Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Venkat - SQL: Create The Following Tables
Uploaded by
Hariprasad Reddy GOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Venkat - SQL: Create The Following Tables
Uploaded by
Hariprasad Reddy GCopyright:
Available Formats
Venkat sql Queries
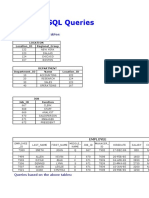
Create the following Tables: LOCATION Location_ID Regional_Group 122 NEW YORK 123 124 167 DALLAS CHICAGO BOSTON DEPARTMENT Name ACCOUNTING RESEARCH SALES OPERATIONS
Department_ID 10 20 30 40
Location_ID 122 124 123 167
JOB Job_ID 667 668 669 670 671 672 Function CLERK STAFF ANALYST SALESPERSON MANAGER PRESIDENT
EMPLOYEE EMPLO YEE_I D 7369 7499 7505 7506 7507 7521 LAST_NA ME SMITH ALLEN DOYLE DENNIS BAKER WARK FIRST_ NAME JOHN KEVIN JEAN LYNN LESLIE CYNTHI A MIDD LE_N AME Q J K S D D JOB_ID 667 670 671 671 671 670 MANA GER_ID 7902 7698 7839 7839 7839 7698 HIRED ATE 17-DEC84 20-FEB85 04-APR85 15MAY-85 10-JUN85 22-FEB85 SALAR Y 800 1600 2850 2750 2200 1250 COMM NULL 300 NULL NULL NULL 500 DEPAR TMENT _ID 20 30 30 30 40 30
Queries based on the above tables: Simple Queries: 1. 2. 3. 4. List all the employee details List all the department details List all job details List all the locations List out first name, last name, salary, commission for all employees
5.
Data Base Testing
Venkat sql Queries 6. 7.
List out employee_id,last name, department id for all employees and rename employee id as ID of the employee, last name as Name of the employee, department id as department ID List out the employees annual salary with their names only.
Where Conditions: 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. List the details about SMITH List out the employees who are working in department 20 List out the employees who are earning salary between 3000 and 4500 List out the employees who are working in department 10 or 20 Find out the employees who are not working in department 10 or 30 List out the employees whose name starts with S List out the employees whose name start with S and end with H List out the employees whose name length is 4 and start with S List out the employees who are working in department 10 and draw the salaries more than 3500 List out the employees who are not receiving commission.
17.
Order By Clause: 18. List out the employee id, last name in ascending order based on the employee id. 19. List out the employee id, name in descending order based on salary column 20. list out the employee details according to their last_name in ascending order and salaries in descending order 21. List out the employee details according to their last_name in ascending order and then on department_id in descending order. Group By & Having Clause: 22. How many employees who are working in different departments wise in the organization 23. List out the department wise maximum salary, minimum salary, average salary of the employees 24. List out the job wise maximum salary, minimum salary, and average salaries of the employees.
25. List out the no. of employees joined in every month in ascending order. 26. List out the no. of employees for each month and year, in the ascending order based on the year, month. 27. List out the department id having at least four employees.
28. How many employees in January month. 29. How many employees who are joined in January or September month. 30. How many employees who are joined in 1985. 31. How many employees joined each month in 1985? 32. How many employees who are joined in March 1985. 33. Which is the department id, having greater than or equal to 3 employees joined in April 1985? Sub-Queries 34. 35. 36. 37. Display the employee who got the maximum salary. Display the employees who are working in Sales department Display the employees who are working as Clerk. Display the employees who are working in New York Find out no. of employees working in Sales department.
38. 39. Update the employees salaries, who are working as Clerk on the basis of 10%.
40. Delete the employees who are working in accounting department. 41. Display the second highest salary drawing employee details. 42. Display the Nth highest salary drawing employee details Sub-Query operators: (ALL, ANY, SOME, EXISTS)
Data Base Testing
Venkat sql Queries
43. 44. 45. 46. List out the employees who earn more than every employee in department 30. List out the employees who earn more than the lowest salary in department 30. Find out whose department has not employees. Find out which department does not have any employees.
