Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Verificación de la capacidad de carga de grúa de 5 toneladas
Uploaded by
Cesar AnayaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Verificación de la capacidad de carga de grúa de 5 toneladas
Uploaded by
Cesar AnayaCopyright:
Available Formats
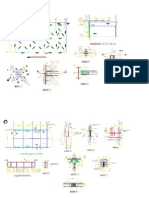
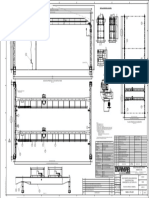
VERIFICACION DE LA CAPACIDAD DEL PUENTE GRA CON TECLE DE 5 TONELADAS DE CAPACIDAD 1.
DISEO ESQUEMATICO: 1499 5900
1499
2350 4420 5 TON 2943
2.
CLCULOS PRINCIPALES
2.1 DCL VIGA PRINCIPAL (ANALIZANDO POSICIN CRTICA LA VIGA HORIZONTAL) VISTA FRONTAL 2950 2950 O F1 49050 N Y
F2
VISTA LATERAL F3 F4 Y 53 F1 F2 Z
2.1.1
CALCULANDO F1 Y F2:
Fy = 0: 49050 = F1 + F2.Sen53 (1) Mo = 0: F1.(5900) =(49050).(2950) Reemplazando en (1): 49050 = 24525 + F2Sen53 2.1.2 CALCULANDO F3 Y F4: F2 = 30709 N F1 = 24525 N
Fz = 0: F3 + F4 = F2Cos53 = 18481N F3 + F4 = 18481N (2) Mo = 0: F3 = 0N Reemplazando en (2): F4 = 18481 N 2.1.3 DIAGRAMAS DE FUERZA Y MOMENTOS:
2950
2950
24525N 49050 N DFC 24525 N
24525N
24525 N
DMF
72349 K N.mm
Para el clculo, se toma la seccin ms crtica la cual, de acuerdo a los diagramas, se encuentra en la parte central. Considerando las caractersticas de la viga: 8 Ix = 184081100 mm^4 Y Iy = 17814750 mm^4 A = 9294 mm^2 13 13/16 X
Se pasa a mostrar los esfuerzos en la seccin: Esfuerzo Cortante (c):
c
Esfuerzo Flector (f)
24525 24525 N 2.64 A 9294 mm 2
72349000 x 175.42 Ix
12691461580 N 69 184081100 mm 2
Hallando el esfuerzo equivalente segn la teora de falla Von Misses:
eq
n : Esfuerzo normal f : Esfuerzo normal flexin c : Esfuerzo cortante t : Esfuerzo cortante por torsin
f 3 c2 t2
2
eq
0 692 32.642 02
eq 69.15
N mm2
Teniendo en cuenta que el material utilizado es Acero Estructural St37 con las siguientes caractersticas: fluencia = 250 N/mm2 B = 400 N/mm2 E = 210000 N/mm2 2.1.4 CALCULANDO EL FACTOR DE SEGURIDAD:
F .S
fluencia 250 3.62 eq 69.15
2.2 DCL VIGA PRINCIPAL (CASO CRTICO PARA APOYO VERTICAL) 300 5600 O X F1 49050 N F2
2.2.1
CALCULANDO F1 Y F2:
Fy = 0: 49050 = F1 + F2.Sen53 (1) Mo = 0: F1.(5900) =(49050).(5600) Reemplazando en (1): 49050 = 46556 + F2Sen53 2.2.2 DCL APOYO VERTICAL F1 = 46556N F2 = 3123 N F1 = 46556 N
Y 4420 X
F1= 46556N
2.2.3
DIAGRAMAS DE FUERZA Y MOMENTOS: DFC F1= 46556N
46556N
F1= 46556N Considerando las caractersticas de la viga: 6 Ix = 17943070 mm^4 Iy = 5629070 mm^4 Y 6 3/16 X A = 4219 mm^2
Se pasa a mostrar los esfuerzos en la seccin: Esfuerzo Normal (n):
46556 A
46556 N 11 4219 mm2
Hallando el esfuerzo equivalente segn la teora de falla Von Misses:
eq
n : Esfuerzo normal f : Esfuerzo normal flexin c : Esfuerzo cortante t : Esfuerzo cortante por torsin
f 3 c2 t2
2
eq n 11
N mm2
Teniendo en cuenta que el material utilizado es Acero Estructural St37 con las siguientes caractersticas: fluencia = 250 N/mm2 B = 400 N/mm2 E = 210000 N/mm2 2.2.4 CALCULANDO EL FACTOR DE SEGURIDAD:
