Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Neurotransmitters
Uploaded by
Aileen AblanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Neurotransmitters
Uploaded by
Aileen AblanCopyright:
Available Formats
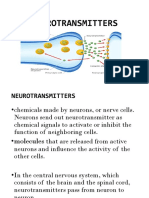
Types of Neurotransmitters Commonly, they are classified into three categories amino acids, monoamines and peptides.
. Neurotransmitters like glutamate, aspartate, glycine, serine and gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) fall into the category of amino acids. On the other hand, dopamine neurotransmitter, serotonin, melatonin, epinephrine and norepinephrine are the monoamine neurotransmitters. Calcitonin, glucagon, vasopressin, oxytocin and betaendorphin are some of the neuroactive peptides. There are about 50 neuroactive peptides till now, with new ones being discovered regularly. Apart from these, acetylcholine, adenosine and nitric oxide are some other noteworthy neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters in the Human Body Acetylcholine It is the first neurotransmitter to be discovered in the year 1921. This neurotransmitter is responsible for stimulating muscles. It activates the motor neurons that control the skeletal muscles. It is also concerned with regulating the activities in certain areas of the brain, which are associated with attention, arousal, learning and memory. People with Alzheimers disease are usually found to have a substantially low level of acetylcholine. Dopamine Dopamine is the neurotransmitter that controls voluntary movements of the body and is associated with the reward mechanism of the brain. In other words, dopamine regulates the pleasurable emotions, and drugs like cocaine, heroin, nicotine, opium, and even alcohol increase the level of this neurotransmitter, for which the user of such drugs feel good. Decreased level of dopamine is associated with Parkinsons disease, while the patients of schizophrenia are usually found to have excess dopamine in the frontal lobes of the brain. Serotonin Serotonin is an important inhibitory neurotransmitter, which has been found to have a significant effect on emotion, mood, and anxiety. It is also involved in regulating sleep, wakefulness and eating. A significantly low serotonin level is found to be associated with conditions like depression, suicidal thoughts and obsessive compulsive disorder. Many antidepressant drugs work by affecting the level of this neurotransmitter. Gamma Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that slows down neuron activity in order to prevent their over excitation, which could lead to anxiety. GABA is a non-essential amino acid, which is produced by the body from glutamic acid. A low level of GABA can have association with anxiety disorders. Alcohol and drugs like barbiturates can influence GABA receptors. Glutamate Glutamate is an excitatory neurotransmitter. It is the most commonly found neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Glutamate is mainly related with functions like learning and memory. An excess of glutamate is however toxic for the neurons. An excessive glutamate production may be related with the disease, known as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) or Lou Gehrigs disease. Epinephrine and Norepinephrine Epinephrine is an excitatory neurotransmitter that is derived from norepinephrine. Epinephrine controls mental focus and attention. Norepinephrine is also an excitatory neurotransmitter and it regulates mood and both physical and mental arousal. Increased secretion of norepinephrine raises heart rate and blood pressure. Endorphins Endorphins are the neurotransmitter that resembles the opioid compounds like opium, morphine, and heroin in structure. In fact, their effect on the body is also similar to the effect produced by the opioid compounds. Like opioids, endorphins can reduce pain, stress and promote calmness and serenity. These are the neurotransmitters that enable some animals to hibernate by slowing down metabolism, respiration and heart rate.
