Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic For Presentation
Uploaded by
Praachi DeshmukhOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic For Presentation
Uploaded by
Praachi DeshmukhCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic for Presentation:
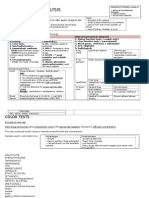
Analysis of Beverages, Analysis of Alcoholic Beverages as per BIS and PFA Act, Detection & Determination of ethanol, furfural, organic acids, aldehydes, chloral hydrate, methanol and ethylene glycol in liquors by colour tests, TLC, GC, & GCMS methods, Distinction between licit & illicit liquors.
By, Praachi Deshmukh MSc I Institute of Forensic Science, Mumbai.
Analysis of Beverages:
Beverages are nothing but Drink / Liquid for human consumption. There are main two types: Alcoholic & Non-Alcoholic Non-Alcoholic Beverage is also called as Carbonated Water means Water (as per PFA std.) impregnated with carbon dioxide under pressure and may contain any of the following singly or in combination: Sugar, liquid glucose, dextrose monohydrate, invert sugar, fructose, honey, fruits and vegetable extractives, permitted flavouring, colouring matter, preservatives, emulsifying and stabilizing agents, citric acid, fumaric acid and sorbitol, tartaric acid, phosphoric acid, lactic acid, ascorbic acid, malic acid, edible gums, edible gelatin, salts of sodium, calcium, magnesium, vitamins, caffeine not exceeding 145 parts per million, ester-gum (glycerol ester of wood rosin) not exceeding 100parts per million, quinine salts (sulphate)<100ppm. It may also contain saccharine sodium,100ppm
Analysis of Nonalcoholic drink:
Tests for presence of Glycerol esters of wood rosins commonly known as ester-gum: 1. Identification: Insoluble in water, soluble in acetone and in benzene 2. IR spectrum: obtain IR spectra of a sample deposited on potassium bromide plate scan between 600 and 4000 wave numbers. Compare with pure ester gum. Tests for Absence of toll oil rosin (Sulphur test): When sulphur containing organic compounds are heated in the presence of sodium formate, sulphur is converted into hydrogen sulphide which is readily detected by use of lead acetate paper. A positive test indicates use of tail oil rosin instead of wood rosin.
Arsenic Not more than 3ppm Lead - Not more than 10ppm Heavy metals - Not more than 40ppm Acid value Between 3 and 9 Hydroxyl number Between 15 & 45. Analysis of Alcoholic Beverages An alcoholic beverage is a drink containing ethanol, commonly known as alcohol. Toddy: Toddy means the sap from coconut, date, toddy palmtree or any other kind of palm tree which has undergone alcoholic fermantation. 1. White cloudy in appearance 2. with sediments on storage, 3. possess characteristic flavour derived from sap 4. fermentaion without adding extraneous alcohol. 5. Also be free from: chloral hydrate, paraldehyde sedative, tranquilizer & artificial sweetener. Standards to be confirmed: Alcohol content Not less than 5%v/v Total acid as tartaric acid - Not more than 400gms Volatile acid as acetic acid Not more than 100gms Analysis of Alcoholic Beverages The BIS (Bureau of Indian Standards) prescribes methods of test for alcoholic drinks. For estimation of esters, higher alcohols, aldehydes, furfural, & methanol GC (gas chromatographic) method is given in Annex A as alternative method. Purpose: To follow 1. Prevention of Food Adultration Act 1954 and rules framed thereunder; 2. Standards of Weights & measures Rules, 1977; & 3. State Excise Duty Rules Alcoholic Drinks : Methods of Test Colour Tests: Qualitative Analysis of Liquor Test for Ethyl Alcohol: 1. Iodoform Test: 1ml sample + 1ml 5% sodium hydroxide + iodine soln dropwise with shaking until liquid becomes persistent dark brown in colour. Keep for 2-3 min. If iodine colour disappears, add more drops of iodine until persistant brown colour. Add few drops of dil sod
