Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CKD
Uploaded by
Marc Lawrence Balderas CAraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CKD
Uploaded by
Marc Lawrence Balderas CAraCopyright:
Available Formats
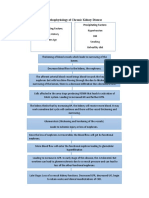
Predisposing Factors:
Age greater than 60 y/o Hereditary
Precipitating factors: Hypertension Increase protein and fat intake
Decreased renal blood flow Diabetes mellitus Urine outflow obstruction
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL)
Increase BUN
Decreased glomerular filtration
Increase serum creatinine
polyuria
Hypertrophy of remaining nephrons
Loss of sodium in urine
dehydration
Inability to concentrate urine
Hyponatremia
Further loss of nephrons function
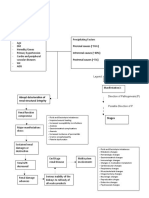
Anxiety related to change in health status, relationships, role function and threat of death.
Loss of non-excretory renal function
Insertion of Intrajugular vein cather
Loss of excretory renal function
Impaired skin integrity related to insertion of permanent IJ catheter secondary to hemodialysis.
HEMODIALYSIS
Risk for infection related to invasive procedures (Insertion of permanent IJ Cath. And hemodialysis).
Failure to convert inactive forms of calcium
Failure to produce eryhtropoietin
Impaired insulin action
Increase Production of lipids
Immune disturbance s
Disturbances in reproduction
Decrease Calcium absorption
Anemia Pallor
Erratic blood glucose levels Vitamin K
Advanced atherosclerosi s
Delayed wound healing
Infection
Decreas e Libido
Infertility
Hypocalcemia
Moriamin forte
Fatigue related to disease states, altered metabolic energy production and anemia.
Kalium Durule
Phosphatidyl Choline
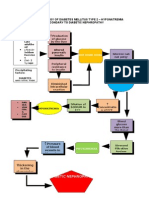
Excretion of nitrogenous waste
Decreased sodium reabsorption in tubule
Decreased potassium excretion
Decreased phosphate excretion
Decreased hydrogen excretion
Uremia Hyperkalemia Hyperphosphatemia Metabolic acidosis
BUN, Creatinine Uric Acid Proteniuria
Water Retention
Excess fluid volume related to accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity secondary to ascites.
Hypertension Peripheral nerve changes Heart Failure
Excess fluid volume related to sodium, chloride and water retention secondary to chronic kidney failure.
Pericarditis
CNS changes Pruritus
Excess fluid volume related to accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity secondary to Acites ascites. Amlodipine Risk for imbalance nutrition: Less than body requirements related to inability to ingest or digest food or absorption nutrients as a result of physiologic factors Decreased cardiac output related to altered myocardial contractility secondary to chronic kidney failure.
Edema
Altered Taste
LEGEND:
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
Bleeding Tendencies
NURSING DIAGNOSIS
TREATMENTS and MEDICATIONS
You might also like
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Renal FailureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Chronic Renal FailureBettinaFernando80% (5)
- As-Built Commercial BLDG.1Document11 pagesAs-Built Commercial BLDG.1John Rom CabadonggaNo ratings yet
- Anthony Robbins - Time of Your Life - Summary CardsDocument23 pagesAnthony Robbins - Time of Your Life - Summary CardsWineZen97% (58)
- Pathophysiology Renal FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology Renal FailureHampson Malekano100% (2)
- Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Schematic Diagramnursing concept maps100% (5)
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument3 pagesChronic Renal FailureIvana Yasmin Bulandres100% (2)
- Pathophysiology CKDDocument1 pagePathophysiology CKDReymon Mary Janine100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Acute Renal FailureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Acute Renal Failuresugarmontejo67% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Acute Kidney Injurymariaclaramutya100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of UTIDocument1 pagePathophysiology of UTIKeannepotz80% (5)
- Pathophysiology: Precipitating FactorDocument6 pagesPathophysiology: Precipitating FactorMark Anthony YabresNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiologybilliam123100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Acute Renal FailureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Acute Renal Failurekristel_nicole18yaho100% (3)
