Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Genetics
Uploaded by
someuser4321Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Genetics
Uploaded by
someuser4321Copyright:
Available Formats
Age: 4th -7th grade Objectives: After this lecture and activity sheet, students will know who
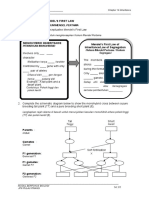
Gregor Mendel was, what he discovered about genetics, what traits are, the difference between genotype and phenotype, what dominant traits are, what recessive traits are, what hybrid means, what alleles are, what a Punnetts Square is, and how to nd phenotype and genotype using it. Lecture: Gregor Mendel, was a monk in Austria in the mid-1800s who raised peas in the monastery gardens. While breeding his peas, he made some big discoveries. They were discoveries about genetics. The peas had several traits he could see. Some plants were tall and some were short. Some had wrinkled pods and some had smooth pods. Some pods were green and some where yellow. The owers were white or purple. Mendel looked at each trait and learned how they were passed down to the offspring plants. Since plants breed using pollen, Mendel controlled which plants pollinated other plants. This was how he discovered many important genetic rules. How an individual looks and what their genetic code is sometimes do not match up. This is the difference between genotype and phenotype. The genotype is the actual genetic make up of an individual. The phenotype is what that individual looks like. Traits that show up more often are called dominant traits. Traits that show up less often are called recessive traits. If an individual with dominant traits breeds with an individual with recessive traits, this can result in a hybrid offspring. Hybrid individuals can look like they have dominant traits (phenotype), but actually be hybrid (genotype). Hybrid plants are different from dominant plants even if they looked the same. Each gene has two chances at a trait two copies two alleles. So a hybrid plant could be carrying the allele for a recessive trait even if you cant see it. So, for example, a hybrid plant might be tall like its dominant parent, but it still could have an allele for shortness that you dont see. This is the difference between genotype and phenotype. The genotype is the actual genetic make up of an individual. The phenotype is what that individual looks like. This can be illustrated with a simple chart. Its called a Punnetts Square. Well use the example of tall pea plants verses short pea plants. When two tall dominant plants breed, all the offspring are tall dominant. When two hybrid plants breed, one in four of the offspring are short. This is a 3:1 ratio. Look at the Punnetts Square to see what kind of offspring you would get from a dominant and hybrid parent mix and two recessive parents. See if you can gure out what the genotype and phentype would be,
KEY
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- Harry Potter Genetics AssignmentDocument9 pagesHarry Potter Genetics AssignmentAli BornsteinNo ratings yet
- Graded Assignment: Lab Report: Genetic Crosses 2Document6 pagesGraded Assignment: Lab Report: Genetic Crosses 2hammmbexdcNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Spongebob Dihybrid AnswersDocument2 pagesSpongebob Dihybrid AnswersLéilaH.Bruno100% (2)
- LS 107 - Midterm 1 Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesLS 107 - Midterm 1 Cheat SheetAudrie L.No ratings yet
- Inheritance Worksheet SolutionsDocument2 pagesInheritance Worksheet SolutionsJia Ru100% (2)
- Sex-Linked Traits Worksheet: Background InformationDocument4 pagesSex-Linked Traits Worksheet: Background InformationWilson RobertsNo ratings yet
- Mendelian Genetics Practice QuestionsDocument10 pagesMendelian Genetics Practice QuestionsPouncingDeer1762No ratings yet
- Non-Mendelian Inheritance Review (Article) - Khan AcademyDocument6 pagesNon-Mendelian Inheritance Review (Article) - Khan AcademyKarren ReyesNo ratings yet
- G9 Science Q1 Week 3 4 Non Mendelian Patterns of InheritanDocument26 pagesG9 Science Q1 Week 3 4 Non Mendelian Patterns of InheritanSandra Lee LigsaNo ratings yet
- DAILY LESSON LOG Grade 9 ScienceDocument40 pagesDAILY LESSON LOG Grade 9 ScienceLouise Meara Severo100% (1)
- Lecture Mendelian GeneticsDocument21 pagesLecture Mendelian GeneticsSunil DhatwaliaNo ratings yet
- Gregor MendelDocument38 pagesGregor MendelKristel SasanaNo ratings yet
- Victoria Vaughn - Codominance, Incomplete Dominance and Multiple Alleles - SinghDocument7 pagesVictoria Vaughn - Codominance, Incomplete Dominance and Multiple Alleles - SinghDallas VaughnNo ratings yet
- 06 Notes Non-Mendelian Genetics StudentDocument20 pages06 Notes Non-Mendelian Genetics StudentPaul AinzaNo ratings yet
- 64 Punnett SquareDocument1 page64 Punnett SquareSarahNo ratings yet
- Sample Weekly Planner 2Document9 pagesSample Weekly Planner 2api-662941487No ratings yet
- Principle of Inheritance and Variation - Practice SheetDocument6 pagesPrinciple of Inheritance and Variation - Practice SheetCHETAN PATILNo ratings yet
- Monster Genetics PredictionsDocument4 pagesMonster Genetics PredictionsM TooSahdyNo ratings yet
- Incomplete and Codominance Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesIncomplete and Codominance Practice ProblemsFarah abu hashimNo ratings yet
- Superhero Genetics ActivityDocument4 pagesSuperhero Genetics ActivityAnna StittNo ratings yet
- Ppt. Mendels Laws of InheritanceDocument29 pagesPpt. Mendels Laws of InheritanceMarkyyyNo ratings yet
- Mendel's Laws of InheritanceDocument5 pagesMendel's Laws of InheritanceMasitah AmzalNo ratings yet
- BIO - 10 - 41 - V2 - DM - Interaction of Allelic and Non-Allelic GenesDocument5 pagesBIO - 10 - 41 - V2 - DM - Interaction of Allelic and Non-Allelic GenesAlbina YulmukhametovaNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument104 pagesGeneticsAlbina AmangaliyevaNo ratings yet
- 7 EpistasisDocument33 pages7 EpistasisDasari SreenivasNo ratings yet
- Bio Revision Questions 4Document6 pagesBio Revision Questions 4Ryan SamuelNo ratings yet
- PDF - Pedigree WorksheetDocument2 pagesPDF - Pedigree Worksheetapi-280769158100% (3)
- Activity Sheet Module 3Document3 pagesActivity Sheet Module 3In Hae ParkNo ratings yet
- BIO152-1L Exercise 2 Mendelian InheritanceDocument6 pagesBIO152-1L Exercise 2 Mendelian InheritancePaulMendozaNo ratings yet
- Genetics ProblemsDocument18 pagesGenetics Problemsprofptrajasekharan100% (7)