hydroxide to remove extra iodine. Add equal volume of water, keep for 10min. Yellow crystalline ppt = positive test for presence of ethanol. 2. Dichromate test: 1ml sample + 0.2ml2%pot dichromate sol + 1ml concn.sulphuric acid = Yellow colour of dichromate changes to green or blue = presence of ethanol. Test for Methanol: 1. Chromtropic test: 1ml sample in tt + 2ml pot permangnate sol = shake well + few crystals of sod bisulphate till disappearance of colour + 1ml chromotropic acid + concn sulpuric acid slowly with inner side wall of the tt upto 15ml. Appearance of violet colour = presence methanol. 2. Schiffs Reagent Test: 4.5ml sample + 0.5ml ethanol + 2ml 3% pot permangnate sol + 2ml phosphoric acid. Keep for 10min. Add 1ml 10%oxalic acid followed by 1ml conc sulpuric acid. + 5ml Schiffs reagent. Keep for 30min. Observe colou, if purple = methanol present. Parallel expt. To be carried out with control and blank. Test for Furfural: 1. 5ml sample + 1ml aniline + 0.5ml hydrochloric acid + Keep for 15 min. = Red colour = Furfural is present. 2. 2ml sample + 0.2ml aniline + 0.4ml glacial acetic acid. Red colour develops in few seconds & reaches its max. intensity in 5-10 minutes, if furfural is present. 2ml sample + 1ml aniline acetate sol. (10%v/v) = Red colour develops at RT 25-30C & reaches its max in 1-5 minutes. = furfural is present. Quantitative Determination Determination of Furfural: If red colour develops in the colour test of furfural, proceed for quantitative estimation. Dilute measured portion of distillate (V1) with 50% furfural free alcohol to 50ml. Add 2ml colourless aniline & then 0.5ml hydrochloric acid. Mix and keep at 15C for 15min. Compare colour developed with std furfural solution. Calculation:
Furfural, gms/100litres of absolute alcohol = W * 1000 * 100*100 / V1 * V2 where, V1 = Volume of experimental solution used for estimation, V2 = Alcohol % by volume. Determination of Ethyl Alcohol Content: By finding out specific gravity of the distillate at a particular temperature with the help of Pyknometer .
Obtain corresponding alcohol percent by volume from the tables given in IS 3506. Determination of Aldehydes: 50ml distillate of liquor + 10ml bisulphite sol = Keep in dark fo 30min with occasional shaking. Add 25ml std iodine sol & back titrate excess against std sodium thiosulphate sol using starch indicator. Run a blank taking 50ml distilled water. The difference in titration value, in ml of sodium thiosulphate sol (V), gives equivalent aldehyde. Calculation: V * 0.0011 * 100 *1000* 2 / V1 V1 = alcohol % by volume Note: 1ml of sodium thiosulphate sol = 0.0011 g of acetaldehyde. Determination of Methanol: Two methods, viz., 1. spectrophotometric method & 2. gas chromatography method are employed. The spectrophotometric method is sufficiently sensitive for routine type of analysis. The gas chromatography method is more sensitive and shall serve as an alternative method. Spectrophotometric Method Spectrophotometer of any make with wavelength range from 350 to 700nm & maximum band width of 5nm. Has to prepare Methanol std sol from stock solution, sod salt of chromtropic acid sol, pot permangnate sol. Distill 50ml of sample, take 40 ml of distillate. Dilute 1ml of distillate to 5ml with dist. Water, shake well, take 1ml of this solution, 1ml dist. Water (for blank), & 1ml of methanol std sol in tt and keep in ice-cold water bath. Add to each tt 2ml pot permangnate, keep for 30min. Decolourise by adding a little sod bisulphite & 1ml chromotropic acid. Mix well, add 15ml sulphuric acid slowly with swirling, place in hot wterbath at 80C for 20min. Observe colour development from violet to red. Cool reaction mixture and measure the absorbance at 575nm using 1cm path length cell. Calculation: Methanol content in g/100litres of absolute ethanol = A2*C*D*1000*100*100 / A1*S where,
A2= Absorbance for sample solution, C= Concentration of methanol std solution, g/ml D= Dilution factor for sample solutuio, A1= Absorbance for methanol std solution, & S= Ethanol content of liquor sample in %v/v. Gas Chromatography Method GC equipped with Flame ionization detector & split injection port with tempretures at 250C. Inject 2microliter of methanol std sol into chromatograph and record chromatogram. Determine the retention time of methanol and n-pentanol. Inject 2 microlire of sample solution into chromatograph and record chromatogram. Calculation: Methanol content in g / 100l absolute alcohol = R2*C*D*1000*100*100 / R1*S where, R2=peak ratio of methanol to n-pentanol for sample solution, C=Concentration of methanol in std solution, D= dilution factor for sample solution, R1= peak ratio of methanol to n-pentanol for std solution, S= ethanol content of liquor sample in percent v/v. Distinction between licit & illicit liquors
