the bottom of the ECU.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
The Ps14 sensor is an optional control system component that is on the aft fan case at the 10:30 position.
The P2.5 sensor is an optional control system component that is installed on the aft side of the fan frame at the 7:30 position.
The Ps3 sensors are inside the ECU. Bleed air is ported from the 3 o'clock position on the CRF to the sensors through a tubing.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Location Right Side View
The components of the control system are listed below. The N1 sensor is installed on the fan frame at the 2 o'clock position.
The N2 sensor is installed on the front right side of the accessory gearbox, inboard of the HMU.
The P4.9 sensor is an optional control system that is on the LPT case at the 3:30 position.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
The fuel temperature sensor is installed between the fuel flow transmitter and the fuel manifolds.
Location
The components of the control system are listed below. The thrust reverser RVDT (rotary variable differential transducer) sensor is installed on a drive pad on top of the center drive unit (CDU) of the thrust reverser.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Purpose
The control system provides a complete range of engine control under all steady state and transient state engine operating conditions. This is done by accurately controlling the fuel flow, primary and parasitic airflows, internal clearances, start sequences and igniter operation. The system also controls the thrust reverser system operation.
Operation
The electrically powered ECU is the primary component of the engine control system. The ECU receives digital and analog data from different parts of the engine and the aircraft. Engine data includes information about speeds, pressures, and temperatures. This information is sent to the ECU by sensors mounted on different locations on the engine. The ECU also receives feedback from various engine actuators and valves. Information from the air system, the start system, the IDG system, the oil system, and the thrust reverser system is also sent to the ECU.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
The aircraft data includes information about the position of the thrust control levers and flight deck switches. In addition, information from the computers and display systems of the aircraft is also routed to the ECU The ECU processes different engine and aircraft inputs. The ECU controls the position of the fuel metering valve in the HMU so that the correct amount of fuel is sent to the combustion chamber, the engine actuators, and the valves. The control system also correctly positions the start system, the ignition system, and the thrust reverser system.
Electronic Control Unit
Location: The electronic control unit (ECU) is on the fan case at the 8:30 position. Identification: The ECU is a computer that is enclosed in an aluminum casing. The ECU contains electrical
connectors for interfacing with different engine and aircraft components. systems and
Purpose:
Controls the functioning of different engine systems and components under all operating conditions Provides inputs for display on the flight deck Checks for malfunctioning of important engine systems and components Allows basic maintenance testing of the engine systems and components
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
As an optional feature, the ECU monitors the functioning of certain engine parameters to help forecast trends in engine performance
Permanent Magnet Alternator
Location: The permanent magnet alternator (PMA) is mounted to the left of the lube and scavenge pump on the forward side of the AGB. Identification: consists of a The PMA
three-phase
magnetic rotor that is contained in a stator housing. Purpose: The PMA provides
electrical power to the ECU during regular engine operation.
Engine Rating/Identification Plug
Location: The engine rating/identification plug is connected to the J11 connector on the ECU and is also attached to the fan case. Identification: rating/identification The plug engine is an
electrical plug that is attached to the fan case by a lanyard. Purpose: The plug provides the thrust and engine configuration information to the ECU for the correct control of engine valves and actuators.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
N1 Sensor
Location: The N1 sensor is installed on the fan frame at the 2 o'clock position. Identification: The N1 sensor is a magnetic three pulse-type sensor and with two
electrical
coils
electrical connectors. Purpose: The N1 sensor provides two fan speed signals to the ECU and one to the flight deck. The fan speed signals help the ECU to perform the engine control functions, and to display the N1 indication on the engine warning display (EWD) on the flight deck.
N2 Sensor
Location: The N2 sensor is installed on the front right side of the accessory gearbox, inboard of the HMU. Identification: The N2 sensor is a magnetic with
pulse-type
sensor
three electrical coils and two electrical connectors. Purpose: The N2 sensor provides two core speed signals to the ECU and one to the flight deck. The core engine speed signals help the ECU to perform the various engine control functions, and to display the N2 indication on the engine warning display (EWD) on the flight deck
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
T4.9 (EGT) Sensors
Location: The T4.9 exhaust gas temperature (EGT) sensors are installed around the outside of the low pressure turbine (LPT) case. Identification: There are eight T4.9 (EGT) sensors that protrude into the discharge
airflow from the high pressure turbine (HPT). Four sensors are connected together using an electrical harness and are in the upper half of the LPT case. The remaining four sensors are connected using a different electrical harness and are in the lower half of the LPT case. Purpose: The T4.9 (EGT) sensors provide the temperature signals of the HPT discharge air to the electronic control unit (ECU). The HPT discharge air temperature helps the ECU to carry out engine control functions. The sensors also display the T4.9 (EGT) indication on the engine warning display (EWD) on the flight deck.
Ps3 Sensors
Location: The Ps3 sensors are inside the ECU. Bleed air is ported from the 3 o'clock position on the CRF to the sensors through a tubing. Identification: There are two Ps3 sensors. Each sensor is a pressure transducer. An air fitting that is located at the 3 o'clock position on the CRF is used to port the air to the two sensors.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Purpose: The purpose of the Ps3 sensors is to provide compressor discharge air pressure input to the ECU. The compressor discharge air pressure input helps the ECU to carry out engine control functions.
PO Sensor
Location: The PO sensor is at the bottom of the ECU. Identification: The PO sensor is the open port on the pressure manifold that is located at the bottom of the ECU. Purpose: The PO sensor provides ambient air pressure input to the ECU. The ambient air pressure input helps the ECU to carry out engine control functions.
T12 Sensor
Location: The T12 sensor is installed on the forward fan case at the 12 o'clock position. Identification: The T12 sensor is a resistant, thermal device that protrudes into the fan inlet airstream. Purpose: The T12 sensor provides a fan inlet air temperature input to the ECU. The fan inlet air temperature input helps the ECU to carry out engine control functions.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Ps12 Sensors
Location: The Ps12 sensors are installed at approximately 10:30 and 1:30 positions on the forward fan case. Identification: There are two Ps12 sensors, both of which are static ports on the fan case. Purpose: The Ps12 sensors provide the fan inlet air pressure to the ECU to help it to carry out engine control functions.
T2.5 Sensor
Location: The T2.5 sensor is mounted on the aft side of the fan frame at the 7:30 position.
Identification:
The
T2.5
sensor
is
resistant, temperature detector-type sensor that protrudes into the HPC inlet airstream. Purpose: The T2.5 sensor provides the HPC inlet air temperature input to the ECU. The HPC inlet air temperature input helps the ECU to carry out engine control functions
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
T3 Sensor
Location: The T3 sensor is installed on the CRF at the 11:30 position. Identification: The T3 sensor is a thermocouple sensor that protrudes into the HPC discharge airflow. Purpose: The T3 sensor provides the temperature of the HPC discharge air to the ECU. The HPC discharge air temperature helps the ECU carry out engine control functions.
