Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4generating An Sap Data Structure
Uploaded by
Swapna KuntamukkalaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
4generating An Sap Data Structure
Uploaded by
Swapna KuntamukkalaCopyright:
Available Formats
GENERATING
AN
SAP
DATA
STRUCTURE:
You can use the ABAP/4 Dictionary to generate data structures for SAP tables in any of the following programming languages: Cobol PL/1 C You can then incorporate these data structures in your data conversion program. For most of the standard SAP batch input programs, SAP has also provided special data structure identifiers. With such an identifier, you can generate a listing of all of the table fields that are required by the corresponding batch input program. You do not need to find out which tables are required for the batch input program and generate their structures individually. If you are creating your own batch input procedure, you may be able to use the standard field listings as well. The names of the special data structure identifiers are documented in the SAP Customizing system. For information on finding the relevant documentation, please see Batch Input Concepts(1). Data Transfer Programs in ABAP/4
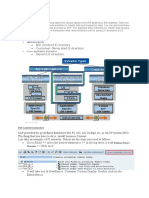
If your data transfer program is written in ABAP/4, you can include data structures of tables in your program with the TABLES instruction. The structure is then read directly from the ABAP/4 Dictionary. In this case, you cannot use the special data structure identifiers provided by the SAP applications. The identifier names are not recognized by the TABLES instruction. Instead, you can find the required table names by checking the transactions that your batch input procedure will be using to enter data. Or you can find the table names in the listings generated by the special identifiers. The diagram below shows the structures of transfer programs in ABAP/4 and as external programs written in other languages.
Including Table Procedure To generate
Structures
in
Transfer
Programs:
ABAP/4
and
Other
Languages
data
structure,
do
the
following:
1. Choose Tools --> ABAP/4 Workbench and then ABAP/4 Dictionary. 2. In the ABAP/4 Dictionary, select Environment --> Generate table description.
With this function, you can generate the structures of one or a group of SAP tables in programming code. You can then add this code to your data transfer program. 3. Specify the programming language in which the structure should be generated and identify the tables to be included. If you wish to use a special structure identifier for a standard SAP batch input report,then enter the identifier in the Key in TSRCG field. Example: The identifier AM-ANLA generates the data structure required for data transfers for the asset management application. 4. The system displays the data structure in list form, as in this example in PL/1 from the asset management application (AM-ANLA): ****************************************************************** * MEMBER GENERATED FROM SAP DATA DICTIONARY * * T A B L E BALTD * * DATE: 08.12.1995 TIME: 17:47:16 * * PLEASE DO NOT CHANGE MANUALLY * ****************************************************************** * 01 BALTD. * * Client (Old Assets Data Takeover AM) 05 MANDT PIC X(3) VALUE SPACE. * Company code 05 BUKRS PIC X(4) VALUE SPACE. * Asset class 05 ANLKL PIC X(8) VALUE SPACE. Choose System --> List --> Save --> File to download the data structure to your workstation or PC.
6)
DATA
CONVERSIONS:
Use the field descriptions that you obtained in Analyzing SAP Transactions(4) or Generating an SAP Data Structure(5) to determine the following: which fields can be taken over directly from your existing data. That is, there is a direct match between an existing data field and the corresponding SAP data field.
for which fields a conversion procedure is necessary for mapping your existing data to the requirements of the SAP System. CoNverting Data from Old Format to SAP Format
Your program must format batch input values just as an on-line user would when typing them in. In particular: The data must be character format. No piece of data may be longer than its target SAP field. If the data is shorter than the target field, you must left-justify it within the SAP field (pad it with blanks at the right end). (7) INITIALIZING AN SAP DATA STRUCTURE:
Standard SAP batch input programs require that every field in a data structure contains either: a value; or a special NODATA marker, which indicates that the no batch input data is required for the field. If you are writing your own data transfer program, you should therefore initialize all of the fields in your batch input data structure with the NODATA character. The NODATA character must occupy the first position in the field, as shown in the figure below. By default, the NODATA character is the forward slash. To initialize a field to NODATA, you must write this character as the first character in the field value.
