Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pharmacology Chart
Uploaded by
PaulaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pharmacology Chart
Uploaded by
PaulaCopyright:
Available Formats
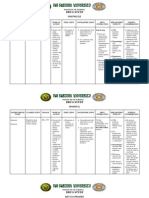
PHARMACOLOGY DRUG CHART EXAM #2
ANTIINFLAMMATORY AGENTS
Drug Name
Disorder/Disease Treated
Therapeutic Effects and Action
Side Effects and Contraindications
NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Agents)
Affect inflammatory process Pain and inflammation Fever and headaches
Relieve pain, reduce elevated body temperature, inhibit platelet aggregation Inhibit biosynthesis of prostaglandin
Gastric irritation if taken without food Sodium and water retention Alcoholic beverages should be avoided Peptic ulcers and gastric bleeding
Salicylates
Inflammation Used as an anti-platelet drug
Decreases inflammatory process by inhibiting prostaglandin Relieve pain by inhibiting enzyme COX
Should not be taken with other NSAIDs Risk for stroke and heart attack (makes blood thinner) so make sure not to take with other anticoagulants Do not take in last trimester of pregnancy Gastric irritation Sodium and water retention
Selective Cox-2 Inhibitors (Second Generation NSAIDs)
Decrease inflammation and pain Severe arthritic conditions Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis Relieves dysmenorrhea Antiinflammatory agents (prednisone, prednisolone, dexamethasone) used in arthritis and control of arthritic flareups (not drug of choice)
Inhibits COX-2 (which normally promotes prostaglandin synthesis) but does not inhibit COX-1
Headaches, dzziness, sinusitis, nausea, flatulence, diarrhea, rash Peripheral edema
Corticosteroids
Suppressing various components of inflammatory process at injured site
Numerous serious side effects associated with prolonged use
Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs)
Alleviate symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis; palliative rather than curative effects; results may take up weeks or months to see
Gold Therapy Depressed migration of leukocytes and suppresses prostaglandin activity Inhibits lysosomal enzymes contained in leukocytes
Dermatitis, urticarial, erythema, alopecia, stomatitis, pharyngitis, gastritis, colitis, hepatitis, severe blood dyscrasias, anaphylactic shock; contraindicated in hemorrhagic conditions and lupus
Antigout Drugs Colchicine
Treats acute symptoms of gout, not effective in decreasing inflammation occurring in other disorders
Inhibits migration of leukocytes to the inflamed site
Gastric irritation, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and abdominal pain; contraindicated in renal, cardiac or GI problems
Uric Acid Inhibitor
Used for gout prevention Helpful for patients with uric acid stones or with blood disorders like leukemia and polycythemia vera
Lowers uric acid levels
Diuresis, alkaline urine, anorexia, nausea, vomitin, diarrhea, stomatitis, dizziness, headache, rash, pruritis, malaise, metallic taste
Uricosurics
Used for gout
Flushed skin, sore gums, headache Increase the rate of uric acid excretion Avoid aspririn because it causes uric by inhibiting reabsorption acid retention
NONOPIOID AND OPIOID ANALGESICS
Drug Name
Disorder/Disease Treated
Therapeutic Effects and Action
Side Effects
NSAIDs
Pain Inflammation Transient ischemic attacks (preventative)
Inhibit prostaglandin synthesis by different forms of COX
Stomach and ulcer bleeding may occur because COX-1 inhibition decreases protection of stomach lining, severe GI problems may also occur, tinnitus, bronchospasm, urticarial (with hypersensitivity) Anorexia, nausea and vomiting as well as rash, severe hypoglycemia, oliguria and urticarial; could cause hemorrhage, hepatotoxicity, hemolytic anemia, leukopenia and thrombocytopenia; contraindicated in severe hepatic or renal disease, alcoholism GI distress, drowsiness, dizziness, sedation, urinary retention, bradycardia, euphoria, hypotension