- CKD PathophysiologyDocument1 pageCKD Pathophysiologynursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Heart FailureDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Heart FailureTiger Knee100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure III With Pleural EffusionDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure III With Pleural EffusionKen100% (1)
- Acute Renal Failure DiagramDocument3 pagesAcute Renal Failure DiagramMichelle BarojaNo ratings yet
- Pahtophysiology of EsrdDocument5 pagesPahtophysiology of EsrdCarl JardelezaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramMeine MheineNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramJake CaballoNo ratings yet
- CKD PathoDocument5 pagesCKD PathoJohn MIchael AusaNo ratings yet
- CKD PathophysiologyDocument1 pageCKD Pathophysiologylloyd_santino67% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Kidney Disease: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Chronic Kidney Disease: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsReina Samson0% (1)
- PatofkuDocument3 pagesPatofkunisaaa88No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology ESRDDocument9 pagesPathophysiology ESRDJaye DangoNo ratings yet
- Hypertension PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesHypertension PathophysiologyJems60% (5)
- ARF PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesARF Pathophysiologykathy100% (9)
- PathoPhysiology of Renal Failure (Overview)Document7 pagesPathoPhysiology of Renal Failure (Overview)Tiger Knee100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of StrokeACe JAyNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (10)
- Age Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat IntakeDocument3 pagesAge Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat Intakenursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failuretinayko100% (1)
- Pathophysiology CHFDocument2 pagesPathophysiology CHFPerry Oliver AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Pathophysio CRF RevisedDocument2 pagesPathophysio CRF Revisedroseanne18No ratings yet
- The Pathology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument4 pagesThe Pathology of Congestive Heart FailureMar Ble50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Liver CirrhosisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Liver CirrhosisAprille Rose UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology (Chronic Renal Failure)Document3 pagesPathophysiology (Chronic Renal Failure)marshmalou86% (7)
- Pathophysiology Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument1 pagePathophysiology Hemorrhagic StrokeJeffrey Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CVDDocument1 pagePathophysiology CVDPamela Shiermaine FilomenoNo ratings yet
- CKD (F&e)Document110 pagesCKD (F&e)Al-nazer Azer Al100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document1 pagePathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2faula rocamora100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure (Condensed) Part 2Document1 pagePathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure (Condensed) Part 2deborah malnegro100% (5)
- Pathophysiology DMDocument1 pagePathophysiology DMMJ AmarilloNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure PathoDocument4 pagesAcute Renal Failure PathoGlenn Asuncion Pagaduan100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of CVADocument1 pagePathophysiology of CVAChristine Joy Ilao PasnoNo ratings yet
- End Stage Renal DiseaseDocument62 pagesEnd Stage Renal DiseaseMae Navidas DigdiganNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Hemor CVADocument4 pagesPathophysiology Hemor CVAMatthew Emmanuel M. Martinez100% (2)
- Congestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesCongestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramJacinthaVanathayahNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart Failurea_samiane64% (11)
- Pathophsyiology of AGEDocument1 pagePathophsyiology of AGEmariaNo ratings yet
- KidneyDocument18 pagesKidneyRacha MougharbelNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure Powerpoint PresentationDocument18 pagesAcute Renal Failure Powerpoint PresentationSteven Paul DaclesNo ratings yet
- MetabolismDocument39 pagesMetabolismTiffany KnepperNo ratings yet
- Etiology: I. Predisposing FactorDocument12 pagesEtiology: I. Predisposing FactorIbcp SalvacionNo ratings yet