Fuel Temperature Sensor
Location: The fuel temperature sensor is installed between the fuel flow transmitter and the fuel manifolds. Identification: The fuel temperature sensor is a thermocouple sensor with two junctions. The two junctions of the thermocouple sensors are immersed in the fuel that flows from the HMU to the fuel manifolds.
Purpose: The fuel temperature sensor measures the temperature of the metered fuel that is discharged from the HMU, and sends this information to the ECU. The ECU uses this signal to control the IDG air/oil cooler control valve.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Thrust Reverser Position Feedback RVDT Sensor
Location: The thrust reverser position feedback RVDT (rotary variable differential transducer) sensor is installed on a drive pad on top of the center drive unit (CDU) of the thrust reverser. Identification: The thrust reverser position feedback RVDT sensor is an electronic components. position sensor The with thrust RVDT mechanical reverser sensor
feedback
contains a reduction gearbox assembly that is attached to dual variable transducers. Purpose: The thrust reverser position feedback RVDT sensor sends information about the position of the translating cowl to the ECU.
T5 Sensor
Location: The T5 sensor is an optional control system component that is installed on the turbine rear frame at the 9:30 position. Identification: The T5 sensor consists of two
thermocouples with junctions at two different locations along the axis of the sensor. Purpose: The T5 sensor provides the total temperature of the LPT discharge airflow to the ECU.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Ps14 Sensor
Location: The Ps14 sensor is an optional control system component that is on the aft fan case at the 10:30 position. Identification: The Ps14 sensor
consists of a probe that is connected to a pressure transducer in the ECU through an external air tube. Purpose: The Ps14 sensor provides the ECU with an indication of the static pressure of the fan discharge airflow for extended condition monitoring of the engine performance.
P2.5 Sensor
Location: The P2.5 sensor is an optional control system component that is installed on the aft side of the fan frame at the 7:30 position. Identification: The P2.5 sensor is a pressure transducer that is connected to the ECU through an external air tube. The air tube ports air to the ECU from the cone-shaped opening on top of the T2.5 sensor. Purpose: The P2.5 sensor provides the ECU with an indication of the pressure of the HPC inlet airstream for extended condition monitoring of the engine performance.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
P4.9 Sensor
Location: The P4.9 sensor is installed at the 3:30 o'clock position on the LPT case, just aft of the forward flange. The P4.9 sensor is optional. Identification: The P4.9
sensor has four cone-shaped total pressure inputs machined into a raised boss on the leading edge of the probe. Purpose: The P4.9 sensor
supplies the total pressure of the LPT inlet airflow to the ECU for extended conditioning monitoring of the engine performance.
Objectives
Air Control System
Given an objective exercise, you will be able to:
Identify Identify Identify Identify Identify
the the the the the
location of the components of the air control system components of the air control system purpose of the components of the air control system purpose of the air control system operation of the air control system
Overview
The air control system consists of different subsystems and components that regulate air in different areas of the engine. The air control system consists of the following subsystems and components:
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Bore cooling system Variable stator vane (VSV) system Variable bleed valve (VBV) system Core compartment cooling system High pressure turbine active clearance control (HPTACC) Low pressure turbine active clearance control (LPTACC) 7th stage delta pressure switches IDG air/oil cooling system
In this lesson, you will learn about the location, identification, and purpose of the components, and operation of the air control system.
Location Left Side View
The components of the air control system are listed below. The bore cooling system consists of components that are installed on the outer surface of the aft fan case and along the length of the core module. The variable bleed valve (VBV) system consists of components that are installed around the hub of the fan frame. The core compartment cooling system consists of components that are on the upper left-hand side of the HPC and around the engine. The components of the low pressure turbine active clearance control (LPTACC) system are installed at the 9 o'clock position on the core engine and also around the LPT. The 7th stage delta pressure switches are installed at the 11:30 position on the outer surface of the HPC case.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Location Right Side View
The components of the air control system are listed below. The high pressure turbine active clearance control (HPTACC) system starts at the 2 o'clock position on the HPC outer case. From this position, the HPTACC system extends around the outer surface of the HPT case. The IDG air/oil cooling system consists of components that are installed on the right hand side of the HPC. The VSV system consists of components that are installed on the outer surface of the HPC from the inlet guide vanes (IGV) to the stage 5 variable stator vanes.
Purpose
The purpose of the air control system is to regulate supply of air through the engine. This ensures proper functioning of different engine control and cooling systems, and optimizes specific fuel consumption.
Operation
Using the core speed and engine temperature inputs, the ECU regulates the opening and closing of the three bore cooling valves on the aft fan case. This makes sure that during cruise conditions, the engine core receives optimum primary airflow.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
The ECU also uses the altitude and fan speed inputs to regulate the opening and closing of the core compartment cooling valve. This makes sure that the core compartment receives the optimum amount of cooling airflow during all operating conditions.
The ECU sends a signal to the hydromechanical unit (HMU) to meter fuel pressure to open or close the HPT and LPT active clearance control valves. This keeps the clearances between the HPT turbine shrouds and the HPT rotor blades and between the LPT turbine shrouds and the LPT rotor blades to a minimum.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
The ECU uses the core speed, the temperature and the altitude inputs to regulate the flow of fuel from the HMU to the variable stator vane (VSV) actuators. The actuators position the variable stator vanes in the HPC to prevent stalling of the compressor and to optimize performance.
Similarly, the ECU uses the core speed, Mach number, and altitude inputs to regulate fuel flow from the HMU to the variable bleed valve (VBV) actuators. The VBV actuators position the variable bleed valves so that an optimum amount of bleed air flows from the LPC to the HPC. This flow of air optimizes compressor performance and prevents stalling.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Bore Cooling System
Location: The bore cooling system consists of components that are installed on the outer surface of the aft fan case and along the length of the core module. Identification: The bore cooling
system consists of three bore cooling valves and pneumatic tubing. Purpose: The function of the bore cooling system is to cool the HPC rotor. However, during cruise conditions, the system optimizes the primary airflow by reducing the cooling airflow to the bore of the HPC.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
VSV System
Location: The variable stator vane (VSV) system consists of components that are installed on the outer surface of the HPC from the inlet guide vanes (IGV) to the stage 5 variable stator vanes. Identification: The VSV system consists of the following components:
Stage 1 variable inlet guide vanes (IGV) Stages 2 to 5 variable stator vanes VSV actuation mechanism
Purpose: The VSV system controls the amount of airflow through the HPC to prevent the compressor from stalling, and to optimize compressor performance.
