Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MCEM Paediatrics Obstetrics and Gyne MCQ
Uploaded by
Ankita SinhaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MCEM Paediatrics Obstetrics and Gyne MCQ
Uploaded by
Ankita SinhaCopyright:
Available Formats
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ
1. Ectopic Pregnancy: (a) If there is a clinical suspicion of ectopic pregnancy, sonography should be performed even in patients with low hCG levels. If there is a clinical suspicion of ectopic pregnancy, sonography should be performed even in patients with low hCG levels. (b) There is a good correlation between the volume of blood loss and vital signs in ruptured ectopic pregnancy. There is poor correlation between the volume of blood loss and vital signs in ruptured ectopics. (c) Fever is rare. (d) No single bhCG level can reliably distinguish between a normal and an ectopic pregnancy. (e) Dilute urine cannot cause a false-negative urine pregnancy test. Dilute urine may cause a false-negative urine pregnancy test. HCG concentrations usually double every 1.4 to two days until six to seven weeks of gestation in viable intrauterine pregnancies. 2. Hyperemesis Gravidarum: (a) Usually has significant abdominal pain. Hyperemesis gravidarum is intractable nausea and vomiting without significant abdominal pain. (b) May result in a low birth weight infant. (c) Can cause hyperkalaemia. Can cause hypokalaemia and ketonemia. (d) Metoclopramide is safe to use in pregnancy. (e) Phenothiazines for nausea and vomiting are a class B ( presumed safe in pregnancy, animal studies) in pregnancy. Phenothiazines are a class C drug in pregnancy(uncertain safety, animal studies show an adverse effect). However they are used widely. Hyperemesis gravidarum is considered the severe end of the spectrum of nausea and vomiting.There is no clear demarcation between common pregnancy-related "morning sickness". Persistent vomiting accompanied by weight loss exceeding 5% of prepregnancy body weight and ketonuria unrelated to other causes is an objective diagnosis. Hyperemesis tends to improve in the last half of pregnancy. 3. Radial head subluxation ( Nursemaids elbow ): (a) The arm is kept in an adducted ,semi-flexed and prone position. The arm is kept in an adducted ,semi-flexed and prone position. The patient is a toddler who will not move the affected arm, but is otherwise not in any distress. (b) The average age is 2-3 years. With a range from 6 months to 7 years. (c) On palpation there is no significant point tenderness or swelling. On palpation there is no significant point tenderness or swelling. (d) The pronation technique for replacement is superior to the supination technique. (e) Girls are affected more commonly than boys. Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e
Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e
Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ
And the left arm is affected more commonly than the right arm. The usual mechanism of injury is axial traction on a pronated forearm with the elbow in extension. With sudden traction on the distal radius, a portion of the annular ligament slips over the head of the radius and slides into the radiohumeral joint, where it becomes trapped. It typically occurs between the ages of one and four years, with a peak incidence between two and three years. The classic history of a "pull injury" is present in approximately 50 percent of cases . Other mechanisms include falling onto the elbow, minor direct trauma to the elbow, or a twisting motion of the arm. Children with RHS may hold the affected arm close to the body with the elbow either fully extended or slightly flexed and the forearm pronated. The child is in little distress unless attempts are made to move the elbow. Supination/flexion and hyperpronation are two techniques for reduction of RHS. Both techniques are effective. Recurrence rates range from 27 to 39 percent. There are no long-term sequelae associated with recurrent RHS. 4. SIDS: (a) Occurs in infants from 1 month to 1 year. SIDS occurs in infants from 1 month to 1 year. (b) There is usually no preceeding dysrhythmias in the preceeding months. Prospective studies monitoring normal infants showed no antecedent dysrhythmias in infants who eventually succumbed to SIDS. (c) The main disturbance in victims appears to be with the infants ventilatory response. The main disturbance in victims appears to be with the infants ventilatory response. (d) Prolonged QT is a rare association. Prolonged QT is a rare association. (e) WPW is a rare association. WPW is a rare association. The main disturbance in victims appears to be with the infant's ventilatory response. SIDS and infantile apnea are related- the exact nature of this relation is uncertain. There are multiple causes of infantile apnea for which the final pathway involves respiratory muscle fatigue. Death is due to respiratory rather than to cardiac arrest. Dysrhythmias probably occur only as a terminal event. Syndromes such as prolonged QT interval or Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome are rare associations. Prospective studies monitoring normal infants showed no antecedent dysrhythmias in infants who died to SIDS. 5. Drugs In Pregnancy: (a) ACE inhibitors cause renal damage and oligohydramnios. ACE inhibitors cause renal damage and oligohydramnios. (b) Retinoic Acid derivatives can cause fetal abnormalities up to 2 years after stopping therapy. Retinoic Acid derivatives can cause fetal abnormalities up to 2 years after stopping therapy. (c) Alcohol is associated with a neonatal goitre. Alcohol can cause fetal growth retardation and a withdrawal syndrome in the newborn. (d) Aminoglycosides can cause lung fibrosis in the fetus. Aminoglycosides can cause vestibular damage to the fetus. (e) Amiodarone can cause neonatal goitre. Amiodarone can cause neonatal goitre. Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ
6. Clavicle fractures: (a) Fractures of the clavicle in the newborn usually result from birth injury. Risk factors include high birth weight and shoulder dystocia.An ED visit may be made when it is noted that the newborn is not moving one arm. (b) The most common mechanism of injury is either a fall onto an outstretched hand or onto the lateral side of the shoulder. The most common mechanism of injury is either a fall onto an outstretched hand or onto the lateral side of the shoulder. (c) Displaced and overlapping fractures do not tend to heal well in mid third clavicular fractures. Displaced and overlapping fractures in mid third clavicular fractures tend to heal well with simple immobilization in a simple sling for 3 to 4 weeks. (d) Fractures at the medial end of the clavicle are common. Fractures at the medial end of the clavicle are uncommon. Most clavicular fractures are middle third fractures.Open reduction and fixation is generally needed for medial third fractures. (e) Distal third fractures almost always require operative fixation. Distal third fractures can mostly be managed conservatively. 7. Pelvic Pain: (a) Patients with pelvic adhesions are at increased risk of adnexal torsion. Ovarian/adnexal torsion is a surgical emergency. The ovary or tubule elements twist on their pedicle, compromising the blood supply and producing ischaemic pain and subsequent necrosis. (b) Mittelschmerz pain occurs at day 20 to 22 of the menstrual cycle. Mittelschmerz pain occurs at day 14 to 16 of the menstrual cycle. (c) Mittelschmerz pain is typically bilateral. Mittelschmerz pain is unilateral, mild to moderate and may last a day or less. Vaginal spotting may occur. (d) Leiomyomas frequently produce acute pain. Leiomyomas or fibroids rarely produce acute pain. If severe pain is present torsion of a pedunculated fibroid or degeneration should be considered. (e) Primary dysmenorrhea occurs most commonly in middle aged women. Primary dysmenorrhea occurs most commonly in young girls just after menarche.Pain is crampy and may be associated with backache or headache or nausea. 8. Henoch-Schonlein Purpura: (a) Does not affect small arteries of the gastrointestinal tract. Henoch-Schonlein Purpura affects small arteries in the kidneys, skin and GI tract. (b) Is most common in 13-16 year olds. Henoch-Schonlein Purpura is most common in 4-11 year olds. (c) Joint pain is most common in the elbows and wrists. Joint pain is most common in the knees and ankles. (d) It is common for nephritis to progress to renal failure. It is rare for nephritis to progress to renal failure. (e) Platelets are invariably low. Tru e Fals e
Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e
Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e
Tru e
Fals e
Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e
Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e
Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e
Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ
Platelets are usually normal. 9. Classical signs of unilateral congenital dislocation of the hip include: (a) Above knee limb shortening. Above knee limb shortening is most obvious when the hips are flexed and the level of the knees are compared. (b) If a child is able to walk with a limp. The child may fall to the affected side. If the dislocation is bilateral there may be a waddling gait. (c) Limitation of abduction. With the hips flexed thighs should normally abduct to 75 degrees. (d) There is upward and outward displacement of both thighs leaving a perineal sign. This is a sign of bilateral dislocation. (e) Skin creases on the front inside of the thigh. Caused by asymetry of the junction of the thigh to the trunk. 10. The following are true for moderately severe croup: (a) Antibiotics are indicated. Croup is a viral infection. (b) Steam Inhalations are useful. Steam Inhalations are of little value and may lead to accidents. (c) Nebulised Salbutamol should be used. Nebulised adrenaline may have a transient effect. (d) Oral Steroids should be used. Inhaled and oral steroids are beneficial. (e) Ribivarin is used. Ribivarin is used in bronchiolitis. Nebulized epinephrine can be repeated every 15 to 20 minutes. The administration of three or more doses within a two- to three-hour time period should prompt initiation of close cardiac monitoring. 11. Pre-eclampsia: (a) Proteinuria is defined as more than 100 mg/24 hours. Proteinuria is defined as more than 300 mg/24 hours. (b) Hypertension is defined as BP > 140/90. Hypertension is defined as BP > 140/90 (c) May complicate 20% of patients. May complicate 5% of patients.(Risk factors for preeclampsia in healthy nulliparous women: a prospective multicenter study. The National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Network of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Units. Preeclampsia developed in 5.3%. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995 Feb;172(2 Pt 1):6428) (d) Can occur from 10 weeks gestation. Clinical presentation is hypertension, proteinuria, and edema in women of 20 weeks or more gestation. (e) Primagravida is a risk factor. Tru e Tru e Tru e Fals e Fals e Fals e Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e
Tru e Tru
Fals e Fals
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ
e Others include chronic hypertension, kidney disease, obesity, DM, multiple gestation, and history of pre-eclampsia. 12. Nice Guidelines:Selection of children ( <16 ) for CT scanning of head: (a) A witnessed loss of consciousness of >5 min is an indication for immediate CT brain scan request. A witnessed loss of consciousness of >5 min is an indication for immendiate CT brain scan. (b) Anterograde amnesia lasting >1 min is an indication for immediate CT scan request. Anterograde amnesia lasting >5 min is an indication for immediate CT scan request. (c) Retrograde amnesia lasting >1 min is an indication for immediate CT scan request. Retrograde amnesia lasting >5 min is an indication for immediate CT scan request. (d) 3 or more discrete episodes of vomiting is an indication for a CT brain scan request. 3 or more discrete episodes of vomiting is an indication for a CT brain scan request. (e) Post traumatic seizure without a history of epilepsy should result in a CT brain scan request. http://www.nice.org.uk 13. Viral Croup: (a) The incubation period of the most common virus to cause viral croup is less than 6 days and the shedding period is about 4 weeks. The incubation period of the most common virus to cause viral croup is less than 6 days and the shedding period is about 2 weeks. (b) Croup is sometimes associated with a low grade fever and the cough is usually worse in the evening and at night-time. Croup is sometimes associated with a low grade fever and the cough is usually worse in the evening and at night-time. (c) Children 3 years to 6 years of age are most commonly affected with viral croup. Children 6 months to 3 years of age are most commonly affected with viral croup, with a peak incidence between 1 and 2 years of age. (d) A 1mm amount of oedema in an infant may cause a reduction of 10% of the cross-sectional area. A 1mm amount of oedema in an infant may cause a reduction of 50% of the crosssectional area. (e) Parainfluenza virus types I, II and III are the most common causes of viral croup. Parainfluenza virus types I, II and III are the most common causes of viral croup. 14. Acute herpetic gingivostomatitis: (a) Typically occurs in 5 to 10 year olds. Acute herpetic gingivostomatitis typically occurs in 1 to 3 year olds. (b) Total length of illness before healing begins is usually about 1 week. The total length of illness before healing begins is usually about 1 week following a 24 to 48 hour prodromal illness with fever. (c) Ulcers normally spare the back of the mouth. In Acute herpetic gingivostomatitis ulcers normally spare the back of the mouth but appear everywhere else in the mouth. (d) Rarely causes lymphadenopathy. Lymphadenopathy is common in acute herpeticgingivostomatitis. Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e e
Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e
Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e
Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e
Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ
(e) Rarely, if ever, results in a child being admitted to hospital. Commonly results in hospitalisation as the child refuses to eat. Herpes gingivostomatitis is the principle manifestation of primary HSV-1 infection. Children who present with gingivostomatitis often require either topical or oral administration of analgesics and, in severe cases, intravenous rehydration. Shortterm relief (10 to 15 minutes) can be achieved via mouth rinses with viscous lidocaine. Studies suggest that acyclovir may be beneficial if begun early during primary (or recurrent) infections since the drug acts only during active viral replication, which generally precedes symptoms. 15. Thromboembolic disease in pregnancy: (a) Incidence of DVT in pregnancy is approximately 2%. Incidence of DVT in pregnancy is 0.5% to 0.7%. (b) Young maternal age is associated with increased risk. Advanced maternal age is associated with increased risk. (c) Increasing parity is associated with increased risk of thromboembolism in pregnancy. Increasing parity is associated with increased risk of thromboembolism in pregnancy. (d) Warfarin is relatively contraindicated in pregnancy. Oral anticoagulants cross the placenta and produce fetal abnormalities. They may also cause fatal fetal haemorrhage. (e) Multiple gestation is associated with an increased risk of thromboembolism. Other risk factors include operative delivery, bedrest, obesity and hypercoagulable states. 16. The following physical findings are suggestive of a secondary headache in children: (a) Bradycardia. (b) Hypertension. (c) Retinal hemorrhage. (d) Petechiae. (e) Facial herpes zoster. Physical findings suggesting secondary headache include an altered mental status , a septic or toxic appearance, a fever, hypertension or hypotension , diaphoresis , facial herpes zoster, petechiae , caf-u-lait spots, hydrocephalus , ptosis , visual field defect , retinal hemorrhage or optic disc distortion , asymmetry of motor or sensory responses , thyromegaly , nuchal rigidity , and a head tilt. 17. Trauma in pregnancy: (a) Abruptio placentae is the number one cause of fetal death after blunt abdominal trauma. Abruptio placentae is the number one cause of fetal death after blunt abdominal trauma. (b) The fetus is not usually in shock unless the mother shows signs of shock. Tru e Tru Fals e Fals Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e Tru e Fals e
Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e
Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ
e Fetus may be in shock prior to the mother showing signs of shock so resuscitation should be aggressive. (c) Treatment priorities in pregnant women are identical to those in non pregnant women. Treatment priorities in pregnant women are identical to those in non pregnant women. (d) The uterus rises above the pelvis after the 10th week in gestation. The uterus rises above the pelvis after the 12th week in gestation. (e) Gravid patients usually have a reduced cardiac output. Gravid patients usually have elevated cardiac output and heart rate. The initial evaluation of the pregnant trauma victim should focus on establishing maternal cardiopulmonary stability. Any treatment required to save the mother's life or treat her critical status should be undertaken, regardless of her pregnancy. Displacing the uterus to the left, off the vena cava, is critical to maximize effectiveness of cardiopulmonary resuscitation in the second half of pregnancy.Abruption leading to nonreasssuring fetal heart rate patterns and death can occur despite relatively mild maternal trauma or discomfort. The majority of women who develop adverse obstetrical outcomes have symptoms such as contractions, vaginal bleeding, or abdominal pain upon initial presentation. 18. Physiology of Pregnancy: (a) 40% increase in circulating blood volume. Maternal cardiovascular changes during pregnancy include a 40% increase in circulating blood volume. (b) 50% increase in resting heart rate. There is about a 15% increase in resting heart rate. (c) During the phase of blood pressure reduction, the diastolic pressure decrease is greater than the systolic pressure decrease. During the phase of blood pressure reduction, the diastolic pressure decrease is greater than the systolic pressure decrease. (d) It is normal to have a more prominent cardiac shadow on the chest X Ray during pregnancy. As the diaphragm pushes the heart up and to the left. (e) The ECG may show right axis deviation in normal pregnancy. The ECG may show left axis deviation in normal pregnancy.As the diaphragm pushes the heart up and to the left. 19. Fractures in children ( Elbow Injuries ): (a) Elbow fractures in children are commonly missed in the ED. Elbow fractures in children are commonly missed in the ED. (b) In lateral elbow X-rays no anterior fat pad should be appreciated. An anterior fat pad can be appreciated even if there is no occult fracture. (c) When a posterior fat pad is visualized, it usually suggests a hemarthrosis secondary to an intraarticular injury When a posterior fat pad is visualized, it usually suggests a hemarthrosis secondary to an intraarticular injury. (d) Supracondylar fractures are common in young children. Supracondylar fractures are among the most common fractures in the under 8 age group. (e) Supracondylar fractures extension type are more common than flexion type. Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e Tru e Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e Fals e Tru e Tru e Tru e e Fals e Fals e Fals e
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ
Much more common and occur when the child falls on an outstretched hand ( FOOSH ). Flexion type occur when a child falls on a flexed elbow. 20. UTI in pregnancy: (a) Ciprofloxacin may be used to treat a UTI during pregnancy. Ciprofloxacin crosses the placenta and concentrates in amniotic fluid. Maternal serum levels may be decreased during pregnancy. Reports of arthropathy (observed in immature animals and reported rarely in humans) have limited the use of fluoroquinolones in pregnancy. (b) Sulphonamides may be used close to term. Sulphonamides may be avoided close to term. (c) Trimethoprim may be used during the first trimester. Trimethoprim may be used after the first trimester. Because trimethoprim may interfere with folic acid metabolism, consider using only if the potential benefit to the mother outweighs the possible risk to the fetus. (d) Urinary tract infection is the most common bacterial infection in pregnancy. Urinary tract infection is the most common bacterial infection in pregnancy. (e) May be treated with 3 days with slow release nitrofurantoin. Also with amoxicillin or cephalexin. Tru e Fals e
Tru e Tru e
Fals e Fals e
Tru e Tru e
Fals e Fals e
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ The following are causes of purpuric lesions in children: (a) Viral illnesses. True ?Some viral illnesses can cause purpuric lesions. (b) Coughing. True ?Forceful coughing can cause petechiae of the face. (c) Vomiting. True ?Forceful vomiting can cause petechiae of the face. (d) Trauma. True ? (e) Henoch Schonlein Purpura. True ? Other causes include meningococcal disease and thrombocytopaenia.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Ectopic pregnancy: (a) A single bhCG level can reliably distinguish between a normal and an ectopic pregnancy. False ?No single bhCG level can reliably distinguish between a normal and an ectopic pregnancy. (b) Dilute urine may cause a false-negative urine pregnancy test. True ? (c) If there is a low level of bhCG there is no indication for ultrasound. False ?If there is a clinical suspicion of ectopic pregnancy, sonography should be performed even in patients with low bhCG levels. (d) Ectopic pregnancy classically presents with abdominal pain with vaginal bleeding or spotting in a woman with amenorrhea. True ?This is true but these symptoms are more commonly seen in threatened or spontaneous abortion than in ectopics. (e) Previous ectopic pregnancy is not a risk factor for a future ectopic. False ?Other risk factors include PID, tubal surgery, IUCD, and ART. HCG concentrations usually double every 1.4 to two days until six to seven weeks of gestation in viable intrauterine pregnancies.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ SIDS: (a) Overall incidence is roughly 5/1000 live births. False ?Overall incidence is roughly 0.8-1/1000 live births. (b) There is a peak at 8 months. False ?There is a peak at 2 months and at 4 months. (c) Before 1 month a child has a better anaerobic capacity to survive. True ?SIDS is rare in the first month of life because the neonate has a better anaerobic capacity for survival. (d) Infection is commonly associated with SIDS in otherwise healthy infants. True ?In healthy infants up to 50% who die from SIDS have an infection, usually a URTI. (e) Prenatal and postnatal maternal smoking increase the incidence of SIDS. True ?Prenatal and postnatal maternal smoking increase the incidence of SIDS.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Perthe's Disease: (a) Presents is children aged 11-13 years. False ?Perthes disease presents in children aged 3-10 years. (b) Girls are affected more than boys. False Boys are affected more than girls( M:F=4:1 ). (c) 95% are unilateral. False ?15% are bilateral. (d) ESR is almost always elevated. False ?ESR is normal. Aseptic necrosis of the upper femoral epiphysis presents with a painful limp.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Physiology of Pregnancy (a) During pregnancy the respiratory rate is increased. False ?The respiratory rate during pregnancy is unchanged. (b) A decrease in PCO2 during pregnancy is usually pathological. False ?As tidal volume is increased in pregnancy a decrease in PCO2 is normal. (c) Functional residual capacity is increased in pregnancy. False ?Functional residual capacity is decreased during pregnancy because the diaphragm is higher. (d) Intestinal motility is increased during pregnancy. False ?Intestinal motility is decreased during pregnancy. (e) Gastric emptying is delayed. True ?And therefore reflux disease is more common.