Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Numeracy Ratio Proportion
Uploaded by
IAS EXAM PORTALOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Numeracy Ratio Proportion
Uploaded by
IAS EXAM PORTALCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic
Numeracy
www.iasexamportal.com
Topic
Ratio & Proportion
To Join Free Coaching for our Next Batch
Click
Here
www.iasexamportal.com
Ratio & Proportion
Ratio
The ratio of two quantities a and b is the fraction and is expressed as a : b. Here a
is the first term or antecedent and b is the second term or consequent. Since the
ratio expresses the number of times one quantity contains the other, it is an abstract
(without units) quantity.
A ratio remains unaltered if its numerator and denominator are multiplied or divided
by the same number.
eg, 4 : 3 is the same as (4 10) : (3 10) ie, 40 : 30.
20 : 15 is the same as
ie, 4 : 3.
A ratio is said to be a ratio of greater or less inequality or of equality according as
antecedent is greater than, less than or equal to consequent.
...)
If a > b, then a : b is called a ratio of greater inequality (eg, 4 : 3, 5 : 2, 11 : 3,
IASEXAMPORTAL.COM
To Join Free Coaching for our Next Batch
Click
Here
www.iasexamportal.com
If a < b, then a : b is called a ratio of less inequality (eg, 3 : 4, 2 : 5, 3 : 11, ...)
If a = b, then a : b is called a ratio of equality (eg, 1 : 1, 3 : 3, 5 : 5, ...)
From this we find that
(i)
If a > b and some positive number is added to each term of a : b, then
the ratio is diminished. If a > b, then (a + x) : (b + x) < a: b.
(ii)
If a < b and some positive number is added to each term of a : b, then
the ratio is increased. If a < b, then (a + x) : (b + x) < a : b.
(iii) If a = b and some positive number is added to each term of a : b, then the ratio
is unaltered. If a = b, then (a + x) : (b + x) = a : b
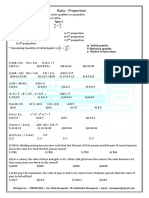
Kinds of Ratios
Duplicate Ratio: a2 : b2 is called duplicate ratio of a : b.
Triplicate Ratio: a3 : b3 is called triplicate ratio of a : b.
IASEXAMPORTAL.COM
To Join Free Coaching for our Next Batch
Click
Here
www.iasexamportal.com
Sub-Duplicate Ratio:
a: b
is called sub-duplicate ratio of a : b.
Sub-triplicate Ratio : 3
a :3b
is called sub-triplicate ratio of a : b.
Compound Ratio : ab : cd is the compound ratio of a : c and b : d. It is the ratio
of the product of the antecedents to that of the consequents of two or more given
ratios.
Inverse Ratio :
1 1
:
a b
is the inverse ratio of a : b.
Componendo and Divedendo: If
a c
, `then
b d
a b c d
a b c d
Proportion
When two ratios are equal, they make a proportion. ie, if then a, b, c and d are in
proportion.
This is represented as a : b : : c : d and is read as a is to b as c is to d.
When a, b, c and d are in proportion, then a and d are called the Extremes and b
and c are called the Means. also, Product of the Means = Product of the
Extremes ie, be = ad.
IASEXAMPORTAL.COM
To Join Free Coaching for our Next Batch
Click
Here
www.iasexamportal.com
Continued Proportion
If three quantities a, b and c are such that a : b : : b : c, then b2 = ac and a, b and c
are in continued proportions. Also, the quantity c is called the third proportion of a
and b.
Fourth Proportion
If four quantities a, b, c and x are such that a : b : : b : c, then ax = be and x is
called the fourth proportion of a, b, and c.
Mean or Second Proportion
If three quantities a, b and x are such that a : x : : x : b, then x2 = ab and x is called
the mean of a and b. Also, If a : b = c : d, then the following properties hold good.
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
b : a = d : c (Invertendo)
a : c = b : d (Alter nendo)
(a + b) : b = (c + d) : d (Componendo)
(a b) : b = (c d) : d (Dividendo)
(v)
a b c d
a b c d
IASEXAMPORTAL.COM
(Componendo - Dividendo)
To Join Free Coaching for our Next Batch
Click
Here
www.iasexamportal.com
Variation
If two quantities x and y are related in such a way that as the quantity x changes it
also brings a change in the second quantity y, then the two quantities are in
variation.