Acetaminophen
Nonprescription reliever of pain
Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis and inhibition of hypothalamic heatregulator center
Morphine
Relieves severe pain
Depression of CNS and pain impulses because of binding to opiate receptor
Meperidine
synthetic opioid used for pain, used in pregnancy
CNS depressant
Decrease in blood pressure Contraindicated in patients with chronic pain, severe liver dysfunction, sickle cell, history of seizures, CAD and cardiac dysrhythmias Make sure to watch respiration and provide adequate hydration Oversedation
Hydromorphone
Relief of moderate to severe pain
Depressant
Patient-Controlled Analgesia (PCA)
Self-administration of pain medication
Same as morphine Transdermal patch that is used during the skin, more potent than morphine Act on peripheral nerves and CNS by inhibiting spontaneous neuronal firing Used in the hopes of decreasing abuse
Transdermal Opioid Analgesics
Treats chronic pain
Irritation of skin, dependence, etc. Low dosages kept especially if in combination with other drugs CNS toxicity from high doses
Adjuvant Analgesics
Relief of pain in neuropathy
Opioid Agonists-Antagonists
Pain relief
ANTIPSYCHOTIC AGENTS
Drug Name
Disorder/Disease Treated
Therapeutic Effects and Action
Side Effects
Sedation, dizziness, headache, dry mouth, nasal congestion, blurred vision, photosensitivity, nausea, constipation, urinary retention, polyuria and peripheral edema Sedation and EPS may occur Drowsiness and anticholinergic effects Weight gain, tremors, and occasional rigidity, orthostatic hypotension, EPS, ECG changes, convulsions, headache, dry mouth, photosensitivity, sexual dysfunction
Phenothiazines
Treats psychotic behavior
Blocks dopamine receptors in the brain and controls psychotic symptoms
Nonphenothiazines
Antipsychotic drug
Blocks dopamine receptors
Atypical Serotonin/Dopamine Antagonists
Treat both positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia
Interferes with binding of dopamine to dopamine (D2) and serotonin receptors
Anxiolytics
Treat anxiety and insomnia
Potentiate gamma-aminobutryic (GABA) effects by binding to specific benzodiazepine receptors and inhibit GABA neurotransmission
Drowsiness, dizziness, weakness, confusion, blurred vision, nausea, V, anorexia, sleep disturbance, restlessness, hallucinations
ANTIDEPRESSANTS AND MOOD STABILIZERS
Drug Name
Disorder/Disease Treated
Therapeutic Effects and Action
Side Effects
Herbal Supplements
Treat depression, manage mild depression
St. Johns Wort decrease reuptake of neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine and dopamine
May interfere with SSRIs which cause serotonin syndromedizziness, headache, sweating, agitation Orthostatic hypotension, sedation, anticholinergic effects, cardiac toxicity and seizures Dry mouth, blurred vision, insomnia, headache, nervousness, anorexia, N, D, suicidal ideation, sexual dysfunction Hypertensive crisis from food-drug interactions, do not take with TCAs, CNS stimulation, agitation, orthostatic hypotension and anti cholinergic effects
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs)
Treat major depression
Block uptake o the neurotransmitters norepinephrine and serotonin Block reuptake of serotonin into the nerve terminal of CNS, do not block uptake of dopamine or norepinephrine
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
Major depressive disorders, anxiety, disorders like OC, panic, phobias, PTSD and other anxiety
Monamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
Treatment of depression
Inactivates norepinephrine, dopamine, epinephrine and serotonin
Lithium (Mood Stabilizer)
Bipolar affective disorder
Calming effect without impairing intellectual activity, controls evidence of flight of ideas and hyperactivity, manic behavior may return of the person stops taking lithium. Alters ion transport in muscle and nerve cells and increases receptor sensitivity to serotonin
