Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Syallabus
Uploaded by
Damo Daran GOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Syallabus
Uploaded by
Damo Daran GCopyright:
Available Formats
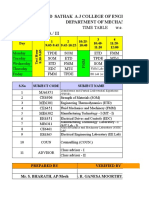
MF9211 ADVANCED MATERIALS TECHNOLOGY L T P C 3 0 0 3 AIM: UNIT I ELASTIC AND PLASTIC BEHAVIOR 10 Elasticity in metals and polymers Anelastic
and visco-elastic behaviour Mechanism of plastic deformation and non metallic shear strength of perfect and real crystals Strengthening mechanisms, work hardening, solid solutioning, grain boundary strengthening, poly phase mixture, precipitation, particle, fibre and dispersion strengthening. Effect of temperature, strain and strain rate on plastic behaviour Super plasticity Deformation of non crystalline materials. UNIT II FRACTURE BEHAVIOUR 10 Griffiths theory, stress intensity factor and fracture toughness Toughening mechanisms Ductile, brittle transition in steel High temperature fracture, creep Larson Miller parameter Deformation and fracture mechanism maps Fatigue, low and high cycle fatigue test, crack initiation and propagation mechanisms and Paris law. Effect of surface and metallurgical parameters on fatigue Fracture of non metallic materials Failure analysis, sources of failure, procedure of failure analysis. UNIT III SELECTION OF MATERIALS 10 Motivation for selection, cost basis and service requirements Selection for mechanical properties, strength, toughness, fatigue and creep Selection for surface durability corrosion and wear resistance Relationship between materials selection and processing Case studies in materials selection with relevance to aero, auto, marine, machinery and nuclear applications Computer aided materials selection. UNIT IV MODERN METALLIC MATERIALS 8 Dual phase steels, High strength low alloy (HSLA) steel, Transformation induced plasticity (TRIP) Steel, Maraging steel, Nitrogen steel Intermetallics, Ni and Ti aluminides smart materials, shape memory alloys Metallic glass and nano crystalline materials. UNIT V NON METALLIC MATERIALS 7 Polymeric materials Formation of polymer structure Production techniques of fibers, foams, adhesives and coating structure, properties and applications of engineering polymers Advanced structural ceramics, WC, TIC, TaC, Al2O3, SiC, Si3N4 CBN and diamond properties, processing and applications. TOTAL: 45 PERIODS REFERENCES: 1. George E.Dieter, Mechanical Metallurgy, McGraw Hill, 1988 2. Thomas H. Courtney, Mechanical Behaviour of Materials, (2nd edition), McGraw Hill, 2000 3. Charles, J.A., Crane, F.A.A. and Fumess, J.A.G., Selection and use of engineering materials, (3rd edition), Butterworth-Heiremann, 2001. 4. Flinn, R.A., and Trojan, P.K., Engineering Materials and their Applications, (4th Edition) Jaico, 1999. 5. ASM Hand book, Vol.11, Failure Analysis and Prevention, (10th Edition), ASM, 2002. 6. Ashby M.F., Material Selection in Mechanical Design, 3rd Edition, Butter Worth 2005. MF9212 AUTOMATED AND COMPUTER INTEGRATED L T P C MANUFACTURING SYSTEM 3 0 0 3 UNIT I INTRODUCTION 6 Introduction to CAD, CAM, CAD/CAM and CIM - Evolution of CIM CIM wheel and cycle Production concepts and mathematical models Simple problems in production models CIM hardware and software Major elements of CIM system Three step process for implementation of CIM Computers in CIM Computer networks for manufacturing The future automated factory Management of CIM Impact of CIM on personnel CIM status. UNIT II AUTOMATED MANUFACTURING SYSTEMS 10
Automated production line system configurations, work part transfer mechanisms Fundamentals of Automated assembly system System configuration, Part delivery at workstations Design for automated assembly Overview of material handling equipments Consideration in material handling system design The 10 principles of Material handling. Conveyor systems Types of conveyors Operations and features. Automated Guided Vehicle system Types of vehicles and AGVs applications Vehicle guidance technology Vehicle management and safety. Storage system performance storage location strategies Conventional storage methods and equipments Automated storage/Retrieval system and Carousel storage system Deadlocks in Automated manufacturing systems Petrinet models Applications in Dead lock avoidance. UNIT III GROUP TECHNOLOGY AND FMS 10 Part families Visual Parts classification and coding Production flow analysis