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ SIDS: (a) Occurs up to 2 years. False ?Ocuurs in infants from 1 month to 1 year. (b) Infants who die from SIDS have a high rate of arrhythmia in the weeks and months prior to death. False ?Prospective studies monitoring normal infants showed no antecedent dysrhythmias in infants who eventually succumbed to SIDS. (c) Infant apnoea is a rare association. False ?The main disturbance in victims appears to be with the infants ventilatory response. (d) Prolonged QT is a common association. False ?Prolonged QT is a rare association. (e) WPW is a common association. False ?WPW is a rare association. The main disturbance in victims appears to be with the infant's ventilatory response. SIDS and infantile apnea are related- the exact nature of this relation is uncertain. There are multiple causes of infantile apnea for which the final pathway involves respiratory muscle fatigue. Death is due to respiratory rather than to cardiac arrest. Dysrhythmias probably occur only as a terminal event. Syndromes such as prolonged QT interval or Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome are rare associations. Prospective studies monitoring normal infants showed no antecedent dysrhythmias in infants who died to SIDS.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Thromboembolism in pregnancy: (a) The incidence of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) in pregnancy is about 0.5%. True ?The incidence of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) in pregnancy is about 0.5%. (b) Multiple gestation is a risk factor for thromboembolism. True ?Advanced maternal age, increasing parity, multiple gestation, operative delivery, bed rest, obesity, history of DVT, and clotting disorders. (c) The post-partum period is a higher risk time for thromboembolism than the antenatal period. False ?The post-partum period is a lower risk time for thromboembolism than the antenatal period. (d) Ventilation perfusion scans may be performed safely in pregnancy. True ? (e) Warfarin does not cross the placenta. False ?Warfarin does cross the placenta. In the 1st trimester it is associated with embryopathy. In the 2nd and 3rd trimesters it is associated with CNS and eye disturbance.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ SIDS: (a) To avoid SIDS an infant should be placed to sleep prone. False ?To avoid SIDS an infant should be placed to sleep supine or on his/her side. (b) There is no link between SIDS and child abuse. False ?Some investigators reported that 10 percent of SIDS cases are due to abuse. (c) Premature infants of low birth weight are at less risk of SIDS. False ?Premature infants of low birth weight are at greater risk of SIDS. (d) Infants of substance-abusing mothers are at greater risk for SIDS. True ?Infants of substance-abusing mothers are at greater risk for SIDS. (e) Acute hypoxic episodes are felt to occur in 99 percent of SIDS cases. False ?Acute hypoxic episodes are felt to occur in 80 percent of SIDS cases. Four groups of infants who appear at increased risk of SIDS have been identified: (1) term infants who have had an Apparent Life Threatening Event (ALTE) (2) premature infants of low birth weight, (3) siblings of infants who have succumbed to SIDS, and (4) infants of substance-abusing mothers.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Radial head subluxation ( Nursemaids elbow ): (a) The arm is kept in an adducted , extended and prone position. False ?The arm is kept in an adducted ,semi-flexed and prone position.The patient is a toddler who will not move the affected arm, but is otherwise not in any distress. (b) On palpation there is significant point tenderness or swelling. False ? On palpation there is no significant point tenderness or swelling. (c) There is no discomfort on palpation of the radial head. False ?There is discomfort on palpation of the radial head. (d) It is always necessary to obtain AP and lateral views of the elbow prior to manipulation. False ?If there is a high degree of clinical suspicion there is no need to obtain an X Ray. (e) The supination technique for replacement is superior to the pronation technique. False ?The pronation technique for replacement is superior to the supination technique. The usual mechanism of injury is axial traction on a pronated forearm with the elbow in extension. With sudden traction on the distal radius, a portion of the annular ligament slips over the head of the radius and slides into the radiohumeral joint, where it becomes trapped. It typically occurs between the ages of one and four years, with a peak incidence between two and three years. The classic history of a "pull injury" is present in approximately 50 percent of cases . Other mechanisms include falling onto the elbow, minor direct trauma to the elbow, or a twisting motion of the arm. Children with RHS may hold the affected arm close to the body with the elbow either fully extended or slightly flexed and the forearm pronated. The child is in little distress unless attempts are made to move the elbow. Supination/flexion and hyperpronation are two techniques for reduction of RHS. Both techniques are effective. Recurrence rates range from 27 to 39 percent. There are no long-term sequelae associated with recurrent RHS.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Epiglottitis: (a) Has a sudden onset. True ?Viral croup has a gradual onset. (b) Is associated with a prominent barking cough. False ?Viral croup is associated with a prominent barking cough but epiglottitis is not. (c) Is rarely associated with a fever. False ?Child often has a fever . In viral croup the child is likely to be apyrexial (d) Is associated with pooling and drooling of secretions. True ? (e) Is associated with continuous stridor. True ?Whearas croup may be associated with intermittent stridor only. Epiglottitis has a peak occurrence during the third year of life, with three-quarters of cases arising between the ages of 1 and 5 years. There is a slight male predominance (approximately 1.2:1). The child experiences a choking sensation and is distressed on inspiration, anxious, restless, and irritable. Speech is described as a "hot potato" voice(the child is speaking with a hot potato in the mouth) and is muffled. Hoarseness, as seen in laryngitis, is uncommon. The child usually assumes a sitting position with arms back, trunk leaning forward, neck hyperextended, and chin thrust forward in an effort to maximize the diameter of the obstructed airway.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Croup: (a) A 10mm amount of oedema in an infant may cause a reduction of 50% of the cross-sectional area. False ?A 1mm amount of oedema in an infant may cause a reduction of 50% of the cross-sectional area. (b) Influenza virus types I, II and III are the most common causes of viral croup. False ?Parainfluenza virus types I, II and III are the most common causes of viral croup. (c) The incubation period of the most common virus to cause viral croup is less than 6 days and the shedding period is about 2 weeks. True ?The incubation period of the most common virus to cause viral croup is less than 6 days and the shedding period is about 2 weeks. (d) Croup is sometimes associated with a low grade fever and the cough is usually worse in the morning time. False ?Croup is sometimes associated with a low grade fever and the cough is usually worse in the evening and at night-time. (e) Children 6 months to 3 years of age are most commonly affected with viral croup, with a peak incidence between 1 and 2 years of age. True ?Children 6 months to 3 years of age are most commonly affected with viral croup, with a peak incidence between 1 and 2 years of age.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ NICE Guidelines:The following are indications for a CT brain scan in a child ( <16 ): (a) Age < 1 year and the presence of a bruise >5cm on the head. True ?Age < 1 year and the presence of a bruise on the head is an indication for a CT Brain scan according to the NICE guidelines. (b) Age < 1 year and the presence of a laceration >5 cm on the head. True ?Age < 1 year and the presence of a laceration >5 cm on the head is an indication for a CT Brain scan according to the NICE guidelines. (c) >2 discrete episodes of vomiting. False ?>3 discrete episodes of vomiting is an indication for a CT Brain scan according to the NICE guidelines. ( >1 in an adult ). (d) Witnessed loss of consciousness >3 min. False ?A witnessed loss of consciousness > 5 min is an indication for a Ct brain scan. (e) Both anterograde or retrograde amnesia > 5 min is an indication for a CT Brain scan in children. True ?Both anterograde or retrograde amnesia > 5 min is an indication for a CT Brain scan in children. http://www.nice.org.uk
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ The following are true in relation to chickenpox: (a) Typically starts on the back. True ?Chickenpox is described as presenting with crops of vesicles of different ages usually starting on the back. (b) The incubation period for chickenpox is 7-10 days. False ?The incubation period for chickenpox is 11-21 days. (c) An individual is infectious from four days before the onset of the rash until there are scabs over all vesicles. True ?An individual is infectious from four days before the onset of the rash until there are scabs over all vesicles. (d) Can be caught from someone with shingles. True ?Chickenpox is highly infectious. (e) It is spread by droplets. True ?95% of adults are immune. Immunity is lifelong. Reye syndrome, is an illness developing during the course of varicella infection in children and presents nausea, vomiting, headache, excitability, delirium, and combativeness with frequent progression to coma. Salicylate use was identified as a major precipitating factor for the development of Reye syndrome and with warnings against the use of aspirin in patients with varicella or influenza this complication has virtually disappeared.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ The following clinical features are more suggestive of acute epiglottitis than croup: (a) Slow onset. False Acute epiglottitis has a rapid onset while croup tends to be preceded by a coryzal illness. (b) High fever >38.5?C. True High fever is a common finding in acute epiglottitis. Children with croup tend to be apyrexial or have a mild fever only. (c) Increased drooling of saliva. False Drooling of saliva is a non-specific sign of upper airway obstruction and may occur with both severe croup and acute epiglottitis. (d) Age over 5 years. True Croup is uncommon above the age of 5 years while acute epiglottitis occurs children up to age 7 and occasionally in older children and adults.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Pharyngitis: (a) Group A beta haemolytic streptococcus pharyngitis is uncommon before 3 years of age. True ?Group A beta haemolytic streptococcus pharyngitis is uncommon before 3 years of age. (b) Group A beta haemolytic streptococcus pharyngitis generally has a gradual onset of sore throat and fever. False ?Group A beta haemolytic streptococcus pharyngitis generally has a sudden onset of sore throat and fever. (c) The tonsils and pharynx generally do not have any exudate in group A beta haemolytic streptococcus. False ?The tonsils and pharynx generally have a moderate amount of exudate in group A beta haemolytic streptococcus. (d) In group A beta haemolytic streptoccus pharyngitis the cervical lymph nodes are generally enlarged. True ?In group A beta haemolytic streptoccus pharyngitis the cervical lymph nodes are generally enlarged. (e) Positive throat cultures may indicate an acute group A beta haemolytic streptococcus infection or a carrier state. True ?Positive throat cultures may indicate an acute group A beta haemolytic streptococcus infection or a carrier state.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Migraine in pregnancy: (a) Pregnancy usually exacerbates classic migraines. False ?Pregnancy usually improves classic migraines. (b) Ergotamine is the drug of choice in pregnancy when migraine occurs. False ? Ergot alkaloids should not be used (ergotamine,phenobarbital ,bromocriptine ,cabergoline,dihydroergotamine ,ergoloid mesylate ,methysergide ) (c) Prophylactic Beta Blocker therapy for migraine is contraindicated in pregnancy. False ?Prophylactic Beta Blocker therapy with propranolol or atenolol for migraine can be used in pregnancy. (d) Codeine for migraine treatment is contraindicated in pregnancy. False ?Paracetamol and codeine can be safely used. (e) Bromocriptine should be used to treat migraine in pregnant women. False ?
