Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tugas 3
Uploaded by
Syaiful RizalOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tugas 3
Uploaded by
Syaiful RizalCopyright:
Available Formats
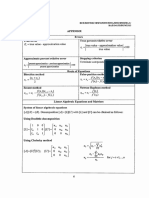
1.
Solve this ODE (4xy + 3y 2 x)dx + x(x + 2y)dy = 0 show whether it is exact or not M (x, y) = y = N (x, y) = x = (4xy + 3y 2 x) y 4x + 6y (x2 + 2xy) x 2x + 2y
(x,y) (x,y) because My = Nx so the ODE is not exact We use Integration Factor assume z = (x, y) in such way
(x, y)M (x, y)dx + (x, y)N (x, y)dy = 0 is Exact ODE, so M y M M+ y y M N y x M N ( ) y x = = = = N x N N+ x x N M x y N M x y N M x y ...............(1) M N y x
So, we use equation (1) with a condition z = (x) = = =
N x M N y x (x2 + 2xy) x 2 +2xy) (4xy+3y 2 x) (x x y (x2 + 2xy) x
4x + 6y 2x 2y 1
= = = 2 1 = x = = = = =
(x2 x x
+ 2xy) 2x + 4y
1 2 x x 2 ln x + Co 2 ln x ln x2 ln x2 ln x2 ln x2
2 1 x 2 x 1 1 ln + C1 ln + C2 ln + C2 C2
= C2 = eC2 = kx2
If we take k = 1 so we get = x2 x2 (4xy + 3y 2 x)dx + x2 (x(x + 2y))dy = 0 (4x3 y + 3x2 y 2 x3 )dx + (x4 + 2x3 y)dy = 0 (4x3 y + 3x2 y 2 x3 ) = 4x3 + 6yx2 y (x4 + 2x3 y) = 4x3 + 6x2 y x The ODE is exact, then we solve it F (x, y) = 4x3 y + 3x2 y 2 x3 dx F (x, y) = (4x3 y + 3x2 y 2 x3 )dx F (x, y) = (4x3 y + 3x2 y 2 x3 )dx
x4 + y 4 F (x, y) dy = x4 + 2x3 y + dy dy F (x, y) = x4 y + x3 y 2 2
x4 + 2x3 y = x4 + 2x3 y + dy dy C = y 0 = So, F (x, y) = x4 y + x3 y 2 2. Solve this equation
x4 4
dy dy
+C
(x + y)2 dx xydy = 0
We solve this problem by using Separated Variable Technic Suppose that: y = vx dy = v x + vx dy = xdv + vdx
Then we have:
(x + vx)2 dx x(vx)(xdv + vdx) (x2 + vx2 + x2 v + v 2 x2 )dx (vx2 (xdv + vdx)) x2 dx + vx2 dx + x2 vdx + v 2 x2 dx (vx3 dv + v 2 x2 dx) x2 dx + 2vx2 dx vx3 dv (x2 + 2vx2 )dx (vx3 )dv x2 (1 + 2v)dx (x3 v)dv
= = = = = =
0 0 0 0 0 0
we have already know that f1 g1 dx + f2 g2 dv = 0 f1 g2 dx + dv = 0 f2 g1 3
so we get, x2 v dv = 0 dx 3 x 1 + 2v v 1 dx dv = 0 x 1 + 2v we solve it by using substitution method
v dv 1+2v
We assume that: u = 1 + 2v du = 2dv du dv = 2 v = 1 + 2v v du u 2
v 1 = ( )( du) 2 u v = ln|u| + c1 2 v ln|1 + 2v| + c1 = 2 And then we get v ln(x) + C0 ( )(ln|1 + 2v|) + C1 = 0..........................................(1) 2
y We subtitute: v = ( x ) to equation (1) then we get
ln(x) (
y 2y )(ln|1 + |) + C = 0 2x x
You might also like
- CFD Study On Effect of Branch Sizes in Human Coronary ArteryDocument139 pagesCFD Study On Effect of Branch Sizes in Human Coronary ArterySyaiful RizalNo ratings yet
- English For MathDocument5 pagesEnglish For MathSyaiful RizalNo ratings yet
- English For MathDocument5 pagesEnglish For MathSyaiful RizalNo ratings yet
- Human AncestorDocument1 pageHuman AncestorSyaiful RizalNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Gaussian Elimination MethodDocument14 pagesGaussian Elimination MethodUmer farooq100% (1)
- Model Question Paper with CBCS SchemeDocument3 pagesModel Question Paper with CBCS SchemeThilak AnandNo ratings yet
- Ordinary Differential EquationsDocument33 pagesOrdinary Differential EquationsTendaiNo ratings yet
- Complex Variable, Laplace & Z-TransformationDocument8 pagesComplex Variable, Laplace & Z-TransformationrahimuddinNo ratings yet