If a batch input program finds NODATA in a field, then the program allows the field to default to its standard value in the SAP transaction that contains the field. Setting the NODATA marker: You can freely select another character as the NODATA marker. Define the new character in the batch input program that reads the data in the BGR00-NODATA field: Data: -NODATA GENERATING A like = SEQUENTIAL bgr00. ''. FILE:
If you are transferring data from a non-SAP System, then you will probably need to use a file as the transfer medium for the data. (For data transfer between SAP Systems, you may be able to use RFC or CPI-C to process data directly in the target SAP System.) The file that you generate should have the following characteristics:
All data should be in character format. This is required by the standard SAP batch input programs. Data must have the logical structure expected by the batch input program.
For a standard SAP batch input program, this requirement means that you have generated the data structure defined for the batch input program. For more information, see Generating an SAP Data Structure(5). You'll find sample code for reading from and writing to a sequential file in Sample Program: Data Transfer(9) .
(9)
SAMPLE
PROGRAM:
DATA
TRANSFER:
The following ABAP/4 program demonstrates the data transfer process. The program does the following: reads customer address data from a sequential file checks the data for unacceptable records performs conversions on the data writes the data back out to a sequential file using the format required by the SAP standard batch input program Batch Input Interface for Customers (ABAP/4 program RFBIDE00).
EXAMPLE: REPORT * SAP TABLES: * Structure DATA: TELE1(10) CUSTNR(8) TITLE(2) NAME1(30) END * Auxiliary DATA: INCLUDE DATA: structures BGR00, of for batch BKN00, data OF TYPE TYPE TYPE TYPE OF structure for BEGIN STRUCTURE END initializing OF OF to input BITFER. processing: BKNA1. transferred: OLDREC, C, C, C, C, OLDREC. fields: AUXREC. BKNA1. AUXREC.
existing BEGIN
be
* DATA: NAME1 TELE1
SAP
fields CUSTNR LIKE LIKE For N
for LIKE
converted
data: BKN00-KUNNR, BKNA1-NAME1, BKNA1-TELF1. fields: I. . character: CASE, CASE, CASE, CASE, CASE.
* DATA: FIELD-SYMBOLS * File PARAMETERS: OLDFILE(20) SAPFILE(20) ERRFILE(20) SESSION(20) NODATA
initializing TYPE
and
session
names, '/tmp/oldfile' '/tmp/sapfile' '/tmp/errfile' 'ADDRDAT' '/'
NODATA LOWER LOWER LOWER LOWER LOWER
DEFAULT DEFAULT DEFAULT DEFAULT DEFAULT
START-OF-SELECTION. OPEN DATASET: SAPFILE FOR ERRFILE FOR * Open * MOVE: SESSION SY-MANDT SY-UNAME NODATA TRANSFER * DO. ADD ASSIGN IF MOVE ENDDO. MOVE * DO. " READ IF batch
OLDFILE FOR OUTPUT OUTPUT input 'O' TO TO TO TO BGR00 session
INPUT IN IN as TO first
IN
TEXT TEXT TEXT SAPFILE
MODE, MODE, MODE.
TO fields TO STRUCTURE 0. with
entry: program: BGR00-STYPE, BGR00-GROUP, BGR00-MANDT, BGR00-USNAM, BGR00-NODATA. SAPFILE. NODATA: N. TO . ENDIF. . BKNA1.
Initialize
data
1 COMPONENT N OF SY-SUBRC NE BGR00-NODATA AUXREC Read Read DATASET SY-SUBRC and
AUXREC EXIT. TO
TO convert data OLDFILE existing
data: record: OLDREC. ENDIF.
NE
0.
INTO EXIT.
