Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 6 Report
Uploaded by
CJ CHCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 6 Report
Uploaded by
CJ CHCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 6 Practical 1.
2 standing wave and partial reflection
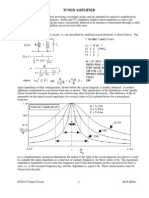
Objectives: 1. To observe partial reflection at a mismatched termination. 2. To observe standing waves on a line with mismatched termination 3. To know that the standing waves are equal to the sum of the incident and reflected waves. Equipments: TLD511 (Transmission line demonstrator), variable phase sine-wave generator (e.g. Feedback VPG608), 600R resistor, 200R resistor, 1k8 resistor, links
TLD511 Transmission line demonstrator
Procedures:
1. The terminators are removed and the generator, two links and a 600R terminator are connected as shown in figure below.
2. On the generator, the frequency is set to about 2.5Hz, and the amplitude is adjusted until the travelling wave on the display is just lighting two sections up and two down in each column of the display. This is called amplitude. 3. The 600R terminator is removed and a standing wave appears. 4. The 1k8 terminator is substituted. Note that the standing wave is reduced. Its minimum and maximum values are noted and the values of the reflected pulse in practical 1.1 are compared. 5. The 1k8 terminator is replaced with one of 200R. units of
Observations:
When the 600R terminator is substituted with 1k8 terminator, it is found that the maximum amplitude obtained is +3 units. A reflection coefficient describes either the amplitude or the intensity of a reflected wave relative to an incident wave, when wave propagation in a medium containing discontinuities is considered. The reflection coefficient is closely related to the transmission coefficient. 1k8 terminator is being replaced with 200R terminator, the results obtained have some similarities. The amplitudes obtained for both are constant positive units when the hold button is pressed. However, the results also show some differences. 1k8 terminator only gives results with positive amplitude while 200R can give result with negative amplitude. Not only that, the maximum amplitude that the 1k8 terminator can give is +3 units whereas the maximum amplitude that 200R terminator can give is only +2 units.
Results:
Steps 1. With 600R terminator (frequency of about 2.5Hz) 2. Remove the 600R terminator 3. Substitute 1k8 terminator
Results Amplitude of +2 units Amplitude of +4 units Step input to B: amplitude of +3 units Step input to A: -amplitude changes from +2 units to +3 units (press holdbutton) -amplitude changes from +1 to 0 and to +1 again (repeatedly)
Diagram (as shown below) 1 2 To B: 3 To A: -4(press hold button) -5 (hold button released
4. Replace 1k8 with one of 200R
Step input to A: To A: -6(press hold button) -amplitude from +2 units to +1unit - 7(hold button (press holdbutton) released) -amplitude from -1 unit to +1unit To B: -8(press hold button) (holdbutton released) Step input to B: -amplitude from constant +1 unit to +1, 0, +1, 0 unit repeatedly(press holdbutton) -amplitude with constant of +1unit (holdbutton released)
Diagram1
Diagram 2
Diagram 3
Diagram 4
Diagram 5
Diagram 6
Diagram 7
Diagram 8
Discussion: The maximum amplitude occurs when the incident and reflected waves are both a maximum at the same time and place. Since the incident wave was amplitude, and the reflection coefficient was , the reflected wave is added to the incident wave gives a maximum of 2 units of 1unit. This
3 units of amplitude. The reflection
coefficients with 200R and with 1k8 terminators were of opposite sign, or equivalently they differed by 180 in phase. Thus the phase of the reflected wave in the one case must differ by 180 from the phase of the other reflected wave. To produce a corresponding change in reflected waves supplied by the variable-phase oscillator, its phase controls must likewise be adjusted by 180 (e.g. in practice on the VPG608 the lead/lag switch must be thrown, the phase control set to the difference between 90 and its former setting).
Conclusion: If a transmission line is correctly terminated, for example in its characteristic impedance, all the power sent down the line is absorbed at the termination and no signal returns. Furthermore, if the line is open circuit or short circuit at the termination, complete reflection of the signal occurs. A wave, travelling in a line of characteristic impedance Zo and incident on a termination of impedance Zb gives rise to a reflected wave those amplitude is that of the original wave reaching the termination multiplied by a reflection coefficient, that has a voltage wave of formula: .