Co-Related Sub Queries: 47. Find out the employees who earn greater than the average salary for their department. Joins Simple join 48. List our employees with their department names 49. Display employees with their designations (jobs) 50. Display the employees with their department name and regional groups. 51. How many employees who are working in different departments and display with department name. 52. How many employees who are working in sales department. 53. Which is the department having greater than or equal to 5 employees and display the department names in ascending order? 54. How many jobs in the organization with designations. 55. How many employees working in New York. Non Equi Join: 56. Display employee details with salary grades. 57. List out the no. of employees on grade wise. 58. Display the employ salary grades and no. of employees between 2000 to 5000 range of salary. Self Join: 59. Display the employee details with their manager names. 60. Display the employee details who earn more than their managers salaries. 61. Show the no. of employees working under every manager. Outer Join: 61. Display employee details with all departments. 62. Display all employees in sales or operation departments. Set Operators: 63. List out the distinct jobs in Sales and Accounting Departments. 64. List out the ALL jobs in Sales and Accounting Departments. 65. List out the common jobs in Research and Accounting Departments in ascending order. Answers 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. SQL > Select * from employee; SQL > Select * from department; SQL > Select * from job; SQL > Select * from loc; SQL > Select first_name, last_name, salary, commission from employee; SQL > Select employee_id id of the employee, last_name name", department id as department id from employee;
Data Base Testing
Venkat sql Queries
7. 8. 9. SQL > Select last_name, salary*12 annual salary from employee SQL > Select * from employee where last_name=SMITH; SQL > Select * from employee where department_id=20
10. SQL > Select * from employee where salary between 3000 and 4500 11. SQL > Select * from employee where department_id in (20,30) 12. SQL > Select last_name, salary, commission, department_id from employee where department_id not in (10,30) 13. SQL > Select * from employee where last_name like S% 14. SQL > Select * from employee where last_name like S%H 15. SQL > Select * from employee where last_name like S___ 16. SQL > Select * from employee where department_id=10 and salary>3500 17. SQL > Select * from employee where commission is Null 18. SQL > Select employee_id, last_name from employee order by employee_id 19. SQL > Select employee_id, last_name, salary from employee order by salary desc 20. SQL > Select employee_id, last_name, salary from employee order by last_name, salary desc 21. SQL > Select employee_id, last_name, salary from employee order by last_name, department_id desc 22. SQL > Select department_id, count(*), from employee group by department_id 23. SQL > Select department_id, count(*), max(salary), min(salary), avg(salary) from employee group by department_id 24. SQL > Select job_id, count(*), max(salary), min(salary), avg(salary) from employee group by job_id 25. SQL > Select to_char(hire_date,month)month, count(*) from employee group by to_char(hire_date,month) order by month 26. SQL > Select to_char(hire_date,yyyy) Year, to_char(hire_date,mon) Month, count(*) No. of employees from employee group by to_char(hire_date,yyyy), to_char(hire_date,mon) 27. SQL > Select department_id, count(*) from employee group by department_id having count(*)>=4 28. SQL > Select to_char(hire_date,mon) month, count(*) from employee group by to_char(hire_date,mon) having to_char(hire_date,mon)=jan 29. SQL > Select to_char(hire_date,mon) month, count(*) from employee group by to_char(hire_date,mon) having to_char(hire_date,mon) in (jan,sep) 30. SQL > Select to_char(hire_date,yyyy) Year, count(*) from