F .S
fluencia 250 23 eq 11
2.2.5
CALCULO DE PANDEO PARA APOYO VERTICAL
PLANO X-X:
F1= 46556N
F1= 46556N
2.2.5.1 CALCULO DE ESBELTEZ
LP ix
ix
Ix 17943070 65.2mm A 4219
LP L / 2 4420 / 2 34 ix 65.2 65.2
34
2.2.5.2 METODO OMEGA (PARA ELEMENTOS ESTRUCTURALES)
F 46556 N 11 A 4219 mm2
Obteniendo de tablas el factor w (St 37 Segn DIN 4114): Con
34
w 1.1
Fadm 14
Kgf N 137.3 mm2 mm2
w. FAdm
(1.1)(11) 137.3
12.1 137.3
Por lo tanto el perfil no fallar por pandeo en el eje X-X. PLANO Y-Y:
F1= 46556N
F1= 46556N
2.2.5.3 CALCULO DE ESBELTEZ
LP iy
iy
Iy A
5629070 37mm 4219
LP L / 2 4420 / 2 60 iy 37 37
60
2.2.5.4 METODO OMEGA (PARA ELEMENTOS ESTRUCTURALES)
F 46556 N 11 A 4219 mm2
Obteniendo de tablas el factor w (St 37 Segn DIN 4114): Con
60
w 1.3
Fadm 14
Kgf N 137.3 2 mm mm2
w. FAdm
(1.3)(11) 137.3
14.3 137.3
Por lo tanto el perfil no fallar por pandeo en el eje Y-Y.
2.3 DCL VIGA PRINCIPAL (CASO CRTICO PARA APOYO INCLINADO) 5600 300 O X F1 49050 N F2
2.3.1
CALCULANDO F1 Y F2:
Fy = 0: 49050 = F1 + F2.Sen53 (1)
Mo = 0: F1.(5900) =(49050).(300) Reemplazando en (1): 49050 = 2494 + F2Sen53 2.3.2 DCL APOYO INCLINADO F2 = 58294 N F1 = 2494 N
F2= 58294N
Y Z 2943
F1= 58294N 2.3.3 DIAGRAMAS DE FUERZA Y MOMENTOS: DFC
F2= 58294 N
58294 N 2943
F1= 58294 N
Considerando las caractersticas de la viga:
5 1/4
Ix = 20070100 mm^4 Iy = 2513640 mm^4 A = 2903 mm^2 Y X 8
Se pasa a mostrar los esfuerzos en la seccin:
Esfuerzo Normal (n)
58294 A
58294 N 20 2903 mm 2
Hallando el esfuerzo equivalente segn la teora de falla Von Misses:
eq
n : Esfuerzo normal f : Esfuerzo normal flexin c : Esfuerzo cortante t : Esfuerzo cortante por torsin
2 2 n f 3 c t 2
eq n 20
N mm2
Teniendo en cuenta que el material utilizado es Acero Estructural St37 con las siguientes caractersticas: fluencia = 250 N/mm2 B = 400 N/mm2 E = 210000 N/mm2 2.3.4 CALCULANDO EL FACTOR DE SEGURIDAD:
F .S
fluencia 250 12.5 eq 20
2.3.5
CALCULO DE PANDEO PARA APOYO VERTICAL
PLANO X-X: F2= 58294 N
2943
F1= 58294 N
2.3.5.1 CALCULO DE ESBELTEZ
LP ix '
ix
I x' 20070100 83mm A 2903
LP L / 2 2943 / 2 18 ix ' 65.2 83
18
2.3.5.2 METODO OMEGA (PARA ELEMENTOS ESTRUCTURALES)
F 58294 N 20 A 2903 mm2
Obteniendo de tablas el factor w (St 37 Segn DIN 4114): Con
18
w 1.04
Fadm 14
Kgf N 137.3 2 mm mm2
w. FAdm
(1.04)(20) 137.3
20.8 137.3
Por lo tanto el perfil no fallar por pandeo en el eje X-X.
PLANO Y-Y: F2= 58294 N
2943
F1= 58294 N
2.3.5.3 CALCULO DE ESBELTEZ
LP iy'
iy'
I y' A
2513640 29mm 2903
LP L / 2 2943 / 2 51 iy' 29 29
51
2.3.5.4 METODO OMEGA (PARA ELEMENTOS ESTRUCTURALES)
F 58294 N 20 A 2903 mm2
Obteniendo de tablas el factor w (St 37 Segn DIN 4114): Con
51
w 1.22
Fadm 14
Kgf N 137.3 mm2 mm2
w. FAdm
(1.22)(20) 137.3
24.4 137.3
Por lo tanto el perfil no fallar por pandeo en el eje Y-Y.