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ In the assessment of a limping child localising pain to the hip joint: (a) Slipped upper femoral epiphysis is most common in the 3-10 year old age group. False Perthes is more common in the 3-10 year old age group, while slipped upper femoral epiphysis is more common in the 10-16 year age group. (b) Perthes disease affects boys more often than girls at a ratio of 4:1 True Slipped upper femoral epiphysis is also more common in boys than girls at a ratio of 3:1. (c) Interruption of Shenton?s line is suggestive of a slipped upper femoral epiphysis. False Shenton?s line applies to the AP view of the pelvis and continues from the inferior border of the femoral neck to the inferior border of the pubic ramus ? it is disrupted with fracture neck of femur. Trethowan?s sign is a line drawn along the superior border of the femoral neck which should normally cut through the femoral epiphysis. If not, this may indicate a slipped upper femoral epiphysis. (d) Radiographic appearances are usually normal in transient synovitis. True
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ The following are correctly paired with regard to fetal effects: (a) Tetracyclines- eighth nerve damage. False ?Tetracyclines cause damage to bones and teeth. (b) Aminoglycosides-Dental discoloration. False ?Aminoglycosides cause vestibular damage. (c) Lithium-neonatal hypothyroidism. True ?Amiodarone may cause neonatal goitre. (d) Sulphonamides-kernicterus. True ? (e) Chloramphenicol- 'grey baby' syndrome. True ? Valproate may cause neural tube damage.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ With regards to ectopic pregnancy's risk factors include: (a) Being a non smoker. False ?Women who have had conservative treatment for ectopic pregnancy are at high risk (15 percent overall) for recurrence. This risk is related to both the underlying tubal disorder that led to the initial ectopic pregnancy and to the choice of treatment procedure. (b) History of in utero exposure to diethylstilbestrol. True ?Disruption of normal tubal anatomy from factors such as infection, surgery, congenital anomalies, or tumors also predispose to ectopic pregnancy. Women with a history of in-utero diethylstilbestrol (DES) exposure have a ninefold-increased risk of ectopic pregnancy due to abnormal tubal morphology and, possibly, impaired fimbrial function. Most contraceptive methods lower the overall risk of ectopic pregnancy by preventing ovulation or conception .However, a woman with an IUD who becomes pregnant is at high risk that the pregnancy is ectopic (c) Multiple sexual partners. True Weak evidence for association exist. (d) Vaginal douching. True Weak evidence for association exist. (e) Previous abdominal surgery. False Previous pelvic surgery is a risk, abdominal surgery is not.HCG concentrations usually double every 1.4 to two days until six to seven weeks of gestation in viable intrauterine pregnancies http://www.aafp.org/afp/20000215/1080.html http://www.jr2.ox.ac.uk/bandolier/booth/hliving/Ectopreg.html http://aje.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/reprint/157/3/185.pdf
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Neonates: (a) Bottle fed neonates have longer durations of fasting between meals than breast fed neonates. True ?Bottle fed neonates have longer durations of fasting between meals than breast fed neonates. (b) Bottle fed neonates require 6-9 feeds per 24 hours. True ?Bottle fed neonates require 6-9 feeds per 24 hours. (c) Neonates begin to put on weight immediately. False ?Neonates lose weight for the 1 st week of life ( up to 10% of their birth weight ). (d) The normal respiratory rate is 30 to 60 breaths/min in infants. True ?The normal respiratory rate is 30 to 60 breaths/min in infants. (e) The incidence of colic is about 13 percent. True ?The incidence of colic is about 13 percent.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Threatened Abortion and Abortion: (a) 20% of pregnancies abort spontaneously. True ?20% of pregnancies abort spontaneously.Chromosomal abnormalities account for most fetal wastage. (b) Rh negative women should receive Rh(D) immune globulin 300 ug IM. True ?Rh negative women should receive Rh(D) immune globulin 300 ug IM. (c) Threatened abortion is vaginal bleeding with partial passage of the conceptus. False ?Incomplete abortion is vaginal bleeding with partial passage of the conceptus and is more likely between 6 and 14 weeks of pregnancy. (d) Incomplete abortion will occur with vaginal bleeding and dilatation of the cervix. False ?Inevitable abortion will occur with vaginal bleeding and dilatation of the cervix. (e) Missed abortion is passage of all fetal tissue before 20 weeks gestation. False ?Missed abortion is fetal death at less than 20 weeks gestation wihout passage of fetal tissue.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ The following pathogens are among the most common causes of pneumonia in neonates: (a) E Coli. True ? (b) Beta-Haemolytic Streptococcus. True ? (c) H. Influenza. False ?In older children strep pneumoniae, H. Influenza and Mycoplasma are common pathogens. (d) Mycoplasma. False ?In older children strep pneumoniae, H. Influenza and Mycoplasma are common pathogens. (e) Chlamydia trachomatis. True ? The common causes of pneumonia in neonates include E Coli, Beta-Haemolytic Streptococcus, Chlamydia Trachomatis, Listeria Monocytogenes, and CMV.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ The following are risk factors for hyperemesis gravidarum: (a) Youth. True ?Youth is a risk factor for hyperemesis gravidarum. (b) Smoking. False ?Non-smokers are more likely to get hyperemesis gravidarum than smokers. (c) Primip. True ?Hyperemesis gravidarum is rare (1/1000).Metoclopramide 10mg IV may be safely given but is associated with dystonic reactions. (d) Multiple Pregnancy. True ?Multiple pregnancy is a risk factor for hyperemesis gravidarum. (e) Molar Pregnancy. True ?Molar Pregnancy is a risk factor for hyperemesis gravidarum. Hyperemesis gravidarum is considered the severe end of the spectrum of nausea and vomiting.There is no clear demarcation between common pregnancy-related "morning sickness". Persistent vomiting accompanied by weight loss exceeding 5% of prepregnancy body weight and ketonuria unrelated to other causes is an objective diagnosis. Hyperemesis tends to improve in the last half of pregnancy.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Headache in children: (a) The vast majority of headaches in children have a benign etiology. True ?The vast majority of headaches in children have a benign etiology. (b) Most children with neurological conditions will have neurological signs. True ?Lewis DW, Qureshi F. Acute headache in children and adolescents presenting to the emergency department. Headache. 2000 Mar;40(3):200-3. PMID: 10759922 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] (c) The brain and most of the overlying meninges have no pain receptors. True ?The brain and most of the overlying meninges have no pain receptors. (d) Pain is perceived from any structure between the scalp epidermis and the skull periosteum. True ?Pain is perceived from any structure between the scalp epidermis and the skull periosteum. (e) Posterior fossa pain can be referred to the occiput. True ?Posterior fossa pain can be referred to the occiput, ear or throat secondary to innervation of the pain nociceptors being innervated by the vagus and glossopharyngeal nerves.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Pharyngitis: (a) Group A beta haemolytic streptococcus pharyngitis is common before 3 years of age. False ?Group A beta haemolytic streptococcus pharyngitis is uncommon before 3 years of age. (b) Group A beta haemolytic streptococcus pharyngitis generally has a sudden onset of sore throat and fever. True ?Group A beta haemolytic streptococcus pharyngitis generally has a sudden onset of sore throat and fever. (c) The tonsils and pharynx generally have a moderate amount of exudate in group A beta haemolytic streptococcus. True ?The tonsils and pharynx generally have a moderate amount of exudate in group A beta haemolytic streptococcus. (d) In group A beta haemolytic streptoccus pharyngitis the cervical lymph nodes are generally not enlarged. False ?In group A beta haemolytic streptoccus pharyngitis the cervical lymph nodes are generally enlarged. (e) Positive throat cultures for group A beta haemolytic streptococcus always indicate acute pharyngeal infection. False ?Positive throat cultures may indicate an acute group A beta haemolytic streptococcus infection or a carrier state.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ
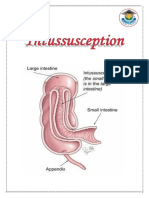
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Intussusception: (a) Occurrence is most common between 4 months and 1 year of age. True ?Occurrence of intussusception is most common between the ages of 4 months and 1 year of age.It usually starts at or near the ileocaecal valve. (b) Between bouts of pain the child is well and active. False ?Between bouts of pain the child lies still and quite,and looks pale. (c) Bilious vomiting may occur. True ?Bilious vomiting and red currant jelly stool may occur. (d) About 85% of cases will be reduced by barium enema. True ?But if present at 24-48 hours are more likely to need operative intervention. (e) An abdominal mass may be felt. True ?An abdominal mass may be felt or even seen between bouts of colic. A lead point is a lesion or variation in the intestine that is trapped by peristalsis and dragged into a distal segment of the intestine, causing intussusception. A Meckel diverticulum, polyp, tumor, hematoma, or vascular malformation can act as a lead point for intussusception. However approximately 75% of cases of intussusception in children are considered to be idiopathic because there is no clear disease trigger or pathological lead point.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ When obtaining intraosseous access: (a) The proximal tibial site is located 2.5cm below the tibial tuberosity on the flat anteromedial surface. True This is the first choice site. (b) Contraindications for intraosseous access include osteopetrosis. True Infection or fracture at, or proximal to, the insertion site and osteogenesis imperfecta are also contraindications. (c) Negative aspiration on insertion indicates incorrect positioning of the needle. False Despite negative aspiration the needle may still be correctly positioned. The position may still be verified by injecting 10mL 0.9 saline under sterile conditions. If flushing is easy and there is no local swelling then the position should be satisfactory. (d) Other insertion sites include the distal femur ? 3cm above the medial lower femoral condyle. False The correct distal femoral position is 3cm above the lateral lower femoral condyle on the anterolateral surface. Others include the distal tibia proximal to the medial malleolus or the sternum, which is also useful in adults.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Medication Toxicity in Pregnancy: (a) Retinoic Acid derivatives can cause fetal abnormalities up to 6 months after stopping therapy. False ?Retinoic Acid derivatives can cause fetal abnormalities up to 2 years after stopping therapy. (b) Alcohol is associated with renal damage and oligohydramnios. False ?Alcohol can cause fetal growth retardation and a withdrawal syndrome in the newborn. (c) Aminoglycosides can cause vestibular damage to the fetus. True ?Aminoglycosides can cause vestibular damage to the fetus. (d) Amiodarone can cause renal damage and oligohydramnios . False ?Amiodarone can cause neonatal goitre. (e) ACE inhibitors are the second line treatment for hypertension in pregnancy. False ?ACE inhibitors cause renal damage and oligohydramnios.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Nice Guidelines:Selection of children ( <16 ) for CT scanning of head: (a) A witnessed loss of consciousness of >1 min is an indication for immediate CT brain scan request. False ?A witnessed loss of consciousness of >5 min is an indication for immendiate CT brain scan. (b) Anterograde amnesia lasting >5 min is an indication for immediate CT scan request. True ?Anterograde amnesia lasting >5 min is an indication for immediate CT scan request. (c) Retrograde amnesia lasting >5 min is an indication for immediate CT scan request. True ?Retrograde amnesia lasting >5 min is an indication for immediate CT scan request. (d) 1 or more discrete episodes of vomiting is an indication for a CT brain scan request. False ?3 or more discrete episodes of vomiting is an indication for a CT brain scan request. (e) Post traumatic seizure in the setting of a history of epilepsy is always an indication for CT Brain scan request. False ?Post traumatic seizure without a history of epilepsy should result in a CT brain scan request. http://www.nice.org.uk
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Croup: (a) Is usually seen in children over 3 years old. False ?Croup is usually seen in children aged 6 months to 3 years. (b) Inspiratory stridor is common. True ?Inspiratory stridor is common in croup due to the passage of air through an inflammed and partially obstructed larynx. (c) Croup is associated with a barking cough which is worse at night time. True ? (d) Temperature is usually severely elevated. False ?Mild temperature and little systemic symptoms is what is usually seen in croup. (e) Parainfluenza virus is the most common pathogen. True ?Parainfluenza virus is the most common pathogen in croup.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ The following are true with regard to chickenpox: (a) The rash occurs before the fever. False ?The fever occurs about 2 days before the rash. (b) Is associated with ulceration of the mouth and vagina. True ? (c) 2-4 crops of vesicles typically occur. True ?Macule...papule...vesicle with red surround...ulcers(mouth and vaginal)...crusting. (d) Aciclovir is licensed as a 7 day course during chickenpox and should be started within 24 hours. True ? (e) Meningitis is a complication. True ?A rare complication along with pneumonia, DIC, LFT derangement, Guillan-Barre, Henochj Schonlein, nephritis, pancreatitis, myositis, myocarditis, orchitis, transverse myelitis, CNS thrombi, purpura fulminans. In healthy children pneumonia is an uncommon complication of varicella. However Varicella pneumonia is the most frequent complication of varicella infection in normal healthy adults and carries an overall mortality of between 10 and 30%. Risk factors linked to the development of varicella pneumonia include cigarette smoking, pregnancy , immunosuppression, and male sex