Direct Variation
The quantity x is in direct variation to y if an increase in x makes y to increase
proportionally. Also a decrease in x makes y to decrease proportionally it can be
expressed as x = ky. Where, k is called the constant of proportionality. eg, Cost is
directly proportional to the number of articles bought.
Inverse Variation
The quantity x is in inverse variation to y if an increase in x makes y to decrease
proportionally. Also, a decrease in x makes y to increase proportionally. It can be
expressed as x k . Where, k is called the constant of proportionality.
y
eg, The time taken by a vehicle in covering a certain distance is inversely
proportional to the speed of the vehicle.
IASEXAMPORTAL.COM
To Join Free Coaching for our Next Batch
Click
Here
Joint Variation
www.iasexamportal.com
If there are more than two quantities x, y and z and x varies with both y and z, then
x is in joint variation to y and z. It can be expressed as x = kyz. Where, k is the
constant of proportionality. eg, Men doing a work in some number of days working
certain hours a day.
IASEXAMPORTAL.COM
To Join Free Coaching for our Next Batch
Click
Here
www.iasexamportal.com
IASEXAMPORTAL.COM
To Join Free Coaching for our Next Batch
Click
Here
www.iasexamportal.com
Buy CSAT Paper -2 Study Kit in Hard Copy:
http://iasexamportal.com/civilservices/study-kit/ias-pre/csat-paper-2
Click Here to Join Online Coaching for CSAT Paper -2:
http://iasexamportal.com/civilservices/courses/ias-pre/csat-paper-2
IASEXAMPORTAL.COM
To Join Free Coaching for our Next Batch
Click
Here
You might also like
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Stress-Free Math: A Visual Guide to Acing Math in Grades 4-9From EverandStress-Free Math: A Visual Guide to Acing Math in Grades 4-9No ratings yet
- Real Estate Math Express: Rapid Review and Practice with Essential License Exam CalculationsFrom EverandReal Estate Math Express: Rapid Review and Practice with Essential License Exam CalculationsNo ratings yet
- Math Ratio & ProportionDocument4 pagesMath Ratio & ProportionVishal Gattani50% (2)
- 1538630079ratio Partnership EbookDocument63 pages1538630079ratio Partnership EbookKumar RajnishNo ratings yet
- GMAT Ratio and ProportionDocument14 pagesGMAT Ratio and ProportionManjula.bsNo ratings yet
- Advanced C++ Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandAdvanced C++ Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL Numerical Aptitude Concepts of GeometryDocument10 pagesSSC CGL Numerical Aptitude Concepts of GeometryIAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- Business Maths - BBA 1yr - Unit 1Document107 pagesBusiness Maths - BBA 1yr - Unit 1ADISH JAINNo ratings yet
- Maths IcseDocument17 pagesMaths IcseSachin Karnik100% (2)
- The Nuts and Bolts of Proofs: An Introduction to Mathematical ProofsFrom EverandThe Nuts and Bolts of Proofs: An Introduction to Mathematical ProofsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Ratio and ProportionsDocument3 pagesRatio and Proportionsumi kalsumNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL Numerical Aptitude Clocks and CalendarDocument5 pagesSSC CGL Numerical Aptitude Clocks and CalendarIAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- Kurva Who PDFDocument16 pagesKurva Who PDFRuth Veraulina100% (2)
- LTE Performance Counter Reference SummaryDocument410 pagesLTE Performance Counter Reference SummarydiporufaiNo ratings yet
- 3 (B) Gupta & Post-Gupta PeriodDocument7 pages3 (B) Gupta & Post-Gupta PeriodIAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- Ratio and ProportionDocument3 pagesRatio and ProportionAbhishek DixitNo ratings yet
- Ratio Proportion and PercentageDocument27 pagesRatio Proportion and PercentageSAMSON ALBERT SALASNo ratings yet
- Business Mathematics: Name: Akanksha S Marlecha Bba-Ib Roll No. 3651Document11 pagesBusiness Mathematics: Name: Akanksha S Marlecha Bba-Ib Roll No. 3651AkankshaNo ratings yet
- ch-6 Ratios and Proportions Quantitative AptitudeDocument12 pagesch-6 Ratios and Proportions Quantitative Aptitudethakkert25No ratings yet