You might also like
- Basic Amplifier Circuits With Bipolar Transistors: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesBasic Amplifier Circuits With Bipolar Transistors: ObjectivesKhalid W Al-sheakhNo ratings yet
- Lem In2000 Paper v4b SroDocument9 pagesLem In2000 Paper v4b SromarinkokNo ratings yet
- Sine Wave Oscillator Circuits ExplainedDocument11 pagesSine Wave Oscillator Circuits ExplainedDimas RioNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 1 AM TransmitterDocument6 pagesExperiment No 1 AM TransmitterashfaqiNo ratings yet
- ELEC3105 Lab4Document10 pagesELEC3105 Lab4James AllenNo ratings yet
- WaveDocument13 pagesWaveBipasna RaiNo ratings yet
- OP Amp OscillatorsDocument5 pagesOP Amp Oscillatorskok6100% (1)
- Lab 1, AmpDocument5 pagesLab 1, AmpDavid KoskiNo ratings yet
- CMOS Function GeneratorDocument3 pagesCMOS Function Generatordborcic61No ratings yet
- Chapter: Amplitude Stabilization of The Harmonic OscillatorDocument10 pagesChapter: Amplitude Stabilization of The Harmonic OscillatordheenadayalanNo ratings yet
- 15 Oscillators 1Document40 pages15 Oscillators 1jatayu2011No ratings yet
- Ee3101 Lab Report ExpDocument16 pagesEe3101 Lab Report ExpyucesNo ratings yet
- Induction Cooking Theory & Operation - PartIVDocument14 pagesInduction Cooking Theory & Operation - PartIVShri KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Chapter8 OscillatorsDocument134 pagesChapter8 OscillatorsNikunj ShahNo ratings yet
- Sample Lab ReportDocument8 pagesSample Lab ReportbakerkjNo ratings yet
- Op Amp Circuits GuideDocument11 pagesOp Amp Circuits Guidelibrian_30005821No ratings yet
- Voltage Controlled OscillatorDocument9 pagesVoltage Controlled Oscillatorbezabwm100% (4)
- Ece326 Lab 3 Exp 19Document8 pagesEce326 Lab 3 Exp 19max1039No ratings yet
- Measuring Total Power of AM TransmitterDocument44 pagesMeasuring Total Power of AM TransmitterNikhil KolheNo ratings yet
- VCO AnalysisDocument14 pagesVCO Analysiskok6100% (2)
- EE680Lab Experiment6-7Document21 pagesEE680Lab Experiment6-7Amro AbusailNo ratings yet
- Function GeneratorDocument7 pagesFunction Generatorakash nairNo ratings yet
- Walkie TalkieDocument7 pagesWalkie Talkiev1009980100% (1)
- OSCILLATORS AND GENERATORSDocument20 pagesOSCILLATORS AND GENERATORSswetha bagadi it's good but how it will workNo ratings yet
- Tarea ElectronicaDocument23 pagesTarea ElectronicaSebastian OrdoñezNo ratings yet
- Ltech ReportDocument19 pagesLtech Reportumesh kubdeNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Transistor Cookbook — Astable and Monostable Multivibrator CircuitsDocument21 pagesBipolar Transistor Cookbook — Astable and Monostable Multivibrator CircuitsBóza GyörgyNo ratings yet
- 1) Wireless Headphone ReceiverDocument28 pages1) Wireless Headphone ReceiverPetarPetrovicNo ratings yet
- NARROW BAND AMPLIFIERSDocument8 pagesNARROW BAND AMPLIFIERSDeepraj BhujelNo ratings yet
- Bridge Oscillator circuit having a resistor of 10kΩ and a variable capacitorDocument6 pagesBridge Oscillator circuit having a resistor of 10kΩ and a variable capacitorحيدر سالمNo ratings yet
- Efca 2 Lab 1vDocument8 pagesEfca 2 Lab 1vM Fa RizNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document7 pagesLab 1Syed AsfandyarNo ratings yet
- Varius and Explanation PDFDocument7 pagesVarius and Explanation PDFnormangNo ratings yet
- School of Electronics and Electrical Engineering, UCD Assignment. 2Document11 pagesSchool of Electronics and Electrical Engineering, UCD Assignment. 2RahulNo ratings yet
- Analogue Electronics Lab ReportDocument8 pagesAnalogue Electronics Lab ReportKing EverestNo ratings yet
- Capacimetre FemtoDocument30 pagesCapacimetre FemtoJean-Marie ChaputNo ratings yet
- OP TypesDocument17 pagesOP TypesAhmad DboukNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Effects in Oscillators and SynthesizersDocument23 pagesNonlinear Effects in Oscillators and SynthesizersAKISNo ratings yet
- TI Analog Design Contest: Waveform GeneratorDocument13 pagesTI Analog Design Contest: Waveform Generatorhv_chillal88No ratings yet