Headache, lethargy, drowsiness, dizziness, etc; urinary incontinence, hyponatremia, clonic movements, stupor, azotemia, leukocytosis, nephrotoxicity
ANTITUBERCULARS, ANTIFUNGALS, PEPTIDES AND METRONIDAZOLE
Drug Name
Disorder/Disease Treated
Therapeutic Effects and Action
Side Effects
Drowsiness, tremors, rash, blurred vision, photosensitivity, tinnitus, dry mouth, constipation, N, V, psychotic behavior, peripheral neuropathy, etc. Anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach cramps, headache, rash and burning sensation in vagina No adverse reactions known High serum levels cause nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity and parasethesias, redness, rash, nausea and vomiting
Antitubercular Drugs
Tuberculosis
Inhibits tubercle cell wall synthesis and blocks pyridoxine which is used for intracellular enzyme production
Antifungal Drugs
Fungal infections; fungistatic or fungicidal depending on dose and susceptibility
Increase permeability of fungal cell membrane (fluconazole)
Peptides
Treat bacterial infections (Polymixin B)
Interfering with cell membrane of bacterium and cause cell death
ANTIVIRALS, ANTIMALARIALS AND ANTIHELMINTICS
Drug Name
Disorder/Disease Treated
Therapeutic Effects and Action
Side Effects
Antiviral Non-HIV Drugs
Prevent or delay the spread of a viral infection
Interference with the synthesis of viral DNA
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, tremors, lethargy, rash, increased bleeding at IV site, urticarial, anemia, gingival hyperplasia, neuropathy, seizures, nephrotoxicity and leukopenia
Antiviral HIV Drugs
Reverse transcriptase inhibitors and protease inhibitors Treats acute malaria; prophylaxis for malaria
Prevents synthesis of DNA and allows T4 lymphocytes to increase initially Increased pH in the malaria parasite inhibits parasitic growth
None noted Anorexia, N, V, D, abdominal cramps, fatigue, ECG changes, hypotension, psychosis
Antimalarial Drugs
Antihelmintic Drugs
Treat parasitic worms
Expels them, I suppose
GI distress and neurologic problems like dizziness, weakness, headache and drowsiness
DRUGS FOR URINARY TRACT DISORDERS
Drug Name
Disorder/Disease Treated
Therapeutic Effects and Action
Side Effects
Urinary Antiseptics and Antiinfectives and Antibiotics
Treat acute and chronic UTIs
Inhibits bacterial enzymes and metabolism
Anorexia, N, V, D discoloration of urine, diarrhea, rash pruritus, dizziness, headache, superinfection, peripheral neuropathy, hemolytic anemia, agranulocytosis GI disturbances, hemolytic anemia, nephrotoxicity, hepatotoxicity
Urinary Analgesics
Relieves urinary pain and burning
Frequency and urgency of urination are relieved Increase tone of detrusor urinal muscle which produces a strong enough contraction strong enough to stimulate urination
Urinary Stimulants
Helps with neurogenic bladders and when bladder function is decreased
None noted
Urinary Antispasmodics/Antimuscarinics
Relief of urinary tract spasms resulting from infection or injury
Antimuscarinic block parasympathetic nerve impulses Antispasmodics direct action of smooth muscle of urinary tract
Contraindicated in urinary or GI obstruction or glaucoma Dry mouth, increased heart rate, dizziness, intestinal distension, constipation
You might also like
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Pharmacology Chart 3Document2 pagesPharmacology Chart 3Omar ClorNo ratings yet
- Pharm MnemonicsDocument33 pagesPharm MnemonicsThomson George75% (4)
- Drug Mechanism Clincal Use Side Effects Antifungal: Amphote Ricin BDocument30 pagesDrug Mechanism Clincal Use Side Effects Antifungal: Amphote Ricin BCess Lagera Ybanez0% (1)
- Pharmacology Complete Drug TableDocument6 pagesPharmacology Complete Drug Tableninja-2001100% (4)
- Pharmacology Drug Chart: Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsDocument18 pagesPharmacology Drug Chart: Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsPadmavathy Naidu Chokkapu100% (2)