" Check data and transfer only certain records: IF OLDREC-CUSTNR(5) NE 'AABBC' OR OLDREC-CUSTNR(6) EQ 'AABBCD' OR OLDREC-TELE1 EQ SPACE. TRANSFER OLDREC TO ERRFILE. * TEXT-001: 'Data not transferred for customer:' WRITE: / TEXT-001, OLDREC-CUSTNR. ELSE. " Convert the customer number to SAP convention: IF OLDREC-CUSTNR+5(1) = 'C'. IF OLDREC-CUSTNR+5(1) = 'D'. ENDIF. " Convert abbreviations to full words: CASE OLDREC-TITLE. WHEN 'Co'. BKNA1-TITLE = 'Company'. WHEN 'Corp'. BKNA1-TITLE = 'Corporation'. WHEN OTHERS. BKNA1-TITLE = NODATA. ENDCASE. " Convert records from old format to SAP format: MOVE: OLDREC-CUSTNR TO CUSTNR, OLDREC-NAME1 TO NAME1, OLDREC-TELE1 TO TELE1. " Fill SAP structures: MOVE: '1' TO BKNOO-STYPE, 'XD02' TO BKNOO-TCODE, CUSTNR TO BKNOO-CKUNNR. MOVE: '2' TO BKNA1-STYPE, 'BKNA1' TO BKNA1-TBNAM, 'TELE1 TO BKNA1-TELF1, NODATA TO BNKA1-SENDE. " Transfer data to SAPFILE: TRANSFER: BKNOO TO SAPFILE, BKNA1 TO SAPFILE. * TEXT-02: 'Data was transferred for customer:' WRITE: / TEXT-002, OLDREC-CUSTNR, BKNOO-CUSTNR. ENDIF. ENDDO. CLOSE DATASET: OLDFILE, SAPFILE, ERRFILE.
(10)
WRITING
BATCH
INPUT
PROGRAM:
PROCEDURE
IN
OVERVIEW:
In general, you can transfer data from an existing system into the SAP System with pre-defined
batch
input
programs,
delivered
with
the
SAP
System.
In some cases, however, you will need to write your own batch input program. For example, the standard SAP batch input programs in an application may not have foreseen the data transfer requirement you have, or you may wish to customize the standard data transfer procedure. To write your own batch input program, you'll need to do the following:
1. Analyze the transaction(s) that you will use to process your batch input data. You may have already done this when you wrote your data transfer program. Please see Writing a Data Transfer Program(3) and Analyzing SAP Transactions(4) for more information. 2. Decide on the batch-input method that you wish to use.
"Classical" batch input -- by way of a batch input session -- is more comfortable. Restartcapability and detailed logging are supported by the batch input management transaction for batch input sessions. Batch input by way of CALL TRANSACTION USING offers faster processing if you need it to get your batch input done in the time slot that is available for it. CALL TRANSACTION USING offers, however, less support for error recovery and management of batch input. For 3. Your detailed information, Write program will please the need see Selecting batch to do a Batch-Input input the Method(11) .
