Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exam 2solution
Uploaded by
James Steven HaneyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exam 2solution
Uploaded by
James Steven HaneyCopyright:
Available Formats
MTH 2613 Elementary Differential Equations Score _____________
Examination 2
Student Name: _______________________________________________________________________________
This exam is a closed book, open notes exam. You are allowed to use a simple, non-integrating calculator. All
work must be shown to receive full credit for the problem. Solutions are to be worked in the space provided.
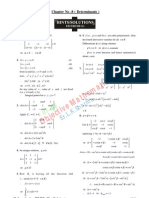
1. Determine the general solution for the given homogeneous differential equations. 20 points
a. 6 11 3 0 y y y '' ' + =
( )( )
2
6 11 3 0
3 1 2 3 0
1 3
,
3 2
m m
m m
m
+ =
=
=
( )
1 3
3 2
1 2
x x
y x c e c e = +
b. 4 8 0 y y y '' ' + + =
2
4 8 0
4 16 32
2
4 4
2 2
2
m m
m
i
i
+ + =
=
= =
( )
2 2
1 2
cos 2 sin2
x x
y x c e x c e x
= +
c. 10 25 0 y y y ''' '' ' + + =
( )
( )
( )
3 2
2
2
10 25 0
10 25 0
5 0
0, 5 mult.2
m m m
m m m
m m
m
+ + =
+ + =
+ =
=
( )
5 5
1 2 3
x x
y x c c e c xe
= + +
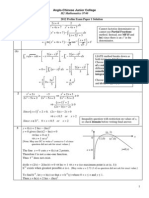
2. Determine the general solution to the differential equation given by tan y y x '' + = . 25 points
Begin by finding the solution to the homogeneous equation:
2
1,2
0
1 0
y y
m
m i
'' + =
+ =
=
1 2
cos sin
c
y c x c x = +
Applying the Variation of Parameters method and replacing the arbitrary constants with unknown functions,
we see
1 2
cos sin
p
y v x v x = + . Differentiating the particular solution and assuming the assumption step,
we see
( ) 1 2 1 2
1 2 1 2
cos sin sin cos
sin cos cos sin
p
p
y v x v x v x v x
y v x v x v x v x
' ' '
= + +
' ' '
= +
Substituting into the given differential equation, we see
1 2 1 2 1 2
1 2
tan
sin cos cos sin cos sin tan
sin cos tan
y y x
v x v x v x v x v x v x x
v x v x x
'' + =
' '
+ + + =
' '
+ =
Using Cramers Rule to determine the unknown functions, we see
( )
1
2
2
0 sin
tan cos
cos sin
sin cos
sin
cos
1
cos 1
cos
cos sec
sin ln sec tan
x
x x
v dx
x x
x x
x
x
dx
x
dx
x
x x dx
x x x
=
=
=
= +
}
}
}
}
2
cos 0
sin tan
cos sin
sin cos
sin
1
sin
cos
x
x x
v dx
x x
x x
x
dx
x dx
x
=
=
=
}
}
}
Thus,
( ) ( )
1 2
cos sin sin ln sec tan cos cos sin cos ln sec tan
p
y v x v x x x x x x x x x x = + = + + = + . And,
the general solution is given by the function
( )
1 2
cos sin cos ln sec tan y x c x c x x x x = + + .