- Development of A High Frequency and High-Voltage Pulse Transformer For A TWT HvpsDocument4 pagesDevelopment of A High Frequency and High-Voltage Pulse Transformer For A TWT HvpsShyam SuryaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Electronics Lab ManualDocument88 pagesAdvanced Electronics Lab ManualsmganorkarNo ratings yet
- AN-30 Log Converters: Application ReportDocument8 pagesAN-30 Log Converters: Application ReportvinodNo ratings yet
- A New PWM DimmerDocument5 pagesA New PWM DimmerNeeraj MuralidharanNo ratings yet
- MFJ - Mfj-989c ManualDocument10 pagesMFJ - Mfj-989c ManualSAJEEV SUKUMARNo ratings yet
- What Is AmplifierDocument18 pagesWhat Is AmplifierEbayLunaNo ratings yet
- Harmonic Generation and Analysis of Non-Linear LoadsDocument20 pagesHarmonic Generation and Analysis of Non-Linear Loadsue06037No ratings yet
- A 200-Watt Push-Pull Class-E AM Transmitter For 1710 KHZDocument18 pagesA 200-Watt Push-Pull Class-E AM Transmitter For 1710 KHZFabrício AngieneNo ratings yet
- Electronique - Audio - Microphone Valve PreampDocument7 pagesElectronique - Audio - Microphone Valve PreampkoukihamedNo ratings yet
- Nollido Acee6l Exp6 Ee2hDocument10 pagesNollido Acee6l Exp6 Ee2hrusselpagaoNo ratings yet
- Exp No. 1 Translines and AntennasDocument10 pagesExp No. 1 Translines and AntennasShairelle Anne Nunez FebrerNo ratings yet
- A Reactance ModulatorDocument17 pagesA Reactance ModulatorAldrin Sagum100% (1)
- AC Circuits PDFDocument6 pagesAC Circuits PDFRANDOLPHENo ratings yet
- Automatic Speed Control For Fans and CoolersDocument54 pagesAutomatic Speed Control For Fans and CoolersPrudhvi Raj63% (8)
- An Efficient Inverter Circuit Design For Driving The Ultrasonic Welding TransducerDocument10 pagesAn Efficient Inverter Circuit Design For Driving The Ultrasonic Welding TransducernewvictorinNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsFrom EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNo ratings yet
- 108TX Data Sheet - 0hhhhhaDocument3 pages108TX Data Sheet - 0hhhhhaCJ CHNo ratings yet
- Te 1142 PRNDocument202 pagesTe 1142 PRNCJ CHNo ratings yet
- 1 Instrument Turbomachinery Inspection Checklist - P844Document6 pages1 Instrument Turbomachinery Inspection Checklist - P844CJ CHNo ratings yet
- Dabai Planting Guide: Budding PropagationDocument6 pagesDabai Planting Guide: Budding PropagationCJ CHNo ratings yet
- Detronas RecordDocument25 pagesDetronas RecordCJ CHNo ratings yet
- Opening Performance ScriptDocument4 pagesOpening Performance ScriptCJ CHNo ratings yet
- How To Choose Your Personal SuccessDocument15 pagesHow To Choose Your Personal SuccessBlackmorthNo ratings yet
- 3300XL NSVDocument28 pages3300XL NSVnabil160874No ratings yet
- 1 Instrument Turbomachinery Inspection Checklist For Integrity Assurance 20190425Document3 pages1 Instrument Turbomachinery Inspection Checklist For Integrity Assurance 20190425CJ CHNo ratings yet
- Dabai Planting Guide: Budding PropagationDocument6 pagesDabai Planting Guide: Budding PropagationCJ CHNo ratings yet
- Gas TurbineDocument5 pagesGas TurbineCJ CHNo ratings yet
- Technical PaperDocument6 pagesTechnical PaperCJ CHNo ratings yet
- Events Safety GuideDocument1 pageEvents Safety GuideCJ CHNo ratings yet
- Spressure-Temperaturerelationshipsingases 000Document13 pagesSpressure-Temperaturerelationshipsingases 000CJ CHNo ratings yet
- BatteryDocument6 pagesBatteryCJ CHNo ratings yet
- Student's Name: Fareeda Chemat Student No: 11806 Programme: Chemical EnaineerinaDocument2 pagesStudent's Name: Fareeda Chemat Student No: 11806 Programme: Chemical EnaineerinaCJ CHNo ratings yet
- Analogue 1 ProjectDocument9 pagesAnalogue 1 ProjectCJ CHNo ratings yet
- Proposed New Academic Calendar 2013: Jan 2013 Trimester May 2013 Trimester Sept 2013 TrimesterDocument2 pagesProposed New Academic Calendar 2013: Jan 2013 Trimester May 2013 Trimester Sept 2013 TrimesterCJ CHNo ratings yet
- Process Control Fundamentals 2Document73 pagesProcess Control Fundamentals 2Otuekong Ukpong100% (2)