employee group by to_char(hire_date,yyyy) having to_char(hire_date,yyyy)=1985 31. SQL > Select to_char(hire_date,yyyy)Year, to_char(hire_date,mon) Month, count(*) No. of employees from employee where to_char(hire_date,yyyy)=1985 group by to_char(hire_date,yyyy),to_char(hire_date,mon) 32. SQL > Select to_char(hire_date,yyyy)Year, to_char(hire_date,mon) Month, count(*) No. of employees from employee where to_char(hire_date,yyyy)=1985 and to_char(hire_date,mon)=mar group by to_char(hire_date,yyyy),to_char(hire_date,mon) 33. SQL > Select department_id, count(*) No. of employees from employee where to_char(hire_date,yyyy)=1985 and to_char(hire_date,mon)=apr group by to_char(hire_date,yyyy), to_char(hire_date,mon), department_id having count(*)>=3
Data Base Testing
Venkat sql Queries
34. SQL > Select * from employee where salary=(select max(salary) from employee) 35. SQL > Select * from employee where department_id IN (select department_id from department where name=SALES) 36. SQL > Select * from employee where job_id in (select job_id from job where function=CLERK 37. SQL > Select * from employee where department_id=(select department_id from department where location_id=(select location_id from location where regional_group=New York)) 38. SQL > Select * from employee where department_id=(select department_id from department where name=SALES group by department_id) 39. SQL > Update employee set salary=salary*10/100 wehre job_id=(select job_id from job where function=CLERK) 40. SQL > delete from employee where department_id=(select department_id from department where name=ACCOUNTING) 41. SQL > Select * from employee where salary=(select max(salary) from employee where salary <(select max(salary) from employee)) 42. SQL > Select distinct e.salary from employee where & no-1=(select count(distinct salary) from employee where sal>e.salary) 43. SQL > Select * from employee where salary > all (Select salary from employee where department_id=30) 44. SQL > Select * from employee where salary > any (Select salary from employee where department_id=30) 45. SQL > Select employee_id, last_name, department_id from employee e where not exists (select department_id from department d where d.department_id=e.department_id) 46. SQL > Select name from department d where not exists (select last_name from employee e where d.department_id=e.department_id) 47. SQL > Select employee_id, last_name, salary, department_id from employee e where salary > (select avg(salary) from employee where department_id=e.department_id) 48. SQL > Select employee_id, last_name, name from employee e, department d where e.department_id=d.department_id 49. SQL > Select employee_id, last_name, function from employee e, job j where e.job_id=j.job_id 50. SQL > Select employee_id, last_name, name, regional_group from employee e, department d, location l where e.department_id=d.department_id and d.location_id=l.location_id 51. SQL > Select name, count(*) from employee e, department d where d.department_id=e.department_id group by name 52. SQL > Select name, count(*) from employee e, department d where d.department_id=e.department_id group by name having name=SALES 53. SQL > Select name, count(*) from employee e, department d where d.department_id=e.department_id group by name having count (*)>=5 order by name 54. SQL > Select function, count(*) from employee e, job j where j.job_id=e.job_id group by function 55. SQL > Select regional_group, count(*) from employee e, department d, location l where e.department_id=d.department_id and d.location_id=l.location_id and regional_group=NEW YORK group by regional_group 56. SQL > Select employee_id, last_name, grade_id from employee e, salary_grade s where salary between lower_bound and upper_bound order by last_name
Data Base Testing
Venkat sql Queries