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Ectopic Pregnancy: (a) Rupture can occur up to 16 weeks gestation. True ?Tubal rupture is thought to be spontaneous, but trauma associated with coitus or a bimanual examination may precipitate tubal rupture. (b) 20% of women with ectopic pregnancy do not complain of abdominal pain. False ?10% of women with ectopic pregnancy do not complain of abdominal pain. (c) 80% of women with ectopic pregnancy have vaginal bleeding. True ?90% have abdominal pain, 80% have vaginal bleeding, 70% give a history of amenorrhea. (d) 10% of women do not give a history of amenorrhea. False ?90% have abdominal pain, 80% have vaginal bleeding, 70% give a history of amenorrhea. (e) Pain may be referred to the shoulder tip. True ?The presence of hemoperitoneum causing diaphragmatic irritation may cause the pain to be referred to the shoulder tip.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Pelvic Inflammatory Disease: (a) The annual rate of PID in industrialized countries is 10 to 20 per 1000 women of reproductive age. True ?The annual rate of PID in industrialized countries is 10 to 20 per 1000 women of reproductive age. (b) Ectopic pregnancy is a long term sequelae. True ?Long-term sequelae include tubal pathology, ectopic pregnancy, and chronic pain. (c) Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis are common causal agents. True ?Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis are common causal agents. (d) 10 to 20 percent of untreated gonococcal or chlamydial cervicitis may progress to PID. True ?10 to 20 percent of untreated gonococcal or chlamydial cervicitis may progress to PID. (e) Younger age is associated with increased risk of PID. True ?Younger age is associated with increased risk of PID. Risk factors for PID within a sexually active population include multiple sexual partners, history of other STDs, history of sexual abuse, and frequent vaginal douching.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Fever in children: (a) The body's thermostat is located in the preoptic region of the anterior hypothalamus. True ?Fever occurs when there is a rise in deep body temperature associated with a resetting of the body's thermostat. (b) Endogenous pyrogens are produced by neutrophils. True ?Endogenous pyrogens are produced by neutrophils. (c) The incidence of meningitis is higher in children with higher fevers than those with lower fevers. True ?The incidence of meningitis is higher in children with higher fevers than those with lower fevers. (d) The incidence of pneumonia and bacteremia is the same in children with higher temperatures in comparison to those with lower temperatures. True ?The incidence of pneumonia and bacteremia is the same in children with higher temperatures in comparison to those with lower temperatures. (e) In infants up to 3 months old the incidence of serious bacterial infection when the infant has a temperature of >38 degrees is less than 5%. True ?In infants up to 3 months old the incidence of serious bacterial infection when the infant has a temperature of >38 degrees is 3-4%.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Clinical features of mild(0-5%)dehydration in infancy include: (a) Sunken eyes. False ?Eyes not sunken in mild dehydration. (b) Loss of skin turgor. False ?Moderately dehydrated(5-10%). (c) In mild dehydration tears are present when a child cries. True ?In mild dehydration tears are present when a child cries. (d) Moist mucous membranes. True ?In mild dehydration the child is expected to have moist mucous membranes. (e) Thirst. True ?In mild dehydration the child is a little thirsty. When assessing dehydration in children the patients mental status is important. A normal mental status usually implies mild dehydration, whereas irritability signifies at least moderate fluid loss. Hypotension indicates hypovolemic shock. Lethargy implies severe volume loss and/or an electrolyte abnormality, especially hypernatremia. Decreased skin turgor and sunken eyes and fontanel imply moderate to severe fluid loss and usually occur when intracellular fluid has had time to diffuse into the intravascular space.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ The following drugs are safe for breast feeding mothers: (a) Oestrogens. False ?This may result in feminization of male infants. (b) Indomethacin. False ?Indomethacin has been reported to cause seizures. (c) Amiodarone. False ?Amiodarone can cause thyroid anomalies. (d) Chloramphenicol. False ?Chloramphenicol may cause a blood dyscrasia. (e) Lithium. False ?Lithium may cause involuntary movements. Other drugs to avoid include cytotoxics ( blood dyscrasia ), gold ( renal impairment and haematological reactions ) , iodides ( thyroid disturbance ),
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Perthes Disease ( Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease ): (a) Usually presnts in children >10 years of age. False ?Perthes disease presents with a painful limp in children aged 3-10 years. It is caused by aseptic necrosis of the upper femoral epiphyses. (b) Boys are affected twice as often as girls. False ?Boys are affected 4 times more frequently than girls. M:F = 4:1. (c) Almost never occurs bilaterally. False ?Perthes disease occurs bilaterally in 15% of cases. (d) WCC and ESR are usually raised. False ?WCC and ESR are normal in perthes disease. (e) Most cases respond to conservative management. True ?Most cases respond to conservative management. Perthes disease is aseptic necrosis of the upper femoral (capital) epiphyses in children aged 3-10 years and presents with a painful limp.Boys are affected 4 times more frequently than girls. M:F = 4:1.Perthes disease occurs bilaterally in 15% of cases. WCC and ESR are normal in perthes disease.Most cases respond to conservative management.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Radial head subluxation ( Nursemaids elbow ): (a) Peak age is 2-3 years. True ?It typically occurs between the ages of one and four years, with a peak incidence between two and three years. (b) Occurs in boys more commonly than girls. False ?Occurs in girls more commonly than boys (c) Right sided injury is more common. False ?Left sided injury is more common as most caregivers are right handed. (d) The most common mechanism is a sudden longitudinal traction on the arm with the elbow extended. True ?The most common mechanism is a sudden longitudinal traction on the arm with the elbow extended. (e) The annular ligament of the radius displaces into the radiocapitellar articulation. True ? The usual mechanism of injury is axial traction on a pronated forearm with the elbow in extension. With sudden traction on the distal radius, a portion of the annular ligament slips over the head of the radius and slides into the radiohumeral joint, where it becomes trapped.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Ectopic Pregnancy: (a) Vaginal bleeding is usually heavy. False ?Vaginal bleeding is usually light. Heavy bleeding is more commonly seen with threatened abortion or other complications of pregnancy. (b) There is a good correlation with the volume of haemoperitoneum and vital signs in ectopic pregnancy. False ?There is a poor correlation with the volume of haemoperitoneum and vital signs in ectopic pregnancy. (c) The rate of increase of B-hCG is greater in ectopic pregnancys than in normal intrauterine pregnancies. False ?The rate of increase of B-hCG is lesser in ectopic pregnancy's than in normal intrauterine pregnancies. (d) An intrauterine pregnancy should be visible at a serum b-hCG level of 6000 mIU/mL. True ?An intrauterine pregnancy should be visible at a serum b-hCG level of 6000 mIU/mL. (e) Ectopic pregnancy occurs in 1-2% of pregnancies. True ?And is the leading cause of maternal death in the first trimester.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ The following are true with regard to febrile convulsions: (a) Is often a simple partial seizure. False ?A febrile convulsion is a tonic/clonic symmetrical generalised seizure with no focal signs. (b) Usually occurs to children >5 years old. False ?It usually occurs to children between 6 months and 5 years. (c) There is often a history of epilepsy. False ?If there is a history of epilepsy a seizure secondary to epilepsy is more likely. (d) Can be prolonged with >5 seizures often each lasting >5 min. False ?A febrile convulsion is diagnosed when there are less than 3 seizures, each lasting <5 min. (e) Almost 3% of children have a febrile convulsion. True ? If the febrile seizure continues for more than five minutes it should be treated. Blood is sent for electrolytes and glucose determination. Intravenous short-acting benzodiazepine such as lorazepam (0.05 to 0.1 mg/kg) may be given initially. If the seizure persists, an additional dose may be given. Persistence of the seizure is rare. When it does, the child can be treated with fosphenytoin (15 to 20 mg/kg IV). If intravenous access is not possible or if the child is being treated at home, diazepam rectal gel may be used (0.5 mg/kg). The fever should be treated when the seizures are controlled
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Chickenpox (a) Incubation period is 21 to 28 days. False (b) Infections until all the lesions have crusted True (c) Central distribution of lesions True (d) New lesions appear in successive crops every 1 to 2 days True (e) Crusts fall off in one to 3 days. False
The incubation period is from 11-21 days.Infections until all the lesions have crusted, with maximal infectivity 24 hours preceding the onset of rash. Crusts fall off within 1 to 3 weeks.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Congenital dislocation of the hip (a) Is more common in boys than girls False (b) Clinical signs include limitation of abduction in flexion True (c) Thigh crease asymmetry is diagnostic False (d) After the age of 1 year cannot be reduced without surgery False (e) Causes scissoring of the legs when the child is held vertically False
It is usually the left side in girls.Clinical signs include limitation of abduction in flexion and shortening of the leg.Thigh crease asymmetry is of no diagnostic value. Diagnosis is confirmed by X Ray. Between the ages of 1 and 2 non operative reduction is still possible in 2/3 cases. Scissoring of the legs when the child is held vertically suggests adductor spasms caused by cerebral palsy.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Drugs in Pregnancy: (a) Phenytoin is associated with neonatal goitre. False ?Phenytoin is associated with cleft lip, cleft palate, and cardiac abnormalities. (b) NSAIDs are associated with an early closure of the ductus arteriosus. True ?Short-term use of NSAIDs in late pregnancy is associated with a significant increase in the risk of premature ductal closure.Koren G, Florescu A, Costei AM, Boskovic R, Moretti ME. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs during third trimester and the risk of premature closure of the ductus arteriosus: a meta-analysis.The Annals of pharmacotherapy (c) Antimalarial drugs may cause cleft lip and palate. False ?Antimalarial drugs may cause methaemoglobinaemia and haemolysis in the neonate. (d) Tetracyclines are associated with damage to the bones and teeth of the neonate. True ?Tetracyclines are associated with damage to the bones and teeth of the neonate. (e) Sulphonylureas are associated with fetal and neonatal hypoglycaemia. True ?Sulphonylureas are associated with fetal and neonatal hypoglycaemia.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ The following are common causes of pneumonia in infants and toddlers: (a) RSV. True ? (b) Parainfluenza Virus. True ? (c) E Coli. False ?E Coli is a common cause of pneumonia in neonates. (d) Listeria Monocytogenes. False ?Listeria Monocytogenes is a common organism that causes pneumonia in neonates. (e) Chlamydia trachomatis. False ?E Coli ,Listeria Monocytogenes,Chlamydia trachomatis,Beta-haemolytic streptococcus and CMV are the organisms which commonly cause pneumonia in neonates. The organisms which commonly cause pneumonia in infants and toddlers are RSV,Parainfluenza virus, Strep Pneumoniae, H. Influenza, and Mycoplasma.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Physiology of Pregnancy: (a) 20% increase in circulating blood volume. False ?Maternal cardiovascular changes during pregnancy include a 40% increase in circulating blood volume. (b) There is about a 15% increase in resting heart rate. True ?There is about a 15% increase in resting heart rate. (c) During the phase of blood pressure reduction, the systolic pressure decrease is greater than the diastolic pressure decrease. False ?During the phase of blood pressure reduction, the diastolic pressure decrease is greater than the systolic pressure decrease. (d) The diaphragm pushes the heart up and to the left. True ?And this produces a larger cardiac shadow. (e) The ECG may show left axis deviation in normal pregnancy. True ?As the diaphragm pushes the heart up and to the left.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome: (a) Usually effects teenagers. False ?6 months to 6 years .In the US: SSSS is most common in children and neonates. It is rare in adults. Internationally: Overall incidence is higher in developing countries. Mortality/Morbidity: Mortality rate from SSSS in children is very low (1-5%), unless associated sepsis or an underlying serious medical condition exists. Mortality rate in adults is higher (as high as 20-30%). Significant morbidity can result from hematologic or local spread of infection. Sex: No gender predilection is documented in children. In adults, the male-to-female ratio is approximately 2:1. Age: SSSS primarily is a disease of children. The disease can occur individually or as outbreaks in nurseries. Most children (62%) are younger than 2 years, and almost all (98%) are younger than 6 years. SSSS is very rare in adults, with fewer than 50 cases formally reported in the literature. Adults with SSSS are most often immunocompromised or have renal failure. (b) The exotoxin produced by staph aureus is responsible. True ?The exotoxin produced by staph aureus is responsible. (c) The prodrome can manifest as fever, malaise and skin tenderness. True ?The prodrome can manifest as fever, malaise and skin tenderness. (d) Mucous membranes are usually involved. False ?Mucous membranes are usually not involved. (e) Nikolsky's sign is usually positive. True ?Nikolsky's sign is usually positive. http://www.emedicine.com/emerg/topic782.htm
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ A 1 year old infant is brought to the emergency department following an emersion: (a) An appropriate estimated weight is 10kg. True ?Weight: 0-3.5 kg, 1 yr-10 kg then 2 x(age+4). (b) An ET tube appropriate size is 5.5mm internal diameter. False ?ETT: 0-3, 1 yr- 4 then age/4+4, at lips: 0-10, 1-11 then age/2+12, at nose: 0-12, 1-13, then age/2+15. (c) 500mcg is an appropriate initial dose of adrenaline. False ?Adrenaline: 0.1 ml/kg of 1:10000(10 mcg/kg). (d) A laryngeal mask appropriate size would be 2.5. False ?LMA: <5 kg- 1, 5-10 kg- 1.5,10-20 kg- 2, 20-30 kg- 2.5, 30-small adult- 3 , adult- 4, large adult5 (e) Defibrillation current should start at 20J. True ?Defibrillation 2 J/kg x 2 then 4 J/kg. Blood volume:70-80 ml/kg, fluid bolus for shock:20 ml/kg
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Periorbital cellulitis: (a) The commonest cause is extension of sinusitis. True ?The commonest cause is extension of sinusitis ,especially ethmoid. (b) Haemophilus influenza is a common causative organism. True ?Haemophilus influenza is a common causative organism. (c) Streptococcus pneumonia is a common causative organism. True ?Streptococcus pneumonia is a common causative organism. (d) Periorbital cellulitis is usually bilateral. False ?Periorbital cellulitis is usually unilateral. (e) Is a more serious condition than orbital cellulitis. False ?Orbital cellulitis is a more serious condiction than peri-orbital cellulitis. Periorbital and orbital cellulitis occur most commonly in children. Orbital cellulitis occurs less commonly, but is more serious than periorbital cellulitis. However, these conditions may be difficult to distinguish clinically, and because orbital cellulitis may be sight- and life-threatening, diagnostic imaging may be required to confirm the diagnosis. Orbital cellulitis (postseptal cellulitis) is localized posterior to the orbital septum, and involves infection of the fat and muscle contained within the bony orbit. In contrast, the soft tissue infection, periorbital cellulitis, is localized anterior to the orbital septum (eg, outside the bony orbit). Orbital cellulitis requires careful monitoring and early intervention to prevent serious complications. On the other hand, mortality and vision loss are extremely rare in periorbital cellulitis. The most common inciting organisms of periorbital cellulitis include Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, other streptococcal species, and anaerobes. Appropriate antibiotics include:Amoxicillin-clavulinic acid 875 mg every 12 hours in adults; 90 mg/kg per day amoxicillin and 6.4 mg/kg per day of clavulanate in two divided doses in children .