- Pharmacology SummaryDocument16 pagesPharmacology Summarysechzhen96% (46)
- Top 200 Drug Study Reference RLPDocument31 pagesTop 200 Drug Study Reference RLPYathrika YathrikaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology SummaryDocument32 pagesPharmacology Summaryminikatiting95% (22)
- Muscarine & Nicotinic: ReceptorDocument26 pagesMuscarine & Nicotinic: ReceptorCess Lagera Ybanez88% (16)
- Drug Interactions 2 Paper PDFDocument2 pagesDrug Interactions 2 Paper PDFAzima AbdelrhamanNo ratings yet
- MBBS Pharmacology PDFDocument20 pagesMBBS Pharmacology PDFAdeeb Aiman Rosli100% (6)
- Pharmacology - Drug ChartsDocument39 pagesPharmacology - Drug ChartsAsim Ishaq100% (5)
- Drug Outline: Autonomic Nervous System Drug Class Drug OtherDocument4 pagesDrug Outline: Autonomic Nervous System Drug Class Drug OtherCess Lagera YbanezNo ratings yet
- A-Autonomic Drugs: 1) CholinergicDocument28 pagesA-Autonomic Drugs: 1) CholinergicMahmoud Ahmed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Antiinfectives Drug TableDocument5 pagesAntiinfectives Drug Tablecdp1587100% (3)
- Pharmacy MnenomicsDocument12 pagesPharmacy MnenomicsNaresh BabuNo ratings yet
- The Principles of Antibiotic Therapy: S. Aureus Streptococcus PneumoniaeDocument16 pagesThe Principles of Antibiotic Therapy: S. Aureus Streptococcus PneumoniaeDianne Chua100% (7)
- Pharm Drug Outline AdrDocument1 pagePharm Drug Outline AdrCess Lagera YbanezNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology MnemonicsDocument17 pagesPharmacology MnemonicsJuvenis SampangNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology MnemonicsDocument17 pagesPharmacology MnemonicsAzfar AkramNo ratings yet
- Cholinergics and Cholinergic BlockersDocument5 pagesCholinergics and Cholinergic Blockersapi-3739910100% (3)
- Diabetes and Endocrine ChartsDocument3 pagesDiabetes and Endocrine ChartsAja Blue86% (7)
- Pharm-Drugs ChartsDocument21 pagesPharm-Drugs ChartsCandace Flowers100% (3)
- Pharmacology MnemonicsDocument24 pagesPharmacology MnemonicsMrs3carpediem0% (1)
- Drug Receptor Types: Cut Here Cut HereDocument60 pagesDrug Receptor Types: Cut Here Cut Heredlneisha61100% (13)
- Bumetanide Torsemide: Desmopressin - V2Document1 pageBumetanide Torsemide: Desmopressin - V2med testNo ratings yet
- Drugs WorksheetDocument16 pagesDrugs Worksheetninja-2001No ratings yet
- Anticoagulants Drug TableDocument1 pageAnticoagulants Drug Tablecdp158767% (3)
- Drugs PharmacologyDocument75 pagesDrugs Pharmacologyapi-25987870100% (16)
- Pharmacology Mnemonics PDFDocument27 pagesPharmacology Mnemonics PDFHasanAli100% (2)
- Nursing School Drug ChartDocument13 pagesNursing School Drug ChartEve Lester100% (3)
- Pharmacology List of DrugsDocument66 pagesPharmacology List of DrugsSohail Adnan100% (2)
- Pharmacology MnemonicsDocument19 pagesPharmacology MnemonicsAl-nazer Azer Al100% (5)
- Pharmacology - Antibiotics Flash CardsDocument20 pagesPharmacology - Antibiotics Flash CardsJamil100% (2)
- Respiratory Drugs XL Chart 3Document2 pagesRespiratory Drugs XL Chart 3cdp1587100% (1)
- 13 How To Survive - PharmacologyDocument34 pages13 How To Survive - Pharmacologysophiesurvivalguides100% (1)
- Refrigerate: Hives, RashDocument5 pagesRefrigerate: Hives, RashstarobinNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Drug ChartDocument1 pageEndocrine Drug ChartJessicaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Test 1Document39 pagesPharmacology Test 1Niki BolinNo ratings yet
