Professional Documents
Culture Documents
QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES Dominance and Reduced Payoff Matrices
Uploaded by
uttamsudhirOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES Dominance and Reduced Payoff Matrices
Uploaded by
uttamsudhirCopyright:
Available Formats
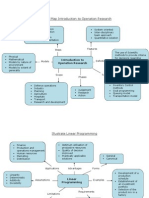
QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES Dominance rule can be applied to Compare the elements in a row with corresponding elements of other rows
and identify dominated row(s) Delete the dominated row(s) and construct reduced payoff matrix Delete the dominated column(s) from the payoff matrix The intercept for X axis cannot be obtained by putting Y = 0 in the constraint. False The rules for obtaining initial feasible solution with the North West Corner rule are Select the upper most left hand corner of the tableau Compare the figures If demand is satisfied move right, if the row is satisfied move down Since the objective function is maximisation, the objective lines must be as far as possible from the origin A decision tree is ______________ to depict sequence of decision to be made A graphic device Mixed strategies game means zero-sum-two-person game with ________ No saddle point In a linear function, each variable appears in one term and only to the first power Simulated experiments are based on random samples drawn from inter arrival and service time distribution KP1 Rs.+ Y.P2 Rs. = maximum is a/an ________ function objective In a m x 2 game, columns offer more choices. False Possible combinations of the strategies shall be X reduces his price while the opponent keeps his price const X reduces his price and the opponent also reduces his price X keeps his price constant but the opponent reduces his price To simulate data for input values of more than one variable, the first two digits and the last two digits may be selected to obtain a pair of two digits random numbers. True The need for mixed constraints in a problem on "product mix" usually arises when it is necessary to produce a _________ quantity of a product Minimum Different criteria suggest different optimal strategies and hence we can conclude that
QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES no single criterion is the best criterion selection of a criterion depends on the decision maker a decision criterion is just a means to convert a problem under uncertainty into a problem under risk Transportation problem involves determination of optimal routes to Minimise shipping costs The negative sign signifies that the straight line slops from lento the right A series of correcting adjustments which are made in different steps Iterations? The figures inserted into the matrix are Self explanatory? The objective function line P = 60x + 20y will have a gradient Of -03 (y = -3x + P/20) All queue situations have Cost implications Constraint represent Straight lines? All points on the line will represent combination of quantities of product To plot a straight line of any constraint we need to find two points that fall on the line The points on each line can be conveniently identified by finding an intercept for the two axis When artificial variables are used, ___________ are taken as the part of the body while finding the initial feasible solution. Slack variables The allocation of a very high cost to prohibited routes automatically includes such routes from optimal solutions. False Infeasible solution result when the problem has not been correctly formulated. True There are two basic approaches to solve a queuing problem; mathematical approach and __________ Simulation approach In simulation model, the results of the system or its components are obtained through sampling
QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES An unbalanced assignment problem is one in which a number of tasks and facilities do not equal each other The procedural steps to obtain an alternate optimal solution are as follows Obtain an optimal solution Select a water square with zero & treat it as( - 0) Assign alternate plus and minus signs on a closed path Quantitative technique employ mathematical models to study the problems Graphical method is used to solve the problem which involve __________ Two unknowns Procedure steps in the graphical solution of a 2 x n game are Check for a saddle point, if it exists the strategies are pure strategies. If it does not exist, go to step 2 Eliminate every dominated column to reduce the size of the game and not essential for the graphical solution Write out constraints for the columns of the payoff matrix Use of slack variables when the restrictions are> - type creates a difficulty. True Problem identification involves specification of constraints identification of alternatives establishing relationship between variables A manager aspiring to be successful must acquire the ability to make decisions. True The service facility can be arranged in any one of the following types single queue single service single queue multiple service multiple queue multiple service Graph of a two-variable-liner-equation is always A straight line The graph of linear inequality is Always a half space Half space in two dimensional coordinates is All of the plane that is on the same side of the line Feasible region is the region defined by The constraints Constraint (x + y <or - 800) states that x + Y is less than or equal to 800. True L.P. deals with assignment problem
QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES portfolio selection staffing problem The value of slack variables depends on the difference between the left and right hand side. True In simulation method, an approximate solution to the problem is obtained through simulated experiments. Travelling salesman problems under special cases in assignment technique are as follows The salesman should not visit the city twice until he has visited all cities No assignment should be made along the diagonal line Management functions are Planning Organisation Control 20x + 10y = 1,200 _____________ Is a constraint When the capacity of warehouses is greater than the requirement, this problem is solved by adding a Dummy consumption centre Hurwicz alpha criterion propagates a midway approach by adding a coefficient of optimism Basic steps in Vagel's Approximation Method are Calculate the difference between each row and column Select the row or column with the largest difference Allocate maximum number of units with minimum cost The tendency of a customer is called Jockeying A L.P. problem may have ________ optimal solution Multiple? =================================================================================== = The knowledge of a game theory is helpful to understand the basic principles of a decision making process. True? Assumptions are made To simplify mathematical models Changes in the situation make The assumptions invalid and mathematical models invalid Simulation models are easily amenable To the changes in the environment Simulation models are Flexible
QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES
System output in a " single-queue-single-server arrangement" equals service rate of service facility in a " single-queue-multiple-servers in series arrangement" equals minimum of service rates of service facilities in a " multiple-queue-multiple-servers in parallel arrangement" equals sum of service rates of service facilities
The __________ represent the consequences of the interactions of the decision alternatives Outcomes The percentage probabilities are then ____________ into cumulative percentage probabilities Aggregated Service facility may be idle at the start in spite of the traffic intensity being greater than unity. True Following are the constraints 2x + y < 1, x < = 2, x + y <= 3 Linear relationships have properties as Proportionality, divisibility Simulation technique has the following limitations Simulation does not produce optimal results Variables at times are difficult to quantify in simulated models Simulation comparatively is a costlier method of analysis The iteration process continues Until the optimum solution is obtained? Programmed decisions are the decisions based on operating programme languages. False Decision variables must assume zero or positive values. True A negative index number indicates Scope for an improvement The problem faced is to decide how to utilise the resources to achieve the _______ Desired objective? The mechanics of the technique are such that each iteration gives an indication of which variable should be ______ to obtain a better solution Queue' is a common phenomenon in our everyday life
QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES The design of the work data sheet varies depending upon The nature of the problem and the type of information required from the experiment Many industrial problems either do not let themselves to a mathematical problem or their analysis is very laborious. True A feasible solution is said to ______ if the number of odd stone squares are less than (m+n- 1) Degenerate The properties of these corner points can be understood by ________ the inequalities into equations Converting? Sequential decisions are those in which the outcome of the first decision affects The choices at the next decision stage L.P. problem involves stages as problem identification problem formulation problem solving A greater than or equal constraint can be augmented by adding a slack variable and an artificial variable. False A prohibited problem can be handled in the transportation problem my assigning a very ____________ High cost With the help of the assignment technique, the solution can be obtained in less time The relationship among the variables should be Linear Quantitative techniques embrace many functional area such as Marketing, production, Quality control Transportation problem can also be termed as Physical distribution of goods Linear Programming Services from supply to demand Both maximisation and minimisation problems cannot be dealt with by graphical methods. False The work data sheet is designed after the rules governing the experiment have been formed The participants to the game who act as decision makers are called players
QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES
Typical example of decision making situations where assignment techniques can be successfully used include assignment of Jobs to machines, Vehicles to routes, Buildings to sites Stepping stone method Evaluating unoccupied cells MODI method Evaluating unoccupied water cells Supply constraints in the transportation tableau Quantities dispatched equal to quantities produced Transportation tableau steps Total individual capacity and demand In a decision tree with terminal values and probabilities the paths not selected are crossed out by two parallel lines Graphical methods requires Plotting lines representing the constraints Drawing an objective function line Selecting an optimal vertex When a L.P. solution is permitted to be _________ large it is known to be unbounded Infinitely In multistage decision processes, decision making is done to reduce overall least cost or maximum profit Flow chart of the steps in the basic procedure helps to so"'" a transportation problem. True When the number of rows are equal to the number of columns, it is called a ___________ Balanced assignment problem Learning curve is a graph in which the performance of an operative is plotted against his name. False Each players knows that to maximise the payoff from the other player, he has to use the conservative minimax criterion to select his best strategy The ____________ is a typical optimisation technique useful in a situation where a certain number of tasks are required to be assigned to an equal number of facilities. Assignment technique =================================================================================== = L.P. finds the quantity of a product to produce at a ___________ Minimum cost The knowledge of the concepts and few logical rules help to provide ___________ into the basic issues
QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES involved in a competitive decision making situation. An improved insight? The presence of zero value of the non-basic variable in the optimal simplex tableau suggests that the current non-basic variable can enter the basis with zero effect on profit Degeneracy occurs when there is a tie for the minimum ratios L.P. is a popular technique for allotting limited resources of a firm in an optimum manner A/an ___________ represents the probability estimate of occurrence of each outcome. Risk When demand exceeds capacity, balance is achieved by adding an additional row of a I an _________ Dummy plant The special cases in linear programming include redundant constraints alternate optimal solution infeasible solution The steps in the simplex method are to repeat steps 6 and 7 until optimal solution is achieved effect improvements (if scope exists) in the current solution read on' optimal solution from the final simplex tableau System input refers to the concise statement of the logic and rules which govern the problem Formulation of L.P. problem involves studying the available data identifying the objective function identifying the restrictions Degeneracy can be resolved by making use of An infinitely small quantity almost close to zero, denoted by an epsilon One or more empty cells if required Treating water cells as stone cells Today, decision making is so important because of Rapid changing technology High degree of uncertainty Business constraints Unbalanced problem occurs when a number of machines are either
QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES More than the number of jobs The event nodes are depicted by a square. False Assignment techniques is also known as a/an ___________ of assignment problems Hungarian method 40x + 10y < = 1600 is an objective function. False Past history is A most frequently used method of predicting probabilities It operates on The principle that the past can always be a guide for the future The method utilises The concept of frequency distribution The individual frequency is Converted into relative frequency Quantitative techniques embraces many ___________ Functional areas Mean arrival rate means the average number of arrivals per _____________ Unit of time The important advantages of the simulation techniques are Simulation models are comparatively more realistic than mathematical models Simulation models are easier to use than mathematical models Computer simulation can process a historical data of several years involving large calculations in few minutes
Balanced assignment problem incorporates no restriction in allocation and involves a minimisation objective In n X n matrix problem, evaluation of each of the combinations will consume hours and become an exercise in futility Standard procedures of the Hungarian method of assignment technique is for balanced problem, minimisation problem, as well as for special situations by adopting additional steps If the constraints are added or subtracted from every element in the cost matrix it minimises the total cost in the original matrix as well as the revised matrix If profit figure have been converted into opportunity costs, the value of the objective function is found by referring to an original profit matrix. True The extreme high cost assigned to the artificial variables automatically ________ them from an optimal solution.
QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES Removes Number of iterations in the transportation problem must be reduced to the minimum by adopting the following rules Make a best possible choice of method for the initial solution Choose row or column having square with the "least" cost Select row or column that allows more units to be allocated at the least cost Decision theory is the study of making a desired choice from a given set of alternatives. False (optimal choice is the correct) System output is dictated by the service time required by the facility The queue system may be designed to minimise the total cost including waiting time cost + service cost Quantitative techniques replace the age old Intuitive and subjective approach of decision making The arrival may either be at a constant rate or at random in accordance with some probability distribution Terminology used in a Games Theory are Play, Player, Strategies, Games (not matching exactly) The theory developed so far is not adequate to solve many competitive business situations. The ________ implies the number of customers in the queue plus those being serviced System length Degeneracy in a transportation may occur in an intermediate tableau when more cells are Vacated It becomes complicated if a sequential block of tag numbers equal to percentage probability of the event, is assigned to each event. False Quantitative techniques can help to analyse his strategies along those of his suppliers and thereby select the best strategy. Addition of services to increase service rate, however increases service cost. True Assumptions made for model II (M/M/C) : ( FCFS) are the arrivals occur complete", at random average arrival rate is less than combined average service rate of all servers the queue of infinite length
QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES
The constraints define the limits within which a solution must be found Sound diagnosis requires measurement of gap between the desired performance and the actual performance identification of the root cause for the gap identification of the restraints in the decision making process Formulation of a L.P. problem means construction of a mathematical solution. False (mathematical model) When the aggregate supply exceeds the aggregate demand, the difference goes to the inventory. True To solve a problem of a maximisation objective, all the elements in the matrix are Subtracted from the largest element in the matrix Simulation has been successfully used to solve a variety of ________ Industrial problems =================================================================================== = Size' represents the number of customers that arrive from time to time for service Categories of decision making are decision making under certainty decision making under risk decision making under conflict In simulation by hand, the most convenient method to obtain required random numbers is to use a random number table In a 2 x n game, rows offer more choices. False Advantages of L.P. are it provides information base for allocation of scarce resources it helps make effective use of factors of production it provides flexibility in analysing multi-dimensional problems For maintenance management, quantitative techniques are used to decide optimum stocking of different spares to predict the useful life of the part to decide on the optimum replacement policy of parts Procedural steps in the graphical method of L.P. are
QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES set up an equation of the objective function set up equations of the constraints identify the feasible solution region Proportionality prohibits that the relationships are directly proportional. False Rules for mixed strategy games are Calculate each row difference Determine ratios of row difference with sum of the row differences as denominator Interchange the ratios A constraint represents an upper limit on the availability of a resource A customer may join the queue and leave the queue without getting service. This action of the customer is called ________ Reneging Quantitative techniques are intended to express the business constraints ___________ Into measurable terms The Transportation tableau can be set up with the following steps Set row for each plant and column for each warehouse Add a row as a demand and a column as the capacity Enter figures of demand and capacity If the data given represents opportunity losses, A pre-requisite to the testing of the initial feasible solution for optimality is to ascertain the sufficiency of the Stone square The points on or below the line 6x + 4y = 3,600 will give a feasible solution for the constraint 6x + 4y <or = 3,600. True Transportation problems are Typical OR techniques Transportation problems can be solved using Linear programming techniques In the transportation problem, the objective is To transport the product from the companies different plants to the companies different warehouses Transportation problem are also encountered When the company has only one plant The final assignment matrix contains _________ the required number of zero elements. More than
QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES
An assignment problem may be visualised as a special case of transportation problems with all supplies equal to 1 and all demands equal to 1. True L.P. is a very ________ for adjusting to meet changing conditions. Good tool Traffic intensity does not signify the likelihood and the extent of queueing. False Unbalanced problem can be balanced by adding ___________ tasks I facilities with zero costs. Dummy An optimum balance between the" cost associated with waiting" and "cost associated with prevention of waiting" may be arrived by introducing more facilities at extra cost by displacing less efficient service facilities by more efficient ones by changing the pattern of arrival of customers for service In simulation model, system input is expressed in the form of ______________ A flow chart Feasible solution is a pair of values of the decision variables That satisfy constraints Following terms are used in connection with L.P. problems decision variables, constraints, objective function An unbalanced assignment problem is one in which a number of tasks and facilities do not equal each other Evaluation of investment proposals and verifying viability of the proposal Is done by investment theory The essential requirement of the variables is that they should not be inter-related. False Two important ___________ of the input process are its size and the pattern of arrival Characteristics Pure strategy game to the first player is maximin value and to the second player, it is a negative of the minimax value Allocation models are used in ______________ Machine loading Basic concept of a mixed strategy game is that it is played a number of times which may not always be the case
QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES
A non-basic variable is added by a modifying and a basic variable. False Graphical method makes use of familiar graphical analysis. True A constraints represents The mathematical equation of the limitations imposed by the problem characteristics An objective function represents the mathematical equation of the major goal of the system In terms of the unknown called decision variables Problem formulation involves The construction of mathematical model from the given data Problem solving involves The selection of appropriate method VAM involves __________ of high penalties and high cost cells. Avoidance 40x + 30y + 0 w1 + 0 w2 =maximum (say P) cannot be the objective function. False The constraint (2x + 4y < or = 200) represented on the graph by a straight line (1) states that 2x + 4y is less than or equal to 200 Today's businessman has to live with a large number of constraints. True Graphical method provides an alternate approach to ____________ The sub-game method Rules concerning constraints in the problem of mixed constraints are Constraints which are "<=" type are reduced to equations by adding slack variables (+11) Constraints which are ">=" type are converted to equations by subtracting by slack variable and adding an artificial variable Constraints which are "=" type are augmented by adding only artificial variables
You might also like
- Elon Musks 3-Step First Principles Thinking - How To Think and Solve Difficult Problems Like ADocument8 pagesElon Musks 3-Step First Principles Thinking - How To Think and Solve Difficult Problems Like AThomas Chinyama100% (3)
- Nutrition Diagnosis From and (ADA)Document177 pagesNutrition Diagnosis From and (ADA)Cyntia ReyesNo ratings yet
- Accountable Talk: Framing Language for Academic SuccessDocument16 pagesAccountable Talk: Framing Language for Academic Successwraysp100% (2)
- Speed Mathematics MultiplicationDocument5 pagesSpeed Mathematics MultiplicationkanmaniNo ratings yet
- Jay Abraham - From Mediocrity To Millions NOTESDocument21 pagesJay Abraham - From Mediocrity To Millions NOTESFaraz Ahmed100% (1)
- Solution Manual To Third Edition AIDocument62 pagesSolution Manual To Third Edition AIPuneet Mehta86% (73)
