Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Iob
Uploaded by
vinoth_172824Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Iob
Uploaded by
vinoth_172824Copyright:
Available Formats
How it began Indian Overseas Bank (IOB) was founded on February 10th 1937, by Shri.M.Ct.M.
Chidambaram Chettyar, a pioneer in many fields - Banking, Insurance and Industry with the twin objectives of specialising in foreign exchange business and overseas banking. IOB had the unique distinction of commencing business on 10th February 1937 (on the inaugural day itself) in three branches simultaneously - at Karaikudi and Chennai in India and Rangoon in Burma (presently Myanmar) followed by a branch in Penang. At the dawn of Independence IOB had 38 branches in India and 7 branches abroad. Deposits stood at Rs.6.64 Crs and Advances at Rs.3.23 Crs at that time. Pre-nationalisation era (1947- 69) During the period, IOB expanded its domestic activities and enlarged its international banking operations. As early as in 1957, the Bank established a training centre which has now grown into a Staff College at Chennai with 9 training centres all over the country. IOB was the first Bank to venture into consumer credit. It introduced the popular Personal Loan scheme during this period. In 1964, the Bank made a beginning in computerisation in the areas of inter-branch reconciliation and provident fund accounts. In 1968, IOB established a full-fledged department to cater exclusively to the needs of the Agriculture sector. . At the time of Nationalisation (1969) IOB was one of the 14 major banks that was nationalised in 1969. On the eve of Nationalisation in 1969, IOB had 195 branches in India with aggregate deposits of Rs. 67.70 Crs. and Advances of Rs. 44.90 Crs. Post - nationalisation era (1969-1992) In 1973, IOB had to wind up its five Malaysian branches as the Banking law in Malaysia prohibited operation of foreign Government owned banks. This led to creation of United Asian Bank Berhad in which IOB had 16.67% of the paid up capital.
In the same year Bharat Overseas Bank Ltd was created in India with 30% equity participation from IOB to take over IOBs branch at Bangkok in Thailand. In 1977, IOB opened its branch in Seoul and the Bank opened a Foreign Currency Banking Unit in the free trade zone in Colombo in 1979. The Bank has sponsored 3 Regional Rural Banks viz. Puri Gramya Bank, Pandyan Grama Bank, Dhenkanal Gramya Bank The Bank setup a separate Computer Policy and Planning Department (CPPD) to implement the programme of computerisation, to develop software packages on its own and to impart training to staff members in this field. Post Reform Period - Unprecedented developments (1992 & after) IOB entered Web site during the month of February 1997. IOB got autonomous status during 1997-98 IOB had the distinction of being the first Bank in Banking Industry to obtain ISO 9001 Certification for its Computer Policy and Planning Department from Det Norske Veritas (DNV), Netherlands in September 1999. This Certification covers Design, Development, Implementation and Maintenance of software developed in-house, procurement and supply of hardware and execution of turnkey projects. IOB started STAR services in December 1999 for speedy realisation of outstation cheques. Now the Banks has 14 STARS centres and one Controlling Centre for providing this service. During 1999, IOB started tapping the potential of internet by enabling ABB card holders in Delhi to pay their telephone bills by just logging on to MTNL web site and by authorising the Bank to debit towards the telephone bills. A Voluntary Retirement Scheme was introduced in the Bank on the lines of IBA package with Boards approval. The scheme was offered to Officers/Employees from December 15, 2000. The Bank made a successful debut in raising capital from the public during the financial year 2000-01, despite a subdued capital market. The issue opened on September 25, 2000 for raising Rs.111.20 crore and was oversubscribed by 1.87 times. The issue closed on September 29, 2000 - on the earliest closing day. The allotment was made in October 2000. Consequent to the public issue, the share of the Government in the Bank's capital came down to 75%. The shares of the Bank
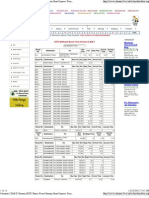
have been listed on the Madras Stock Exchange (Regional), Stock Exchange at Mumbai and the National Stock Exchange of India Ltd. IOB bagged the NABARD's award for credit linking the highest number of Self Help Groups for 2000-2001 among the Banks in Tamil Nadu. IDRBT (Institute for Development and Research in Banking Technology) conferred the Best Award under Banking Technology to IOB. The award was given for the innovative use of banking applications on INFINET (Indian Financial Network) for the year 2001. Mobile banking under SMS technology implemented in Ahmedabad and Baroda. Pilot run of Phase I of the Internet Banking commenced covering 34 branches in 5 Metropolitan centres. IOB was one among the first to join Reserve Bank of Indias negotiated dealing system for security dialing online. The Bank has finalised an e-commerce strategy and has developed the necessary internet banking modules in-house. For the first time a Total Branch Automation package developed in-house has been customised in one of the Overseas Branches of the Bank. Most software developed in-house. IOBNET connects Central Office with all Regional Office. The Bank has paid a maiden dividend of 10% p.a for 2000-01, followed by 12% during 2001-02. PERFORMANCE HIGHLIGHTS - 30.06.2008 2.DEPOSITS: Total deposits grew from Rs.70205 crore as on 30th June 2007 to Rs,85001 crore as on 30th June 2008 registering an increase of Rs.14796 crore and growth percentage of 21.08%. 3.ADVANCES: Gross Advances increased from Rs. 48610 crore as on 30th June 2007 to Rs.63419 crore as on 30th June 2008, recording an increase of Rs 14809 crore and growth percentage of 30.46%. 4.OPERATING PROFIT: The operating profit for Q1 of 2008-09 is at Rs.241.18 crore as against the operating profit of Rs.409.17 crore for Q1 of 2007-08. This decrease in the first quarter of this year is mainly due to loss booked on account of inter segment category transfer of securities and loss on sale of securities and provision for wage arrears.