Grouping of parts and Machines by rank order clustering method Benefits of GT Case studies. FMS Components workstations FMS layout configurations Computer control systems FMS planning and implementation issues Architecture of FMS flow chart showing various operations in FMS Machine cell design Composite part concept, Holier method, Key machine concept Quantitative analysis of FMS Bottleneck model Simple and complicated problems Extended Bottleneck model sizing the FMS FMS applications, Benefits. UNIT IV PROCESS PLANNING 10 Process planning Activities in process planning, Informations required. From design to process planning classification of manufacturing processes Selection of primary manufacturing processes selecting among casting process, forming process and machining process. Sequencing of operations according to Anteriorities various examples forming of Matrix of Anteriorities case study. Typical process sheet case studies in Manual process planning. Computer Aided Process Planning Process planning module and data base Variant process planning Two stages in VPP Generative process planning Flow chart showing various activities in generative PP Semi generative process planning. UNIT V TYPES OF PROCESS CONTROL AND AUTOMATIC DATA CAPTURE 9 Introduction to process model formulation linear feed back control systems Optimal control Adaptive control Sequence control and PLC. Computer process control Computer process interface Interface hardware Computer process monitoring Direct digital control and Supervisory computer control. Overview of Automatic identification methods Bar code technology Other Automatic data capture technologies. TOTAL : 45 PERIODS REFERENCES: 1. Mikell P.Groover, Automation, Production system and Computer integrated Manufacturing, Prentice Hall of India Pvt. Ltd., 2008. 2. Radhakrishnan,P., Subramanian,S., and Raju,V., CAD/CAM/CIM New Age International Publishers, 2000. 3. James A.Retrg, Herry W.Kraebber, Computer Integrated Manufacturing, Pearson Education, Asia, 2001. 4. Gideon Halevi and Ronald D.Weill, Principles of Process Planning, Chapman Hall, 1995. 5. Viswanathan,N., and Narahari,Y., Performance Modeling and Automated Manufacturing Systems, Prentice Hall of India Pvt. Ltd., 2000. 6. Kant Vajpayee,S., Computer Integrated Manufacturing, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi, 2007. 7. Alavudeen and Venkateshwaran, Computer Integrated Manufacturing, PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, 2008.
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Me 4400 MCQDocument11 pagesMe 4400 MCQschaudhary93348% (23)
- Bollard Catalog - SPDocument28 pagesBollard Catalog - SPrisiana_limuriaNo ratings yet
- Introduction of IS2062 E250 Grade ADocument2 pagesIntroduction of IS2062 E250 Grade AnareshNo ratings yet
- AISI Steel Plate Engineering Data Vol1&2 2012 PDFDocument134 pagesAISI Steel Plate Engineering Data Vol1&2 2012 PDFJose Felix AcevedoNo ratings yet
- BotlsDocument32 pagesBotlsJohn Lancer FabonNo ratings yet
- Correct AnswerDocument6 pagesCorrect AnswerDamo Daran GNo ratings yet
- Correct AnswerDocument6 pagesCorrect AnswerDamo Daran GNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Heavily Loaded RC Link BeamDocument17 pagesDesign and Analysis of Heavily Loaded RC Link BeamWasin WaiyasusriNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundation NotesDocument11 pagesPile Foundation Notesramya manirajanNo ratings yet
- Forge WeldingDocument2 pagesForge WeldingDamo Daran GNo ratings yet
- Emm April May 2010 Solved QPDocument30 pagesEmm April May 2010 Solved QPDamo Daran GNo ratings yet
- Assignment Unit 1Document2 pagesAssignment Unit 1Damo Daran GNo ratings yet
- Emm May June 2011 Solved QPDocument32 pagesEmm May June 2011 Solved QPDamo Daran GNo ratings yet
- Set 1 em Ques & AnsDocument4 pagesSet 1 em Ques & AnsDamo Daran GNo ratings yet
- Aero - 4Document2 pagesAero - 4Damo Daran GNo ratings yet
- Fifth UnitDocument1 pageFifth UnitDamo Daran GNo ratings yet
- Etd SyllabusDocument2 pagesEtd SyllabusDamo Daran GNo ratings yet
- Theory of MachinesDocument62 pagesTheory of MachinesAbhinav DubeyNo ratings yet
- Ohamed Sathak A.J. College of Engineering, Chennai Internal Assessment Test-IDocument1 pageOhamed Sathak A.J. College of Engineering, Chennai Internal Assessment Test-IDamo Daran GNo ratings yet
- To Jack The Aircraft From Its Steady PositionDocument2 pagesTo Jack The Aircraft From Its Steady PositionDamo Daran GNo ratings yet