You might also like
- Toxicological AnalysisDocument9 pagesToxicological AnalysissarahabdullahNo ratings yet
- ColorimetryDocument21 pagesColorimetryM.PRASAD NAIDUNo ratings yet
- Ninhydrin TestDocument3 pagesNinhydrin Testchanchan26100% (1)
- Forensic - PoisonsDocument36 pagesForensic - PoisonsNitin Sherwal100% (1)
- HPTLC-High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography: - Piyush L. Agrawal M.pharm - (Q.A.)Document39 pagesHPTLC-High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography: - Piyush L. Agrawal M.pharm - (Q.A.)Piyush Agrawal100% (2)
- NinhydrinDocument5 pagesNinhydrinMahboob Iqbal0% (1)
- Standard Operating Procedure: Biosystems Ba400Document5 pagesStandard Operating Procedure: Biosystems Ba400Mohamad QinaoiNo ratings yet
- Forensic Laborartory by Mr. Dinesh HarpalaniDocument17 pagesForensic Laborartory by Mr. Dinesh HarpalaniSaurabh Singh Rajput100% (1)
- Presentation On Forensic ToxicologyDocument23 pagesPresentation On Forensic ToxicologyZaba Gillani100% (1)
- Acute & Chronic Toxicity TestingDocument33 pagesAcute & Chronic Toxicity Testingaziskf0% (1)
- HPLC Analysis of Vitamin CDocument1 pageHPLC Analysis of Vitamin CHuong NguyenNo ratings yet
- 5.hafta Ingilizce Bik Pratik-3Document7 pages5.hafta Ingilizce Bik Pratik-3ManjuNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Enumeration of Bacteria in Water and FoodDocument30 pagesIsolation and Enumeration of Bacteria in Water and FoodOld Lake100% (1)
- Forensic ToxicologyDocument32 pagesForensic Toxicologychrisr310100% (1)
- Staining TechniquesDocument19 pagesStaining TechniquesSwayamprakash PatelNo ratings yet
- Tramadol Hydrochloride PDFDocument32 pagesTramadol Hydrochloride PDFMy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Mass Spectroscopy and Raman Spectroscopy.Document27 pagesMass Spectroscopy and Raman Spectroscopy.kritika100% (4)
- Paint ChipDocument6 pagesPaint ChipatirahNo ratings yet
- Application of Column Chromatography in PharmacyDocument5 pagesApplication of Column Chromatography in PharmacyJay Shah100% (2)
- Colorimetric+Determination+of+Skin+Colour 2007Document11 pagesColorimetric+Determination+of+Skin+Colour 2007mirza nadeemNo ratings yet
- Forensic Toxicology: DR Sagal Omar Anatomical PathologistDocument16 pagesForensic Toxicology: DR Sagal Omar Anatomical PathologistCabdiNo ratings yet
- Drug Elimination: Termination of Drug ActionDocument80 pagesDrug Elimination: Termination of Drug ActionLidyaNo ratings yet
- Hair Dye Chemical SensitizationDocument18 pagesHair Dye Chemical SensitizationSarah CarrollNo ratings yet
- Colorimeter PDFDocument9 pagesColorimeter PDFEnrique VidalNo ratings yet
- LC MsDocument24 pagesLC MsVshn VardhnNo ratings yet
- 5 CH104 Paper and TLCDocument18 pages5 CH104 Paper and TLCHemma KusumaningrumNo ratings yet
- HPLCDocument8 pagesHPLCAdi KusumaNo ratings yet
- Gravimetric AnalysisDocument5 pagesGravimetric AnalysisjeffjerardcandaNo ratings yet
- Protein Extraction From AlgaeDocument8 pagesProtein Extraction From AlgaecookooponyNo ratings yet
- Principles of IR SpectrosDocument6 pagesPrinciples of IR SpectrosSHEHA NUR AZZAHRA IBRAHIM -No ratings yet
- ASTDR - Toxicological Profil of CadmiumDocument487 pagesASTDR - Toxicological Profil of CadmiumpangkoklunNo ratings yet
- Unit - Iii ChromatographyDocument18 pagesUnit - Iii ChromatographyUdayaraj NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Collection of Biological Samples in Forensic ToxicologyDocument53 pagesCollection of Biological Samples in Forensic ToxicologyJhoŋ AcerosNo ratings yet
- Volumetric AnalysisDocument7 pagesVolumetric AnalysisZari Sofia LevisteNo ratings yet
- Spectrophotometric and Chromatographic Analysis of Amino Acids Present in Leaves of Ailanthus ExcelsaDocument5 pagesSpectrophotometric and Chromatographic Analysis of Amino Acids Present in Leaves of Ailanthus ExcelsaRam VijayNo ratings yet