57. SQL > Select grade_id, count(*) from employee e, salary_grade s where salary between lower_bound and upper_bound group by grade_id order by grade_id desc 58. SQL > Select grade_id, count(*) from employee e, salary_grade s where salary between lower_bound and upper_bound and lower_bound>=2000 and lower_bound<=5000 group by grade_id order by grade_id desc 59. SQL > Select e.last_name emp_name, m.last_name, mgr_name from employee e, employee m where e.manager_id=m.employee_id 60. SQL > Select e.last_name emp_name, e.salary emp_salary, m.last_name, mgr_name, m.salary mgr_salary from employee e, employee m where e.manager_id=m.employee_id and m.salary<e.salary 61. SQL > Select m.manager_id, count(*) from employee e, employee m where e.employee_id=m.manager_id group by m.manager_id 62. SQL > Select last_name, d.department_id, d.name from employee e, department d where e.department_id(+)=d.department_id 63. SQL > Select last_name, d.department_id, d.name from employee e, department d where e.department_id(+)=d.department_id and d.department_idin (select department_id from department where name IN (SALES,OPERATIONS)) 64. SQL > Select function from job where job_id in (Select job_id from employee where department_id=(select department_id from department where name=SALES)) union Select function from job where job_id in (Select job_id from employee where department_id=(select department_id from department where name=ACCOUNTING)) 65. SQL > Select function from job where job_id in (Select job_id from employee where department_id=(select department_id from department where name=SALES)) union all Select function from job where job_id in (Select job_id from employee where department_id=(select department_id from department where name=ACCOUNTING)) 66. SQL > Select function from job where job_id in (Select job_id from employee where department_id=(select department_id from department where name=RESEARCH)) intersect Select function from job where job_id in (Select job_id from employee where department_id=(select department_id from department where name=ACCOUNTING)) order by function 1.To fetch ALTERNATE records from a table. (EVEN NUMBERED) select * from emp where rowid in (select decode(mod(rownum,2),0,rowid, null) from emp); 2.To select ALTERNATE records from a table. (ODD NUMBERED) select * from emp where rowid in (select decode(mod(rownum,2),0,null ,rowid) from emp); 3.Find the 3rd MAX salary in the emp table. select distinct sal from emp e1 where 3 = (select count(distinct sal) from emp e2 where e1.sal <= e2.sal); 4.Find the 3rd MIN salary in the emp table. select distinct sal from emp e1 where 3 = (select count(distinct sal) from emp e2where e1.sal >= e2.sal); 5.Select FIRST n records from a table. select * from emp where rownum <= &n; 6.Select LAST n records from a table
Data Base Testing
Venkat sql Queries
select * from emp minus select * from emp where rownum <= (select count(*) - &n from emp); 7.List dept no., Dept name for all the departments in which there are no employees in the department. select * from dept where deptno not in (select deptno from emp); alternate solution: select * from dept a where not exists (select * from emp b where a.deptno = b.deptno); altertnate solution: select empno,ename,b.deptno,dname from emp a, dept b where a.deptno(+) = b.deptno and empno is null; 8.How to get 3 Max salaries ? select distinct sal from emp a where 3 >= (select count(distinct sal) from emp b where a.sal <= b.sal) order by a.sal desc; 9.How to get 3 Min salaries ? select distinct sal from emp a where 3 >= (select count(distinct sal) from emp b where a.sal >= b.sal); 10.How to get nth max salaries ? select distinct hiredate from emp a where &n = (select count(distinct sal) from emp b where a.sal >= b.sal); 11.Select DISTINCT RECORDS from emp table. select * from emp a where rowid = (select max(rowid) from emp b where a.empno=b.empno); 12.How to delete duplicate rows in a table? delete from emp a where rowid != (select max(rowid) from emp b where a.empno=b.empno); 13.Count of number of employees