You might also like
- Problemas resueltos de Hidráulica de CanalesFrom EverandProblemas resueltos de Hidráulica de CanalesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Expresionismo Estructural Pier Luigi Nervi Félix CandelaDocument105 pagesExpresionismo Estructural Pier Luigi Nervi Félix CandelaMaria De Jesus OrtizNo ratings yet
- Grua Viajera Doble Puente Sobre RielDocument8 pagesGrua Viajera Doble Puente Sobre RielArmando MaciasNo ratings yet
- Curso Puente GrúaDocument105 pagesCurso Puente GrúaAndres Jara AliagaNo ratings yet
- Asme B 30.5 EspañolDocument65 pagesAsme B 30.5 EspañolLeidy Garzon100% (1)
- Ficha 5 Simbología de SoldaduraDocument3 pagesFicha 5 Simbología de Soldaduraluiseandrade1981100% (2)
- Protocolo de Prueba de Carga Del Puente GrúaDocument6 pagesProtocolo de Prueba de Carga Del Puente GrúaAbel Valderrama PerezNo ratings yet
- Informe de Inspección Puentes Grúa Andes PetroleumDocument6 pagesInforme de Inspección Puentes Grúa Andes PetroleumSantiago Montengro100% (1)
- Puente GruaDocument11 pagesPuente Gruagerardo488100% (2)
- Informe de Calculo Spreader 4m - 150 Ton Rev00Document15 pagesInforme de Calculo Spreader 4m - 150 Ton Rev00Sotil Morales Alfredo100% (1)
- Yale Global King B, C, D-Frame Wire Rope Hoist 2018 Oct 11353399 Rev ABDocument67 pagesYale Global King B, C, D-Frame Wire Rope Hoist 2018 Oct 11353399 Rev ABMARTIN FLORESNo ratings yet
- Memoria de Calculo AlmoadillaDocument10 pagesMemoria de Calculo AlmoadillaPablo Andres Peña Oliva100% (2)
- Memoria de Calculo para Puente GruaDocument17 pagesMemoria de Calculo para Puente GruaWaldo Antonio Quijada Vicencio0% (1)
- Cálculo viga puente grúaDocument90 pagesCálculo viga puente grúaXamir Suarez Alejandro75% (4)
- Diseño Puentes GrúaDocument12 pagesDiseño Puentes GrúaAriel José Moreno Herrera100% (5)
- Dis - Columnas y VigasDocument30 pagesDis - Columnas y VigasRicardo Rios MendezNo ratings yet
- Gestion de Riesgos Con EslingasDocument34 pagesGestion de Riesgos Con EslingasIvan Alejandro RohrNo ratings yet
- Diseño de Sistemas de Soporte para Puentes Grua.Document15 pagesDiseño de Sistemas de Soporte para Puentes Grua.Jose ManzanarezNo ratings yet
- Grua en BanderaDocument39 pagesGrua en BanderaEsteban GracidaNo ratings yet
- Manual de Producto: Grúa Pluma Giratoria ABUSDocument58 pagesManual de Producto: Grúa Pluma Giratoria ABUSAlexis GodoyNo ratings yet
- Diseño grúa portátil aluminioDocument12 pagesDiseño grúa portátil aluminioHecThor LizarragaNo ratings yet
- Mantenimiento Puente GruaDocument32 pagesMantenimiento Puente GruaElias Pereira100% (3)
- OREJADocument18 pagesOREJARichard GarciaNo ratings yet
- Curso Capacitacion RiggerDocument50 pagesCurso Capacitacion RiggerJosé Muñoz100% (1)
- Memorias de capacitación en izaje de cargasDocument96 pagesMemorias de capacitación en izaje de cargasCarlos Felipe Orjuela Ramírez50% (2)
- AA01 Curso Grúas Torre ECOE Rev00Document168 pagesAA01 Curso Grúas Torre ECOE Rev00Ronie ApazaNo ratings yet
- Reparacion de PlumaDocument6 pagesReparacion de PlumaeduardoNo ratings yet
- Concreto ArmadoDocument67 pagesConcreto ArmadoFreddy Umeres AguilarNo ratings yet
- Sw-Gt-Utpa-R-274 Informe Vigas Metalicas UtpaDocument27 pagesSw-Gt-Utpa-R-274 Informe Vigas Metalicas Utpacielo108No ratings yet
- Puente GruaDocument3 pagesPuente GruaMario YañezNo ratings yet
- Clase Horacio - Puente GruaDocument7 pagesClase Horacio - Puente GruaGabii PintosNo ratings yet