program. following:
read data in, often from a sequential file that has been exported from another system or prepared by a data transfer program if necessary, perform data conversions or error-checking prepare the data for batch input processing by storing the data in the batch input data structure, BDCDATA. generate a batch input session for classical batch input, or process the data directly with CALL TRANSACTION USING. RELATED BDC BDC BDC BDC MySAP SAP PART METHOD CODE TABLE and form,over POSTS FIVE CODE MASTER CONTROL strategies introduction
SESSION SAMPLE
SAMPLE CUSTOMER
sales definition,full
distribution veiw and
SAP SAP What What
Full form of planning and distribution of goods full form for mrp,sales and materiel planning is SAP and Why do we are in need of It is SAP Full form and its definition part one
SAP Full form and introduction part two SAP architecture,its full form of working and enjoy sap products SAP journey from R/3 towards MySAP.com MySAP technology RFC,BAPI,ALE and IDOC overveiw MySAP new generation technologies overview EnjoySAP introduction and Business Process of SAP XML with ALE,IDOC and BAPI Support this blog with Your Google Vote here @ Labels: ABAP BDC COMPLETE
You might also like
- SAP interface programming with RFC and VBA: Edit SAP data with MS AccessFrom EverandSAP interface programming with RFC and VBA: Edit SAP data with MS AccessNo ratings yet
- Study On Microsoft SAP BW Data Extract: Bill FaisonDocument35 pagesStudy On Microsoft SAP BW Data Extract: Bill FaisonvinaybhideNo ratings yet
- PROC REPORT by Example: Techniques for Building Professional Reports Using SAS: Techniques for Building Professional Reports Using SASFrom EverandPROC REPORT by Example: Techniques for Building Professional Reports Using SAS: Techniques for Building Professional Reports Using SASNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Tutorials in Bapi-SAP ABAPDocument116 pagesStep by Step Tutorials in Bapi-SAP ABAPNelson GarciaNo ratings yet
- 123step by Step Tutorials in Bapi Sap Abap PDF FreeDocument116 pages123step by Step Tutorials in Bapi Sap Abap PDF FreeReign AckermannNo ratings yet
- ABAP For StudentsDocument84 pagesABAP For StudentsMichelle Shaw50% (2)
- ABAP5Document2 pagesABAP5prasureshNo ratings yet
- BDC & Programming Interfaces (Scheduling) : SAP R/3 Document: BDC ConceptDocument0 pagesBDC & Programming Interfaces (Scheduling) : SAP R/3 Document: BDC ConceptFernando BernardiNo ratings yet
- SAP ABAP On HANA - Basic ProgrammingDocument20 pagesSAP ABAP On HANA - Basic ProgrammingMãllésh ÑããýãkNo ratings yet
- Working With Database Tables Student VersionDocument12 pagesWorking With Database Tables Student VersionSuresh babuNo ratings yet
- Exp 0002Document8 pagesExp 0002iicewebcomNo ratings yet
- PPDS Basic Configuration GuideDocument16 pagesPPDS Basic Configuration GuideSrini Donapati100% (1)
- BDC - Batch InputDocument52 pagesBDC - Batch InputRoberto MartínezNo ratings yet
- How To Set Up Data Sources For CR in 90, Version For SAP HANADocument8 pagesHow To Set Up Data Sources For CR in 90, Version For SAP HANAgabrielNo ratings yet
- B1H 90 HT SetUpDSForCRL PDFDocument8 pagesB1H 90 HT SetUpDSForCRL PDFLuis EmilioNo ratings yet
- AbapDocument69 pagesAbapKata Naresh BabuNo ratings yet
- Change Document3a Step by StepDocument15 pagesChange Document3a Step by Stepwysoki1982No ratings yet
- Good Abap Programming Practice Manual in Sap BW Incl Hana PDFDocument69 pagesGood Abap Programming Practice Manual in Sap BW Incl Hana PDFIbou100% (3)
- 2 - ABAP Program AnalysisDocument32 pages2 - ABAP Program AnalysisAdjie Kastaman Tujuh DuaNo ratings yet