- S09 Lec PesticidesDocument42 pagesS09 Lec Pesticidesmalak amerNo ratings yet
- Saliva As A Forensic ToolDocument3 pagesSaliva As A Forensic ToolPeertechz Publications Inc.No ratings yet
- SpectrosDocument28 pagesSpectrosPraveen Kumar AvvaruNo ratings yet
- URIC ACID LyphoDocument2 pagesURIC ACID LyphoDharmesh Patel50% (2)
- Introduction CM8002 Forensic ScienceDocument67 pagesIntroduction CM8002 Forensic ScienceKelly MerieNo ratings yet
- 5.DNA PolimorfismDocument95 pages5.DNA PolimorfismGrassellaNo ratings yet
- Absorbance and Fluorescence Spectroscopies of Green Fluorescent ProteinDocument24 pagesAbsorbance and Fluorescence Spectroscopies of Green Fluorescent ProteinMadel Tutor ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Assay of Sodium BenzoateDocument6 pagesAssay of Sodium BenzoateMeziane BouktitNo ratings yet
- Role of Analytical Chemists in Industry - 2Document22 pagesRole of Analytical Chemists in Industry - 2hemakumarbNo ratings yet
- Phytochemical Screening of Coriander Sativum LinnDocument5 pagesPhytochemical Screening of Coriander Sativum LinnMusfira Dewy SuardiNo ratings yet
- 03e Separation of Benzoic Acid and NaphthaleneDocument3 pages03e Separation of Benzoic Acid and NaphthaleneReyo VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- FDA's Overview of The Guidance For Industry: Control of Nitrosamine Impurities in Human DrugsDocument57 pagesFDA's Overview of The Guidance For Industry: Control of Nitrosamine Impurities in Human DrugsPravin GaIkwadNo ratings yet
- Nephelometry and TurbidimetryDocument21 pagesNephelometry and TurbidimetrySrikrishnaNo ratings yet
- Method Development and Validation of Roflumilast in TabletDocument6 pagesMethod Development and Validation of Roflumilast in TabletjamonlineNo ratings yet
- RNA Extraction Is The Purification ofDocument3 pagesRNA Extraction Is The Purification ofAli Akand Asif100% (1)
- Toxicology Case Studies Carbon MonoxideDocument5 pagesToxicology Case Studies Carbon MonoxideMark Jayson T. AsinoNo ratings yet
- High Performance Liquid Chromatography: Barba, Biadomang, Dulos CHEM 127.1Document48 pagesHigh Performance Liquid Chromatography: Barba, Biadomang, Dulos CHEM 127.1Karina NarcisoNo ratings yet
- Chemiluminescence and Bioluminescence MeasurementsDocument11 pagesChemiluminescence and Bioluminescence MeasurementsShelma Fitri AinulshidqiNo ratings yet
- Recombinant ReportDocument4 pagesRecombinant Report门门No ratings yet
- Ant4516 ACTIVITY 2 WORKSHEETDocument9 pagesAnt4516 ACTIVITY 2 WORKSHEETPrince Tafari MartinNo ratings yet
- Application of HPLCDocument11 pagesApplication of HPLCIts KazmiNo ratings yet
- Collection & Preservation of VisceraDocument4 pagesCollection & Preservation of VisceraBOBIN SARMANo ratings yet
- Forensic ToxicologyDocument11 pagesForensic ToxicologySeptiandry Ade PutraNo ratings yet
- 15 Spektro 01 Aas and AesDocument81 pages15 Spektro 01 Aas and AesmaudyNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Chromatography Spray ReagentsDocument17 pagesPreparation of Chromatography Spray Reagentshosseini_9864No ratings yet
- Shimadzu - Determination of 59 Potential Allergens in Perfumes by Comprehensive GCXGC (QMS)Document6 pagesShimadzu - Determination of 59 Potential Allergens in Perfumes by Comprehensive GCXGC (QMS)FavioNo ratings yet
- Rasa Rat Nasa Muc ChayaDocument8 pagesRasa Rat Nasa Muc ChayatemmNo ratings yet
- Manual FM200 PDFDocument44 pagesManual FM200 PDFDIOGO FRANCO PUREZANo ratings yet
- Template IJoSTDocument8 pagesTemplate IJoSTanatun nisa munamahNo ratings yet
- ChemCAD Assignment SPR05Document3 pagesChemCAD Assignment SPR05laiping_lum0% (1)
- tmp327F TMPDocument228 pagestmp327F TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- ABB Epoxy PoleDocument11 pagesABB Epoxy Poleminsoo11No ratings yet
- Radiative Heat Transfer in Participating Media A ReviewDocument20 pagesRadiative Heat Transfer in Participating Media A ReviewSanjeevan Lakra0% (1)
- IBR Design Calculations - FinalDocument6 pagesIBR Design Calculations - Finalshazan100% (1)
- Centrifugal Compressors SRLDocument20 pagesCentrifugal Compressors SRLsammar_10No ratings yet