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Radial head subluxation ( Nursemaids elbow ): (a) Peak age is 5-6 years. False ?Peak age is 2-3 years. (b) Occurs in girls more commonly than boys. True ?Radial head subluxation occurs in girls more commonly than boys. (c) Left sided injury is more common. True ?Left sided injury is more common as most caregivers are right handed. (d) The most common mechanism is a fall on the outstretched hand with the elbow extended. False ?The most common mechanism is a sudden longitudinal traction on the arm with the elbow extended. (e) The annular ligament of the radius displaces into the radiocapitellar articulation. True ? The usual mechanism of injury is axial traction on a pronated forearm with the elbow in extension. With sudden traction on the distal radius, a portion of the annular ligament slips over the head of the radius and slides into the radiohumeral joint, where it becomes trapped. It typically occurs between the ages of one and four years, with a peak incidence between two and three years. The classic history of a "pull injury" is present in approximately 50 percent of cases . Other mechanisms include falling onto the elbow, minor direct trauma to the elbow, or a twisting motion of the arm. Children with RHS may hold the affected arm close to the body with the elbow either fully extended or slightly flexed and the forearm pronated. The child is in little distress unless attempts are made to move the elbow. Supination/flexion and hyperpronation are two techniques for reduction of RHS. Both techniques are effective. Recurrence rates range from 27 to 39 percent. There are no long-term sequelae associated with recurrent RHS.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Asthma in Pregnancy: (a) There are no differences in the outcome of pregnancies in well-controlled asthmatics versus the general population. True ?There are no differences in the outcome of pregnancies in well-controlled asthmatics versus the general population. Poorly controlled asthmatics have worse outcomes. (b) Asthma improves during pregnancy in 33% of patients. True In 1/3 rd of patients there is an improvement in their asthma, in 1/3 rd of patients their asthma is stable and in 1/3 rd of patients their asthma disimproves. (c) Oral prednisolone may be used as it does not cross the placenta. True ?Oral prednisolone may be used as it does not cross the placenta. (d) Sodium Cromoglycate may not be used in pregnancy. False ?Sodium Cromoglycate may be used in pregnancy. (e) The PEFR in pregnant women is between 380 and 550 L per min. True ?This is unaltered in pregnancy.The PEFR in pregnant women is between 380 and 550 L per min.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Neonates: (a) Breast fed neonates have longer durations of fasting between meals than bottle fed neonates. False ?Bottle fed neonates have longer durations of fasting between meals than breast fed neonates. (b) Bottle fed neonates require 6-9 feeds per 24 hours. True ?Bottle fed neonates require 6-9 feeds per 24 hours. (c) Neonates lose weight for the 1 st week of life. True ?Neonates lose weight for the 1 st week of life.( up to 10% of their birth weight ). (d) An increase in intake of human milk will increase the water content of the neonates stools. True ?An increase in intake of human milk will increase the water content of the neonates stools. (e) The normal respiratory rate is 15 to 20 breaths/min in infants. False ?The normal respiratory rate is 30 to 60 breaths/min in infants.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Abruptio Placentae: (a) Hypertension is a risk factor. True ?Placental abruption is defined as decidual hemorrhage leading to the premature separation of the placenta prior to delivery of the fetus. The major clinical features are vaginal bleeding and pain accompanied by uterine hypertonicity, uterine contractions, and a nonreassuring fetal heart rate pattern. Placental abruption complicates about 1 in 100 births. (b) Young maternal age is a risk factor. False ?Advanced maternal age is a risk factor. (c) Primagravidity is a risk factor. False ?Multiparity is a risk factor. (d) Smoking is a risk factor. True ? (e) Abdominal trauma is a risk factor. True ? Other risk factors include cocaine use and previous abruption.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ The following drugs are safe in the first 16 weeks of pregnancy: (a) Sodium Valproate. False In the first 16 weeks of pregnancy sodium valproate may cause neural tube defects. (b) Phenytoin. False ?In the first 16 weeks of pregnancy phenytoin may lead to facial fusion abnormalities such as cleft lip and palate. (c) SSRI. False A recently released Danish study has suggested that pregnant women who take SSRI antidepressant medicines in early pregnancy may have an increased risk of giving birth to an infant with heart problems. In this study, infants exposed to SSRI antidepressants during the first 3 months of pregnancy had a 60% higher chance of having developing a heart problem compared with infants whose mothers did not take SSRI antidepressants. Early information from another study in the US suggests that the use of the SSRI antidepressant paroxetine may be associated with an increased risk of birth defects, particularly heart problems. In this study, infants of mothers given paroxetine in early pregnancy were 2.2 times more likely to have a birth defect compared with infants of mothers given other antidepressants. (d) Carbimazole. False ?Carbimazole can cause neonatal goitre. (e) Gentamicin. False Gentamicin can cause VIIIth nerve deafness in the newborn.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ SIDS: (a) To avoid SIDS an infant should be placed to sleep supine or on his/her side. True ?To avoid SIDS an infant should be placed to sleep supine or on his/her side. (b) There is a link between SIDS and child abuse. True ?Some investigators reported that 10 percent of SIDS cases are due to abuse. (c) Premature infants of low birth weight are at greater risk of SIDS. True ?Premature infants of low birth weight are at greater risk of SIDS. (d) Siblings of infants who have succumbed to SIDS are at greater risk. True ?Siblings of infants who have succumbed to SIDS are at greater risk. (e) Acute hypoxic episodes are felt to occur in 80 percent of SIDS cases. True ?Acute hypoxic episodes are felt to occur in 80 percent of SIDS cases. Four groups of infants who appear at increased risk of SIDS have been identified: (1) term infants who have had an Apparent Life Threatening Event(ALTE), (2) premature infants of low birth weight, (3) siblings of infants who have succumbed to SIDS, and (4) infants of substance-abusing mothers.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Physiology of Pregnancy: (a) Haemoglobin concentration remains unchanged. False ?There is a drop in haemoglobin concentration due to dilution though the total amount of red blood cells increases. (b) Reticulocyte count increases during the second half of pregnancy. True ?Reticulocyte count increases during the second half of pregnancy. (c) Leucocyte numbers are normally increased above 13000 in the second half of pregnancy. False ?Leucocyte function is depressed during the second half of pregnancy. (d) ESR remains unchanged during pregnancy. False ?ESR increases during pregnancy. (e) By the second trimester the GFR may increase by 20%. False ?By the second trimester the GFR may increase by 50%.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Non accidental injury should be suspected in the following circumstances: (a) Subdural haematoma in an infant or toddler. True ?After a head injury NAI should be suspected if the child has retinal haemorrhages, a subdural haematoma, an occipital skull fracture or a wide comminuted fracture. (b) Early presentation after the injury. False Late presentation after the injury should make one suspicious of non accidental injury. Especially to an unknown doctor. (c) Accompanying adult is a parent. False (d) Torn frenulum of the upper lip. True NAI should be suspected if a child has a torn frenulum of the upper lip, perineal wounds and burns, cigarette burns, 'glove and stocking' burns following forced immersion in bath water. (e) Retinal haemorrhages. True Also conjunctival and vitreous haemorrhages.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Thromboembolism in pregnancy: (a) The incidence of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) in pregnancy is about 2%. False ?The incidence of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) in pregnancy is about 0.5%. (b) Increasing parity is a risk factor for thromboembolism. True ?Advanced maternal age, increasing parity, multiple gestation, operative delivery, bed rest, obesity, history of DVT, and clotting disorders. (c) The post-partum period is a lower risk time for thromboembolism than the antenatal period. True ?The post-partum period is a lower risk time for thromboembolism than the antenatal period. (d) Ventilation perfusion scans may not be performed safely in pregnancy. False ?Ventilation perfusion scans may be performed safely in pregnancy. (e) Warfarin is non-teratogenic after the 1st trimester. False ?Warfarin does cross the placenta. In the 1st trimester it is associated with embryopathy. In the 2nd and 3rd trimester's it is associated with CNS and eye disturbance.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Ectopic pregnancy: (a) Is the leading cause of maternal death in pregnancy. False ?Is the leading cause of maternal death in the first trimester. (b) Occurs in 5% of all pregnancies. False ?Ectopic pregnancy occurs in 1-2% of all pregnancies. (c) 50% of ectopic pregnancies are ruptured at the time of presentation. False ?20% of ectopic pregnancies are ruptured at the time of presentation. (d) Previous ectopic pregnancy is not a risk factor for future ectopic pregnancy. False ?Cigarette smoking in the periconceptional period increases the risk of ectopic pregnancy in a dose-dependent manner. This may be the result of impaired immunity in smokers, predisposing them to pelvic inflammatory disease, or to impairment in tubal motility. (e) Diethylstilbestrol exposure is a risk factor for ectopic pregnancy. True ? Other risk factors for ectopic pregnancy include history of PID, surgical procedures on the fallopian tubes, previous EP, IUCD, and assisted reproduction techniques.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Pelvic Pain: (a) Up to 5% of women have some degree of endometriosis. False ?Up to 15% of women have some degree of endometriosis.After dysmenorrhoea it is the most common etiology for cyclic pain in women of reproductive age. (b) By the age of 40, 10% of all women will have developed fibroids. False ?By the age of 40, 20% of all women will have developed fibroids.These are the most common pelvic tumor. They are more common, have an increased rate of growth and are frequently multiple in black women. (c) Fibroids are frequently mutiple in black women. True ?They are more common, have an increased rate of growth and are frequently multiple in black women. (d) Ovarian cysts are the most common noninfectious cause of acute pelvic pain. True ?Ovarian cysts are the most common noninfectious cause of acute pelvic pain. (e) Ovarian cyst enlargement is never asympyomatic. False ?Ovarian cyst enlargement may be asymptomatic.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome: (a) There is usually painless erythema and blistering of the skin. False ?Usually painful with a positive nikolskys sign. (b) Nikolsky's sign is usually negative. False ?Nikolsky'a sign is usually positive. (c) Bullae and vesicles rarely occur around the mouth. False Bullae and vesicles frequently start around the mouth. (d) Toxic epidermal necrolysis is a possible differential diagnosis. True ?Toxic epidermal necrolysis is a possible differential diagnosis. (e) Drug reactions are a possible alternative diagnosis. True ?Drug reactions are a possible alternative diagnosis. http://www.emedicine.com/emerg/topic782.htm