- Core Abap NotesDocument38 pagesCore Abap NotesvbvrkNo ratings yet
- Sap Abap Interview Q & ADocument32 pagesSap Abap Interview Q & AKaustav PyneNo ratings yet
- Sap BodsDocument38 pagesSap BodsTrishul SampathNo ratings yet
- BDCDOCUMENTATIONDocument48 pagesBDCDOCUMENTATIONapi-3730718No ratings yet
- SAP R/3 System Overview & ABAP/4 ProgrammingDocument48 pagesSAP R/3 System Overview & ABAP/4 Programmingsales1510No ratings yet
- BDC Recording Procedure: Sap Sm35Document13 pagesBDC Recording Procedure: Sap Sm35vidyadhar_kNo ratings yet
- Easytreve FAQDocument12 pagesEasytreve FAQdhanalekshmirameshNo ratings yet
- Material Master Template - PRE PRDS (JW-FG-CR BGH) - 05-04-2024Document206 pagesMaterial Master Template - PRE PRDS (JW-FG-CR BGH) - 05-04-2024Jai Narayan SharmaNo ratings yet
- BDC & File HandlingDocument83 pagesBDC & File HandlingSrikanth Sarguneswaran100% (1)
- ABAP On HANA Interview QuestionsDocument20 pagesABAP On HANA Interview QuestionsShashikantNo ratings yet
- VATDateDocument8 pagesVATDateYanetzi VargasNo ratings yet
- SAP ABAP Interview Questions Top 50Document7 pagesSAP ABAP Interview Questions Top 50pal singhNo ratings yet
- BC420 - 46C - 005principles of Standard Data TransferDocument14 pagesBC420 - 46C - 005principles of Standard Data TransfermkumarshahiNo ratings yet
- Sap Abap Interview QuestionsDocument8 pagesSap Abap Interview Questionsamarsngh194No ratings yet
- Basics For Inline Declarations With Sap-Abap Author: Pradyut S. Vyas Mentored By: Pranesh KumarDocument5 pagesBasics For Inline Declarations With Sap-Abap Author: Pradyut S. Vyas Mentored By: Pranesh KumarsathishNo ratings yet
- A Detail Description On Subroutine PoolDocument11 pagesA Detail Description On Subroutine Poolroys4396510No ratings yet
- Form Builder - InterfaceDocument19 pagesForm Builder - InterfaceNaresh ChinthagumpalaNo ratings yet
- What Is Data ExtractionDocument13 pagesWhat Is Data ExtractionSuraj PillaiNo ratings yet
- Abap News For Release 740 Sp05 1Document37 pagesAbap News For Release 740 Sp05 1Surya Reddy LakshminarasimhaNo ratings yet
- BDC Using CALL TRANSACTION MethodDocument8 pagesBDC Using CALL TRANSACTION Methodpepe2000No ratings yet
- LSMWDocument7 pagesLSMWPatil MgNo ratings yet
- Abapfaq 120516010452 Phpapp01Document10 pagesAbapfaq 120516010452 Phpapp01Bhavani SimgamsettiNo ratings yet
- 100 Abap Questions: ABAP Development FAQ Types of ReportsDocument6 pages100 Abap Questions: ABAP Development FAQ Types of ReportsMani KandanNo ratings yet
- PdsDocument2 pagesPdsSatyabrata NathNo ratings yet
- ETL Development StandardsDocument6 pagesETL Development StandardsvinayaartalaNo ratings yet
- Abap InterviewDocument25 pagesAbap InterviewDinesh Reddy VootkuriNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SAP SmartFormsDocument14 pagesIntroduction To SAP SmartFormsseventhhemanthNo ratings yet
- ABAP Training For Functional Consultants 60Document62 pagesABAP Training For Functional Consultants 60abbas910% (1)
- Advanced Form Sap AbapDocument25 pagesAdvanced Form Sap AbapJulio RafaelNo ratings yet
- Source Data For QM - Selected Set CodeDocument6 pagesSource Data For QM - Selected Set CodesapppqmmanloNo ratings yet
- Project For TMS: People Also AskDocument8 pagesProject For TMS: People Also AskDhananjay MishraNo ratings yet
- My BookDocument15 pagesMy BookDeepaNarendraNo ratings yet
- SAP S4HANA Migration Object ModelerDocument18 pagesSAP S4HANA Migration Object ModelerpeenNo ratings yet
- SAS Interview Questions and AnswersDocument107 pagesSAS Interview Questions and AnswersmeenaNo ratings yet
- Sap Abap Material ChandraDocument170 pagesSap Abap Material Chandragvrahul100% (1)