- Ma 333 MDocument13 pagesMa 333 MdeztruktorNo ratings yet
- Ventilation Rates - ASHRAE 62.1-2013-2Document4 pagesVentilation Rates - ASHRAE 62.1-2013-2Mohammed Abdul MoiedNo ratings yet
- Zangar C Water Percolation 5 Water OcrDocument86 pagesZangar C Water Percolation 5 Water Ocrreem.ranoom.moonNo ratings yet
- S1 Types of Energies and Energy TransferDocument25 pagesS1 Types of Energies and Energy TransferGkid GkidNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Tent StructuresDocument65 pagesAnalysis of Tent Structuressri_amartNo ratings yet
- Multi Field Coupling Dynamic Modeling and Simula 2014 Simulation Modelling PDocument24 pagesMulti Field Coupling Dynamic Modeling and Simula 2014 Simulation Modelling P刘文No ratings yet
- Cuphea OilDocument8 pagesCuphea Oilmssganesh1305No ratings yet
- Punjab Boards 10th Class Physics Book English Medium 6368072829234769390 PDFDocument201 pagesPunjab Boards 10th Class Physics Book English Medium 6368072829234769390 PDFSaqib SaleemNo ratings yet
- Theories of FailureDocument77 pagesTheories of FailureAnonymous 6HADGUEXDNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Powerpoint IIDocument34 pagesChapter 6 Powerpoint IIhdavey100% (1)
- Brochure - Joint Sealants For Building Envelope WaterproofingDocument36 pagesBrochure - Joint Sealants For Building Envelope WaterproofingBudi Max100% (1)
- Tri State Mining District: OverviewDocument10 pagesTri State Mining District: OverviewChristopher WisemanNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Quarter 4 - Week 4 Module 4: PH of Buffer SolutionsDocument12 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Quarter 4 - Week 4 Module 4: PH of Buffer SolutionsHazel EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- SM1F03NSK SinopowerDocument11 pagesSM1F03NSK SinopowerleandroNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Aspects in The OxidationDocument5 pagesKinetic Aspects in The OxidationKatiane MesquitaNo ratings yet
- Fabr Pneumatic 033009Document28 pagesFabr Pneumatic 033009daniper89No ratings yet
- Analytica Chimica Acta: Jacopo La Nasa, Francesca Modugno, Matteo Aloisi, Anna Lluveras-Tenorio, Ilaria BonaduceDocument8 pagesAnalytica Chimica Acta: Jacopo La Nasa, Francesca Modugno, Matteo Aloisi, Anna Lluveras-Tenorio, Ilaria Bonaducejuanda.scienceNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Helical Coil Heat Exchangers: by V.Swapna Priya Guide R S MauryaDocument23 pagesAnalysis of Helical Coil Heat Exchangers: by V.Swapna Priya Guide R S MauryaSwapna Priya VattemNo ratings yet
- Insert.C.f.a.s. Lipids.03018415001.V7.enDocument2 pagesInsert.C.f.a.s. Lipids.03018415001.V7.enGuneyden Guneyden100% (1)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Process Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityFrom EverandProcess Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (90)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsFrom EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsNo ratings yet
- Sodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyFrom EverandSodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (21)
- Guidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisFrom EverandGuidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableFrom EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsFrom EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (146)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideFrom EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNo ratings yet
- Tribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsFrom EverandTribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsFrom EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Bioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookFrom EverandBioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Transformer: The Deep Chemistry of Life and DeathFrom EverandTransformer: The Deep Chemistry of Life and DeathRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Water-Based Paint Formulations, Vol. 3From EverandWater-Based Paint Formulations, Vol. 3Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressFrom EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)