VBV System
Location: The variable bleed valve (VBV) system consists of components that are installed around the hub of the fan frame. Identification: The system consists of the following components:
Variable bleed valves (VBV) VBV actuation mechanism
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Purpose: The VBV system regulates the flow of air to the HPC by controlling the amount of bleed from the LPC. This helps to prevent the compressor from stalling, and also optimizes compressor performance.
Core Compartment Cooling System
Location: The core compartment cooling system consists of components that are on the upper left-hand side of the HPC and around the engine. Identification: consists of components:
The system the following
Core compartment cooling valve Core compartment cooling manifold Fan discharge air duct
Purpose: The core compartment cooling system cools and removes fumes from the closed engine core compartment. The core compartment cooling system provides maximum cooling airflow to the core compartment during all operating conditions. However, during cruise, the supply of the cooling airflow is reduced to optimize engine performance.
HPT Active Clearance Control
Location: The high pressure turbine active clearance control (HPTACC) system starts at the 2 o'clock position on the HPC outer case. From this position, the HPTACC system extends around the outer surface of the HPT case.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Identification: The HPTACC system consists of the following components:
HPTACC valve HPTACC manifold
Purpose: The function of the HPTACC system is to regulate the flow of cooling air to the HPT case and minimize clearances
between the HPT shrouds and the HPT rotor blades. This helps to improve the specific fuel consumption of the engine.
LPT Active Clearance Control
Location: The components of the low pressure turbine active clearance control (LPTACC) system are installed at the 9 o'clock position on the core engine and also around the LPT. Identification: The LPTACC system consists of the following components:
LPTACC valve LPTACC manifold
Purpose: The purpose of the LPTACC system is to regulate the flow of cooling air to the LPT case to minimize clearances between the LPT shrouds and the LPT rotor blades. This helps to improve the specific fuel consumption of the engine during cruise conditions.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
7th Stage Delta Pressure Switches
Location: The 7th stage delta pressure switches are installed at the 11:30 position on the outer surface of the HPC case. Identification: There are two 7th stage delta pressure switches, both of which are installed in a rectangular unit. Each switch is a double-pole, double-throw type. Purpose: The function of the 7th stage delta pressure switches is to monitor air pressure in the 7th stage manifolds. In the event of a duct leakage, a fault indication signal is sent to the ECU.
IDG Air/Oil Cooling System
Location: The IDG air/oil cooling system consists of components that are installed on the righthand side of the HPC. Identification: IDG air/oil The cooling
system consists of the following components:
IDG air/oil cooler IDG air/oil cooler shutoff valve
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Purpose: The purpose of the IDG air/oil cooling system is to regulate the flow of fan discharge air to the IDG air/oil cooler during cruise conditions. This is done to optimize specific fuel consumption.
Objectives
Oil System
Given an objective exercise, you will be able to: Identify Identify Identify Identify Identify the the the the the location of the components of the oil system components of the oil system purpose of the components of the oil system purpose of the oil system operation of the oil system
Overview
The oil system consists of the following components that function together to distribute oil to engine bearings, gears, and other components for lubrication and cooling:
Oil tank Oil tank pressurization valve Oil tank filler cap Oil tank quantity transmitter Lube and scavenge pump Oil pressure transmitters Oil pressure signal amplifier Low oil pressure switch Oil temperature sensor Master chip detector Fuel/oil heat exchanger Servo fuel heater Scavenge oil filter Scavenge oil filter differential pressure switch
In this lesson, you will learn about the location, identification, and purpose of the components, and operation of the oil system.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Location Left Side View
The oil system consists of components that are listed below. The master chip detector (MCD) is installed in the main scavenge line aft of the AGB, at the 6 o'clock position.
The oil pressure signal amplifier is installed on the aft fan case at approximately 7 o'clock position.
The oil pressure transmitters are installed on a bracket in front of the lube and scavenge pump.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
The low oil pressure switch is installed on the forward end of the lube and scavenge pump.
The oil temperature sensor is installed on a flange in the oil scavenge line, just inboard of the lube and scavenge pump.
The lube and scavenge pump is installed on the forward left side of the AGB, just inboard of the hydraulic pump.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Location Right Side View
The oil system consists of components that are listed below. The oil tank is installed on the aft fan case at the 3 o'clock position. The oil tank pressurization valve is installed on top of the oil tank, to the right of the scavenge return tube.
The oil tank filler cap is installed on the upper right side of the oil tank on top of the scupper drain.
The oil tank quantity transmitter is installed on top of the oil tank, to the left of the scavenge return tube.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
The fuel/oil heat exchanger is installed on the inboard side of the fuel pump.
The servo fuel heater is installed on the right side of the AGB, just below the heat shield.
The scavenge oil filter is installed on the aft fan case at the 3:30 position, below the oil tank.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
The scavenge oil filter differential pressure switch is installed on a bracket at the 3:30 position on the aft fan case, just above the scavenge oil filter.
Purpose
The oil system distributes lubricating oil to the engine sump bearings, and gears, and recycles oil from different areas of the engine for reuse. In addition, the oil system indicates information about oil system parameters such as oil quantity, oil pressure, and oil temperature to the ECU.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Operation
The oil in the oil tank flows to the lube and scavenge pump. Here, the oil is pressurized and sent through the oil filter to the oil nozzles in the engine sumps, the AGB, and the transfer gearbox (TGB). A small portion of the pressurized oil is sent to the low oil pressure switch and to the oil pressure transmitters. The lube and scavenge pump gathers the scavenge oil from the sumps and the gearboxes and sends it to a common scavenge line. The scavenge oil then flows over the oil temperature sensor and the master chip detector. Later, the scavenge oil flows through the servo fuel heater, the fuel/oil heat exchanger, the scavenge oil filter, and finally into the oil tank. Signals from all oil system sensors, except the low oil pressure switch, are transmitted to the ECU for monitoring system conditions and indications on the flight deck.
Oil Tank
Location: The oil tank is installed on the aft fan case at the 3 o'clock position.
Identification: The oil tank is made of aluminum, and consists of two oil chambers. The oil tank is equipped with an internal air/oil separator, an oil quantity sensor, an external sight gage, a pressurizing valve, and a relief valve.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Purpose: The oil tank is a reservoir that is used to store engine oil. The oil tank also delivers the stored engine oil to the lube and scavenge pump.
Oil Tank Pressurization Valve
Location: The oil tank pressurization valve is installed on top of the oil tank, to the right of the scavenge return tube.
Identification: The oil tank pressurization valve is connected to the A-sump through a vent tube. Purpose: The oil tank pressurization valve maintains a positive head pressure on the oil in the tank. The positive head pressure makes sure that a constant and pressurized oil feed is available to the lube and scavenge pump at all times.
