Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geomorphology
Uploaded by
Kristin SheafferCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Geomorphology
Uploaded by
Kristin SheafferCopyright:
Available Formats
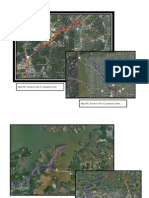
GEO 4121 Geomorphology Lab Field Project 2012 Entrainment occurs when particles resting on the streambed are
mobilized. For this to occur, the shear stress exerted by the fluid must exceed critical shear stress of the grains resting on the riverbed. This is an important concept in the study of fluvial geomorphology and river restoration. For this years project we will be looking at depths and associated discharges necessary to mobilize different size fractions of sediment along a small creek near Phil Hardberger park in San Antonio. We will compare these values to an area of the channel where the banks have been stabilized, to prevent stream erosion, and determine the maximum depth and flow velocity since the time of reinforcement. Project Guidelines (what should be included in your report): Title: Tells the reader what the paper is specifically about in relatively few words. Introduction: Tells the reader about the topic, why its relevant, and gives a general outline of the paper. Previous Work: Discusses what has already been done/what is known about the topic, and gives references. Methods: How was the research carried out? You should provide enough detail that someone with knowledge of the topic could reproduce the experiment. Since this paper is field-based, this section should also include a brief description of the study site (relevant to the project). Results: Discuss the results of your field work and analysis. Also include any problems you may have had. Include tables and figures in this section. Discussion: Do your results answer your research question/objective? Why or why not? Is this consistent with/different from previous work? Discuss any errors or limitations with your research. Conclusion: What conclusions can you make based on your research? Dont just summarize, discuss how your findings fit in with the big picture. Why did you do this research? How is it useful? References cited: Include all references cited.
Plagiarism: Dont present others ideas as your own. Dont copy sentences from papers without properly citing the work. If evidence of plagiarism is found, you will not be given credit for the paper and you are subject to disciplinary action according to University policy. You will turn in one paper per group with your field data. However, you must do your own work for the remaining parts of the assignment and turn in your own calculations, graphs, tables, and papers. Timeline for completion: October 6th or 14th: Collect field data (20 points) November 13th or 15th (by 2:00 pm)*: Turn in calculations, tables, and figures (40 points) December 4th or 6th (by 2:00 pm)*: Report due (40 points) *Turn in on your lab day Details, Expectations, and Equations for paper Field portion: During the field exercise, identify a representative reach to make your measurements (walk along stream bed to assess the range of channel variability). Note distance from bridge. Give a description of the study area in your methods section. Sample bed material using Wolman pebble count Measure chanel width(s) Measure slope In class/at home portion: Make a frequency histogram: clast size on X axis and frequency on Y axis, use Wentworth classification to show size ranges for each column Also work out the percentage in each size class, and cumulative percent curve Use the curve to determine your D16, D50, D84, and D100
Use the following equations to determine the water depth and associated flow velocity necessary to move each of the above size fractions. ci = c/( s)gDi
c=gRS ci =Shields parameter for dimensionless critical shear stress (determine from Shields diagram) c = critical shear stress s =Density of sediment (what is the composition of this sediment, determine density, in kg/m3) Di=median diameter of the particle IN METERS, not mm (your D16, D50, D84, and D100) g=gravitational constant (9.81 m/s2) =density of water (1000 kg/m3) s=density of sediment (in kg/m3) R=hydraulic radius (can be approximated with depth for wide and shallow channels) S=slope of the water surface
In this scenario you may substitute d for R. Solve for d to determine depths Keulegan Equation: U/U*=2.5ln(11d/ks) U*=(ghS) ks=6.8D50 U=average velocity (m/s) U*=shear velocity d=depth ks=equivalent sand roughness height
You might also like
- Mass ExtinctionsDocument29 pagesMass ExtinctionsKristin SheafferNo ratings yet
- Faint Young Sun: Effective Radiating T of EarthDocument25 pagesFaint Young Sun: Effective Radiating T of EarthKristin SheafferNo ratings yet
- Stillwater 2Document64 pagesStillwater 2Kristin SheafferNo ratings yet
- Daisy WorldDocument24 pagesDaisy WorldKristin SheafferNo ratings yet
- Stillwater 2Document64 pagesStillwater 2Kristin SheafferNo ratings yet
- Ig RXDocument42 pagesIg RXKristin SheafferNo ratings yet