- Ratio and Proportion Are Explained Majorly Based On FractionsDocument8 pagesRatio and Proportion Are Explained Majorly Based On FractionsmehalaNo ratings yet
- Ratio and Proportion, Indices, Logarithms: Chapte RDocument53 pagesRatio and Proportion, Indices, Logarithms: Chapte Raayushi JainNo ratings yet
- Ratio & Proportion ConceptsDocument5 pagesRatio & Proportion ConceptsGauri PhadkeNo ratings yet
- Disha Publication AFCAT Ratio Proportion & Variations PDFDocument23 pagesDisha Publication AFCAT Ratio Proportion & Variations PDFAnonymous sQ0klTOzglNo ratings yet
- Understanding Ratio and ProportionDocument9 pagesUnderstanding Ratio and ProportionrajanrajguruNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Ability: Ratio and ProportionDocument25 pagesQuantitative Ability: Ratio and ProportionJack Lawes100% (1)
- 16808ratio ProportionDocument85 pages16808ratio ProportionRajib DasNo ratings yet
- RatioDocument46 pagesRatioGagan BossNo ratings yet
- 1652156684ratio Mixture Alligations EbookDocument48 pages1652156684ratio Mixture Alligations EbookivenkataramaiahNo ratings yet
- Ratio and ProportionsDocument2 pagesRatio and Proportionsvawom884No ratings yet
- RatioLog and ProportionDocument6 pagesRatioLog and ProportionshlokNo ratings yet
- Ratio and ProportionDocument56 pagesRatio and ProportionDivya JijuNo ratings yet
- Problems on Bill Discounting SolvedDocument20 pagesProblems on Bill Discounting SolvedFirdoseNo ratings yet
- Ratio and Proportion, RaviDocument85 pagesRatio and Proportion, RaviShrishailamalikarjunNo ratings yet
- Ratios and proportions explainedDocument2 pagesRatios and proportions explainedNagaNo ratings yet
- Ratio and Proportion ShortcutsDocument5 pagesRatio and Proportion ShortcutsKai Chung TamNo ratings yet
- Ratio and Proportion Guidebook: Learn Key Concepts With ExamplesDocument39 pagesRatio and Proportion Guidebook: Learn Key Concepts With ExamplesdarshanshankarNo ratings yet
- RATIO PROPORTION PERCENTAGEDocument4 pagesRATIO PROPORTION PERCENTAGEVidhyashree YadavNo ratings yet
- Aptitude::: Ratio and ProportionDocument10 pagesAptitude::: Ratio and ProportionJan JanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Ratio and ProportionDocument29 pagesLecture 5 Ratio and Proportionsingh11_amanNo ratings yet
- Ratio and Proportion FundamentalsDocument11 pagesRatio and Proportion Fundamentalsumi kalsumNo ratings yet
- Ratio, Proportion, Indices and Logarithms ExplainedDocument56 pagesRatio, Proportion, Indices and Logarithms ExplaineddbNo ratings yet
- Property DefinitionDocument2 pagesProperty Definitionapi-314809600No ratings yet
- Ratio and Proportion, AgrawalDocument4 pagesRatio and Proportion, AgrawalShrishailamalikarjunNo ratings yet
- Ratios and Proprotions (APTITUDE)Document12 pagesRatios and Proprotions (APTITUDE)harishsharma22No ratings yet
- Proportion: Lesso ns5Document14 pagesProportion: Lesso ns5Sophia MagdaraogNo ratings yet
- Ratio Proportion ChapterDocument3 pagesRatio Proportion Chaptersani devNo ratings yet
- Some Important PointsDocument2 pagesSome Important PointswithraviNo ratings yet
- R, M & A EbookDocument21 pagesR, M & A EbookNAVYANo ratings yet
- GP - Apti - Ratio and ProportionsDocument6 pagesGP - Apti - Ratio and Proportionsdikshant SolankiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Everyday MathDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Everyday MathKamran AliNo ratings yet
- Ratio ProportionDocument24 pagesRatio ProportionKritvee ModiNo ratings yet
- RATIO, PROPORTIONS & AGE - 1st - Chapter PDFDocument13 pagesRATIO, PROPORTIONS & AGE - 1st - Chapter PDFsivaguruNo ratings yet
- Ratio, Proportion and Percentages Formulas and TricksDocument3 pagesRatio, Proportion and Percentages Formulas and TricksVenkataramanareddy Sura100% (1)
- Ratio & Proportion RelationshipDocument54 pagesRatio & Proportion RelationshipShubham TiwariNo ratings yet
- Ratio and ProportionDocument2 pagesRatio and ProportionBautista Ayesha Mikhaila (A-kun)No ratings yet
- Aptitude PresentationDocument15 pagesAptitude Presentationsourabh vermaNo ratings yet