You might also like
- Inhibitory NeurotransmittersDocument11 pagesInhibitory NeurotransmittersAi NeeriNo ratings yet
- NeurotransmittersDocument22 pagesNeurotransmittersKj Banal100% (1)
- NeurotransmitterDocument1 pageNeurotransmitterZeeham EscalonaNo ratings yet
- "Neurotransmitter": Supporting Lecturer: NOVIA SINATA, M.Si, AptDocument24 pages"Neurotransmitter": Supporting Lecturer: NOVIA SINATA, M.Si, AptAmoxicilliartha RivanolaNo ratings yet
- 9 NeurotransmittersDocument48 pages9 NeurotransmittersYolanda UlmiNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM Types of Neurotransmitters PDFDocument7 pagesBIOCHEM Types of Neurotransmitters PDFTammy StephanieNo ratings yet
- Working BrainDocument76 pagesWorking BrainHarshal NimjeNo ratings yet
- AntideprresentDocument54 pagesAntideprresentHadiqa KhanNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument42 pagesThe Nervous Systemshamma younes salem ali al housaniNo ratings yet
- NeurotransmittersDocument11 pagesNeurotransmittersapi-286518624100% (1)
- EE 671 - Neural Networks: Nervous System Source: Ulty/farabee/biobk/biobooktoc - HTMLDocument29 pagesEE 671 - Neural Networks: Nervous System Source: Ulty/farabee/biobk/biobooktoc - HTMLtmkiran100% (1)
- Introduction To Neurotransmitters: BY: Mudasir Maqbool Mohmad Amin DarDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Neurotransmitters: BY: Mudasir Maqbool Mohmad Amin DarKAMYA SRIDHARAN 20214044100% (1)
- 2019 Mood Disorders and AntidepressantsDocument29 pages2019 Mood Disorders and Antidepressantsgowod86101No ratings yet
- Drug Summary Drug Fill-In-The-Blank Ws NT Drug Review Key 2Document3 pagesDrug Summary Drug Fill-In-The-Blank Ws NT Drug Review Key 2api-261267976No ratings yet
- Neurotransmitter Release and ProcessDocument14 pagesNeurotransmitter Release and ProcessRain TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.1 - Nervous SystemDocument50 pagesChapter 2.1 - Nervous SystemHaizmeer BonzieNo ratings yet
- NeurotransmittersDocument63 pagesNeurotransmittersNeelu Soni100% (1)
- LECTURE 1 The Nature of PsychologyDocument59 pagesLECTURE 1 The Nature of PsychologyColossal HeartNo ratings yet
- BioPsy C4Document85 pagesBioPsy C4Arei DomingoNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 - Neurobiologic ComponentDocument44 pagesTopic 7 - Neurobiologic ComponentJemimah Adaclog100% (1)
- Sleep Disturbances: Presented By, Maria JacobDocument61 pagesSleep Disturbances: Presented By, Maria Jacobmaria jacob100% (1)
- Glutamate & Gaba: NeurotransmittersDocument33 pagesGlutamate & Gaba: NeurotransmittersPanchitaJuarezNo ratings yet
- NeurotransmittersDocument4 pagesNeurotransmittersSalman Khan100% (1)
- Biological Bases Study GuideDocument13 pagesBiological Bases Study Guideapi-421695293No ratings yet
- Depression Medications ExplainedDocument5 pagesDepression Medications ExplainedxyzNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia Roles in Sensorimotor ControlDocument4 pagesCerebellum and Basal Ganglia Roles in Sensorimotor ControlAko Si Ate LayLayNo ratings yet
- Brain CellsDocument4 pagesBrain CellsJulius RicardeNo ratings yet
- Understanding Antipsychotic Drugs for SchizophreniaDocument34 pagesUnderstanding Antipsychotic Drugs for SchizophreniamariaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Chapter # 7Document69 pagesNervous System: Chapter # 7saddam ud dinNo ratings yet
- Neuron Structure and Function ExplainedDocument9 pagesNeuron Structure and Function Explainedvpilania2008100% (1)
- Psychotherapeutic Drugs GuideDocument12 pagesPsychotherapeutic Drugs Guidecamile buhanginNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine Glands & Their HormonesDocument35 pagesThe Endocrine Glands & Their HormonesEtta Sagita Leonora100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - Biological Foundations of BehaviorDocument50 pagesChapter 3 - Biological Foundations of BehaviorShermel Joy SolisNo ratings yet