5.NET PROFIT: Net profit for Q1 of 2008-09 is at Rs,255.97 crore and this figure is lower by Rs.12.52 crores when compared to the net profit of Rs.268.49 crore booked during Q1 of 2007-08. 6.TOTAL INCOME: Total income for Q1 of 2008-09 is at Rs. 2186.83. crore while the same was at Rs.1907.79 crore for Q1 of 2007-08. The increase in terms of percentage works out to 14.63%. Interest Income has gone up to Rs.2217.08 crore from 1846.21 crore recording a percentage increase of 20.09%. Other income has gone down due to loss on sale and category transfer loss on investments. 7.TOTAL EXPENSES: Total expense for Q1 of 2008-09 is at Rs.1945.64 crore and the same for the corresponding quarter last year was at Rs.1498.62 crore, recording a percentage increase of 29.83%. The interest expenses has gone up from Rs.1137.20 crore to Rs.1490.91 crore with percentage increase of 31.10%. 8.NET INTEREST INCOME: Net interest income for Q1 of 2008-09 is at Rs.726.17crore while the same was at Rs 709.02 crore for the corresponding quarter last year. The percentage increase is 2.42. 9.CRAR: CRAR under BASEL I as on 30-6-08 is at 11.41%; with TIER I component at 7.63%. Under BASEL II, the ratio is at 11.25%. CRAR under BASEL I as on 30.6.07 was at 13.31%. The slide in the ratio over the year is due to increased volume of business and consequent increase in risk weighted assets. The risk weighted assets increased from Rs.55025 crores to Rs.71597 crore during one year period. The bank has not raised any capital from the market during the one year period. Bank is well above the required CRAR ratio. 10.BUSINESS PER EMPLOYEE: Increased from Rs.4.81 crore as on 30.6.07 to Rs.5.93 crore as on 30.6.08. 11.NETINTEREST MARGIN: NIM was at 3.71% for the quarter ended 30th June 2007 and the ratio is at 3.12% for the quarter ended 30th June 2008. The slide is attributable to pressure on margin i.e. increase in interest on deposits with out corresponding increase in interest income from advances/investment. NII growth is minimal. 12..RETURN ON AVERAGE ASSETS: The ratio has come down from 1.27% to 0.99% over one year period. 13.CREDIT DEPOSIT RATIO: Improved to 74.61% from 69.24% over one year period.
14.CASA: The share of low cost deposits to total deposits has come down from 32.76% to 30.55% during one year period. This trend is sought to be arrested by vigorous compaign for low cost deposits and launching of new products like IOB Gold and Silver Savings Accounts and IOB Classic and Super Current Accounts. 15.NPA MANAGEMENT: Gross NPA over one year period has come down from Rs.1137 crore to Rs.1099 crore bringing down the Gross NPA percentage from 2.34% to 1.73%. However Net NPA percentage has gone up from 0.50% to 0.75% over one year period. 16.TOTAL CAPITAL FUNDS: Total capital funds of the bank increased to Rs.8170 crore from Rs.7324 crores over one year period due to internal accretion. 17.BOOK VALUE PER SHARE: Book value per share of the bank has gone up to Rs.91.40 from Rs.76.12 over one year period. IOB and Society IOB has been committed to and involved in various social causes, the most prominent being women empowerment - the Sakthi IOB Chidambaram Chettiar Memorial Trust and IOB's Promotion of the Agricultural Seed Bank. The Sakthi IOB Chidambaram Chettiyar Memorial Trust is a public charity trust initiated by the Bank and its Staff Representative organisations in February 1996 in memory of Shri M.Ct.M.Chidambaram Chettiyar, the founder of IOB. Objective: To enable women in the lower strata of society to equip themselves with the essential skills and knowledge required for embarking on a career of their choice.
IOB's Promotion of Pulses Seed Bank is a project in association with M.S.Swaminathan Research Foundation, Chennai for the establishment of Seed Banks in various villages under Dryland farming. Objective: Most small and marginal farmers in the rain fed areas pay less attention to cultivating pulses consequently leading to the decline of productivity in this sector. This scheme is intended to increase the production of pulses in dryland farming.