- Ratio - Proportion - Variation: Chapter - 2Document5 pagesRatio - Proportion - Variation: Chapter - 2class xNo ratings yet
- Ratio Proportion Banking RatioandProportion 959035-PrintDocument59 pagesRatio Proportion Banking RatioandProportion 959035-PrintPappu kumarNo ratings yet
- Module 2A - Ratio and Proportion Student HandoutDocument5 pagesModule 2A - Ratio and Proportion Student HandoutShivaraj PatilNo ratings yet
- L-1 Ratio and ProportionDocument31 pagesL-1 Ratio and ProportionUjwal MantriNo ratings yet
- Ration and PropDocument3 pagesRation and PropMary Joy Sarzuela PelaezNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Ability: © 2016 SMART Training Resources Pvt. LTDDocument258 pagesQuantitative Ability: © 2016 SMART Training Resources Pvt. LTDsierraNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Self-Learning Module 8Document48 pagesMathematics: Self-Learning Module 8no oneNo ratings yet
- Old NCERT PDF For IAS UPSC ExamsDocument1 pageOld NCERT PDF For IAS UPSC ExamsIAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- 4 (C) Climatic Regions of The WorldDocument13 pages4 (C) Climatic Regions of The WorldIAS EXAM PORTAL100% (1)
- 10 (B) The Rise of Neo-Nationalists or ExtremistsDocument18 pages10 (B) The Rise of Neo-Nationalists or ExtremistsIAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- 9 (B) The National Movements in 1940sDocument22 pages9 (B) The National Movements in 1940sIAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power in IndiaDocument10 pagesNuclear Power in IndiaIAS EXAM PORTAL100% (1)
- 6 (C) The Saints of Medieval IndiaDocument12 pages6 (C) The Saints of Medieval IndiaIAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- Green Development InitiativeDocument7 pagesGreen Development InitiativeIAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- 7 (C) Prime MinisterDocument4 pages7 (C) Prime MinisterIAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- Solar Power in IndiaDocument9 pagesSolar Power in IndiaIAS EXAM PORTAL100% (1)
- 9 (C) Chronology of The National MovementDocument24 pages9 (C) Chronology of The National MovementIAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- 10 (A) Nature and Causes For The Rise of National MovementDocument21 pages10 (A) Nature and Causes For The Rise of National MovementIAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- 6 (B) Vijayanagar EmpireDocument4 pages6 (B) Vijayanagar EmpireIAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- 9 (A) The Beginning of The Gandhian EraDocument16 pages9 (A) The Beginning of The Gandhian EraIAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- 9 (C) State LegislatureDocument7 pages9 (C) State LegislatureIAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- 1 (C) Historical Background & Origin of Indian ConstitutionDocument5 pages1 (C) Historical Background & Origin of Indian ConstitutionIAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL Numerical Aptitude Introduction To DIDocument5 pagesSSC CGL Numerical Aptitude Introduction To DIIAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL Numerical Aptitude Basic AlgebraDocument11 pagesSSC CGL Numerical Aptitude Basic AlgebraIAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL Numerical Aptitude Volume and Surface Area of Solid FiguresDocument6 pagesSSC CGL Numerical Aptitude Volume and Surface Area of Solid FiguresIAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL Reasoning Sitting ArrangementsDocument5 pagesSSC CGL Reasoning Sitting ArrangementsIAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL Reasoning Arithmetical Reasoning Chapter - 11Document5 pagesSSC CGL Reasoning Arithmetical Reasoning Chapter - 11IAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL Numerical Aptitude Area of Plane FiguresDocument7 pagesSSC CGL Numerical Aptitude Area of Plane FiguresIAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- Online Coaching SSC CGL Tier 1 Reasoning Alphabet TestDocument6 pagesOnline Coaching SSC CGL Tier 1 Reasoning Alphabet TestIAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL Numerical Aptitude Simple InterestDocument4 pagesSSC CGL Numerical Aptitude Simple InterestIAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- SSC Online Coaching CGL Tier 1 GK Indian PolityDocument7 pagesSSC Online Coaching CGL Tier 1 GK Indian PolityIAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL English Language Phrasal VerbDocument5 pagesSSC CGL English Language Phrasal VerbIAS EXAM PORTALNo ratings yet