3. Determine the general solution to the given system of equations. 25 points
2 2 1
2 3
dx dy
x y
dt dt
dx dy
y
dt dt
+ = + +
+ = +
Begin by converting the equation to differential operator notation and isolating the nonhomogeneous terms:
( )| | ( )| |
| | ( )| |
2 2 1
2 1 3
D x D y
D x D y
+ =
+ =
Eliminating the x terms and solving for ( ) y t , we see
( )| | ( )| | ( )
( ) | | ( )( )| | ( )
( ) ( )( ) ( )| | ( ) ( )
( )( )| |
2 2 1
2 2 2 1 2 3
2 2 2 1 1 2 3
2 1 6
D D x D D y D
D D x D D y D
D D D D y D D
D D y
+ =
=
=
=
Solving the homogeneous problem, we see
( )( ) 2 1 0
2,1
m m
m
=
=
2
1 2
t t
c
y c e c e = +
Using the Method of Undetermined Coefficients to solve for the nonhomogeneous term with
p
y At B = + ,
we see
( ) ( ) ( )
3 2 6
0 3 2 6
0 3
y y y
A At B
A B
'' ' + =
+ + =
= =
( )
2
1 2
3
t t
y t c e c e = +
Solving the second equation for
dx
dt
and substituting into the first equation, we can solve for ( ) x t :
( )
2 2
1 2 1 2
2
1 2
1
2
2
1
2 3 2
2
3 5
2 2
t t t t
t t
dy
x y
dt
c e c e c e c e
c e c e
| |
= +
|
\ .
= + +
= +
Thus, the general solution is given by
( )
( )
2
1 2
2
1 2
3 5
2 2
3
t t
t t
x t c e c e
y t c e c e
= +
= +
4. Find two power series solutions to the differential equation given by ( ) 1 0 y x y y '' ' + = . 30 points
Recall, the derivatives for the arbitrary power series are given by
( )
( )
( ) ( )
0
1
1
2
2
1
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
y x c x
y x nc x
y x n n c x
=
=
' =
'' =
Substituting into the given differential equation,
( ) ( )
( )
2 1
2 1 0
2 1
2 1 1 0
1 1 0
1 0
n n n
n n n
n n n
n n n n
n n n n
n n n n
n n c x x nc x c x
n n c x nc x nc x c x
= = =
= = = =
+ =
=
Adjusting the summations to be expansions of the function ( )
k
y x x = , we see
( )( ) ( )
2 1
0 1 0 0
2 1 1 0
k k k k
k k k k
k k k k
k k c x kc x k c x c x
+ +
= = = =
+ + + =
Extracting the 0 k = terms and combining the summations, we see
( )( ) ( )
( )( ) ( )
( )( ) ( ) ( )
2 1
0 1 0 0
2 1 0 2 1
1
2 1 0 2 1
1
2 1 1 0
2 2 1 1 0
2 2 1 1 1 0
k k k k
k k k k
k k k k
k
k k k k
k
k
k k k
k
k k c x kc x k c x c x
c c c k k c kc k c c x
c c c k k c k c k c x
+ +
= = = =
+ +
=
+ +
=
+ + + =
+ + + + = (
+ + + + + = (
Solving for the coefficients, we see
( )
2 1 0
2 1 0
2 0
1
2!
c c c
c c c
=
= +
( )
( )
2 1
2 1
2 0
1
, 1
2
k k k
k k k
k c c c
c c c k
k
+ +
+ +
+ =
= + >
+
Expanding the summation, we see
( ) ( ) ( )
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
3 2 1 1 0 1 1 0
4 3 2 1 0 1 0 1 0
5 4 3 1 0 1 0 1 0
1 1 1 1
1: 3
3 3 2 3!
1 1 1 1 1
2: 3 6 4
4 4 3! 2! 4!
1 1 1 1 1
3: 6 4 3 18 8
5 5 4! 3! 5!
k c c c c c c c c
k c c c c c c c c c
k c c c c c c c c c
| |
= = + = + + = +
|
\ .
| |
= = + = + + + = +
|
\ .
| |
= = + = + + + = +
|
\ .
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
6 5 4 1 0 1 0 1 0
7 6 5 1 0 1 0 1 0
1 1 1 1 1
4: 18 8 6 4 48 28
6 6 5! 4! 6!
1 1 1 1 1
5: 48 28 18 8 156 68
7 7 6! 5! 7!
k c c c c c c c c c
k c c c c c c c c c
| |
= = + = + + + = +
|
\ .
| |
= = + = + + + = +
|
\ .