- Mental Disorders and ComorbidityDocument24 pagesMental Disorders and ComorbidityFrida Neila RahmatikaNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology: The Nervous System ExplainedDocument29 pagesHuman Physiology: The Nervous System Explainedzandrex delunaNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitters overviewDocument17 pagesNeurotransmitters overviewManisanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Dopamine NeurotransmitterDocument3 pagesDopamine NeurotransmitterPrabha Amandari SutyandiNo ratings yet
- Brain Disorders: A2 Biology Unit 5 Topic 8Document16 pagesBrain Disorders: A2 Biology Unit 5 Topic 8Yasmin FarhanNo ratings yet
- NEUROTRANSMITTER FUNCTIONSDocument23 pagesNEUROTRANSMITTER FUNCTIONSPrabJot SinGhNo ratings yet
- Brain and Behavior: Psychiatry IDocument40 pagesBrain and Behavior: Psychiatry IDeepak BamNo ratings yet
- Rtms Technique and Current Status: Dr. Shravan KumarDocument78 pagesRtms Technique and Current Status: Dr. Shravan KumarfitriaNo ratings yet
- Functional Neuroanatomy of BrainDocument50 pagesFunctional Neuroanatomy of BrainAsim ShresthaNo ratings yet
- My Assignment On NeurotransmitterDocument8 pagesMy Assignment On NeurotransmitterSiti Fairuz HassanNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitters and Neuromodulators: Understanding Communication in the Nervous System (39Document41 pagesNeurotransmitters and Neuromodulators: Understanding Communication in the Nervous System (39afiwahyu100% (1)
- Neurobiologic Theories AND Psychopharmacology: BY Group 1Document15 pagesNeurobiologic Theories AND Psychopharmacology: BY Group 1PALEN, DONNA GRACE B.No ratings yet
- Role of SSRIs in Psychiatric DisordersDocument38 pagesRole of SSRIs in Psychiatric Disordersfaisalnadeem100% (1)
- Pharmacology of Autonomic Nervous System 2013Document166 pagesPharmacology of Autonomic Nervous System 2013Adimera TsehayeNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Gland Final 2Document8 pagesAdrenal Gland Final 2Std DlshsiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Autonomic PharmacologyDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Autonomic PharmacologyPranalosaNo ratings yet
- Spinal CordDocument4 pagesSpinal CordMabel LynNo ratings yet
- Biological Bases of BehaviorDocument87 pagesBiological Bases of BehaviorJirahNo ratings yet
- Serotonin (5-HT)Document35 pagesSerotonin (5-HT)adeesasaadNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument17 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviorAasma IsmailNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Chemistry I: 4 Year, 7 SemesterDocument58 pagesMedicinal Chemistry I: 4 Year, 7 SemesterKhan NehalNo ratings yet
- Cranial and Spinal NervesDocument5 pagesCranial and Spinal NervesEijunNo ratings yet
- Biopsychology I - Anatomy of The Nervous System PDFDocument96 pagesBiopsychology I - Anatomy of The Nervous System PDFThomas Cheah100% (1)
- NeurotransmittersDocument36 pagesNeurotransmittersDr. M. Prasad NaiduNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Psychology PSY 101: Lecture 3/ Modules 3 & 4 Biological Psychology Lecturer: Catherine SesayDocument48 pagesIntroduction To Psychology PSY 101: Lecture 3/ Modules 3 & 4 Biological Psychology Lecturer: Catherine SesayNgaima SesayNo ratings yet
- ReceptorsDocument9 pagesReceptorsrajenderNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - PhysioDocument5 pagesModule 3 - PhysioVidisha KandwalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Bullets - MCHN ReviewerDocument18 pagesNursing Bullets - MCHN ReviewerAileen AblanNo ratings yet
- A Dream Within A DreamDocument2 pagesA Dream Within A DreamAileen AblanNo ratings yet
- 5 Theories For Mental HealthDocument22 pages5 Theories For Mental HealthAileen AblanNo ratings yet
- A Dream Within A DreamDocument2 pagesA Dream Within A DreamAileen AblanNo ratings yet
- Daily Nutritional Guide Pyramid For FilipinosDocument1 pageDaily Nutritional Guide Pyramid For FilipinosAileen AblanNo ratings yet
- Case Pres With NCP at PNPDocument33 pagesCase Pres With NCP at PNPsitaw80% (10)
- C-Section Case Study: Nursing Care for Caesarian DeliveryDocument17 pagesC-Section Case Study: Nursing Care for Caesarian DeliveryLourd Andrew VillegasNo ratings yet