Oil Tank Filler Cap
Location: The oil tank filler cap is installed on the upper right side of the oil tank on top of the scupper drain. Identification: The oil tank filler cap
contains a self-sealing flapper valve. Purpose: The oil tank filler cap seals the opening that is used to manually fill oil in the oil tank.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Oil Tank Quantity Transmitter
Location: The oil tank quantity transmitter is installed on top of the oil tank, to the left of the scavenge return tube. Identification: The oil tank quantity transmitter consists of a number of reed switches and a float assembly with magnets installed on it. The transmitter has two sensing circuits, each of which sends signals to the ECU through separate cables. Purpose: The transmitter indicates the oil level in the oil tank to the ECU. The ECU then transmits this information to the flight deck.
Lube and Scavenge Pump
Location: The lube and scavenge pump is installed on the forward left side of the AGB, just inboard of the hydraulic pump.
Identification:
The
lube
and
scavenge pump is a rotary vane-type pump. The shaft of the lube and scavenge pump is driven by the AGB. The pump has one pressure element and five scavenge elements. In
addition, the pump consists of six mesh inlet screens, an outlet filter, and an anti-static check valve.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Purpose: The lube and scavenge pump delivers pressurized oil to the engine bearing in the four sumps and to the gears in the AGB and the transfer gearbox. In addition, the pump also collects the engine oil from the sumps and the gearboxes for reuse.
Oil Pressure Transmitters
Location: The oil pressure transmitters are installed on a bracket in front of the lube and scavenge pump. Identification: There are two oil pressure transmitters that are placed adjacent to each other. Each transmitter is a piezoelectric device. Purpose: The oil pressure transmitters
provide electrical signals that indicate oil pressure conditions within the bearing sumps. These electrical signals are transmitted to the ECU for display on the flight deck.
Oil Pressure Signal Amplifier
Location: The oil pressure signal amplifier is installed on the aft fan case at approximately 7
o'clock position.
Identification: The oil pressure signal amplifier is an electrical
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
component that is mounted on the aft fan case using a clamp and nut arrangement. Purpose: The oil pressure signal amplifier amplifies the signals received from the two oil pressure transmitters before sending them to the ECU.
Low Oil Pressure Switch
Location: The low oil pressure switch is installed on the forward end of the lube and scavenge pump. Identification: The low oil pressure switch consists of a Belleville-type bellows whose motion is controlled by a negative-rate snap ring. Purpose: The low oil pressure switch provides a signal to the aircraft indicating and warning systems when the oil pressure is low.
Oil Temperature Sensor
Location: The oil temperature sensor is installed on a flange in the oil scavenge line, just inboard of the lube and
scavenge pump. Identification: The oil
temperature sensor consists of two thermocouples that are
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
in a stainless steel shell. An electrical connector from each thermocouple provides an electrical signal to the ECU. Purpose: The oil temperature sensor indicates the engine oil temperature to the ECU. The ECU transmits the engine oil temperature information to the flight deck on the aircraft engine warning display (EWD) system.
Master Chip Detector
Location: The master chip detector (MCD) is installed in the main scavenge line aft of the AGB, at the 6 o'clock position.
Identification: The MCD is a bayonet, three-pin type, permanent magnet probe that is fitted in a housing. The MCD is immersed in the scavenge oil that is flowing from the lube and scavenge pump to the servo fuel heater. Purpose: The MCD traps magnetic particles that are suspended in the scavenge oil.
Fuel/Oil Heat Exchanger
Location: The fuel/oil heat exchanger is installed on the fuel pump on the inboard side. Identification: The fuel/oil heat exchanger is made up of a number of chambers containing tubes and baffles. The fuel/oil heat exchanger also has an oil bypass valve.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Purpose: The function of the fuel/oil heat exchanger is to cool the engine oil and also to heat the engine fuel. Cooling of the oil helps in maintaining the oil viscosity, and heating of the engine fuel prevents icing and improves atomization
Servo Fuel Heater
Location: The servo fuel heater is installed on the right side of the AGB, just below the heat shield. Identification: The servo fuel heater is a fuel/oil heat exchanger containing chambers
with tubes and baffles. The servo fuel heater also contains a high-
pressure, delta pressure oil bypass valve, and a thermal bypass valve. Purpose: The servo fuel heater provides additional heating of the fuel before the fuel flows to the servo section of the HMU.
Scavenge Oil Filter
Location: The scavenge oil filter is located on the aft fan case at the 3:30 position, below the oil tank.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Identification: The scavenge oil filter consists of a removable filter bowl and a disposable filter element. The scavenge oil filter also contains a shutoff valve and a bypass valve. Purpose: The scavenge oil filter removes contamination from the engine oil before the oil flows into the oil tank.
Scavenge Oil Filter Differential Press. Switch
Location: The scavenge oil filter differential pressure switch is installed on a bracket at the 3:30 position on the aft fan case, just above the scavenge oil filter. Identification: The scavenge oil filter differential Belleville-type pressure bellows. switch The contains of a the
motion
bellows is controlled by a negative rate snap ring. Purpose: The scavenge oil filter differential pressure switch measures the differential
pressure across the inlet and outlet of the scavenge oil filter. The switch provides an indication of the impending bypass of the oil filter to the flight deck.
Objectives
Start System
Given an objective exercise, you will be able to:
Identify Identify Identify Identify Identify
the the the the the
location of the components of the start system components of the start system purpose of the components of the start system purpose of the start system operation of the start system
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Overview
The start system consists of the following components:
Starter Starter air valve
The components of the start system function together to provide the initial starting torque to the engine core to start the combustion process. In this lesson, you will learn about the location, identification, and purpose of the components, and the operation of the start system.
Location Left Side View
The start system consists of components that are listed below. The starter is clamped to the aft face of the AGB at the 6 o'clock position.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
The starter air valve is installed aft of the air starter at the 6 o'clock position on the AGB.
Purpose
The start system provides driving torque to the AGB. The driving torque to the AGB accelerates the HPC rotor from rest to a sufficiently high rotational speed to start self-sustaining combustion of fuel. The start system also helps to motor the engine for dry and wet operation during maintenance.
Operation On receiving the engine start signal from the flight deck, the
ECU sends an electrical signal to the starter air valve. This opens the butterfly valve in the starter air valve and high pressure air from a ground power unit (GPU) or an auxiliary power unit (APU), flows to the starter, causing the gears to rotate.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
The rotating starter gears cause the starter output shaft to rotate, which drives the AGB. The AGB provides driving torque to the core engine. At a certain speed, combustion begins to occur, and engine speed increases. When the core engine speed reaches a certain value, the starter disengages from the AGB. The ECU stops the electrical signal to the starter air valve, thus ending air supply to the starter.