Substituting into the arbitrary power series, we see the solution is given by
( )
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
( ) ( )
2 3 4 5
0 1 2 3 4 5
2 3 4 5
0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0
6 7
1 0 1 0
2 3 4 5 6 7
0
............
1 1 1 1
3 6 4 18 8
2! 3! 4! 5!
1 1
48 28 156 68 ...........
6! 7!
1 1 4 8 28 68
1 ...........
2! 3! 4! 5! 6! 7!
y x c c x c x c x c x c x
c c x c c x c c x c c x c c x
c c x c c x
c x x x x x x
= + + + + + +
= + + + + + + + + +
+ + + +
(
= + + + + + +
(
2 3 4 5 6 7
1
1 3 6 18 48 156
...........
2! 3! 4! 5! 6! 7!
c x x x x x x x
+
(
+ + + + + +
(
You might also like
- Solutions Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems 5edDocument496 pagesSolutions Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems 5edRicardo Vega100% (6)
- 2009 NJC SH2 H2 Mathematics Prelim Paper 2 SolutionsDocument21 pages2009 NJC SH2 H2 Mathematics Prelim Paper 2 SolutionsNicholas ChoyNo ratings yet
- PJC h2 Math p1 SolutionsDocument13 pagesPJC h2 Math p1 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- 2012 ACJC Prelim H2 Math SolnDocument15 pages2012 ACJC Prelim H2 Math Solnckhowh_23284524667% (3)
- 2013 - 2014 H2 Maths JJC Promo SolnsDocument11 pages2013 - 2014 H2 Maths JJC Promo SolnsLionel Torres LeeNo ratings yet
- Cape Pure Mathematics Unit 2module 1: Complex Numbers and Calculus IiDocument20 pagesCape Pure Mathematics Unit 2module 1: Complex Numbers and Calculus IiCarlon BairdNo ratings yet
- 2010 TJC SolDocument12 pages2010 TJC SolPooja KapurNo ratings yet
- H2 MATHEMATICS PAPER 1 SOLUTIONSDocument15 pagesH2 MATHEMATICS PAPER 1 SOLUTIONSnej200695No ratings yet
- AMO (2014 Past Papers) Secondary - 1: Yto Maths CentreDocument23 pagesAMO (2014 Past Papers) Secondary - 1: Yto Maths CentreHtay Htay Win100% (3)
- Advanced Engineering Mathematics Solutions (2-4 2-7&2-10)Document26 pagesAdvanced Engineering Mathematics Solutions (2-4 2-7&2-10)Fa VelizNo ratings yet
- DeretDocument88 pagesDeretMuhammad WildanNo ratings yet
- CH 3.6: Variation of Parameters: T G y T Q y T P yDocument9 pagesCH 3.6: Variation of Parameters: T G y T Q y T P yPercdc DavaoNo ratings yet
- EE - 210 - Exam 3 - Spring - 2008Document26 pagesEE - 210 - Exam 3 - Spring - 2008doomachaleyNo ratings yet
- HCI H2 Math Prelim Paper 1 SolutionsDocument12 pagesHCI H2 Math Prelim Paper 1 Solutionsnej200695No ratings yet
- Power Series SolutionsDocument30 pagesPower Series SolutionsAli AbdullahNo ratings yet
- 2 Overview of Numerical AnalysisDocument59 pages2 Overview of Numerical AnalysisVashish RamrechaNo ratings yet
- BT2 Revision Package Solutions (2008 Prelims)Document111 pagesBT2 Revision Package Solutions (2008 Prelims)gerwynngNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument8 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- MJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Document22 pagesMJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- 2007 YJC Paper 1solDocument12 pages2007 YJC Paper 1solYudi KhoNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Review: Opp Hyp Hyp Opp Adj Hyp Hyp Adj Opp Opp Adj AdjDocument6 pagesTrigonometry Review: Opp Hyp Hyp Opp Adj Hyp Hyp Adj Opp Opp Adj Adjkoulis19920% (1)
- 05.2 Power SeriesDocument30 pages05.2 Power SeriesKhasan MustofaNo ratings yet
- QN Solution 1: H2 Math Paper 1Document11 pagesQN Solution 1: H2 Math Paper 1Alex SoonNo ratings yet