- Problem Solving in Mathematics (Year 2) PDFDocument80 pagesProblem Solving in Mathematics (Year 2) PDFjamesNo ratings yet
- LP Solved ProblemsDocument5 pagesLP Solved ProblemsAaronLumibao100% (1)
- Problem Solving Critical Thinking PresentationDocument8 pagesProblem Solving Critical Thinking Presentationapi-539853533No ratings yet
- Forecasting Cable Subscriber Numbers with Multiple RegressionDocument100 pagesForecasting Cable Subscriber Numbers with Multiple RegressionNilton de SousaNo ratings yet
- Thomas Lockwood Edgar Papke Innovation by Design PDFDocument196 pagesThomas Lockwood Edgar Papke Innovation by Design PDFGerman Guzman RiañoNo ratings yet
- EXCEL SOLVER LPDocument52 pagesEXCEL SOLVER LPfdesdunes00100% (2)
- Assignment TechniqueDocument16 pagesAssignment TechniqueRahul KhoslaNo ratings yet
- Project On Linear Programming ProblemsDocument29 pagesProject On Linear Programming ProblemsVinod Bhaskar67% (129)
- E C S A: P P L I C A T I O N O R M Egistration As A Rofessional Ngineering EchnologistDocument27 pagesE C S A: P P L I C A T I O N O R M Egistration As A Rofessional Ngineering EchnologistLungisaniNo ratings yet
- (Edda Luzzatto, Giordano Dimarco) Collaborative LeDocument419 pages(Edda Luzzatto, Giordano Dimarco) Collaborative Lepippinlam100% (2)
- CS10-1L SyllabusDocument6 pagesCS10-1L SyllabusNapoleon Pineda IIINo ratings yet
- Maths ProjectDocument20 pagesMaths ProjectChirag JoshiNo ratings yet
- Maximizing Profits with Linear ProgrammingDocument23 pagesMaximizing Profits with Linear ProgrammingAjay Vernekar100% (1)
- Operation Management (MB0048)Document7 pagesOperation Management (MB0048)Sagar TankNo ratings yet
- LP Quantitative TechniquesDocument29 pagesLP Quantitative TechniquesPrateek LoganiNo ratings yet
- TheoryDocument5 pagesTheorysonali guptaNo ratings yet
- Master of Business Administration-MBA Semester 1 MB0048 - Operations Research - 4 Credits (Book ID: B1631) Assignment Set - 1 (60 Marks)Document7 pagesMaster of Business Administration-MBA Semester 1 MB0048 - Operations Research - 4 Credits (Book ID: B1631) Assignment Set - 1 (60 Marks)Vikas WaliaNo ratings yet
- Vijay Maths ProjectDocument54 pagesVijay Maths ProjectVijay MNo ratings yet
- What is Operations ResearchDocument10 pagesWhat is Operations ResearchSHILPA GOPINATHANNo ratings yet
- LINEAR PROGRAMMING: OPTIMIZING WITH CONSTRAINTSDocument19 pagesLINEAR PROGRAMMING: OPTIMIZING WITH CONSTRAINTSChristian paul ArnaizNo ratings yet
- MGMT ScienceDocument35 pagesMGMT ScienceraghevjindalNo ratings yet
- Operations Research Assignment Problem Solved by Hungarian MethodDocument22 pagesOperations Research Assignment Problem Solved by Hungarian MethodmonikachandraNo ratings yet
- MB0032 Set-1Document9 pagesMB0032 Set-1Shakeel ShahNo ratings yet
- What Is Linear Programming?Document5 pagesWhat Is Linear Programming?RenukaSaxenaNo ratings yet
- Project On Linear Programming ProblemsDocument32 pagesProject On Linear Programming ProblemsJeeban BaralNo ratings yet
- Un US1 GW A0 WDWDocument6 pagesUn US1 GW A0 WDWFuturamaramaNo ratings yet
- RM 6 OptimizationDocument30 pagesRM 6 Optimizationmeyu721No ratings yet
- Gradient Descent AlgorithmDocument5 pagesGradient Descent AlgorithmravinyseNo ratings yet
- Quntiative Techniques 2 SonuDocument11 pagesQuntiative Techniques 2 SonuSonu KumarNo ratings yet
- Maths Project Class 12Document13 pagesMaths Project Class 12Anshul Kumar RoyNo ratings yet
- Unit IiiDocument27 pagesUnit Iiimahih16237No ratings yet
- Written Report Bor Grp6Document17 pagesWritten Report Bor Grp6arrisAlyssaNo ratings yet
- Linear Regression For BeginnersDocument4 pagesLinear Regression For BeginnersrajatNo ratings yet
- MB0048 Concept MapDocument14 pagesMB0048 Concept MapGopalakrishnan KuppuswamyNo ratings yet
- Isn't Linear Regression From Statistics?Document4 pagesIsn't Linear Regression From Statistics?umang rajanNo ratings yet
- Op Tim IzationDocument21 pagesOp Tim IzationJane-Josanin ElizanNo ratings yet
- Ch10tif (Determining How Cost Behave)Document35 pagesCh10tif (Determining How Cost Behave)Mary Grace Ofamin100% (1)
- Types of Machine LearningDocument63 pagesTypes of Machine Learningwilliamkin14No ratings yet
- Mba or Unit-Iii NotesDocument12 pagesMba or Unit-Iii NotesAmruta PeriNo ratings yet
- Operational ResearchDocument50 pagesOperational ResearchpavithraveluNo ratings yet
- Operational Research NotesDocument16 pagesOperational Research NotesVansh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Optimization Tech AssigmentDocument12 pagesOptimization Tech AssigmentberzunaNo ratings yet
- SMU Assignment Solve Operation Research, Fall 2011Document11 pagesSMU Assignment Solve Operation Research, Fall 2011amiboi100% (1)