- Cálculo de elementos de máquinas I - Transmisión por correasDocument53 pagesCálculo de elementos de máquinas I - Transmisión por correasRuben ChumaceroNo ratings yet
- 1 Pa 001 RD PDFDocument1 page1 Pa 001 RD PDFpausides QueralesNo ratings yet
- ASME B 30.2 - Puentes Gruas RESUMENDocument4 pagesASME B 30.2 - Puentes Gruas RESUMENAnonymous fBIEWgmRzNo ratings yet
- Informe #000141 - Informe - Tecnico - Cancha - San - MartinDocument10 pagesInforme #000141 - Informe - Tecnico - Cancha - San - Martinjohard monroyNo ratings yet
- Calculo Estructural de Puente Grua PDFDocument16 pagesCalculo Estructural de Puente Grua PDFDanielle StephensNo ratings yet
- Aparejador MG 06Document8 pagesAparejador MG 06Geraldine SaenzNo ratings yet
- Operador Gruas MG 09 PDFDocument13 pagesOperador Gruas MG 09 PDFRick DanNo ratings yet
- Inspección horquillas cargadoresDocument2 pagesInspección horquillas cargadoresIng YÔrland R. BlancoNo ratings yet
- Adms Uploads Catalogos 45 Catalogo Novex 2008Document142 pagesAdms Uploads Catalogos 45 Catalogo Novex 2008rafael112712No ratings yet
- VZ GH Oga 052021Document6 pagesVZ GH Oga 052021Juan Camilo GomezNo ratings yet
- (Fome) Normartiva DIRECTEMAR 2015 2Document20 pages(Fome) Normartiva DIRECTEMAR 2015 2AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Certificado AutoelevadorDocument1 pageCertificado AutoelevadorLeonardo JorgeNo ratings yet
- NTP 737Document9 pagesNTP 737arepacfr8797No ratings yet
- Formato Inspección Anclaje PortatilDocument1 pageFormato Inspección Anclaje PortatilSergio AltamarNo ratings yet
- Acciones Del Puente Grua - 2018Document17 pagesAcciones Del Puente Grua - 2018Jonatan BentosNo ratings yet
- Ficha Tecnica de Air Rock DrillDocument1 pageFicha Tecnica de Air Rock DrillP Leon JaramilloNo ratings yet
- Procedimientos de Inspeccion de EquiposDocument12 pagesProcedimientos de Inspeccion de Equiposliss2903100% (1)
- GarrasDocument6 pagesGarrasCataclonuno UnoNo ratings yet
- AN120055.002 - Instrucciones de Montaje Polipasto de CableDocument12 pagesAN120055.002 - Instrucciones de Montaje Polipasto de CableCristian Garcia GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Izaje 200Document23 pagesIzaje 200NAO_198No ratings yet
- H207 - Cálculo de Presión Superficial de Orugas Sobre TerrenoDocument5 pagesH207 - Cálculo de Presión Superficial de Orugas Sobre Terrenocesar bardalesNo ratings yet
- Solucionario Rigger R02Document12 pagesSolucionario Rigger R02MANUEL CASTILLONo ratings yet
- Bechtel INCO Pelambres Puente Grua ADIC 8 Ton MJKG-0001 Econ REV 2 para Ing PDFDocument26 pagesBechtel INCO Pelambres Puente Grua ADIC 8 Ton MJKG-0001 Econ REV 2 para Ing PDFTomás Venegas PardoNo ratings yet
- Capitulo 2, Diseño de Silo EurocodigoDocument7 pagesCapitulo 2, Diseño de Silo EurocodigoPablo YañezNo ratings yet
- Plan de Izaje y Descarga - UnimaqDocument18 pagesPlan de Izaje y Descarga - UnimaqRaul Herencia MontesinosNo ratings yet
- Cálculos de transmisión por engranajes para sistema de producciónDocument135 pagesCálculos de transmisión por engranajes para sistema de producciónDaniel PortilloNo ratings yet
- Trabajo Colaborativo Fase 4 Grupo 212018 78Document8 pagesTrabajo Colaborativo Fase 4 Grupo 212018 78Thayra Mosquera RiveraNo ratings yet
- AlvarezMaldonado Itzel M12S2Al3Document9 pagesAlvarezMaldonado Itzel M12S2Al3Itzel AlvarezNo ratings yet
- PA-01 S ES531-J 2023-1.pdf (1)Document2 pagesPA-01 S ES531-J 2023-1.pdf (1)Piero Axel Chalco EstradaNo ratings yet