in department wise. select count(EMPNO), b.deptno, dname from emp a, dept b where a.deptno(+)=b.deptno group by b.deptno,dname; 14. Suppose there is annual salary information provided by emp table. How to fetch monthly salary of each and every employee? select ename,sal/12 as monthlysal from emp; 15.Select all record from emp table where deptno =10 or 40. select * from emp where deptno=30 or deptno=10; 16.Select all record from emp table where deptno=30 and sal>1500. select * from emp where deptno=30 and sal>1500; 17.Select all record from emp where job not in SALESMAN or CLERK. select * from emp where job not in ('SALESMAN','CLERK');
Data Base Testing
Venkat sql Queries
18.Select all record from emp where ename in 'BLAKE','SCOTT','KING'and'FORD'. select * from emp where ename in('JONES','BLAKE','SCOTT','KING','FORD'); 19.Select all records where ename starts with S and its lenth is 6 char. select * from emp where ename like'S____'; 20.Select all records where ename may be any no of character but it should end with R. select * from emp where ename like'%R'; 21.Count MGR and their salary in emp table. select count(MGR),count(sal) from emp; 22.In emp table add comm+sal as total sal . select ename,(sal+nvl(comm,0)) as totalsal from emp; 23.Select any salary <3000 from emp table. select * from emp where sal> any(select sal from emp where sal<3000); 24.Select all salary <3000 from emp table. select * from emp where sal> all(select sal from emp where sal<3000); 25.Select all the employee group by deptno and sal in descending order. select ename,deptno,sal from emp order by deptno,sal desc; 26.How can I create an empty table emp1 with same structure as emp? Create table emp1 as select * from emp where 1=2; 27.How to retrive record where sal between 1000 to 2000? Select * from emp where sal>=1000 And sal<2000 28.Select all records where dept no of both emp and dept table matches. select * from emp where exists(select * from dept where emp.deptno=dept.deptno) 29.If there are two tables emp1 and emp2, and both have common record. How can I fetch all the recods but common records only once? (Select * from emp) Union (Select * from emp1) 30.How to fetch only common records from two tables emp and emp1? (Select * from emp) Intersect (Select * from emp1) 31. How can I retrive all records of emp1 those should not present in emp2? (Select * from emp) Minus (Select * from emp1)
Data Base Testing
Venkat sql Queries
32.Count the totalsa deptno wise where more than 2 employees exist. SELECT deptno, sum(sal) As totalsal FROM emp GROUP BY deptno HAVING COUNT(empno) > 2
Data Base Testing
You might also like
- SQL Query Interview Questions With Answers: Table - EmployeedetailsDocument59 pagesSQL Query Interview Questions With Answers: Table - EmployeedetailsNidhi SharmaNo ratings yet
- SQL Task-1: Table Name: EmployeeDocument23 pagesSQL Task-1: Table Name: Employeesmit19978No ratings yet
- Performance Report SummaryDocument13 pagesPerformance Report SummaryHariprasad Reddy GNo ratings yet
- SQL Query ExerciseDocument5 pagesSQL Query ExerciseRahul ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Create Int Varchar Date Varchar State Varchar: Emp - Piyush Employeeid Empname 30 Dob City 20 20Document10 pagesCreate Int Varchar Date Varchar State Varchar: Emp - Piyush Employeeid Empname 30 Dob City 20 20piyushsingh83100% (1)
- Joins and Sub QueriesDocument10 pagesJoins and Sub Queriesganesh_g_1No ratings yet
- Find NTH Highest Salary - SQLDocument18 pagesFind NTH Highest Salary - SQLSudipan SinghaNo ratings yet
- SQL QueryDocument8 pagesSQL QueryParveen ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Correlated Queries, Nested Queries, and Common Table ExpressionsDocument40 pagesCorrelated Queries, Nested Queries, and Common Table ExpressionsdiekoNo ratings yet
- SQL Queries (Interview Questions and Answers On "SQL Select" - ExamplesDocument6 pagesSQL Queries (Interview Questions and Answers On "SQL Select" - ExamplesSai PernamittaNo ratings yet