- 100-Bed General Hospital LayoutDocument1 page100-Bed General Hospital LayoutAshish chauhanNo ratings yet
- Q1. Read The Passage Given Below and Answer The Questions That FollowDocument2 pagesQ1. Read The Passage Given Below and Answer The Questions That FollowUdikshaNo ratings yet
- Immunology Serology Blood BankingDocument5 pagesImmunology Serology Blood BankingEdsss Villar100% (3)
- الورقة الثالثة- القبالة-2Document4 pagesالورقة الثالثة- القبالة-2Habebt MusabNo ratings yet
- Prevention Strategies For Periodontal Disease - Chapter 16Document10 pagesPrevention Strategies For Periodontal Disease - Chapter 16Daniah MNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy and LevetiracetamDocument53 pagesEpilepsy and LevetiracetamHasan Ahmed KhanNo ratings yet
- Jacked at Home - Bodyweight Muscle-Building WorkoutsDocument6 pagesJacked at Home - Bodyweight Muscle-Building Workoutsmohamed aliNo ratings yet
- GENETIC DISORDERS AND CYTOGENETICSDocument7 pagesGENETIC DISORDERS AND CYTOGENETICSsmilechance8No ratings yet
- The Precious Little Black Book DownloadDocument226 pagesThe Precious Little Black Book DownloadAsanda YekiNo ratings yet
- Paul B. Bishop, DC, MD, PHD, Jeffrey A. Quon, DC, PHD, FCCSC, Charles G. Fisher, MD, MHSC, FRCSC, Marcel F.S. Dvorak, MD, FRCSCDocument10 pagesPaul B. Bishop, DC, MD, PHD, Jeffrey A. Quon, DC, PHD, FCCSC, Charles G. Fisher, MD, MHSC, FRCSC, Marcel F.S. Dvorak, MD, FRCSCorlando moraNo ratings yet
- Prepositions of Time ExplainedDocument18 pagesPrepositions of Time ExplainedyuèNo ratings yet
- API SM Part 1Document7 pagesAPI SM Part 1Ronaldo JanglinNo ratings yet
- Being A Medical DoctorDocument14 pagesBeing A Medical DoctorMichael Bill GihonNo ratings yet
- Ethics in Practice - at End of Life - Part 1Document20 pagesEthics in Practice - at End of Life - Part 1anushavergheseNo ratings yet
- 380 Final PaperDocument46 pages380 Final Paperapi-538048965No ratings yet
- Human Sexual Response Physiology PhasesDocument2 pagesHuman Sexual Response Physiology PhasesLovely HerreraNo ratings yet
- 0007PNTDocument11 pages0007PNTPau Lo JakobyNo ratings yet
- 31congenital GlaucomasDocument12 pages31congenital GlaucomasShari' Si WahyuNo ratings yet
- Second Trimester Complications 2015Document64 pagesSecond Trimester Complications 2015gibreilNo ratings yet
- Stericon Plus BioindicatorDocument4 pagesStericon Plus Bioindicatorupt labkeswanbaliNo ratings yet
- STP 1560-2013Document346 pagesSTP 1560-2013HieuHTNo ratings yet
- Ten Trends To Watch in The Coming Year - The EconomistDocument1 pageTen Trends To Watch in The Coming Year - The EconomistAnonymous KaoLHAkt100% (1)
- Heart Failure Lily ModifiedDocument57 pagesHeart Failure Lily ModifiedSabila FatimahNo ratings yet
- Stefan White, Andrew Sinclair (Auth.), John M. Hutson, Garry L. Warne, Sonia R. Grover (Eds.) - Disorders of Sex Development_ an Integrated Approach to Management-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (20Document327 pagesStefan White, Andrew Sinclair (Auth.), John M. Hutson, Garry L. Warne, Sonia R. Grover (Eds.) - Disorders of Sex Development_ an Integrated Approach to Management-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (20Aakanksha MehtaNo ratings yet
- HISTORY AND PHYSICAL EXAMINATION (Putul)Document2 pagesHISTORY AND PHYSICAL EXAMINATION (Putul)Reshma Francis100% (1)
- PDF Passive Leg Raise PLR Test Stroke Volume Index SviDocument3 pagesPDF Passive Leg Raise PLR Test Stroke Volume Index SviNama ManaNo ratings yet
- Regional Studies in Marine ScienceDocument11 pagesRegional Studies in Marine ScienceBOUCHNANNo ratings yet
- Enemies of BeerDocument24 pagesEnemies of Beerpana0048100% (1)
- Everett Association of School Administrators (EASA) Administrative HandbookDocument46 pagesEverett Association of School Administrators (EASA) Administrative HandbookJessica OlsonNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Hygiene and SafetyDocument34 pagesLaboratory Hygiene and SafetyResmiNo ratings yet