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Acute otitis media in children: (a) Streptococcus faecalis is a common organism. False ?Streptococcus pneumoniae is a common organism ( >40% of cases ). (b) Microorganisms enter the middle ear via the eustachian tube. True ?So that organisms that colonise the nasopharynx frequently cause AOM. (c) Haemophilus influenza may cause up to 20% of cases. False ?Haemophilus influenza may cause up to 40% of cases. (d) Moraxella catarrhalis is a very rare cause of acute otitis media. False ?Moraxella catarrhalis( 3rd commonest organism) may cause acute otitis media in up to 15% of cases. (e) Chlamydia pneumoniae may be a causative organism, particularly in children older than 4 years. False ?Chlamydia pneumoniae may be a causative organism, particularly in children younger than 6 months.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Drug toxicity in pregnacy: (a) Tetracyclines are associated with vestibular damage. False ?Tetracyclines are associated with damage to the bones and teeth of the neonate. (b) Sulphonylureas are associated with neural tube defects. False ?Sulphonylureas are associated with fetal and neonatal hypoglycaemia. (c) Phenytoin is associated with grey baby syndrome. False ?Phenytoin is associated with cleft lip, cleft palate, and cardiac abnormalities. (d) NSAIDS are used to treat patent ductus arteriosus. True NSAIDS are used to treat patent ductus arteriosus. (e) Antimalarial drugs may cause neural tube defects. False ?Antimalarial drugs may cause methaemoglobinaemia and haemolysis in the neonate.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Meningitis: (a) Kernig's sign is positive when there is resistance to extending the knee when the hip is flexed. True ?Kernig's sign is positive when there is resistance to extending the knee when the hip is flexed. (b) Brudzinski's sign is positive when there is flexion of the head on flexing the hip. False ?Brudzinski's sign is positive when there is flexion of the hips on bending the head forward. (c) Ceftriaxone is an appropriate anti-biotic. True ?Ceftriaxone is an appropriate anti-biotic. (d) Ofloxacin is an appropraite anti-biotic. False ?The quinolones are mainly active against gram negative bacteria. (e) Pyogenic CSF is usually clear. False ?Often turbid. Aseptic meningitis usually has clear CSF. Early intravenous administration of dexamethasone has been evaluated as adjuvant therapy in an attempt to diminish the rate of hearing loss and other neurological complications as well as mortality in selected patients with bacterial meningitis. Dexamethasone is given 15 to 20 minutes before or at the time of antibiotic administration.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Patients are at increased risk of developing ectopic pregnancy if: (a) They have known endometriosis. True ?There is a well known association between endometriosis and ectopic pregnancy. (b) They take the COCP. False The risk of ectopic pregnancy is decreased in women taking the COCP. (c) They use condoms during sex. False ?There is no increased risk of ectopic pregnancy if condoms are used. (d) The patient uses a contraceptive diaphragm. False ?There is no increased risk of ectopic pregnancy if the patient uses a contraceptive diaphragm. (e) Past history of pelvic surgery. True ?Especially a past history of tubal ligation. The major cause of ectopic pregnancy is disruption of normal tubal anatomy from factors such as infection, surgery, congenital anomalies, or tumors. Women with a history of in-utero diethylstilbestrol (DES) exposure have a ninefold-increased risk of ectopic pregnancy due to abnormal tubal morphology and, possibly, impaired fimbrial function. Most contraceptive methods lower the overall risk of ectopic pregnancy by preventing ovulation or conception .However, a woman with an IUD who becomes pregnant is at high risk that the pregnancy is ectopic.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Acute Otitis Media in Children: (a) The cartilage that supports the eustachian tube is more stiff in children than in adults and this increases there susceptibility to OM. False ?The cartilage that supports the eustachian tube is less stiff in children than in adults and this increases there susceptibility to OM. (b) There is no increased susceptibility to OM in children with allergies. False ?Allergies and URTI's can obstruct the eustachian tube and predispose to OM. (c) Amoxicillin-clavulinic acid is appropriate antibiotic therapy for middle ear infections. True ?Strep pneumonia and haemophilus influenza are the most common organisms. (d) Moraxella catarrhalis is reponsible for middle ear infections in up to 35% of cases. False ?Moraxella catarrhalis is reponsible for middle ear infections in up to 15% of cases. (e) Trimethoprim is a reasonable choice of anti-biotic for middle ear infections. True ?
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Meningitis: (a) E.Coli is a cause of meningitis in infants. False ?E.Coli is a cause of meningitis in neonates. Netilmicin 2mg/kg/8h IV is a drug of choice. (b) Haemophilus influenza usually causes meningitis in the under 4's. True ?But haemophilus influenza meningitis is rare where vaccination is the rule.Otitis may predispose to haemophilus meningitis. (c) Upper respiratory tract infections predispose to streptococcus meningitis. True ?Also pneumonia, skull fracture's and meningocoele. (d) Microabscesses in many organs are associated with E. Coli menigitis. False ?In meningitis caused by listeria monocytogenes microabscesses may form in many organs. (e) Haemophilus is a gram positive rod. False ?Haemophilus is a gram negative rod seen in pairs or chains.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ The standard childhood immunisation schedule includes: (a) DTP, polio and Hib at 2,3 and 4 months. True At risk children may receive vaccination against TB and Hep B at birth. (b) DTP booster at 2 years. False DTP booster is given at 4-5 years (c) At risk children may receive vaccination against TB and Hep B at birth. True (d) MMR is given at 12-15 months. True
At two months old the child is vaccinated against diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whooping cough), polio and Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib)as well as Pneumococcal infection. At three months old the child is vaccinated against DTP, polio and Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) as well as Meningitis C. At four months old the child is vaccinated against DTP, polio and Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) as well as Meningitis C and Pneumococcal infection. At around 12 months the child is vaccinated against haemophilus influenza type b (Hib) and meningitis C. At around 13 months old the child is vaccinated against measles, mumps and rubella and pneumococcal infection . At three years and four months or soon after the child is again vaccinated against DTP and polio as well as measles, mumps and rubella. At thirteen to eighteen years old the child is again vaccinated against diphtheria, tetanus, and polio. http://www.immunisation.nhs.uk/Immunisation_Schedule
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ UTI in pregnancy: (a) Is the second commonest cause of bacterial infections in pregnancy. False ?UTI is the most common bacterial infection in pregnancy. (b) Nitrofurantoin is safe in pregnancy. True ?Category B ( presumed safe, animal studies).100mg od po. (c) Cephalexin 500mg po qid may be used safely in pregnancy. True ?Category B ( presumed safe, animal studies). (d) Amoxicillin is safe in pregnancy. True ?Category B ( presumed safe, animal studies). (e) Pyelonephritis may require a longer course of out patient oral antibiotics. False ?Pyelonephritis should be admitted for IV antibiotics because of increased risk of preterm labor and sepsis.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Asthma in pregnancy: (a) Poorly controlled/Severe asthmatics have worse outcomes. True ?Slight increase in the risk of preterm birth, stillbirth, and low-birth-weight babies. (b) Asthma very rarely disimproves during pregnancy. False ?In 1/3 rd of patients there is an improvement in their asthma, in 1/3 rd of patients their asthma is stable and in 1/3 rd of patients their asthma disimproves. (c) Oral prednisolone may not be used in pregnancy. False ?Oral prednisolone may be used as it does not cross the placenta. (d) Beta Agonists are contraindicated in pregnancy. False ?Beta Agonists are used to treat asthma exacerbation in pregnancy. (e) Peak Expiratory Flow Rate is lower in pregnant women False ?PEFR is not altered in pregnant women.The range is between 380 and 550 L per min.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Ectopic Pregnancy: (a) Is the leading cause of 1st trimester maternal pregnancy related death. True ?Ectopic Pregnancy is the leading cause of 1st trimester maternal pregnancy related death. (b) Fertilization of the oocyte usually occurs in the ampullary segment of the fallopian tube. True ?Fertilization of the oocyte usually occurs in the ampullary segment of the fallopian tube. (c) The vast majority of ectopic pegnancys occur in the ovary. False ?The vast majority of ectopic pregnancy's occur in the fallopian tube. (d) Most women have amenorrhea for at least 4 weeks prior to presentation. True ?70% of women present with amenorrhea with a history of 4 to 12 weeks. (e) There is usually a good correlation between physical signs and volume of blood loss in ruptured ectopic pregnancy. False ?There is often a poor correlation between physical signs and volume of blood loss.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Otitis Media: (a) 6-8 years old children are at greatest risk of development. False ?Infants and very young children are at greatest risk of development. Daly KA, Giebink GS: Clinical epidemiology of otitis media. Pediatr Infect Dis J 19:S31, 2000. (b) The risk is not higher in children who use pacifiers. False ?The risk is higher in children who use pacifiers. (c) Incidence is lower in children who sleep prone. False ?Incidence is higher in children who sleep prone. (d) Middle ear effusions may persist for weeks or months. True ?Middle ear effusions may persist for weeks or months.Up to 2/3rds of children still have middle ear effussions at 2 weeks. (e) Bacteria enter the ear via the eustachian tube. True ?Bacteria enter the ear via the eustachian tube.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Normal physiological ranges in a 3 year old include (a) Weight of 14kg. True Weight is approximately (age + 4) x 2 (b) Systolic blood pressure of 80-100mmHg. True Systolic blood pressure of 80-100mmHg. (c) Total blood volume of 800mL. False Total blood volume is 75-80mL/kg therefore in a 3 year old should be between 1050-1120mL (d) Pulse rate of 95-140. True Pulse rate of 95-140.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Headache in children: (a) Primary headaches are physiological. True ?Migraine or tension headache are examples of primary headaches. A cause of a secondary headache is a brain tumor. (b) Secondary headaches have an anatomic basis. True ?Secondary headaches have an anatomic basis such as a vascular malformation, or tumor. (c) Head tilt is suggestive of a headache because of an anatomic lesion. True ?Head tilt is suggestive of a headache because of an anatomic lesion. (d) Gait disturbance is suggestive of a headache because of an anatomic lesion. True ?Gait disturbance is suggestive of a headache because of an anatomic lesion. (e) Retinal Haemorrhage is suggestive of a headache because of an anatomic lesion. True ?Retinal Haemorrhage is suggestive of a headache because of an anatomic lesion. Features suggesting secondary headache include acute onset, worst ever headache ,a posttraumatic , a headache that awakens the child from sleep , a headache with fever, a headache aggravated by sneezing, coughing, or the valsalva maneouver, lying down , morning vomiting, altered mental status , change in behavior , change in pattern, toxic exposure ,or a positive family history for migraines or subarachnoid hemorrhage.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Otitis Media: (a) Infants and very young children are at greatest risk of development. True ?Infants and very young children are at greatest risk of development, peak incidence is 6months to 1 1/2 years. Daly KA, Giebink GS: Clinical epidemiology of otitis media. Pediatr Infect Dis J 19:S31, 2000. (b) The risk is not higher in children who are exposed to tobacco smoke. False ?The risk is higher in children who are exposed to tobacco smoke. (c) Incidence is lower in breast fed children. True ?Incidence is lower in breast fed children. (d) Middle ear effusions almost always clear up within about 10 days to 2 weeks. False ?Middle ear effusions may persist for weeks or months. (e) Bacteria generally enter the middle ear by the child poking or inserting something into the external auditory canal. False ?Bacteria enter the ear via the eustachian tube. .