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)From EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- NAPLEX Practice Question Workbook: 1,000+ Comprehensive Practice Questions (2023 Edition)From EverandNAPLEX Practice Question Workbook: 1,000+ Comprehensive Practice Questions (2023 Edition)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- MULTISTATE PHARMACY JURISPRUDENCE EXAMINATION (MPJE): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandMULTISTATE PHARMACY JURISPRUDENCE EXAMINATION (MPJE): Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: A Companion Handbook with Illustrations: Pharmacology: A Companion Handbook with IllustrationsFrom EverandPharmacology: A Companion Handbook with Illustrations: Pharmacology: A Companion Handbook with IllustrationsRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Fun with Pharmacology: Pharmacology Made SimpleFrom EverandFun with Pharmacology: Pharmacology Made SimpleRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- AnalgesicsDocument1 pageAnalgesicsPaul AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug General Action Specific Action Indications Contraindications Adverse Reaction Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageName of Drug General Action Specific Action Indications Contraindications Adverse Reaction Nursing ResponsibilitiesNicole SooNo ratings yet
- Common Medical Surgical MedicationsDocument36 pagesCommon Medical Surgical MedicationsAshley Etheredge100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudySuzette Rae Tate0% (1)
- Pain Medications: Dr. Ave Olivia Rahman, Msc. Bagian Farmakologi Fkik UnjaDocument49 pagesPain Medications: Dr. Ave Olivia Rahman, Msc. Bagian Farmakologi Fkik UnjaHawa Ambarwati100% (1)
- Drug Study: OmeprazoleDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Omeprazoleclau_latojaNo ratings yet
- AnalgesicsDocument20 pagesAnalgesicsPamela Ria HensonNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 pagesDrug AnalysisAbby BorabienNo ratings yet
- Pharm 2 TestDocument7 pagesPharm 2 TestJaime HayesNo ratings yet
- Analgesic Anti Pyre Tic Agents PiatosDocument27 pagesAnalgesic Anti Pyre Tic Agents Piatosunno hiquianaNo ratings yet
- Drug 1Document5 pagesDrug 1Jesamine MayNo ratings yet
- RUSS Emergency DrugDocument6 pagesRUSS Emergency DrugKat BausaNo ratings yet
- NURS 370CL (Drug Card Monistat)Document2 pagesNURS 370CL (Drug Card Monistat)PaulaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Growth and DevelopmentDocument9 pagesPediatric Growth and DevelopmentPaula100% (4)
- NURS 370CL (Drug Card Template)Document1 pageNURS 370CL (Drug Card Template)PaulaNo ratings yet
- Nurs 410 (Ch1-10 Vocab)Document12 pagesNurs 410 (Ch1-10 Vocab)PaulaNo ratings yet
- NURS 370CL (Drug Card Hemabate)Document2 pagesNURS 370CL (Drug Card Hemabate)PaulaNo ratings yet
- Nurs 370cl (Drug Card Mgso4)Document2 pagesNurs 370cl (Drug Card Mgso4)PaulaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Drug Interactions and Over-The-Counter DrugsDocument3 pagesChapter 8 - Drug Interactions and Over-The-Counter DrugsPaulaNo ratings yet
- NURS 370CL (Drug Card Dibucaine)Document2 pagesNURS 370CL (Drug Card Dibucaine)PaulaNo ratings yet
- NURS 370CL (Drug Card Insulin)Document2 pagesNURS 370CL (Drug Card Insulin)PaulaNo ratings yet
- NURS 370CL (Drug Card - Terazol)Document2 pagesNURS 370CL (Drug Card - Terazol)PaulaNo ratings yet
- NURS 370CL (Drug Card Calcium Gluc)Document2 pagesNURS 370CL (Drug Card Calcium Gluc)PaulaNo ratings yet
- NURS 350 Chart (29-31)Document7 pagesNURS 350 Chart (29-31)PaulaNo ratings yet
- NURS 350 Outline (Ch6)Document6 pagesNURS 350 Outline (Ch6)PaulaNo ratings yet
- NURS 350 Outline (Ch7)Document3 pagesNURS 350 Outline (Ch7)PaulaNo ratings yet
- NURS 350 Outline (Ch1)Document4 pagesNURS 350 Outline (Ch1)PaulaNo ratings yet
- NURS 350 Outline (Ch5)Document9 pagesNURS 350 Outline (Ch5)PaulaNo ratings yet
- NURS 350 Outline (Ch4)Document1 pageNURS 350 Outline (Ch4)PaulaNo ratings yet
- NURS 350 Outline (Ch3)Document4 pagesNURS 350 Outline (Ch3)PaulaNo ratings yet
- NURS 350 Outline (Ch2)Document2 pagesNURS 350 Outline (Ch2)PaulaNo ratings yet
- NURS 350 Outline (Ch4.1)Document5 pagesNURS 350 Outline (Ch4.1)PaulaNo ratings yet
- NURS 350 (Pharm Formula Card)Document2 pagesNURS 350 (Pharm Formula Card)PaulaNo ratings yet