Starter
Location: The starter is clamped to the aft face of the AGB at the 6 o'clock position. Identification: The starter consists of a single-stage turbine, an output shaft, and several bearings and gears that are contained in a metal housing. One end of the housing has a port for air inlet. The other end of the housing has a port for the output shaft.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Purpose: The starter supplies driving torque to turn the AGB. The starter also drives the AGB for wet and dry engine motoring during maintenance.
Starter Air Valve
Location: The starter air valve is installed aft of the air starter at the 6 o'clock position on the AGB.
Identification: The starter air valve consists of the following components:
Valve body assembly Actuator assembly Relief valve assembly Solenoid valve assembly Position switch assembly
Purpose: The starter air valve initiates, and later, stops the flow of pressurized air to the starter.
Objectives
Ignition System
Given an objective exercise, you will be able to:
Identify Identify Identify Identify Identify
the the the the the
location of the components of the ignition system components of the ignition system purpose of the components of the ignition system purpose of the ignition system operation of the ignition system
Overview
The ignition system consists of the following components:
Ignition exciters Ignition leads Igniters
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
In this lesson, you will learn about the location, identification, and purpose of the components, and operation of the ignition system.
Location Left Side View
The ignition system consists of the components that are listed below. The ignition exciters are installed on the aft fan case at the 8 o'clock position.
The ignition leads begin from the ignition exciters on the aft fan case, and go down to the 6 o'clock position on it. The leads now pass to the HMU along the right side of the core module. Finally, the leads connect to the igniters on the compressor rear frame (CRF).
Location Right Side View
The ignition system consists of the components that are listed below. The igniters are installed on the right side of the compressor rear frame at the 3:30 and 5 o'clock positions.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Purpose
The ignition system supplies the electrical spark required for combustion of the fuel/air mixture during the starting operation and for continuous ignition operation.
Operation
The aircraft electrical system supplies 115-volt, AC power signal to the ECU. The ECU sends this electrical signal to the ignition exciters. The ignition exciters now convert AC power to DC, and send high voltage current to the igniters through the ignition leads.
Ignition Exciters
Location: The ignition exciters are installed on the aft fan case at the 8 o'clock position. Identification: The engine
contains two ignition exciters, 'A' and 'B'. Each exciter
consists of an aluminum case,
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
which contains electrical circuits. Each sealed case is pressurized with dry air. An input electrical connector provides power from the ECU to the exciter. An output electrical connector transmits power from the exciter to the igniter plugs through the ignition leads. Purpose: The exciters convert 115-volt AC current received from the ECU to 14,000 to 18,000-volt DC output. This DC output is then supplied to the igniters at a rate of approximately one electrical pulse per second.
Ignition Leads
Location: The ignition leads begin from the ignition exciters on the aft fan case, going down to the 6 o'clock position on it. The leads then pass by the HMU along the right side of the core module. Finally, the leads connect to the igniters on the compressor rear frame (CRF). Identification: There are two ignition leads. Each lead consists of an insulated wire in a sealed flexible conduit, which has a copper inner braid and a nickel outer braid. The aft ends of the leads allow fan discharge air to pass through the conduit for cooling. Purpose: The ignition leads deliver high voltage, low current electrical signals from the ignition exciters to the igniters.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Igniters
Location: The igniters are installed on the right side of the CRF at the 3:30 and 5 o'clock positions. Identification: There are two igniters. Each igniter consists of a center electrode that is insulated from the outer shell. When installed, the tip of this electrode extends through ferrules into the outer liner of the combustion chamber. Purpose: The igniters provide electrical sparks to start combustion.
IDG oil Cooling System
Objectives
Given an objective exercise, you will be able to:
Identify Identify Identify Identify Identify
the the the the the
location of the components of the IDG oil cooling system components of the IDG oil cooling system purpose of the components of the IDG oil cooling system purpose of the IDG oil cooling system operation of the IDG oil cooling system
Overview
The integrated drive generator (IDG) oil cooling system consists of the following components:
IDG air/oil cooler IDG air/oil cooler shutoff valve IDG fuel/oil heat exchanger
In this lesson, you will learn about the location, identification, and purpose of the components, and operation of the IDG oil cooling system.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Location Right Side View
The components of the IDG oil cooling system are listed below. The IDG air/oil cooler is installed on a bracket on the right side of the high pressure compressor (HPC) at the 3 o'clock position.
The IDG air/oil cooler shutoff valve is installed on a bracket on the right side of the HPC at the 3 o'clock position.
The IDG fuel/oil heat exchanger is installed on the right side of the accessory gearbox (AGB), just below the servo fuel heater.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Purpose
The IDG air/oil cooling system helps to cool the heated IDG oil flowing through the IDG.
Operation
Hot oil in the IDG flows to the IDG air/oil cooler, where the oil is cooled by fan discharge air that blows in through the IDG air/oil cooler shutoff valve. The oil then enters the IDG fuel/oil heat exchanger where the oil is further cooled by the fuel flowing through the IDG fuel/oil heat exchanger.
IDG Air/Oil Cooler
Location: The IDG air/oil cooler is installed on a bracket on the right side of the high pressure compressor (HPC) at the 3 o'clock position. Identification: The IDG air/oil cooler is a tubeand-fin type heat exchanger. The IDG air/oil cooler consists of tubes that are surrounded by cooling fins. The cooler has inlets for air and oil, and an outlet for the oil.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Purpose: The IDG air/oil cooler provides cooling of the IDG oil that flows through the IDG air/oil cooler.
IDG Air/Oil Cooler Shutoff Valve
Location: The IDG air/oil cooler shutoff valve is installed on a bracket on the right side of the HPC at the 3 o'clock position. Identification: The IDG air/oil cooler shutoff valve consists of a butterfly valve and has an inlet connection for the 11th stage muscle air and an electrical connection for the ECU cable. Purpose: The IDG air/oil cooler shutoff valve controls the flow of air through the IDG air/oil cooler.
IDG Fuel/Oil Heat Exchanger
Location: The IDG fuel/oil heat exchanger is installed on the right side of the accessory gearbox (AGB), just below the servo fuel heater. Identification: The IDG fuel/oil heat exchanger consists of a number of metallic tubes that are enclosed in a rectangular metal box. The box
contains baffles and chambers, and has an inlet port and an outlet port.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Purpose: The IDG fuel/oil heat exchanger cools the IDG oil that flows through the tubes of the heat exchanger.
Objectives
Vibration Monitoring System
Given an objective exercise, you will be able to:
Identify system Identify Identify system Identify Identify
the location of the components of the vibration monitoring the components of the vibration monitoring system the purpose of the components of the vibration monitoring the purpose of the vibration monitoring system the operation of the vibration monitoring system
Overview
The vibration monitoring system consists of the following components:
No. 1 bearing accelerometer CRF accelerometer Remote charge converter
In this lesson, you will learn about the location, identification, and purpose of the components, and the operation of the vibration monitoring system.