- SystemsDocument11 pagesSystemsthe_govNo ratings yet
- TT R03Document63 pagesTT R03Damo Daran GNo ratings yet
- AERO R13 Sem3 PDFDocument12 pagesAERO R13 Sem3 PDFDamo Daran GNo ratings yet
- CheckDocument1 pageCheckDamo Daran GNo ratings yet
- Smart MaterialsDocument19 pagesSmart MaterialsDamo Daran GNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Cutting: Chapter-20Document26 pagesFundamentals of Cutting: Chapter-20rameshNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Cutting: Chapter-20Document26 pagesFundamentals of Cutting: Chapter-20rameshNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Engineering Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesPower Plant Engineering Lesson PlanDamo Daran GNo ratings yet
- Gas Dynamics and Jet PropulsionDocument317 pagesGas Dynamics and Jet PropulsionVinoth RajaguruNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Cutting: Chapter-20Document26 pagesFundamentals of Cutting: Chapter-20rameshNo ratings yet
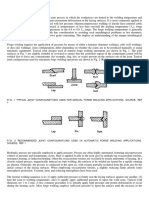
- Friction Stir Welding and ProcessingDocument78 pagesFriction Stir Welding and Processingdrey127No ratings yet
- Aero GliderDocument1 pageAero GliderDamo Daran GNo ratings yet
- Laser Surface Treatment of Magnesium Alloy With WC Powder: Archives of Materials Science and EngineeringDocument4 pagesLaser Surface Treatment of Magnesium Alloy With WC Powder: Archives of Materials Science and EngineeringDamo Daran GNo ratings yet
- Engg ZC241-L11Document56 pagesEngg ZC241-L11Damo Daran GNo ratings yet
- Chapter RegsgvDocument4 pagesChapter RegsgvDamo Daran GNo ratings yet
- Reg. No.: Model ExamDocument3 pagesReg. No.: Model ExamDamo Daran GNo ratings yet
- Copeland KapacitetsregleringDocument27 pagesCopeland KapacitetsregleringEmmanuel MunozNo ratings yet
- Foam Dam Brochure REV 0 1210Document2 pagesFoam Dam Brochure REV 0 1210Ildegar PuertaNo ratings yet
- Greenheck DGXDocument72 pagesGreenheck DGXBrad GNo ratings yet
- PDC - TR 06 02 PDFDocument227 pagesPDC - TR 06 02 PDFHelenNo ratings yet
- Basic Comparison Extruder Slipformer enDocument7 pagesBasic Comparison Extruder Slipformer enOmar MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Technical DocumentationDocument84 pagesTechnical Documentationpotolok7767100% (2)
- 25.03 - Vitaulic RanuradoDocument3 pages25.03 - Vitaulic RanuradoABAD ALEXANDER MORENO ZÁRATENo ratings yet
- Simply Supported Beam With Support Added at Midspan To Prevent Excessive DeflectionDocument2 pagesSimply Supported Beam With Support Added at Midspan To Prevent Excessive DeflectionShiela GonzalesNo ratings yet
- 11 Refractory Weld Studs Sunbelt Stud Welding CatalogDocument14 pages11 Refractory Weld Studs Sunbelt Stud Welding CatalogKotenguNo ratings yet
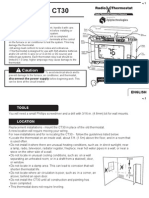
- 2GIG ZWave CT30e Thermostat Installation GuideDocument19 pages2GIG ZWave CT30e Thermostat Installation Guideyamimaker2002No ratings yet
- Viking Series 90 Operating & Maintenance Instructions: FiltersDocument15 pagesViking Series 90 Operating & Maintenance Instructions: FiltersninatenaNo ratings yet
- AZ LicensesDocument29 pagesAZ LicensessivaNo ratings yet
- P334e MasterLife SRA 900Document3 pagesP334e MasterLife SRA 900Stevens NinanyaNo ratings yet
- Knauf Product Catalogue Aug2019 WEBDocument28 pagesKnauf Product Catalogue Aug2019 WEBeka suryanaNo ratings yet
- Wood-Based Composite PDFDocument28 pagesWood-Based Composite PDFJayant Kumar JhaNo ratings yet
- Cladire Birouri Etaj CurentDocument6 pagesCladire Birouri Etaj CurentpintileirobertNo ratings yet
- ASTM D3689-90 (1995) Stand Pile TestDocument11 pagesASTM D3689-90 (1995) Stand Pile TestSoonHan WaiNo ratings yet
- Parameters of GeosyntheticsDocument2 pagesParameters of GeosyntheticsCHANNo ratings yet
- Lowara SV PDFDocument72 pagesLowara SV PDFsebastmNo ratings yet
- Good (ELEC6089) Power Cable Insulation DesignDocument22 pagesGood (ELEC6089) Power Cable Insulation DesignvahrmNo ratings yet
- Bridge Works - MiscellaneousDocument26 pagesBridge Works - MiscellaneousamitjustamitNo ratings yet
- Technical HP Factsheet For WebDocument12 pagesTechnical HP Factsheet For WebDanutz MaximNo ratings yet
- PZ Access Scaffolding 2019Document40 pagesPZ Access Scaffolding 2019Derek HeaneyNo ratings yet
- (N) TMCGEH3S 3x120sqmm Orange TPU JacketDocument3 pages(N) TMCGEH3S 3x120sqmm Orange TPU JacketAbl Jara MamaniNo ratings yet