- BPC Embedded Interview QuestionsDocument88 pagesBPC Embedded Interview QuestionsSandeep SagarNo ratings yet
- Basic of AdobeformDocument9 pagesBasic of Adobeformbuggujha01No ratings yet
- Source Data For ProductDocument143 pagesSource Data For ProductSwethaPriyaSampathaRaoNo ratings yet
- How To Set Up Data Sources For CR Layouts in B1HDocument9 pagesHow To Set Up Data Sources For CR Layouts in B1Hivan pereiraNo ratings yet
- Table NameDocument43 pagesTable Nameevil66inNo ratings yet
- Recommendation For V R Siddharth Jujjavarapu MelbourneDocument1 pageRecommendation For V R Siddharth Jujjavarapu MelbourneSwapna KuntamukkalaNo ratings yet
- SAP CRM 7.0 For Newbies (Part 1) Simple BOL Object Creation For CRM Webclient UIDocument9 pagesSAP CRM 7.0 For Newbies (Part 1) Simple BOL Object Creation For CRM Webclient UIMehmet Onur MutluNo ratings yet
- How To Guide Business Object Layer ProgrammingDocument48 pagesHow To Guide Business Object Layer Programmingsharib_honeyNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programming Model 1Document41 pagesObject Oriented Programming Model 1Swapna KuntamukkalaNo ratings yet
- Sap CRM WebclientDocument6 pagesSap CRM WebclientSwapna Kuntamukkala0% (1)
- ABAP ObjectsOODocument39 pagesABAP ObjectsOOSwapna KuntamukkalaNo ratings yet
- Modifying Screen Fields SAP ABAPDocument19 pagesModifying Screen Fields SAP ABAPsampath30712350% (2)
- Achieving Control-Break Statements Functionality in Smart FormsDocument7 pagesAchieving Control-Break Statements Functionality in Smart FormsSwapna KuntamukkalaNo ratings yet
- Abap Objects 1ooDocument149 pagesAbap Objects 1ooSwapna KuntamukkalaNo ratings yet
- Custom GenIL BOL For Z-Tables With RelationshipsDocument12 pagesCustom GenIL BOL For Z-Tables With RelationshipsSrikanth Kishan0% (1)
- Composition On GrailsDocument22 pagesComposition On GrailsHemendra SabharwalNo ratings yet
- Data DictionaryDocument20 pagesData Dictionaryparthasc1982No ratings yet
- Search HelpsDocument20 pagesSearch HelpsEmilSNo ratings yet
- Overview of ERP - Enterprise Resource PlanningDocument24 pagesOverview of ERP - Enterprise Resource PlanningSwapna KuntamukkalaNo ratings yet
- Abap TrainingDocument379 pagesAbap TrainingSwapna KuntamukkalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 28: Introduction To Dialog ProgrammingDocument11 pagesChapter 28: Introduction To Dialog ProgrammingSwapna Kuntamukkala100% (1)
- Smartforms Demo On Copies Window (Real Time Scenario)Document5 pagesSmartforms Demo On Copies Window (Real Time Scenario)Kabil RockyNo ratings yet
- Faq's On Abap Cross Applications - Sap AbapDocument6 pagesFaq's On Abap Cross Applications - Sap AbapSathish BollabattulaNo ratings yet
- Creating Smartform For The PreDocument6 pagesCreating Smartform For The PreSwapna KuntamukkalaNo ratings yet
- Demo On Bar Code Printing Using SAP ScriptsDocument14 pagesDemo On Bar Code Printing Using SAP ScriptsSwapna KuntamukkalaNo ratings yet
- Draw Vertical Lines To Fill The Entire Main Window in SmartFormDocument7 pagesDraw Vertical Lines To Fill The Entire Main Window in SmartFormSwapna KuntamukkalaNo ratings yet
- Converting SMART FORMS Output To PDF FormatDocument4 pagesConverting SMART FORMS Output To PDF FormatSwapna KuntamukkalaNo ratings yet
- Calling Smart Form Using Driver ProgramDocument2 pagesCalling Smart Form Using Driver ProgramSwapna KuntamukkalaNo ratings yet
- BDC Table Control Is An Area On The Screen in Which You Can Display Data in Tabular FormDocument10 pagesBDC Table Control Is An Area On The Screen in Which You Can Display Data in Tabular FormSwapna KuntamukkalaNo ratings yet
- Working With Secondary WindowDocument4 pagesWorking With Secondary WindowSwapna KuntamukkalaNo ratings yet