- AI Lec5Document42 pagesAI Lec5Asil Zulfiqar 4459-FBAS/BSCS4/F21No ratings yet
- Linear Programming Optimization with Graphical and Simplex MethodsDocument29 pagesLinear Programming Optimization with Graphical and Simplex MethodsMuhhamed NuuraniNo ratings yet
- Operations ResearchDocument3 pagesOperations ResearchconcepcionjhamailaannedNo ratings yet
- Linearprograming Chapter1Document21 pagesLinearprograming Chapter1rahul10janNo ratings yet
- PRACTICE EXAM ON MANAGEMENT SCIENCE TECHNIQUESDocument8 pagesPRACTICE EXAM ON MANAGEMENT SCIENCE TECHNIQUESsNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Application of Linear ProgrammingDocument6 pagesLiterature Review On Application of Linear ProgrammingafmabreouxqmrcNo ratings yet
- Operations ResearchDocument58 pagesOperations Researchshailja SinghNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming: by Nagendra Bahadur Amatya Head of DepartmentDocument29 pagesLinear Programming: by Nagendra Bahadur Amatya Head of Departmentrahul_sahniNo ratings yet
- St. Xavier's University KolkataDocument40 pagesSt. Xavier's University KolkataME 26 PRADEEP KUMARNo ratings yet
- Integration and DifferentiationDocument27 pagesIntegration and DifferentiationJane-Josanin ElizanNo ratings yet
- Linear RegressionDocument29 pagesLinear RegressionSoubhav ChamanNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Methodology of Operations ResearchDocument5 pagesDiscuss The Methodology of Operations Researchankitoye0% (1)
- Linear Regression Modelling and AnalysisDocument17 pagesLinear Regression Modelling and AnalysisSavitha ElluruNo ratings yet
- ML 2012 Lab 06 SolutionsDocument4 pagesML 2012 Lab 06 SolutionsAurobindo SarkarNo ratings yet
- TG7 Acc115Document12 pagesTG7 Acc115XieNo ratings yet
- LINEAR PROGRAMMING OVERVIEWDocument9 pagesLINEAR PROGRAMMING OVERVIEWjonty777No ratings yet
- Understanding Response Surfaces: Central Composite Designs Box-Behnken DesignsDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Response Surfaces: Central Composite Designs Box-Behnken DesignsMonir SamirNo ratings yet
- Week 3a - PPT 3 - AMG 211 (Linear Programming)Document17 pagesWeek 3a - PPT 3 - AMG 211 (Linear Programming)not funny didn't laughNo ratings yet
- Problem SolvingDocument13 pagesProblem SolvingChad McdonaldNo ratings yet
- Using graphical method to solve the linear programming.:ريرقتلا نساDocument5 pagesUsing graphical method to solve the linear programming.:ريرقتلا نساQUSI E. ABDNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming Model Formulation and Graphical SolutionDocument3 pagesLinear Programming Model Formulation and Graphical SolutionxyzNo ratings yet
- Design ProcessDocument1 pageDesign ProcessuttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- Design ProcessDocument1 pageDesign ProcessuttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- Symbiosis Centre For Distance LearningDocument4 pagesSymbiosis Centre For Distance LearningSridhar SundaramNo ratings yet
- Sales Forecasting or Demand Management 2. Sales and Operations Planning 3. Production Planning 4. Material Requirements Planning 5. Inventory ReductionDocument1 pageSales Forecasting or Demand Management 2. Sales and Operations Planning 3. Production Planning 4. Material Requirements Planning 5. Inventory ReductionuttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- HR Out 5Document1 pageHR Out 5uttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- Inventory 2. Receivable 3. CashDocument1 pageInventory 2. Receivable 3. CashuttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- HR Out 2Document1 pageHR Out 2uttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- Design ProcessDocument1 pageDesign ProcessuttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- Prof. R.K. Sharma Director: Dr. S.K. GuptaDocument3 pagesProf. R.K. Sharma Director: Dr. S.K. GuptauttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- Symbiosis Centre For Distance LearningDocument4 pagesSymbiosis Centre For Distance LearningSridhar SundaramNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma ApplicationsDocument16 pagesSix Sigma ApplicationsuttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma ApplicationsDocument16 pagesSix Sigma ApplicationsuttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- O Stocks of Raw Materials o Work-In-Progress o Finished Goods o Trade Debtors o Prepayments o Cash BalancesDocument1 pageO Stocks of Raw Materials o Work-In-Progress o Finished Goods o Trade Debtors o Prepayments o Cash BalancesuttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management