- Chart TemplateDocument1 pageChart TemplatePaulaNo ratings yet
- VERGARA - RPH Reflection PaperDocument2 pagesVERGARA - RPH Reflection PaperNezer Byl P. VergaraNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Newtonian and Non-Newtonian Fluid and Give Example For Each Case?Document11 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Newtonian and Non-Newtonian Fluid and Give Example For Each Case?MOHAMED ABD ELGHANYNo ratings yet
- Swiss Army Triplet 1Document2 pagesSwiss Army Triplet 1johnpwayNo ratings yet
- Ass AsDocument23 pagesAss AsMukesh BishtNo ratings yet
- ANTINEOPLASTICSDocument21 pagesANTINEOPLASTICSGunjan KalyaniNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 Harmonics & FiltersDocument25 pagesUnit-5 Harmonics & FiltersBhanu100% (1)
- Action Plan in T.L.E Project Title Objectives Activities Person-In-Charge Time Frame Success IndicatorDocument1 pageAction Plan in T.L.E Project Title Objectives Activities Person-In-Charge Time Frame Success IndicatorEdelmar BenosaNo ratings yet
- Installation of Submarine PE PipesDocument84 pagesInstallation of Submarine PE Pipeswaseemiqbal133100% (2)
- Citrus Information Kit-Update: Reprint - Information Current in 1998Document53 pagesCitrus Information Kit-Update: Reprint - Information Current in 1998hamsa sewakNo ratings yet
- MC4 CoCU 6 - Welding Records and Report DocumentationDocument8 pagesMC4 CoCU 6 - Welding Records and Report Documentationnizam1372100% (1)
- Rosewood Case AnalysisDocument5 pagesRosewood Case AnalysisJayant KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Sips 1328Document64 pagesSips 1328Jean Claude De AldánNo ratings yet
- Aex-Kissan KeralaDocument25 pagesAex-Kissan Keralabsh08070No ratings yet
- 835 (Health Care Claim PaymentAdvice) - HIPAA TR3 GuideDocument306 pages835 (Health Care Claim PaymentAdvice) - HIPAA TR3 Guideअरूण शर्माNo ratings yet
- Microsome S9 Prep ProtocolDocument22 pagesMicrosome S9 Prep ProtocolSAN912No ratings yet
- An Introduction To Routine and Special StainingDocument13 pagesAn Introduction To Routine and Special StainingBadiu ElenaNo ratings yet
- On The Wings of EcstasyDocument79 pagesOn The Wings of Ecstasygaya3mageshNo ratings yet
- Chromatographic Separation PDFDocument7 pagesChromatographic Separation PDFNicolle CletoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Strategy Analysis and Choice: Strategic Management: A Competitive Advantage Approach, 16e (David)Document27 pagesChapter 6 Strategy Analysis and Choice: Strategic Management: A Competitive Advantage Approach, 16e (David)Masum ZamanNo ratings yet
- PretestDocument8 pagesPretestAlmonte Aira LynNo ratings yet
- Performance Task 2Document3 pagesPerformance Task 2Edrose WycocoNo ratings yet
- Industrial Motor Control Part IDocument38 pagesIndustrial Motor Control Part Ikibrom atsbha100% (2)
- Technical Rockwell Automation FactoryTalk HistorianDocument6 pagesTechnical Rockwell Automation FactoryTalk HistorianAmit MishraNo ratings yet
- 00022443the Application of A Continuous Leak Detection System To Pipelines and Associated EquipmentDocument4 pages00022443the Application of A Continuous Leak Detection System To Pipelines and Associated EquipmentFaizal AbdullahNo ratings yet
- ING C1 CO JUN2016 CorrectorDocument6 pagesING C1 CO JUN2016 CorrectoraciameNo ratings yet
- The Determinants of Corporate Dividend PolicyDocument16 pagesThe Determinants of Corporate Dividend PolicyRutvikNo ratings yet
- C103 - General Checklist - ISO-IEC 17025:2017 Accreditation of Field Testing and Field Calibration LaboratoriesDocument19 pagesC103 - General Checklist - ISO-IEC 17025:2017 Accreditation of Field Testing and Field Calibration LaboratorieshuidhyiuodghNo ratings yet
- FIGMADocument22 pagesFIGMACessNo ratings yet
- The Handmaid's TaleDocument40 pagesThe Handmaid's Taleleher shahNo ratings yet
- Jy992d66901 CDocument6 pagesJy992d66901 CMaitry ShahNo ratings yet