- Working With Smart StylesDocument5 pagesWorking With Smart StylesSwapna KuntamukkalaNo ratings yet
- Draw Vertical Lines To Fill The Entire Main Window in SmartFormDocument7 pagesDraw Vertical Lines To Fill The Entire Main Window in SmartFormSwapna KuntamukkalaNo ratings yet
- Batch Input Sessions Enter Data NonDocument12 pagesBatch Input Sessions Enter Data NonSwapna KuntamukkalaNo ratings yet
- How To Set Up Standard Roles in SAP HANADocument23 pagesHow To Set Up Standard Roles in SAP HANANaveenNo ratings yet
- Red Hat Directory Server 10: Performance Tuning GuideDocument56 pagesRed Hat Directory Server 10: Performance Tuning GuideMunshi H HaqueNo ratings yet
- Automatic Timetable Generation ReportDocument17 pagesAutomatic Timetable Generation ReportKalidindi TejasreeNo ratings yet
- MidDocument24 pagesMidAndreea Alexandra AlbuNo ratings yet
- Debugger MipsDocument79 pagesDebugger Mipscarver_uaNo ratings yet
- 101 Programming Tips and Tricks PDFDocument132 pages101 Programming Tips and Tricks PDFPasi Lassila100% (1)
- AIX (R) Version 7.1 Commands Reference, V - IBMDocument792 pagesAIX (R) Version 7.1 Commands Reference, V - IBMslimane00No ratings yet
- ABB I-Bus Eib / KNX Application Unit AB/S 1.1 With The Application Logic Time 200 IO/1.4 For The ETS3Document52 pagesABB I-Bus Eib / KNX Application Unit AB/S 1.1 With The Application Logic Time 200 IO/1.4 For The ETS3ramblicasNo ratings yet
- Question Bank (I Scheme)Document2 pagesQuestion Bank (I Scheme)Adeel Tariq100% (1)
- Zeus Spy Eye Banking Trojan AnalysisDocument31 pagesZeus Spy Eye Banking Trojan Analysisswinki3No ratings yet
- Sudesh New ResumeDocument2 pagesSudesh New Resumemanvar5No ratings yet
- Contacts LogDocument320 pagesContacts LogAndré MacedoNo ratings yet
- Understanding and Interpreting The New GAMP 5 Software CategoriesDocument12 pagesUnderstanding and Interpreting The New GAMP 5 Software Categorieskrisna8154No ratings yet
- DBMS2Document54 pagesDBMS2SwaggerChicNo ratings yet
- 3 - Course PlanDocument2 pages3 - Course PlanRajeshwari R PNo ratings yet
- Open Gapps LogDocument2 pagesOpen Gapps LogAlvaro ReyesNo ratings yet
- Nokia 7360 ISAM FX Shelf ANSI For POL DataSheetDocument3 pagesNokia 7360 ISAM FX Shelf ANSI For POL DataSheetandrew chiangNo ratings yet
- Arma Server Web Admin - ARMA 3 - COMMUNITY MADE UTILITIES - Bohemia Interactive Forums PDFDocument1 pageArma Server Web Admin - ARMA 3 - COMMUNITY MADE UTILITIES - Bohemia Interactive Forums PDFBMikeNo ratings yet
- Karel The Robot Learns JavaDocument39 pagesKarel The Robot Learns JavaTugce TasciNo ratings yet
- Intructions GcitDocument1 pageIntructions Gcitiñaki gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Computer Servicing SystemDocument4 pagesComputer Servicing SystemLouie RamosNo ratings yet
- Install Wekan Kanban Board System On Ubuntu 20.04 - 18.04 - ComputingForGeeksDocument19 pagesInstall Wekan Kanban Board System On Ubuntu 20.04 - 18.04 - ComputingForGeeksCarlos Andrey MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Product Manual 26912 (Revision D, 12/2018) : Digital Valve Positioner (DVP) Service Tool ManualDocument194 pagesProduct Manual 26912 (Revision D, 12/2018) : Digital Valve Positioner (DVP) Service Tool Manualalex pereira pinheiroNo ratings yet
- Burma Information Technology Team (BIT) : Ultrasurf Your-Freedom Internet Explorer Mozilla Proxy ServerDocument10 pagesBurma Information Technology Team (BIT) : Ultrasurf Your-Freedom Internet Explorer Mozilla Proxy ServerLet's Work TogetherNo ratings yet
- Practice Exercise ThreadsDocument3 pagesPractice Exercise Threadskyle ferrerNo ratings yet