- Ratio and Proportion: A B A BDocument40 pagesRatio and Proportion: A B A BMuhammad Arslan Rafiq KhokharNo ratings yet
- Derivative of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsDocument4 pagesDerivative of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsKristan Glen PulidoNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsDocument2 pagesInverse Trigonometric FunctionsArman SinghNo ratings yet
- Tips Tricks and Formulae On Ratio and ProportionDocument6 pagesTips Tricks and Formulae On Ratio and ProportionmsmgectNo ratings yet
- 1 RatioDocument2 pages1 RatioAnu GraphicsNo ratings yet
- BMI Girl TableDocument7 pagesBMI Girl TableVienny Widhyanti RosaryaNo ratings yet
- Freudian PsychoanalysisDocument108 pagesFreudian PsychoanalysisPja ShanthaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Akuntansi Dan Keuangan FEB Universitas Budi Luhur: Capital Adequacy Ratio Loan To Deposit Ratio NON PerformingDocument12 pagesJurnal Akuntansi Dan Keuangan FEB Universitas Budi Luhur: Capital Adequacy Ratio Loan To Deposit Ratio NON Performingzhafirah nurhasanahNo ratings yet
- Bmi TVL or PrintingDocument13 pagesBmi TVL or PrintingJose C. Lita JrNo ratings yet
- Jsunil Tutorial Panjabi Colony Gali O1: UNIT-6 TrigonometryDocument6 pagesJsunil Tutorial Panjabi Colony Gali O1: UNIT-6 TrigonometryAkshay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Second Order SystemsDocument13 pagesAnalysis of Second Order SystemsChamod DissanayakeNo ratings yet
- Derivatives - Important FormulaeDocument1 pageDerivatives - Important FormulaegnathwNo ratings yet
- BLDocument4,282 pagesBLSumit RathodNo ratings yet
- School Canteen Feeding Program 2019 2020 K 6 1Document20 pagesSchool Canteen Feeding Program 2019 2020 K 6 1MaryRoseTrinidadNo ratings yet
- Exercise 11.1 Page No: 11.17: Differentiate The Following Functions From The First Principles: 1. e SolutionDocument183 pagesExercise 11.1 Page No: 11.17: Differentiate The Following Functions From The First Principles: 1. e SolutionMayank ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Z Scores and T Scores-1Document2 pagesZ Scores and T Scores-1api-302331744No ratings yet
- Ratios Rates ProportionsDocument2 pagesRatios Rates ProportionsUmu Yumumu100% (1)
- Ratio Proportion PDF by Governmentadda PDFDocument81 pagesRatio Proportion PDF by Governmentadda PDFNikita SabaleNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Analisis Kinerja Keuangan Pada PT AstraDocument18 pagesJurnal Analisis Kinerja Keuangan Pada PT AstraAbet TebaiNo ratings yet
- Elipse SheetDocument23 pagesElipse SheetHimanshu TiwariNo ratings yet
- Example of Calculus 1 by ClipvidvaDocument60 pagesExample of Calculus 1 by ClipvidvaTanawat ChansophonkulNo ratings yet
- 11th +JEE+2021 2022+L-1+Derivatives PDFDocument70 pages11th +JEE+2021 2022+L-1+Derivatives PDFVishal Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- WK 1 Introduction and Definition of DerivativesDocument20 pagesWK 1 Introduction and Definition of DerivativesrenatoamarNo ratings yet
- Roblox script to customize character parts and jointsDocument6 pagesRoblox script to customize character parts and jointsnigger kidNo ratings yet
- 11 - Differential Equations PDFDocument9 pages11 - Differential Equations PDFthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Lista de Funciones DAXDocument21 pagesLista de Funciones DAXfrbadillaNo ratings yet
- Formulario para Derivadas - SymbolabDocument2 pagesFormulario para Derivadas - SymbolabAbraham CandiaNo ratings yet
- Measuring Change: Differentiation: Skills Check 1 ADocument25 pagesMeasuring Change: Differentiation: Skills Check 1 Ajulia brossardNo ratings yet