Crucial for Manufacturing SuccessDocument1 pageInventory Management Crucial for Manufacturing SuccessuttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: Boyce Manufacturing Co. Ltd. For Giving Me An Opportunity To Prove My Worthiness in TheDocument1 pageAcknowledgement: Boyce Manufacturing Co. Ltd. For Giving Me An Opportunity To Prove My Worthiness in TheuttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- Godrej Group Corporate Profile and HistoryDocument1 pageGodrej Group Corporate Profile and HistoryuttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- Home 1Document56 pagesHome 1uttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty in Logistics ServicesDocument1 pageCustomer Satisfaction and Loyalty in Logistics ServicesuttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- The history and services of Karvy Consultants LimitedDocument1 pageThe history and services of Karvy Consultants LimiteduttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- Investment 6Document1 pageInvestment 6uttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- Project Report on Investment & Mutual Funds at Karvy Stock BrokingDocument1 pageProject Report on Investment & Mutual Funds at Karvy Stock BrokinguttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- Phase Ii: Qualitative ResearchDocument1 pagePhase Ii: Qualitative ResearchuttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- ProjectsDocument1 pageProjectsuttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- Investment 3Document1 pageInvestment 3uttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- Customers Perception Towards E-Banking Services: A Project Report Submitted During Digital Marketing Course ofDocument1 pageCustomers Perception Towards E-Banking Services: A Project Report Submitted During Digital Marketing Course ofuttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- 90 RichoDocument1 page90 RichouttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- Investment 2Document1 pageInvestment 2uttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- Banking Services" Is Carried Out by Us Under The Guidance of Our HonorableDocument1 pageBanking Services" Is Carried Out by Us Under The Guidance of Our HonorableuttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- InsuranceDocument1 pageInsuranceuttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- Areas of Improvement?: Ricoh India LimitedDocument1 pageAreas of Improvement?: Ricoh India LimiteduttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: (Taken From TheDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: (Taken From TheRosefa RendonNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 POA 2024Document1 pageGrade 8 POA 2024Sabelo james BhembeNo ratings yet
- Kebitaraan Stem Dalam Ekosistem Sekolah - Pemangkin Kemajuan NegaraDocument74 pagesKebitaraan Stem Dalam Ekosistem Sekolah - Pemangkin Kemajuan NegaraAsmah AliasNo ratings yet
- Accenture - Open Innovation at Huawei TechnologiesDocument6 pagesAccenture - Open Innovation at Huawei TechnologiesAndrey PritulyukNo ratings yet
- Heriot-Watt Sustainability Eng B477-SUE - 201819Document6 pagesHeriot-Watt Sustainability Eng B477-SUE - 201819Mohammed SaifNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - How To Teach GrammarDocument13 pagesModule 4 - How To Teach GrammarAzizan ShafieNo ratings yet
- Solving Public ProblemsDocument448 pagesSolving Public ProblemsDiegoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Academic Laboratory: Operating InstructionsDocument36 pagesPre-Academic Laboratory: Operating InstructionsPATRIOTSKULLZNo ratings yet
- Training Regulations for Welding NCIII (SMAWDocument64 pagesTraining Regulations for Welding NCIII (SMAWRocz RocoNo ratings yet
- Lay-Counsellor India LancetDocument12 pagesLay-Counsellor India Lancetমোঃ সিফাতুল ইসলামNo ratings yet
- BBA Course CatalogueDocument80 pagesBBA Course CatalogueKapil AroraNo ratings yet
- It Grade10 Pat 2013Document27 pagesIt Grade10 Pat 2013DrAzTik0% (1)
- 3 Domains Verb ObjectivesDocument13 pages3 Domains Verb ObjectivesBot Ching MacRiverNo ratings yet
- Final-Article-Role of Mathematics in The Development of Society-NCERDocument14 pagesFinal-Article-Role of Mathematics in The Development of Society-NCERMicol Sancho100% (1)
- BOW in MATHDocument42 pagesBOW in MATHFay BaysaNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineer Kusuma Yadav resumeDocument2 pagesCivil Engineer Kusuma Yadav resumecaddNo ratings yet
- Glynn, 1996Document32 pagesGlynn, 1996Austin DressmanNo ratings yet
- O DDocument78 pagesO DSachinNo ratings yet