- 8051 Micro ControllerDocument38 pages8051 Micro ControllerKumar RathoreNo ratings yet
- 1.3 PPT - Measure of Query CostDocument42 pages1.3 PPT - Measure of Query Costamaan100% (1)
- Game LogDocument10 pagesGame LogПара ШокNo ratings yet
- Course On FunctionsDocument45 pagesCourse On FunctionsVartika VashistaNo ratings yet
- SC 092540Document700 pagesSC 092540Shashikant MauryaNo ratings yet
- Dark Data: Why What You Don’t Know MattersFrom EverandDark Data: Why What You Don’t Know MattersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyFrom EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (228)
- iPhone 14 Guide for Seniors: Unlocking Seamless Simplicity for the Golden Generation with Step-by-Step ScreenshotsFrom EverandiPhone 14 Guide for Seniors: Unlocking Seamless Simplicity for the Golden Generation with Step-by-Step ScreenshotsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Chip War: The Fight for the World's Most Critical TechnologyFrom EverandChip War: The Fight for the World's Most Critical TechnologyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (82)
- Grokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleFrom EverandGrokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (16)
- Blockchain Basics: A Non-Technical Introduction in 25 StepsFrom EverandBlockchain Basics: A Non-Technical Introduction in 25 StepsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (24)
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102From EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Optimizing DAX: Improving DAX performance in Microsoft Power BI and Analysis ServicesFrom EverandOptimizing DAX: Improving DAX performance in Microsoft Power BI and Analysis ServicesNo ratings yet
- Fusion Strategy: How Real-Time Data and AI Will Power the Industrial FutureFrom EverandFusion Strategy: How Real-Time Data and AI Will Power the Industrial FutureNo ratings yet
- Starting Database Administration: Oracle DBAFrom EverandStarting Database Administration: Oracle DBARating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- iPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]From EverandiPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Business Intelligence Strategy and Big Data Analytics: A General Management PerspectiveFrom EverandBusiness Intelligence Strategy and Big Data Analytics: A General Management PerspectiveRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- CompTIA A+ Certification All-in-One Exam Guide, Eleventh Edition (Exams 220-1101 & 220-1102)From EverandCompTIA A+ Certification All-in-One Exam Guide, Eleventh Edition (Exams 220-1101 & 220-1102)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- SQL QuickStart Guide: The Simplified Beginner's Guide to Managing, Analyzing, and Manipulating Data With SQLFrom EverandSQL QuickStart Guide: The Simplified Beginner's Guide to Managing, Analyzing, and Manipulating Data With SQLRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (46)
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam Core 1 220-1001 and Exam Core 2 220-1002From EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam Core 1 220-1001 and Exam Core 2 220-1002Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CompTIA Security+ All-in-One Exam Guide, Sixth Edition (Exam SY0-601)From EverandCompTIA Security+ All-in-One Exam Guide, Sixth Edition (Exam SY0-601)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)


































































































































![iPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/audiobook_square_badge/728318688/198x198/f3385cbfef/1714829744?v=1)