Activities: The Districts of Ramanathapuram and Pudukottai in Tamil Nadu were chosen for the 1st Phase of this project. The aim of this project is... To increase the availability of good quality seeds at the right time to the small and marginal farmers The provision of market linkages for pulses Sending in experts from the MSSR Foundation for demonstration of pulses cultivation in the rain fed areas
You might also like
- A Study On Deposit Mobilisation of Indian Overseas Bank With Reference To Velachery BranchDocument3 pagesA Study On Deposit Mobilisation of Indian Overseas Bank With Reference To Velachery Branchvinoth_172824100% (1)
- Design and Development of Student Information System in Kongu Engineering CollegeDocument1 pageDesign and Development of Student Information System in Kongu Engineering Collegevinoth_172824No ratings yet
- Bonafide Certificate: of Student Information System in Kongu Engineering College"Document9 pagesBonafide Certificate: of Student Information System in Kongu Engineering College"vinoth_172824No ratings yet
- A Study of Bank Deposits and Mobilisation With Reference To Nationalised BanksDocument100 pagesA Study of Bank Deposits and Mobilisation With Reference To Nationalised Banksvinoth_17282475% (24)
- Cheat Book For Cricket 07Document21 pagesCheat Book For Cricket 07vinoth_172824No ratings yet
- SetcDocument12 pagesSetcvinoth_172824100% (1)
- Bus TimingDocument52 pagesBus Timingvinoth_17282429% (7)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Mcom ProjectDocument61 pagesMcom Projectsonali wadate100% (1)
- CH10 Revised ADocument16 pagesCH10 Revised AMaimoona Ghani0% (1)
- DLP Trial BalanceDocument6 pagesDLP Trial Balancerachel100% (1)
- OM1 Practice Exam2Document5 pagesOM1 Practice Exam2nonysinghNo ratings yet
- MBA ProjectDocument15 pagesMBA ProjectkrishnithyanNo ratings yet
- Payroll AccountingDocument26 pagesPayroll AccountingShean VasilićNo ratings yet
- SubhashDocument1 pageSubhashsubhash221103No ratings yet
- BudgetDocument5 pagesBudgetGimson D ParambilNo ratings yet
- Buss 207Document80 pagesBuss 207Kelvin Lee100% (1)
- SBI International Access US Equity FoFDocument26 pagesSBI International Access US Equity FoFRoshanR.NawaleNo ratings yet
- Present Worth Analysis of Equal-Life Alternatives: ExampleDocument13 pagesPresent Worth Analysis of Equal-Life Alternatives: ExamplePA SampaioNo ratings yet
- Accounting Activity 4Document2 pagesAccounting Activity 4Ar JayNo ratings yet
- ApgvbnoDocument10 pagesApgvbnoJeshiNo ratings yet
- AFM Assignment (2019)Document9 pagesAFM Assignment (2019)Videhi BajajNo ratings yet
- Act 328 Finance Act 1986Document28 pagesAct 328 Finance Act 1986Adam Haida & CoNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Tax Estimation and Collection System On Category "C"Tax Payers in Case of Goba Town Administration Revenue Office South East EthiopiaDocument8 pagesAssessment of Tax Estimation and Collection System On Category "C"Tax Payers in Case of Goba Town Administration Revenue Office South East EthiopiaGudeta Dekema100% (1)
- Agragian DisputesDocument4 pagesAgragian DisputesCharlotte RiveraNo ratings yet
- Quiz MasterDocument109 pagesQuiz MasterYonatan WadlerNo ratings yet
- Ac3101 Homebranch 1Document5 pagesAc3101 Homebranch 1jumbo hotdogNo ratings yet
- A Business Plan Checklist and For Presentation Grading System 1Document1 pageA Business Plan Checklist and For Presentation Grading System 1chbarcenalNo ratings yet
- 6018-P1-LEMBAR KERJA AKUNTANSI. Jawaban Uk 2019Document58 pages6018-P1-LEMBAR KERJA AKUNTANSI. Jawaban Uk 2019adiirwanto80% (5)
- Books of AccountsDocument31 pagesBooks of AccountsFerly Mae ZamoraNo ratings yet
- R12x Oracle Payroll Fundamentals Configuration (Global) - D60571GC10Document3 pagesR12x Oracle Payroll Fundamentals Configuration (Global) - D60571GC10lava.cupidNo ratings yet
- Audit of Prepayment and Intangible Asset: Problem 6-1Document42 pagesAudit of Prepayment and Intangible Asset: Problem 6-1Un knownNo ratings yet
- Corporate FinanceDocument418 pagesCorporate FinanceLusayo Mhango100% (2)
- Vietnam Property Investment GuideDocument13 pagesVietnam Property Investment GuideakanagesNo ratings yet
- PFRS 5 QuizzerDocument1 pagePFRS 5 QuizzerRhea LalasNo ratings yet
- Under Armour Case Analysis - OK & ZAMORADocument30 pagesUnder Armour Case Analysis - OK & ZAMORASun Reong100% (5)
- Government Auditing and Accounting For NPODocument65 pagesGovernment Auditing and Accounting For NPOAljon Fabrigas SalacNo ratings yet
- SAP FICO Training Tutorials - ContentsDocument4 pagesSAP FICO Training Tutorials - ContentsPANTUGNo ratings yet