- Ebb4043 Electrical and Energy System Test 1Document7 pagesEbb4043 Electrical and Energy System Test 1CJ CHNo ratings yet
- CO#1 Describe, Analyze, and Design of Basic BJT & NMOS Differential AmplifierDocument6 pagesCO#1 Describe, Analyze, and Design of Basic BJT & NMOS Differential AmplifierCJ CHNo ratings yet
- Analogue II Lab 3Document4 pagesAnalogue II Lab 3CJ CHNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document5 pagesChapter 12CJ CHNo ratings yet
- Moral Issue Connected With SuicideDocument27 pagesMoral Issue Connected With SuicideCJ CHNo ratings yet
- Moral Issue Connected With SuicideDocument27 pagesMoral Issue Connected With SuicideCJ CHNo ratings yet
- Ap02Document3 pagesAp02Zoran ConstantinescuNo ratings yet
- Wave Optics Solutions – Fringe Patterns and IntensitiesDocument15 pagesWave Optics Solutions – Fringe Patterns and Intensitiesashu mishraNo ratings yet
- Exp No. 1 Translines and AntennasDocument10 pagesExp No. 1 Translines and AntennasShairelle Anne Nunez FebrerNo ratings yet
- 2 - Basic CBL TheoryDocument52 pages2 - Basic CBL TheoryRolando Gabriel Segovia Perez100% (1)
- Principles of SpectrophotometryDocument2 pagesPrinciples of SpectrophotometryVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Wave propagation fundamentalsDocument9 pagesWave propagation fundamentalsSiva KumarNo ratings yet
- A Review of Microfiber and Nanofiber Based Optical Sensors PDFDocument26 pagesA Review of Microfiber and Nanofiber Based Optical Sensors PDFliton_kabirNo ratings yet
- A Dual Wideband Bandpass Filter For WLAN and 5G Wi-Fi ApplicationsDocument4 pagesA Dual Wideband Bandpass Filter For WLAN and 5G Wi-Fi Applicationsnassimo nassimoNo ratings yet
- G4 WavesDocument112 pagesG4 WavesZohair Haddad100% (1)
- Introduction To Social Work 12th Edition Farley Test BankDocument28 pagesIntroduction To Social Work 12th Edition Farley Test Bankjojyhys50% (2)
- ECMC1T4Document2 pagesECMC1T4kprk414No ratings yet
- Dispersion in Optical FiberDocument36 pagesDispersion in Optical FiberSonakshi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - LasersDocument21 pagesModule 5 - LasersMahek KhushalaniNo ratings yet
- Micheslon'S Interferometer: ConstructionDocument5 pagesMicheslon'S Interferometer: Construction21MS0073KritarthaNo ratings yet
- Design of Series Feed Microstrip Patch Antenna Array Using HFSS SimulatorDocument4 pagesDesign of Series Feed Microstrip Patch Antenna Array Using HFSS SimulatoridescitationNo ratings yet
- MicrowaveDocument33 pagesMicrowaveSalmaan HaiderNo ratings yet
- Jules Lissajous and His FiguresDocument5 pagesJules Lissajous and His FiguresRavider JadejaNo ratings yet
- ODE Lecture Notes Section 3.8 1 of 14Document14 pagesODE Lecture Notes Section 3.8 1 of 14Pritib KumarNo ratings yet
- Grades 10 Daily Lesson Log: Understanding the Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument5 pagesGrades 10 Daily Lesson Log: Understanding the Electromagnetic SpectrumLYNO REY TEJADA100% (1)
- Physics Gr.12 Monthly Note 2ndDocument45 pagesPhysics Gr.12 Monthly Note 2ndTebarek SitotawNo ratings yet
- Antenna 5Document30 pagesAntenna 5Frederico MailaNo ratings yet
- RF and Microwave Engineering Lab Manual-Lab 01Document10 pagesRF and Microwave Engineering Lab Manual-Lab 01usama khalid50% (2)
- Radar Systems Question Bank (R16) : Essay Questions: Unit-1Document3 pagesRadar Systems Question Bank (R16) : Essay Questions: Unit-1Rohit PenkiNo ratings yet
- MD0279 RTT-MD0006 V1Document2 pagesMD0279 RTT-MD0006 V1tajinder123No ratings yet
- Stationary WavesDocument15 pagesStationary WavesFatima BibiNo ratings yet
- SASW measurements at NEES Garner Valley Test SiteDocument12 pagesSASW measurements at NEES Garner Valley Test SiteAntonio Enriquez ArvizuNo ratings yet
- Unlocking Potentials of Microwaves For Food Safety and QualityDocument18 pagesUnlocking Potentials of Microwaves For Food Safety and QualityAlan JerishNo ratings yet
- QuakeDocument18 pagesQuakeSushrava KsNo ratings yet
- Wolf ToneDocument7 pagesWolf Toneapi-242289612No ratings yet
- Experiment 7Document19 pagesExperiment 7Kyle PeñarroyoNo ratings yet