- DSI Specification v01-01-00 r11 PDFDocument87 pagesDSI Specification v01-01-00 r11 PDFcpcdbrNo ratings yet
- POSTMAN Complete Reference Guide For API TestingDocument6 pagesPOSTMAN Complete Reference Guide For API TestingHariprasad Reddy GNo ratings yet
- Informatica QuestionnaireDocument79 pagesInformatica Questionnairelokeshscribd186No ratings yet
- SQL Query Assignment for University DatabaseDocument2 pagesSQL Query Assignment for University DatabaseArun ChakrabartiNo ratings yet
- Subqueries To Solve Queries QuestionsDocument41 pagesSubqueries To Solve Queries QuestionsAmrit MadhavNo ratings yet
- SQL Queries for Employee DatabaseDocument9 pagesSQL Queries for Employee DatabaseSaurabh GuptaNo ratings yet
- SQL QueriesDocument6 pagesSQL QueriesMohan GindiNo ratings yet
- SQL QueriesDocument9 pagesSQL QueriesThirupathireddy MadireddyNo ratings yet
- SQL Queries GcreddyDocument11 pagesSQL Queries GcreddyMaheshwar ReddyNo ratings yet
- SQL QueriesDocument4 pagesSQL QueriesG.C.ReddyNo ratings yet
- WWW Srikanthtechnologies Com Oracle Dec9 Hrqueries HTMLDocument14 pagesWWW Srikanthtechnologies Com Oracle Dec9 Hrqueries HTMLShakthi VelNo ratings yet
- SQL Queries With SolutionDocument4 pagesSQL Queries With Solutionクマー ヴィーンNo ratings yet
- Export SQL Query To PDFDocument2 pagesExport SQL Query To PDFDanaNo ratings yet
- Hibernate Native SQL Query ExampleDocument12 pagesHibernate Native SQL Query Examplerdelmiro36No ratings yet
- Sqlqueries IMP Interview Questions-2Document39 pagesSqlqueries IMP Interview Questions-2abhash royNo ratings yet
- SQL QueriesDocument6 pagesSQL QueriesPurnima KNo ratings yet
- TSQLDocument2 pagesTSQLNidhi PatankarNo ratings yet
- Joins Based QueryDocument7 pagesJoins Based QueryAli AzgarNo ratings yet
- SQL Basic QueriesDocument19 pagesSQL Basic Queriesamrit_singh_27_39No ratings yet
- Course Completion Certificate From QSpidersDocument1 pageCourse Completion Certificate From QSpidersHARNITH EVILLNo ratings yet
- SQL LabDocument3 pagesSQL LabGaurav PaliwalNo ratings yet
- PL - SQL AssignmentDocument4 pagesPL - SQL Assignmentamit kumarspNo ratings yet
- SQL QueriesDocument6 pagesSQL QueriesGeneral weedNo ratings yet
- IT 450 Oracle SQL Assignment 1Document1 pageIT 450 Oracle SQL Assignment 1Kevin DossNo ratings yet
- SQL AssignmentDocument36 pagesSQL AssignmentIshandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- 3.SQL Queries DDLDocument61 pages3.SQL Queries DDLAnkit RajputNo ratings yet
- (Iii) Financial Accounting (Iv) Student ManagementDocument13 pages(Iii) Financial Accounting (Iv) Student ManagementVertechNo ratings yet
- Qno. 5 SQL 2014 Q.Paper: (B) Write The SQL Queries (1 To 4)Document37 pagesQno. 5 SQL 2014 Q.Paper: (B) Write The SQL Queries (1 To 4)Jayne AnnthoinetteNo ratings yet
- SQL Queries On Company DatabaseDocument3 pagesSQL Queries On Company DatabasePranshik Warrior100% (1)
- SQL Self JoinsDocument2 pagesSQL Self JoinssudhavishuNo ratings yet
- Common SQL QueriesDocument42 pagesCommon SQL Queriesbhaskar1234567No ratings yet
- SQL - Practice AssignmentsDocument3 pagesSQL - Practice AssignmentsJaganathan SekarNo ratings yet
- SQL Queries Multiple JoinDocument12 pagesSQL Queries Multiple Joinshyam15287100% (1)
- SQL Queries, Programming, Triggers Chapter 5Document42 pagesSQL Queries, Programming, Triggers Chapter 5Maung GirilayaNo ratings yet
- Structured Query Language (SQL) : AdvantDocument19 pagesStructured Query Language (SQL) : AdvantshailajaNo ratings yet
- SQL NotesDocument18 pagesSQL NotesBaljit KaurNo ratings yet
- Questions On SubqueryDocument5 pagesQuestions On SubquerysuhasNo ratings yet
- Extra QueriesDocument17 pagesExtra QueriesAkhileshNo ratings yet
- Database Schema for Library Management SystemDocument15 pagesDatabase Schema for Library Management SystemTejas GuptaNo ratings yet