- Runge-Kutta 4th Order Method for Solving Differential EquationsDocument13 pagesRunge-Kutta 4th Order Method for Solving Differential EquationsFarhan AbbasNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS G8 Q1 W5 - Abshalom Legaspi v.2Document13 pagesMATHEMATICS G8 Q1 W5 - Abshalom Legaspi v.2Ochia JustineNo ratings yet
- Tma 4165 Eks V17 enDocument2 pagesTma 4165 Eks V17 ensalimNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Equation: Solved ExampleDocument32 pagesTrigonometric Equation: Solved Example10x RiderNo ratings yet
- Approx SolutionsDocument10 pagesApprox SolutionsGopal KondaguntaNo ratings yet
- Systems of Equations Substitution PDFDocument4 pagesSystems of Equations Substitution PDFCharish Jane Antonio CarreonNo ratings yet
- MA Ordinary Differential EquationsDocument11 pagesMA Ordinary Differential EquationsNikhilSharmaNo ratings yet
- Solution To The Diffusion Equation: Ole Witt-Hansen 2018Document7 pagesSolution To The Diffusion Equation: Ole Witt-Hansen 2018حمامة السلامNo ratings yet
- P1-Differentiation and IntegrationDocument5 pagesP1-Differentiation and IntegrationArrow GamingNo ratings yet
- MATH103 ch3Document83 pagesMATH103 ch3merlin otemakumiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics II Even Sem Mid Term 2017-18 (DITUStudentApp)Document2 pagesEngineering Mathematics II Even Sem Mid Term 2017-18 (DITUStudentApp)Niban IlawurNo ratings yet
- Errors True Error True Percent Relative Error: AppendixDocument5 pagesErrors True Error True Percent Relative Error: AppendixSin ChienNo ratings yet
- CalculusDocument3 pagesCalculusmuhamad dimas arifin a.k.a Ahmd El Arf100% (1)
- International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer: Dejan BrkicDocument3 pagesInternational Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer: Dejan BrkicSagar DhuriNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 2, Module 2 Solving Equations Transformable Into Quadratic EquationDocument14 pagesMathematics: Quarter 2, Module 2 Solving Equations Transformable Into Quadratic EquationManelyn TagaNo ratings yet
- Lecture06 Macro LWRDocument44 pagesLecture06 Macro LWREduardo HerreraNo ratings yet
- The Laplace TransformDocument34 pagesThe Laplace Transformjkligvk. jukjNo ratings yet
- Shearer Levy Chapter 8Document20 pagesShearer Levy Chapter 8Daniel ComeglioNo ratings yet
- Section 5: Finite Volume Methods For The Navier Stokes EquationsDocument27 pagesSection 5: Finite Volume Methods For The Navier Stokes EquationsUmutcanNo ratings yet
- 6-2 (Alt) Solving Inequalities With MultDocument7 pages6-2 (Alt) Solving Inequalities With MultMr. AulisioNo ratings yet
- Precalculus - Worksheet: FX X X X FDocument3 pagesPrecalculus - Worksheet: FX X X X FteachopensourceNo ratings yet
- 6 Substitution Methods, Homogeneous Equa-Tions, Bernoulli EquationsDocument14 pages6 Substitution Methods, Homogeneous Equa-Tions, Bernoulli EquationsFurkan ErdenNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations Book Math 2420 Resources1 PDFDocument155 pagesDifferential Equations Book Math 2420 Resources1 PDFIqra JawedNo ratings yet
- DifferentialDocument402 pagesDifferentialMartínez Gutiérrez MoisésNo ratings yet
- CFD Mid1 ExamDocument12 pagesCFD Mid1 ExamJoshua SimonNo ratings yet
- 250 - Quadratic Equation With ExplanationDocument106 pages250 - Quadratic Equation With ExplanationShubha MajumdarNo ratings yet