Location Left Side View
The components of the vibration monitoring system are listed below. The No. 1 bearing accelerometer, also called the fan vibration sensor, is installed in the A-sump. The No. 1 bearing accelerometer is bolted to the No. 1 bearing housing at the 6 o'clock position. The accelerometer lead extends through the fan frame strut at the 7 o'clock position.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
The CRF accelerometer, also called the N2 vibration sensor, is installed on the CRF forward flange at the 10 o'clock position. The accelerometer lead extends to a bracket on the HPC stator case at the 11 o'clock position.
Location Right Side View
The vibration monitoring system consists of components that are listed below. The remote charge converter (RCC) is installed on the aft fan case at the 5 o'clock position.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Purpose
The vibration monitoring system senses the engine vibration levels and provides the flight deck with an indication of an abnormal engine operation.
Operation
The No.1 bearing accelerometer and the CRF accelerometer sense the vibrations around their installed locations and send indications to the RCC as analog inputs. The RCC amplifies these weak signals and sends them to the engine interface and vibration monitoring unit (EIVMU). The EIVMU then converts the analog signals to digital output and sends them to the flight deck for display on the system display (SD).
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
No. 1 Bearing Accelerometer
Location: The No. 1 bearing accelerometer, also called the fan vibration sensor, is installed in the A-sump. It is bolted to the No. 1 bearing housing at the 6 o'clock position. The accelerometer lead extends through the fan frame strut at the 7 o'clock position. Identification: The No. 1 bearing accelerometer consists of a pickup, an electrical lead, and a connector. Purpose: The No. 1 bearing accelerometer senses the vibration levels in the areas around the fan rotor and the LPT rotor.
CRF Accelerometer
Location: The CRF accelerometer, also called the N2 vibration sensor, is installed on the CRF forward flange at the 10 o'clock position. The accelerometer lead extends to a bracket on the HPC stator case at the 11 o'clock position. Identification: The CRF accelerometer consists of a pickup, an electrical lead, and a connector. Purpose: The CRF accelerometer senses the vibration levels in the areas around the HPC rotor and the HPT rotor.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Remote Charge Converter
Location: The remote charge converter (RCC) is installed on the aft fan case at the 5 o'clock position. Identification: The RCC consists of two
identical processing channels with associated circuitry, and three electrical connectors. Purpose: The RCC amplifies the weak vibration signals received from the the CRF No. 1 bearing
accelerometer
and
accelerometer
before transmitting them to the EIVMU.
Objectives
Drain System
Given an objective exercise, you will be able to: Identify Identify Identify Identify Identify the the the the the location of the components of the drain system components of the drain system purpose of the components of the drain system purpose of the drain system operation of the drain system
Overview
The drain system consists of the following components:
Drain tubes Drain mast
In this lesson, you will learn about the location, identification, and purpose of the components, and the operation of the drain system.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Location Left Side View
The drain system consists of components that are listed below. The drain mast is installed at the 6 o'clock position at the end of the tube bundle.
The drain tubes originate from different locations on the engine, from the accessories, and the pylon drain cavities. The drain tubes converge at the 6 o'clock position on the engine to form the tube bundle, or go directly overboard through the nacelle.
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
Purpose
The drain system collects and carries overboard all toxic and flammable fluids and vapors that accumulate in the nacelle and engine cavities through outlets in the nacelle.
Operation
The drain tubes collect leaking or overflowing fluids and vapors from different locations. These locations are the fuel manifold, the pylon, the IDG, the starter, the hydraulic pumps, the HMU, the HPTACC, the LPTACC, the VSV, and the VBV. The collected fluids and vapors are then transported overboard through openings in the nacelle.
Drain Tubes
Location: The drain tubes originate from different locations on the engine, the accessories, and the pylon drain cavities. The drain tubes converge at the
Created by Rafik Chabou
ENGINE CF6-80E1
General Familiarization
6 o'clock position on the engine to form the tube bundle at the drain mast, or go directly overboard through openings in the nacelle. Identification: The drain tubes consist of a series of tubes. Purpose: The drain tubes collect and carry overboard all overflowing or leaking fluids and vapors from the engine, the accessories, and the pylon drain cavities.
Drain Mast
Location: The drain mast is installed at the 6 o'clock position at the end of the tube bundle.
Identification: The drain mast is bolted to the lower portion of the bifurcation and comes out through the thrust reverser cowl doors. Purpose: The drain mast provides a centralized collection point from where fluids and vapors that are transported by the drain tubes are directed overboard.
You might also like
- EPR Vs N1Document9 pagesEPR Vs N1Xana Amaral100% (1)
- Ata 49 Apu PDFDocument177 pagesAta 49 Apu PDFAaron Harvey100% (4)
- EvansDocument64 pagesEvansS BhoopalNo ratings yet