- SQL: Queries, Constraints, Triggers, Null: February 18, 2014Document67 pagesSQL: Queries, Constraints, Triggers, Null: February 18, 2014Maria EstradaNo ratings yet
- Create A Database Company Contains Tables Employee, Department, Dept - Locations, Project, Works - On, DependentDocument8 pagesCreate A Database Company Contains Tables Employee, Department, Dept - Locations, Project, Works - On, Dependentanj071091100% (1)
- Analyze Aggregate Row FunctionsDocument19 pagesAnalyze Aggregate Row Functionsdevang100% (1)
- Homework Assignment #1 SQL QueriesDocument3 pagesHomework Assignment #1 SQL QueriesGaurRavi50% (2)
- Constraints Primary Constraints: Primary, Unique, Check, References) Secondary Constraints: Not Null, Default)Document126 pagesConstraints Primary Constraints: Primary, Unique, Check, References) Secondary Constraints: Not Null, Default)api-303626427No ratings yet
- Oracle SQLDocument49 pagesOracle SQLPraneeth NeelisettyNo ratings yet
- Lab Assignment SQL QueriesDocument4 pagesLab Assignment SQL Queriessandeep b tNo ratings yet
- Department of Computing: CS-220: Database Systems Class: BSCS-4CDocument14 pagesDepartment of Computing: CS-220: Database Systems Class: BSCS-4CRehan Mahmood100% (1)
- SQL Queries Interview Questions and Answers - Query ExamplesDocument2 pagesSQL Queries Interview Questions and Answers - Query ExamplesdippuneNo ratings yet
- SQL AssignmentDocument4 pagesSQL AssignmentShridhar ShirdhoneNo ratings yet
- Practice Ques: Select As FromDocument3 pagesPractice Ques: Select As Fromilakkiya RNo ratings yet
- PL SQL-4Document188 pagesPL SQL-4kavi_aravamuthan9884No ratings yet
- ATP Transacction Flow ProcessDocument1 pageATP Transacction Flow ProcessHariprasad Reddy GNo ratings yet
- Performance Test Report: Cycle 1Document40 pagesPerformance Test Report: Cycle 1Hariprasad Reddy GNo ratings yet
- Here Was A Dog Called ElleotDocument1 pageHere Was A Dog Called ElleotHariprasad Reddy GNo ratings yet
- User Scenario 1: Identifying The UI (When The User Logs As Just A PPD and Not and LEP With Only User Role)Document45 pagesUser Scenario 1: Identifying The UI (When The User Logs As Just A PPD and Not and LEP With Only User Role)Hariprasad Reddy GNo ratings yet
- QTP Technical QuestionsDocument14 pagesQTP Technical Questionskarthick_49No ratings yet
- ChaduvuinnerDocument4 pagesChaduvuinnerHariprasad Reddy GNo ratings yet
- User Scenario 1: Identifying The UI (When The User Logs As Just A PPD and Not and LEP With Only User Role)Document45 pagesUser Scenario 1: Identifying The UI (When The User Logs As Just A PPD and Not and LEP With Only User Role)Hariprasad Reddy GNo ratings yet
- Here Was A Dog Called ElleotDocument1 pageHere Was A Dog Called ElleotHariprasad Reddy GNo ratings yet
- Vbscript: Vbscipt User'S Guide Vbscript Langauge ReferenceDocument331 pagesVbscript: Vbscipt User'S Guide Vbscript Langauge Referenceanon_987603882No ratings yet
- SQLDocument10 pagesSQLHariprasad Reddy GNo ratings yet
- VB Script General ExamplesDocument12 pagesVB Script General ExamplesHariprasad Reddy GNo ratings yet
- Test Case Path Test Case Name Test DescriptionDocument9 pagesTest Case Path Test Case Name Test DescriptionHariprasad Reddy GNo ratings yet
- VBScript in QTPDocument30 pagesVBScript in QTPsachxn100% (22)
- VBScripting For QTPDocument78 pagesVBScripting For QTPAmardeep KumarNo ratings yet
- VB Script General ExamplesDocument12 pagesVB Script General ExamplesHariprasad Reddy GNo ratings yet
- User GuideDocument174 pagesUser Guidemanojinfa9No ratings yet
- User GuideDocument174 pagesUser Guidemanojinfa9No ratings yet
- Datastage Interview QuestionsDocument22 pagesDatastage Interview Questionsanilsoft.comNo ratings yet
- Application KeywordDocument15 pagesApplication KeywordHariprasad Reddy GNo ratings yet
- Application KeywordDocument15 pagesApplication KeywordHariprasad Reddy GNo ratings yet
- FiltersDocument1 pageFiltersHariprasad Reddy GNo ratings yet
- Scenario 3 Navigate From A Page To OtherDocument144 pagesScenario 3 Navigate From A Page To OtherHariprasad Reddy GNo ratings yet