- Ejem FlujoHeuristico&CCDocument8 pagesEjem FlujoHeuristico&CCGerardo Barron Pachas100% (1)
- Diseño y cálculo de un eje y rodamientos para una trituradora de plásticosDocument21 pagesDiseño y cálculo de un eje y rodamientos para una trituradora de plásticosLuis RauseoNo ratings yet
- Tercer Trabajo EncargadoDocument13 pagesTercer Trabajo EncargadoJamil FigueroaNo ratings yet
- PPSDocument26 pagesPPSJulissa Espinoza NinahuillcaNo ratings yet
- Tubosistemas Abril 2019 GERFORDocument24 pagesTubosistemas Abril 2019 GERFORLoperacoNo ratings yet
- Arquitecto Frank GheriDocument11 pagesArquitecto Frank GheriCARMEN QUISPE LIMPENo ratings yet
- Especificaciones Tecnicas Pecco Chaca 20221212 165221 780Document66 pagesEspecificaciones Tecnicas Pecco Chaca 20221212 165221 780Nilton Evans Castellanos Q.No ratings yet
- Grupo 05 - Tarea 04 RVDocument40 pagesGrupo 05 - Tarea 04 RVMarxoo AfkNo ratings yet
- Afuso Minoru Diseño Estructural Concreto BarrancoDocument117 pagesAfuso Minoru Diseño Estructural Concreto BarrancoluisNo ratings yet
- Universidad de Sucre 2012 Propuesta de CDocument109 pagesUniversidad de Sucre 2012 Propuesta de Cjhonjar2014No ratings yet
- Analisis de Precio Unitario Puente Vado PDFDocument21 pagesAnalisis de Precio Unitario Puente Vado PDFAntonio Rodríguez OrtízNo ratings yet
- 1 Catalogo GaestopasDocument226 pages1 Catalogo GaestopasguerrerocobachoNo ratings yet
- PLYCEMDocument2 pagesPLYCEMNoMW EndgameNo ratings yet
- Habilitación Urbana RneDocument8 pagesHabilitación Urbana RneJonathan Dueñas SánchezNo ratings yet
- Catálogo ApacheDocument57 pagesCatálogo ApacheJose Miguel Ramirez FernandezNo ratings yet
- Edificio Charlone 960 2Document4 pagesEdificio Charlone 960 2Darwin Stefano Chinchay NavarroNo ratings yet
- SECS 24 DE MAIO, BrazilDocument9 pagesSECS 24 DE MAIO, BrazilmelizaNo ratings yet
- Torre de Alta TensiónDocument5 pagesTorre de Alta TensiónSheiner Huamanchaqui IlizarbeNo ratings yet
- Informe de Maquinarias para Una CarreteraDocument28 pagesInforme de Maquinarias para Una CarreteraIoman PCNo ratings yet
- Cantidad de Cables en Tubería ConduitDocument16 pagesCantidad de Cables en Tubería ConduitCristian Delgado MolinaNo ratings yet
- Diseño Del Sistema AcuapónicoDocument2 pagesDiseño Del Sistema Acuapónicoruddymachicado100% (1)
- Caldera de RecuperacionDocument2 pagesCaldera de RecuperacionchristianNo ratings yet
- Tablero de Fibra de Densidad MediaDocument2 pagesTablero de Fibra de Densidad MediaDavid Alexander RojasNo ratings yet
- Primer Informe-Practicas Pre-ProfesionalesDocument24 pagesPrimer Informe-Practicas Pre-ProfesionalesDaniel PiscoyaNo ratings yet
- Introduccion y Clasificacion PuentesDocument3 pagesIntroduccion y Clasificacion PuentesNathalie Le NoirNo ratings yet
- Simbología y descripción de elementos hidráulicos en planos de plomeríaDocument1 pageSimbología y descripción de elementos hidráulicos en planos de plomeríaLuis Quintana diazNo ratings yet
- MEMORIA DESCRIPTIVA AlisDocument10 pagesMEMORIA DESCRIPTIVA AlisJuliom Parraga MatosNo ratings yet
- MEMORIA DE CALCULOS Estructural de AulaDocument47 pagesMEMORIA DE CALCULOS Estructural de AulaPold Silva SanchezNo ratings yet
- Proyecto Pronoei - ArquitecturaDocument36 pagesProyecto Pronoei - ArquitecturaJesussito Huacre PalominoNo ratings yet
- Calculo de LetrerosDocument5 pagesCalculo de LetrerosDanny QuispeNo ratings yet