- Kombinatorika - ZadaciDocument7 pagesKombinatorika - ZadacirakivanNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument5 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Junior College Math Paper SolutionsDocument15 pagesJunior College Math Paper SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- One Mark For Each Intercept Down Ward.: A A X yDocument14 pagesOne Mark For Each Intercept Down Ward.: A A X yKarabo MailulaNo ratings yet
- AE 321 - Solution of Homework #5: (5×5 25 POINTS)Document9 pagesAE 321 - Solution of Homework #5: (5×5 25 POINTS)Arthur DingNo ratings yet
- DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS TEST 2 ANSWER SCHEMEDocument4 pagesDIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS TEST 2 ANSWER SCHEMEJimmy TeowNo ratings yet
- C5.MDOF1 Compatibility Mode PDFDocument16 pagesC5.MDOF1 Compatibility Mode PDFArThur BangunNo ratings yet
- Mi h2 Math Solutions p1Document10 pagesMi h2 Math Solutions p1jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- 2012 JC2 Preliminary Exam H2 Math Paper 1 SolutionsDocument10 pages2012 JC2 Preliminary Exam H2 Math Paper 1 SolutionsHuixin LimNo ratings yet
- Chinese Remainder TheoremDocument7 pagesChinese Remainder TheoremManohar NVNo ratings yet
- 004 - s02 - The Lorentz GroupDocument4 pages004 - s02 - The Lorentz GroupBradley NartowtNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Home Work Test/Mathematics: Trigonometric Ratio & Equation HWT - 1Document6 pagesSolutions To Home Work Test/Mathematics: Trigonometric Ratio & Equation HWT - 1varunkohliinNo ratings yet
- CH 2.6: Exact Equations & Integrating Factors: y y X N y X MDocument10 pagesCH 2.6: Exact Equations & Integrating Factors: y y X N y X MOmegle ConvosNo ratings yet
- 2006 AJC H2 MY SolnDocument9 pages2006 AJC H2 MY Solnjunie9201No ratings yet
- Mid IDocument11 pagesMid IpassmefoolNo ratings yet
- F C D I: Jesús Rubí MirandaDocument2 pagesF C D I: Jesús Rubí Mirandalmarobesg94No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Linear SystemDocument12 pagesLecture 2 Linear SystemEbrahim Abdullah HanashNo ratings yet
- L-6 de Series SolutionDocument88 pagesL-6 de Series SolutionRiju VaishNo ratings yet
- Answers For Chapter 13Document51 pagesAnswers For Chapter 13karensheuNo ratings yet
- More Trigonometric SubstitutionDocument35 pagesMore Trigonometric SubstitutionArsalan JumaniNo ratings yet
- Ministerul Invatamintului Tineretului din Republica MoldovaDocument8 pagesMinisterul Invatamintului Tineretului din Republica Moldovadanutzamihairo4738No ratings yet
- Yjc h2 Math p1 SolutionsDocument12 pagesYjc h2 Math p1 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 SolutionDocument5 pagesChapter 1 SolutionFaraa BellaNo ratings yet
- MST209 2005solutionsDocument6 pagesMST209 2005solutionsrashismart2000No ratings yet
- 2009 2 Art 04Document8 pages2009 2 Art 04Raja RamNo ratings yet
- L03 Rev2 LCCDE LaplaceTransform PDFDocument45 pagesL03 Rev2 LCCDE LaplaceTransform PDFJoseph Angelo BuenafeNo ratings yet
- EGM6341 Sol HW 01Document22 pagesEGM6341 Sol HW 01Redmond R. ShamshiriNo ratings yet
- Binomial Theorem FormulaDocument13 pagesBinomial Theorem FormulaLordOnBoardNo ratings yet