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Placental Abruption: (a) Is associated with pre-eclampsia. True ? (b) Is less common in smokers. False Placental abruption is more common in smokers. (c) May complicate external cephalic version. True ?Placental abruption may complicate external cephalic version. (d) May present with backache. True ? (e) May be complicated by DIC. True Placental abruption may be complicated by DIC because of thromboplastin release. Placental abruption is defined as decidual hemorrhage leading to the premature separation of the placenta prior to delivery of the fetus. The major clinical features are vaginal bleeding and pain accompanied by uterine hypertonicity, uterine contractions, and a nonreassuring fetal heart rate pattern. Placental abruption complicates about 1 in 100 births.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Salter and Harris Fractures: (a) In type I fractures the width of the physis is decreased. False A type 1 fracture is a transverse fracture through the hypertrophic zone of the physis.The width of the physis is increased. The growing zone of the physis usually is not injured, and growth disturbance is uncommon. (b) A type II fracture is a fracture through the physis and the metaphysis, but the epiphysis is not involved in the injury. True ?A type II fracture is a fracture through the physis and the metaphysis, but the epiphysis is not involved in the injury. (c) Type III is the most common type of Salter-Harris fracture. False ?Type II is the most common type of Salter-Harris fracture. (d) A type III fracture is a fracture through the physis and the epiphysis. True ?A type III fracture is a fracture through the physis and the epiphysis. (e) A type IV injury is a compression or crush injury of the epiphyseal plate with no associated epiphyseal or metaphyseal fracture. False ?A type V injury is a compression or crush injury of the epiphyseal plate with no associated epiphyseal or metaphyseal fracture. A type 1 fracture is a transverse fracture through the hypertrophic zone of the physis. In this injury, the width of the physis is increased. The growing zone of the physis usually is not injured, and growth disturbance is uncommon. A type II fracture is a fracture through the physis and the metaphysis, but the epiphysis is not involved in the injury.A type III fracture is a fracture through the physis and the epiphysis.A Type IV fracture involves all 3 elements of the bone: The fracture passes through the epiphysis, physis, and metaphysis.A type V injury is a compression or crush injury of the epiphyseal plate with no associated epiphyseal or metaphyseal fracture.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ The following are true with regard to ectopic pregnancy: (a) Pelvic inflamatory disease is associated with the greatest risk. True http://www.aafp.org/afp/20000215/1080.html (b) Endometriosis is a risk factor. True Pelvic inflamatory disease is associated with the greatest risk. Damage to the tubes, fertility drugs, a previous ectopic, or previous pelvic surgery are others. (c) It is the second commonest cause of maternal mortality in the first trimester. False It is the leading cause of maternal mortality in the first trimester and accounts for 10 to 15 percent of all maternal deaths (d) 20% implant in the ovary. False ?3% implant in the ovary, cervix or peritoneum. 97% implant in the fallopian tube. (e) The number of ectopic pregnancies has decreased in the past few decades False The number of ectopic pregnancies has dramatically increased in the past few decades. The rise can be attributed partly to increases in certain risk factors but mostly to improved diagnostics. Some ectopic pregnancies detected today, for instance, would have spontaneously resolved without detection or intervention in the past. Cigarette smoking in the periconceptional period increases the risk of ectopic pregnancy in a dosedependent manner. This may be the result of impaired immunity in smokers, predisposing them to pelvic inflammatory disease, or to impairment in tubal motility.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Trauma in pregnancy: (a) Gravid patients usually have decreased systolic and diastolic blood pressure. True ?Gravid patients usually have decreased systolic and diastolic blood pressure by 5-15mmHg. (b) Gravid patients usually have decreased WCC. False ?Gravid patients usually have increased WCC. (c) Gravid patients usually have an increased respiratory rate. False ?Gravid patients usually have no change in their respiratory rate. (d) Gravid patients usually have an increased tidal volume. True ?Gravid patients usually have an increased tidal volume. (e) The pelvis provides protection to the uterus until the 12th week of gestation. True ?At this stage the uterus rises above the pelvis. The initial evaluation of the pregnant trauma victim should focus on establishing maternal cardiopulmonary stability. Any treatment required to save the mother's life or treat her critical status should be undertaken, regardless of her pregnancy. Displacing the uterus to the left, off the vena cava, is critical to maximize effectiveness of cardiopulmonary resuscitation in the second half of pregnancy.Abruption leading to nonreasssuring fetal heart rate patterns and death can occur despite relatively mild maternal trauma or discomfort. The majority of women who develop adverse obstetrical outcomes have symptoms such as contractions, vaginal bleeding, or abdominal pain upon initial presentation.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ In hand, foot and mouth disease: (a) The cause is herpes simplex virus infection. False (b) Teenagers are most likely to be affected. False (c) The vesicular rash is confined to the hands , feet and mouth. False (d) There are little or no systemic features. False (e) Spontaneous resolution occurs within 2 to 3 days. False
Hand foot and mouth disease is caused by the coxsackie virus. Young children are the most common group to be affected. As well as the hands, feet and mouth the nappy area may also be affected.The child may be febrile and unwell. Resolution occurs within 1 week.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome: (a) Streptococcal scarlet fever is a differential diagnosis. True ?Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (SSSS) is a syndrome of acute exfoliation of the skin following an erythematous cellulitis. SSSS is caused by an exotoxin from a staphylococcal infection. SSSS also is known as Ritter von Ritterschein disease in newborns, Ritter disease, Lyell disease, and staphylococcal epidermal necrolysis. (b) Blisters may be biopsied for diagnosis. True ? (c) Staph Aureus may be cultured from nose or oropharynx for diagnosis. True ? (d) Penicillin antibiotics are part of the management. True ?And fluids (e) Erythema Multiforme is a differential diagnosis. True ?http://www.emedicine.com/emerg/topic782.htm Lab Studies: White blood count (WBC) may be elevated; however, often WBC is normal. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) frequently is elevated. A polymerase chain reaction (PCR) serum test for the toxin is available. Cultures of bullae are negative. Blood culture Usually negative in children Usually positive in adults A Gram stain and/or culture from the remote infection site may confirm staphylococcal infection. Procedures: Frozen section of the peeled skin confirms the site of cleavage as superficial. Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) shows deeper cleavage below the epidermis.
MCEM Pediatrics and O & G MCQ
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- RACGP Bridging Course AMC PDFDocument97 pagesRACGP Bridging Course AMC PDFAnkita Sinha67% (3)
- MCEM Anatomy MCQDocument44 pagesMCEM Anatomy MCQAnkita Sinha100% (1)
- MCEM MCQ PharmacologyDocument147 pagesMCEM MCQ PharmacologyAnkita Sinha67% (3)
- Abdominal Pain, Vomitting & ConstipationDocument77 pagesAbdominal Pain, Vomitting & ConstipationShermin ShakilNo ratings yet
- MCEM Pathology MCQDocument109 pagesMCEM Pathology MCQAnkita Sinha100% (2)
- AMC QuestionsDocument50 pagesAMC QuestionsAnkita SinhaNo ratings yet
- Radiology EssentialsDocument308 pagesRadiology EssentialsDeborah Anasthasia PakpahanNo ratings yet
- Congenital Anomalies of GiDocument94 pagesCongenital Anomalies of GiPadmaNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Surgery Paper 3Document13 pages3.2 Surgery Paper 3Muwanga faizo100% (1)
- SLRC Pedia PresentationDocument141 pagesSLRC Pedia Presentationapi-3764215100% (2)
- Pediatric NursingDocument187 pagesPediatric Nursingirene8000100% (2)
- MCEM Clinical Knowledge MCQDocument276 pagesMCEM Clinical Knowledge MCQAnkita SinhaNo ratings yet
- Plab 2 MaterialDocument24 pagesPlab 2 MaterialradugaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric RadiologyDocument82 pagesPediatric Radiologyabakferro0% (1)
- Bowel Obstruction - ppt1Document30 pagesBowel Obstruction - ppt1Elfrida Aulia100% (1)
- MCEM Evidenced Based Medicine MCQDocument93 pagesMCEM Evidenced Based Medicine MCQAnkita Sinha100% (2)
- MCEM Toxicology MCQDocument110 pagesMCEM Toxicology MCQAnkita Sinha100% (4)
- Surgery Lecture NotebookDocument317 pagesSurgery Lecture Notebookタヨ アヨデレNo ratings yet
- Amc - Note DR Salman SIddique PDFDocument536 pagesAmc - Note DR Salman SIddique PDFAnkita Sinha100% (3)
- IntussusceptionDocument60 pagesIntussusceptionAhmad Abu KushNo ratings yet
- Pedia Disorders Upgraded For Lnu CaDocument6 pagesPedia Disorders Upgraded For Lnu Cashirlenedel cariñoNo ratings yet
- Developing A Simple Application Using SAP Business WorkflowDocument12 pagesDeveloping A Simple Application Using SAP Business Workflowribana1234No ratings yet
- HR TablesDocument14 pagesHR TablesAnkita SinhaNo ratings yet
- E Procurement (NXPowerLite) - SCMDocument17 pagesE Procurement (NXPowerLite) - SCMAnkita SinhaNo ratings yet
- MCEM Microbiology MCQDocument8 pagesMCEM Microbiology MCQAnkita SinhaNo ratings yet
- MCEM Pathophysiology MCQDocument13 pagesMCEM Pathophysiology MCQAnkita Sinha100% (1)
- Activity 7 - GARCES 109LECDocument10 pagesActivity 7 - GARCES 109LECSherlyn Miranda GarcesNo ratings yet
- Acute Abdomen in ChildrenDocument61 pagesAcute Abdomen in ChildrenWorku KifleNo ratings yet
- Bab 84 Meckel's DivertikulumDocument8 pagesBab 84 Meckel's DivertikulumDede IskandarNo ratings yet
- Food Protein-Induced Allergic Proctocolitis of Infancy - UpToDateDocument14 pagesFood Protein-Induced Allergic Proctocolitis of Infancy - UpToDateLisa MaNo ratings yet
- Peds1114 Neonatal VomitingDocument24 pagesPeds1114 Neonatal VomitingABDILLAHNo ratings yet
- Physical ExaminationgiDocument61 pagesPhysical ExaminationgiHei LeeNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Surgery Notes For NursesDocument8 pagesPediatric Surgery Notes For NursesAhmed SamyNo ratings yet
- Bowel Obstruction 2015Document16 pagesBowel Obstruction 2015Maria Alejandra Siachoque JaraNo ratings yet
- IntussusceptionDocument19 pagesIntussusceptionarialNo ratings yet
- PBL 1Document111 pagesPBL 1fahmi rosyadiNo ratings yet
- 12 - Paediatric Abdomen RadiologyDocument74 pages12 - Paediatric Abdomen RadiologyMaria DoukaNo ratings yet
- Disturbances in Absorption and EliminationDocument120 pagesDisturbances in Absorption and EliminationBeBs jai SelasorNo ratings yet
- Invaginasi Jurnal2 PDFDocument4 pagesInvaginasi Jurnal2 PDFZieky YoansyahNo ratings yet
- Radiological Anatomy of The Colon and Rectum in Children: Gastroenterology & Hepatology: Open AccessDocument5 pagesRadiological Anatomy of The Colon and Rectum in Children: Gastroenterology & Hepatology: Open AccesseugeniaNo ratings yet
- Infantile Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis - UpToDateDocument22 pagesInfantile Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis - UpToDateNELFA MOLINA DUBÓNNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Surgical EmergenciesDocument26 pagesPediatric Surgical EmergenciesTarek yahiaNo ratings yet
- Copy CHH Case PresentationDocument61 pagesCopy CHH Case PresentationKrista BugashNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Pain in ChildrenDocument21 pagesAbdominal Pain in ChildrenDaniel RajNo ratings yet
- IntussusceptionDocument8 pagesIntussusceptionMohamed Na3eemNo ratings yet