- MNT Penyakit GinjalDocument41 pagesMNT Penyakit GinjalNurfitriana DwiNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Sonia Dagar: Renal FailureDocument40 pagesPresented By: Sonia Dagar: Renal FailureRavanshi ThakurNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument36 pagesChronic Kidney Diseasejabir100% (1)
- Alternative NamesDocument67 pagesAlternative NamespashaNo ratings yet
- Renal Failure Acute and Chronic: NPN 200 Medical Surgical Nursing IDocument31 pagesRenal Failure Acute and Chronic: NPN 200 Medical Surgical Nursing IJuan ValadezNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Sumit Kumar, MD, MPH Presbyterian Hospital, Dallas, TXDocument47 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: Sumit Kumar, MD, MPH Presbyterian Hospital, Dallas, TXAnn Michelle TarrobagoNo ratings yet
- HYPOCALCEMIADocument27 pagesHYPOCALCEMIAJeffri SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument3 pagesChronic Renal FailureJashine DajayNo ratings yet
- Taxation Law 1Document7 pagesTaxation Law 1jalefaye abapoNo ratings yet
- Coco Mavdi Esl5Document6 pagesCoco Mavdi Esl5gaurav222980No ratings yet
- C++ Program To Create A Student Database - My Computer ScienceDocument10 pagesC++ Program To Create A Student Database - My Computer ScienceSareeya ShreNo ratings yet
- IbmautomtiveDocument38 pagesIbmautomtiveMeltz NjorogeNo ratings yet
- Course DescriptionDocument54 pagesCourse DescriptionMesafint lisanuNo ratings yet
- Scrum Handbook: Scrum Training Institute PressDocument66 pagesScrum Handbook: Scrum Training Institute PressFranky RiveroNo ratings yet
- Chunking Chunking Chunking: Stator Service IssuesDocument1 pageChunking Chunking Chunking: Stator Service IssuesGina Vanessa Quintero CruzNo ratings yet
- Channel & Lomolino 2000 Ranges and ExtinctionDocument3 pagesChannel & Lomolino 2000 Ranges and ExtinctionKellyta RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Windows Intrusion Detection ChecklistDocument10 pagesWindows Intrusion Detection ChecklistJosé Tomás García CáceresNo ratings yet
- 2432 - Test Solutions - Tsol - 2432 - 21702Document5 pages2432 - Test Solutions - Tsol - 2432 - 21702Anmol PanchalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AmplifierDocument8 pagesIntroduction To AmplifierElaine BicolNo ratings yet
- Design and Optimization of A Medium Altitude Long Endurance UAV Wingbox StructureDocument8 pagesDesign and Optimization of A Medium Altitude Long Endurance UAV Wingbox StructureamirNo ratings yet
- Steel Price Index PresentationDocument12 pagesSteel Price Index PresentationAnuj SinghNo ratings yet
- Strategic Capital Management: Group - 4 Jahnvi Jethanandini Shreyasi Halder Siddhartha Bayye Sweta SarojDocument5 pagesStrategic Capital Management: Group - 4 Jahnvi Jethanandini Shreyasi Halder Siddhartha Bayye Sweta SarojSwetaSarojNo ratings yet
- Nyambe African Adventures An Introduction To African AdventuresDocument5 pagesNyambe African Adventures An Introduction To African AdventuresKaren LeongNo ratings yet
- Strategic Audit of VodafoneDocument35 pagesStrategic Audit of VodafoneArun Guleria89% (9)
- The Beauty of Laplace's Equation, Mathematical Key To Everything - WIRED PDFDocument9 pagesThe Beauty of Laplace's Equation, Mathematical Key To Everything - WIRED PDFYan XiongNo ratings yet
- Donnan Membrane EquilibriaDocument37 pagesDonnan Membrane EquilibriamukeshNo ratings yet
- Angelo (Patrick) Complaint PDFDocument2 pagesAngelo (Patrick) Complaint PDFPatLohmannNo ratings yet
- Perturbation MethodsDocument29 pagesPerturbation Methodsmhdr100% (1)
- For ClosureDocument18 pagesFor Closuremau_cajipeNo ratings yet
- Contemp Person Act.1Document1 pageContemp Person Act.1Luisa Jane De LunaNo ratings yet
- Level Swiches Data SheetDocument4 pagesLevel Swiches Data SheetROGELIO QUIJANONo ratings yet
- Design Practical Eden Swithenbank Graded PeDocument7 pagesDesign Practical Eden Swithenbank Graded Peapi-429329398No ratings yet
- Saif Powertec Limited Project "Standard Operating Process" As-Is DocumentDocument7 pagesSaif Powertec Limited Project "Standard Operating Process" As-Is DocumentAbhishekChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Controlled DemolitionDocument3 pagesControlled DemolitionJim FrancoNo ratings yet
- BSDDocument26 pagesBSDEunnicePanaliganNo ratings yet
- Bulletin PDFDocument2 pagesBulletin PDFEric LitkeNo ratings yet