- Mineral Names and Compositions You Should KnowDocument3 pagesMineral Names and Compositions You Should KnowKristin SheafferNo ratings yet
- GeomorphDocument3 pagesGeomorphKristin SheafferNo ratings yet
- Chicago Manual of Style Sample PaperDocument20 pagesChicago Manual of Style Sample PaperposthocNo ratings yet
- Molecular Geometry and Bonding TheoriesDocument8 pagesMolecular Geometry and Bonding TheoriesKristin SheafferNo ratings yet
- Lab Outline LectureDocument3 pagesLab Outline LectureKristin SheafferNo ratings yet
- 2 Absorvs ConcentrationDocument2 pages2 Absorvs ConcentrationKristin SheafferNo ratings yet
- Absorvs ConcentrationDocument2 pagesAbsorvs ConcentrationKristin SheafferNo ratings yet
- Chs 9Document10 pagesChs 9Kristin SheafferNo ratings yet
- Project To X-Sec Abeyta FixedKNSDocument1 pageProject To X-Sec Abeyta FixedKNSKristin SheafferNo ratings yet
- Structures Field Trip A AshDocument8 pagesStructures Field Trip A AshKristin SheafferNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- FYP GuidelinesDocument9 pagesFYP GuidelinesAsh WinNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Economics and Financial MarketsDocument4 pagesFundamentals of Economics and Financial MarketsluluNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Research IntroductionDocument29 pagesHow To Write A Research IntroductionFerdinand VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Writing A Book Sample Project PDFDocument76 pagesWriting A Book Sample Project PDFArka0% (1)
- Hypothesis TestingDocument20 pagesHypothesis TestingHamza KhanNo ratings yet
- Sexology MidwiferyDocument216 pagesSexology MidwiferyMarcel Ghidusul100% (3)
- Cognitive Psychology: Introduction and OverviewDocument15 pagesCognitive Psychology: Introduction and OverviewDamielle DacanayNo ratings yet
- Regression ExampleDocument7 pagesRegression ExamplerasnimNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Report Front PagesDocument13 pagesSummer Training Report Front PagesVISHAL RATHOURNo ratings yet
- STS Programme Schedule by Date As at 0407019Document51 pagesSTS Programme Schedule by Date As at 0407019RJ TutorialsNo ratings yet
- Bystranowski 2021Document23 pagesBystranowski 2021irmNo ratings yet
- Lembar Perbaikan ThesisDocument7 pagesLembar Perbaikan Thesisenda suhendaNo ratings yet
- Yolanda Paramitha ProceedingDocument6 pagesYolanda Paramitha Proceedingyolanda paramithaNo ratings yet
- Theories Factors On Affecting MotivationsDocument3 pagesTheories Factors On Affecting MotivationsRod P. Panganiban100% (1)
- Zurek Cadena-180708-As-16b4a2Document3 pagesZurek Cadena-180708-As-16b4a2api-160171849No ratings yet
- Illustrating Random Sampling PDFDocument1 pageIllustrating Random Sampling PDFHeaven SyNo ratings yet
- Water Research: Microplastics in Freshwaters and Drinking Water: Critical Review and Assessment of Data QualityDocument14 pagesWater Research: Microplastics in Freshwaters and Drinking Water: Critical Review and Assessment of Data QualityMochamadAliHaidarNo ratings yet
- Part 1 - Unit 7 of 7 Procedures, Analysis, Conclusions, and DocumentationDocument14 pagesPart 1 - Unit 7 of 7 Procedures, Analysis, Conclusions, and DocumentationMuhammad Shahzad KhanNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal RubricDocument1 pageResearch Proposal RubricGeraldNo ratings yet
- 2 - 23 - A Survey of Vision-Language Pre-Training From The Lens of Multimodal Machine TranslationDocument10 pages2 - 23 - A Survey of Vision-Language Pre-Training From The Lens of Multimodal Machine TranslationPhạm Thanh TrườngNo ratings yet
- Abbott Farm Interpretive PlanDocument324 pagesAbbott Farm Interpretive PlanGraziano SerraNo ratings yet
- Udl Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesUdl Lesson Planapi-535388004No ratings yet
- PreviewDocument24 pagesPreviewFrediyanto HendrayaniNo ratings yet
- The Problem' of Sexual FantasiesDocument20 pagesThe Problem' of Sexual FantasiesJorge Echavarría CarvajalNo ratings yet
- Effect of Compensation On Job Performance: An Empirical StudyDocument15 pagesEffect of Compensation On Job Performance: An Empirical StudyAbdullah AfzalNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Analysis of Icici Bank: A Research Project OnDocument155 pagesFundamental Analysis of Icici Bank: A Research Project Onanunaykumar7847No ratings yet
- Testing Sexual Orientation: A Scientific and Legal Analysis of Plethysmography in Asylum and Refugee Status ProceedingsDocument30 pagesTesting Sexual Orientation: A Scientific and Legal Analysis of Plethysmography in Asylum and Refugee Status ProceedingsLGBT Asylum NewsNo ratings yet
- Criminological Research 1 Notes PrelimDocument9 pagesCriminological Research 1 Notes PrelimRosalinda Achacoso BoiserNo ratings yet
- For Statsprob 1st PPT in 2nd SemDocument7 pagesFor Statsprob 1st PPT in 2nd SemAyesha MhallawiNo ratings yet
- Research Methods in Taxation Ethics: Developing The Defining Issues Test (DIT) For A Tax-Specific ScenarioDocument20 pagesResearch Methods in Taxation Ethics: Developing The Defining Issues Test (DIT) For A Tax-Specific ScenarioDulcianeFortesNo ratings yet