- Volare Questions - AerodynamicsDocument45 pagesVolare Questions - Aerodynamicspontoo67% (3)
- TFE 731 Chap 73Document34 pagesTFE 731 Chap 73Egor85100% (2)
- Trent 700 73-Aj366Document246 pagesTrent 700 73-Aj366ArabyAbdel Hamed Sadek100% (1)
- Borescope BelendingDocument2 pagesBorescope BelendingArabyAbdel Hamed SadekNo ratings yet
- D20 25 30 33 35NXP Stage-V (Sb1800e)Document768 pagesD20 25 30 33 35NXP Stage-V (Sb1800e)Yuda PratamaNo ratings yet
- A330 Important PointsDocument4 pagesA330 Important PointsArindam Dutta100% (1)
- Engine Change BootstrapDocument5 pagesEngine Change Bootstrapolegprikhodko2809No ratings yet
- 49 Honeywell 131-9A Diff L3 Aug09 XDocument36 pages49 Honeywell 131-9A Diff L3 Aug09 XHo Viet Thang100% (1)
- Volare Questions - NavigationDocument62 pagesVolare Questions - NavigationChabou Rafik100% (1)
- Volare Questions - MeteorologyDocument86 pagesVolare Questions - Meteorologypontoo100% (5)
- Volare Questions - Human FactorDocument85 pagesVolare Questions - Human Factorpontoo100% (2)
- CFM56-5A-5B CO-063 Basic Engine Feb2014Document27 pagesCFM56-5A-5B CO-063 Basic Engine Feb2014Kelik Arif100% (1)
- V2500 Line and Base Maintenance Power PlantDocument42 pagesV2500 Line and Base Maintenance Power PlantHENIGUEDRINo ratings yet
- All Parts of Starter Motor and FunctionDocument4 pagesAll Parts of Starter Motor and FunctionBeverly Sotomayor CrisologoNo ratings yet
- A330 PneumaticDocument27 pagesA330 PneumaticTienek Lee100% (1)
- Trent 700 Propulsion System OverviewDocument66 pagesTrent 700 Propulsion System OverviewShusant Saha100% (3)
- Atco 27 Rider ManualDocument34 pagesAtco 27 Rider ManualBestManuals4u100% (1)
- 145 ORGSbyCompanyNameDocument253 pages145 ORGSbyCompanyNameChabou RafikNo ratings yet
- A330 (GE CF6-80E1) : Engine & Correlated ATA 71 Up 80Document394 pagesA330 (GE CF6-80E1) : Engine & Correlated ATA 71 Up 80Diego Rafael50% (2)
- Wren 80i Gas Turbine Engine Tech SpecsDocument25 pagesWren 80i Gas Turbine Engine Tech SpecsAlex Stihi100% (1)
- COMMERCIAL AIRCRAFT ENGINES POWERING A318-A321Document2 pagesCOMMERCIAL AIRCRAFT ENGINES POWERING A318-A321syahirazaihadNo ratings yet
- CFM International CFM56: Type National Origin Manufacturer First Run Major ApplicationsDocument13 pagesCFM International CFM56: Type National Origin Manufacturer First Run Major ApplicationsBeing AirWindNo ratings yet
- Volare Answers - Airplane SystemsDocument5 pagesVolare Answers - Airplane SystemsChabou Rafik0% (2)
- CTC-601 - Lexis - LEAP ENGINES - Sep 15 - (USB CD Lexis Version Only)Document9 pagesCTC-601 - Lexis - LEAP ENGINES - Sep 15 - (USB CD Lexis Version Only)estevamjr100% (4)
- 70 Power Plant CFM 56Document322 pages70 Power Plant CFM 56Agam Septiana100% (1)
- APU 131-9A: Vibhu Agrawal Ets/Cte, Ial, HydDocument105 pagesAPU 131-9A: Vibhu Agrawal Ets/Cte, Ial, HydAnirban MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Volare Questions - InstrumentationDocument46 pagesVolare Questions - Instrumentationpontoo33% (3)
- Analysis Calculation Performance Engine Turbofan Cfm56Document8 pagesAnalysis Calculation Performance Engine Turbofan Cfm56AswanTajuddin100% (1)
- Engine CFM56Document7 pagesEngine CFM56raisiflyNo ratings yet
- Volare Questions - Airplane SystemsDocument68 pagesVolare Questions - Airplane Systemspontoo100% (2)
- Fan Trim BalanceDocument44 pagesFan Trim BalanceSylvester Obara100% (1)
- Trent 700 Series Issue 03Document9 pagesTrent 700 Series Issue 03HelloWorldNo ratings yet
- Choice Global Support Capability: Flight HoursDocument9 pagesChoice Global Support Capability: Flight HoursGenaro Rodriguez100% (2)
- Volare Answers - Ops ProceduresDocument3 pagesVolare Answers - Ops ProcedurespontooNo ratings yet
- 49 Apu PDFDocument238 pages49 Apu PDFIvan Fauzi100% (1)
- CTC-063 Basic EngineDocument173 pagesCTC-063 Basic EngineIzwan Z100% (2)
- 49 Apu PDFDocument110 pages49 Apu PDFyogaga100% (2)
- Pages From 70 Power Plant Iae v2500Document2 pagesPages From 70 Power Plant Iae v2500AldoNo ratings yet
- 787 Propulsion SystemDocument9 pages787 Propulsion Systemdapdaniel100% (1)
- Cfm56-3 Engine Regulation by CFMDocument43 pagesCfm56-3 Engine Regulation by CFMnono92100% (5)
- 1 - Cowling&EBU (CF6-80E1)Document9 pages1 - Cowling&EBU (CF6-80E1)Chabou_r1627100% (3)
- ATA 77 EngineDocument16 pagesATA 77 EnginebrandonNo ratings yet
- Volare Questions - Mass and BalanceDocument33 pagesVolare Questions - Mass and Balancepontoo50% (2)
- SAMGONG-MITSUBISHI S3037 Purifier Instruction ManualDocument101 pagesSAMGONG-MITSUBISHI S3037 Purifier Instruction Manualpescarra-167% (3)
- 737MAX OIL SERVICING Best PracticesDocument5 pages737MAX OIL SERVICING Best PracticesrakeshNo ratings yet
- 70 Power Plant CFM 56 PDFDocument392 pages70 Power Plant CFM 56 PDFAnonymous 298xlo3uU100% (2)
- Ata 75 CF6-80C2Document14 pagesAta 75 CF6-80C2ccoyure100% (2)
- Cf6 80c2 Engine.Document7 pagesCf6 80c2 Engine.Harsh Ambhore100% (1)
- Hot Air 787 Vs A330Document11 pagesHot Air 787 Vs A330Addison SchonlandNo ratings yet
- ATA 28 Fuel Level 3Document128 pagesATA 28 Fuel Level 3miguel angel camargo chevel0% (1)
- 70 Power Plant CFM 56Document152 pages70 Power Plant CFM 56juan carlos balderas silvaNo ratings yet
- A319/A320/A321 APU Technical Training ManualDocument172 pagesA319/A320/A321 APU Technical Training ManualSelcuk GuncanNo ratings yet
- Mio Mxi 125 Parts CatalogDocument56 pagesMio Mxi 125 Parts CatalogEvangelista Daryl Angelo68% (72)
- TM 5-2815-232-14 TECHNICAL MANUALDocument868 pagesTM 5-2815-232-14 TECHNICAL MANUALdiegoblakin74% (23)
- CFM56-3 Turbofan Engine OverviewDocument52 pagesCFM56-3 Turbofan Engine OverviewEfrain Ramos100% (2)
- 70 Power Plant Iae v2500Document466 pages70 Power Plant Iae v2500Joydeep Sengupta100% (1)
- Volare ATPL Question BankDocument3 pagesVolare ATPL Question Bankmomanbh0% (3)