- Test Case Path Test Case Name Test DescriptionDocument9 pagesTest Case Path Test Case Name Test DescriptionHariprasad Reddy GNo ratings yet
- InformaticaDocument3 pagesInformaticaChandrasekar VempalleeNo ratings yet
- Seleniul ContentsDocument3 pagesSeleniul ContentsHariprasad Reddy GNo ratings yet
- Seleniul ContentsDocument3 pagesSeleniul ContentsHariprasad Reddy GNo ratings yet
- Seleniul ContentsDocument3 pagesSeleniul ContentsHariprasad Reddy GNo ratings yet
- Auxillary Memory Organization by Sanjiv NambiarDocument26 pagesAuxillary Memory Organization by Sanjiv NambiaredaklavanNo ratings yet
- Write A Python Program Using List and Their Built in FunctionsDocument11 pagesWrite A Python Program Using List and Their Built in Functions18bcs097 M. SanthiyaNo ratings yet
- PeopleSoft Finance DR ProceduresDocument4 pagesPeopleSoft Finance DR ProceduresSRINIVAS KOTTENo ratings yet
- Abbreviations List for IT and Computer ScienceDocument2 pagesAbbreviations List for IT and Computer ScienceShakeelAhmedNo ratings yet
- Lookup Functions GuideDocument12 pagesLookup Functions GuideFarhad AhmedNo ratings yet
- # Product No. Description Serial NoDocument4 pages# Product No. Description Serial NoAhmed AbdelfattahNo ratings yet
- RAID LevelsDocument29 pagesRAID Levelstariqzia42No ratings yet
- 4G KPI Report Acceptance-WS RSLTE-LNBTS-2-day-PM 24227-2020 10 05-15 55 15 434Document140 pages4G KPI Report Acceptance-WS RSLTE-LNBTS-2-day-PM 24227-2020 10 05-15 55 15 434Hubert ArthurNo ratings yet
- Openzfs Basics: George Wilson Matt AhrensDocument39 pagesOpenzfs Basics: George Wilson Matt Ahrensindians jonesNo ratings yet
- AppSync 4.0 User and Administration GuideDocument342 pagesAppSync 4.0 User and Administration GuidePavan NavNo ratings yet
- Array OOPDocument9 pagesArray OOPRalph Laurence G VisayaNo ratings yet
- Scsiflash-2 Ethernet Command InstructionsDocument9 pagesScsiflash-2 Ethernet Command InstructionsMiguelNo ratings yet
- Counting Sort - GoodDocument8 pagesCounting Sort - Goodyt peekNo ratings yet
- How To Create A Physical Standby Database in ORACLE 9iDocument4 pagesHow To Create A Physical Standby Database in ORACLE 9iRahul Gupta100% (2)
- DB AsciiDocument3 pagesDB AsciiAbby ARNo ratings yet
- Python Course Content Core Concepts and Advanced FeaturesDocument10 pagesPython Course Content Core Concepts and Advanced FeaturesNive SNo ratings yet
- SamKnows testing methodologyDocument3 pagesSamKnows testing methodologyCHEA HKNo ratings yet
- Timers, Serial Port & Interrupts in 8051Document51 pagesTimers, Serial Port & Interrupts in 8051Sureka N Assistant Professor - ECENo ratings yet
- System32 Exe Fajlovi ObjasnjenjaDocument7 pagesSystem32 Exe Fajlovi ObjasnjenjasnowynsNo ratings yet
- MySQL Multiple Choice Questions and Loan Account Table ExercisesDocument11 pagesMySQL Multiple Choice Questions and Loan Account Table ExercisesDheeraj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Smart. Safe. Secure. Seagate Surveillance-Specialized StorageDocument4 pagesSmart. Safe. Secure. Seagate Surveillance-Specialized Storagewacked motorNo ratings yet
- Manual TekelekDocument713 pagesManual TekelekJavier VasquezNo ratings yet
- Arch 21Document4 pagesArch 21Nishant JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Lecture 3 - Installing Domain ControllersDocument24 pagesModule 3 - Lecture 3 - Installing Domain ControllersZeeshan BhattiNo ratings yet
- Hadoop Tutorials: Daniel Lanza Zbigniew BaranowskiDocument49 pagesHadoop Tutorials: Daniel Lanza Zbigniew BaranowskiRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- Midteknologi Com Blog Mikrotik ScriptsDocument25 pagesMidteknologi Com Blog Mikrotik Scriptsakun youtubeNo ratings yet
- Install at or LogDocument1 pageInstall at or LogDani JunjiNo ratings yet
- Localhost 1947 Int DiagnosticsDocument7 pagesLocalhost 1947 Int DiagnosticsMichael Steinhorst AlcantaraNo ratings yet