- Unit VDocument10 pagesUnit VAbinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Two DOFDocument78 pagesTwo DOFMazhar Ali100% (1)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- A Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"From EverandA Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- FormasDocument8 pagesFormaspigotoNo ratings yet
- CIRCO MATEMATICO Alianza Editorial Martin Gardner 1985Document238 pagesCIRCO MATEMATICO Alianza Editorial Martin Gardner 1985jsantosr2001No ratings yet
- 1st Periodical Exam in Math 7-LONGDocument2 pages1st Periodical Exam in Math 7-LONGDianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- Maths Common ErrorDocument9 pagesMaths Common ErrorHemantPandayNo ratings yet
- Essential Calculus. Early Transcendentals Formulae Booklet 2Document10 pagesEssential Calculus. Early Transcendentals Formulae Booklet 2Loh Jun XianNo ratings yet
- Ratio and Proportion: Mathematics For Engineering TechniciansDocument15 pagesRatio and Proportion: Mathematics For Engineering TechniciansImranNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections Worksheet: Equations, Foci, EccentricitiesDocument2 pagesConic Sections Worksheet: Equations, Foci, EccentricitiesbhartNo ratings yet
- Maths Term 2 PracticeDocument2 pagesMaths Term 2 PracticeSambhav SinghalNo ratings yet
- AP Calc BC Part 2Document31 pagesAP Calc BC Part 2Jiwon ShinNo ratings yet
- Victoria Reyes ES 2019 1st State of the School Address SummaryDocument3 pagesVictoria Reyes ES 2019 1st State of the School Address SummaryIrra ReyesNo ratings yet
- Calculus FormulaDocument2 pagesCalculus FormulaGeramagliquiangNo ratings yet
- TS SSC MaterialDocument5 pagesTS SSC Materialindian2013No ratings yet
- Resume-Keara Mountain BaileyDocument2 pagesResume-Keara Mountain Baileyapi-251035870No ratings yet
- Uptown School - Admission RequirementsDocument2 pagesUptown School - Admission RequirementsfarraheshamNo ratings yet
- AREA UNDER CURVE IIT ADV Previous Year Q Bank Till 2020Document10 pagesAREA UNDER CURVE IIT ADV Previous Year Q Bank Till 2020Arnav SinghalNo ratings yet
- Reading Preparedness As An Element in Developing Reading SkillsDocument9 pagesReading Preparedness As An Element in Developing Reading SkillsasakapaaaaaNo ratings yet
- IGO 2014 - 2021 Problems and SolutionsDocument275 pagesIGO 2014 - 2021 Problems and SolutionsCyka BlyatNo ratings yet
- Angles and Parallel Lines GuideDocument7 pagesAngles and Parallel Lines GuidemuralleNo ratings yet
- 04 Skema Tlo Mte3101Document6 pages04 Skema Tlo Mte3101Siti KhadijahNo ratings yet
- PTA Narrative and OfficersDocument2 pagesPTA Narrative and OfficersJennelyn CalilanNo ratings yet
- Flyer+ +How+to+Excel+in+Law+SchoolDocument1 pageFlyer+ +How+to+Excel+in+Law+Schools0falaNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument29 pagesThesisapi-250700589100% (1)
- Rabbit FinalDocument3 pagesRabbit FinalcleannnmNo ratings yet
- Complex NumbersDocument15 pagesComplex NumbersCYNo ratings yet
- Mikho ResumeDocument2 pagesMikho Resumeapi-283579568No ratings yet
- Milam Candice ResumeDocument1 pageMilam Candice Resumeapi-277775718No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Maths Notes - Circles PDFDocument14 pagesCBSE Class 11 Maths Notes - Circles PDFBhawani Singh Balot100% (1)
- Worksheet On Set and Venn DiagramDocument20 pagesWorksheet On Set and Venn DiagramMario Bacani Pidlaoan100% (1)
- Math SetDocument15 pagesMath SetLyra FloridoNo ratings yet