- Study Questionnaire Ata 70-80 B1Document9 pagesStudy Questionnaire Ata 70-80 B1suriya100% (2)
- All Tool ListsDocument367 pagesAll Tool ListsArabyAbdel Hamed Sadek0% (1)
- CFM56Document5 pagesCFM56Anonymous wkL8YVBENo ratings yet
- Complete Range of Yamaha Genuine Spare Parts ListDocument460 pagesComplete Range of Yamaha Genuine Spare Parts ListShantanu YadavNo ratings yet
- Ctc-214 Basic EngineDocument365 pagesCtc-214 Basic Engineernesto rodriguezNo ratings yet
- A330 Rolls-Royce RB211-Trent 700 Virtual Reality 360Document20 pagesA330 Rolls-Royce RB211-Trent 700 Virtual Reality 360Edison Vianney Cardona Montoya100% (2)
- Iae Engine: Oat Colder ThenDocument1 pageIae Engine: Oat Colder ThenBharat Bhushan100% (1)
- Pw4000-100 - Opencowl Inspection GuideDocument63 pagesPw4000-100 - Opencowl Inspection Guidegayathrisicwai100% (8)
- Operating Instruction Diesel EngineDocument142 pagesOperating Instruction Diesel EngineFreddy SuhartonoNo ratings yet
- Done By:: Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology ThiruvananthapuramDocument48 pagesDone By:: Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology Thiruvananthapuramsrijani pal100% (1)
- CFM56 5C - Ang 2Document2 pagesCFM56 5C - Ang 2pullu p joseNo ratings yet
- CF34-3 Engine Notes Chapter 72 Course NotesDocument30 pagesCF34-3 Engine Notes Chapter 72 Course NotesinternetsurfingNo ratings yet
- Flight Operations Support DocumentDocument143 pagesFlight Operations Support DocumentMarcinNo ratings yet
- CFM Technical DataDocument2 pagesCFM Technical DataArturoACE100% (6)
- Air Conditioning B787 Verslag - OdtDocument6 pagesAir Conditioning B787 Verslag - OdtLaty Bling100% (1)
- 27 BeamerDocument226 pages27 BeamerashufriendluckyNo ratings yet
- Fan Lub CFM56-7 - HandbookDocument44 pagesFan Lub CFM56-7 - HandbookANDRANo ratings yet
- RVSMDocument40 pagesRVSMs gNo ratings yet
- Piaggio Carnaby Cruiser 300 Ie (En)Document326 pagesPiaggio Carnaby Cruiser 300 Ie (En)Manualles78% (9)
- Ata 75 CFM56-3Document17 pagesAta 75 CFM56-3ccoyure100% (1)
- 2 Engine GeneralDocument23 pages2 Engine GeneralChabou Rafik100% (1)
- Go Indigo GoDocument8 pagesGo Indigo GoAkshay PushpanNo ratings yet
- PrattWhit DIF Book 1Document107 pagesPrattWhit DIF Book 1luis Minaya100% (1)
- Iae V2500 Engine Questions: TH THDocument12 pagesIae V2500 Engine Questions: TH THRafael SantosNo ratings yet
- 2 Engine GeneralDocument23 pages2 Engine GeneralChabou Rafik100% (1)
- 032 - Performance - . - PerformancesDocument3 pages032 - Performance - . - PerformancesViorel CroitoruNo ratings yet
- 062 - Radionavegacion - . - Radio NavigationDocument3 pages062 - Radionavegacion - . - Radio NavigationViorel CroitoruNo ratings yet
- Volare Answers - MeteorologyDocument6 pagesVolare Answers - Meteorologymomanbh0% (1)
- Volare Answers - Human FactorDocument6 pagesVolare Answers - Human FactorpontooNo ratings yet
- Volare Answers - InstrumentationDocument3 pagesVolare Answers - InstrumentationBalaji DurairajNo ratings yet
- Aa - NL Publications Jar AmdtsDocument4 pagesAa - NL Publications Jar AmdtsChabou RafikNo ratings yet
- Volare Answers - Mass and BalanceDocument2 pagesVolare Answers - Mass and Balancehusseinih100% (1)
- Jaa - NL IntroductionDocument6 pagesJaa - NL IntroductionChabou RafikNo ratings yet
- ATPL-Air Law Professione Volare-AnswersDocument4 pagesATPL-Air Law Professione Volare-AnswerspatrouilledeafranceNo ratings yet
- AGMTGL010Document2 pagesAGMTGL010Chabou RafikNo ratings yet
- JAA ECAC Member StatesDocument1 pageJAA ECAC Member StatesChabou RafikNo ratings yet
- Annex 1Document1 pageAnnex 1Chabou RafikNo ratings yet
- Cap 768Document194 pagesCap 768Chabou RafikNo ratings yet
- Jar-Std 4A: Basic Instrument Training Devices: Oint Viation UthoritiesDocument12 pagesJar-Std 4A: Basic Instrument Training Devices: Oint Viation UthoritiesChabou RafikNo ratings yet
- TGL ListDocument3 pagesTGL ListChabou RafikNo ratings yet
- Toro Side Winder Owners ManualDocument60 pagesToro Side Winder Owners Manualrusselguthrie_398315No ratings yet
- All Lubrico Products - SEP2017Document2 pagesAll Lubrico Products - SEP2017Mario CoronadoNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1 Mooring:: Aircraft Ground Handling and Support EquipmentDocument24 pagesUNIT-1 Mooring:: Aircraft Ground Handling and Support EquipmentPrasanth ViratNo ratings yet
- Blackhawk 325 AmpDocument6 pagesBlackhawk 325 AmpMureithi SamNo ratings yet
- T603 MECH Parts CatalogueDocument376 pagesT603 MECH Parts CataloguesteveNo ratings yet
- Dash (Oct, 2015) EURO III VXDocument147 pagesDash (Oct, 2015) EURO III VXKishonkumar KishonNo ratings yet
- Nammdlha 000059Document111 pagesNammdlha 000059Edson CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- EuropeDocument107 pagesEuropeMd. Salim UddinNo ratings yet
- CM6200 Installv2Document33 pagesCM6200 Installv2Will AshburnNo ratings yet
- Ag 1500Document37 pagesAg 1500the70767% (3)
- Sil99 2Document28 pagesSil99 2Christian100% (1)
- Manual Husqvarna 36Document22 pagesManual Husqvarna 36José Manuel Arrojo MacíasNo ratings yet
- Transporte de Los Generadores de Gas Rb211 y Avon Rolls Royce 3Document12 pagesTransporte de Los Generadores de Gas Rb211 y Avon Rolls Royce 3Denis JimenezNo ratings yet
- SUZUKI DT30 Servisnaya InformatsiyaDocument4 pagesSUZUKI DT30 Servisnaya InformatsiyaRedyard PravdorubNo ratings yet
- 2012 Arctic Cat RovDocument219 pages2012 Arctic Cat RovJennifer SchulerNo ratings yet
- HYDRAULIC SYSTEM OVERVIEWDocument27 pagesHYDRAULIC SYSTEM OVERVIEWFulvio Bolao100% (1)
- Iskra Starter MotorsDocument25 pagesIskra Starter Motorsosobax100% (1)
- ECB Priority III: Deutz - Starter MotorDocument7 pagesECB Priority III: Deutz - Starter MotorMarcelo OlivaresNo ratings yet
- SPC V15 V12 BS Iv Ug Rev 14 Aug 18Document90 pagesSPC V15 V12 BS Iv Ug Rev 14 Aug 18Bharat MalviyaNo ratings yet