Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Grammar For 1º-2º Eso-1
Uploaded by
Anastasia GarcíaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Grammar For 1º-2º Eso-1
Uploaded by
Anastasia GarcíaCopyright:
Available Formats
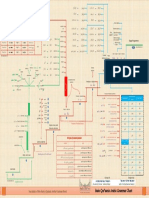
English grammar for 1 and 2 ESO
English Department. IES Hermgenes Rodrguez
PERSONAL PRONOUNS (pronombres personales)
I You He She It
SINGULAR
Yo T l Ella Ello (animales o cosas)
PLURAL
We You They
Nosotros as Vosotros as Ellos as
VERB TO BE (ser / estar)
AFFIRMATIVE I am Im You are Youre He / she / it is He / she / its We are Were You are Youre They are Theyre NEGATIVE Im not You arent He / she / it isnt We arent You arent
They arent
INTERROGATIVE Am I? Are you? Is he / she / it? Are we? Are you? Are they?
A/AN (un/ una), SOME (algunos/ algunas/ algo de)
A + consonant: a house, a person, a bag... An + vowel: an apple, an elephant, an intelligent person Some: Algunos, algunas, algo de: Some houses, some water
PLURAL FORMS (los plurales)
Forma normal: Nombre + -s: house-houses Cuando el nombre acaba en O, -S, -SS, -SH, -CH, -X: Nombre + -es: dish-dishes Cuando el nombre acaba en consonante +Y: Se quita la Y y se pone el nombre + -ies: diary-diaries
IRREGULAR PLURALS (plurales irregulares)
SINGULAR Child Man Woman Mouse Fish Sheep Tooth Foot PLURAL Children Men Women Mice Fish Sheep Teeth Feet SIGNIFICADO Nio-os Hombre-s Mujer-es Ratn-ratones Pez-peces Oveja-s Diente-s Pie-s
PREPOSITIONS OF TIME AT, IN, ON (preposiciones de tiempo at, in, on)
Preposicin AT ON Se usa con: Horas: at 7 oclock, at midnight Night: at night Das: On Monday, on Sunday Fechas: On May, 14th Partes del da (menos night): In the morning, in the afternoon Meses: In January Estaciones: In the summer Aos: In 2006
IN
English grammar for 1 and 2 ESO
English Department. IES Hermgenes Rodrguez
PREPOSITIONS OF PLACE (preposiciones de lugar)
next to (near)
VERB TO HAVE (GOT) (haber / tener)
AFFIRMATIVE I have (got) Ive (got) You have (got) Youve (got) He / she / it has (got) He / she / its (got) We have (got) Weve (got) You have (got) Youve (got) They have (got) Theyve (got) NEGATIVE I havent (got) You havent (got) He / she / it hasnt (got) We havent (got) You havent (got) They havent (got) INTERROGATIVE Have I (got)? Have you (got)? Has he / she / it (got)? Have we (got)? Have you (got)? Have they (got)?
THERE IS, THERE ARE (el hay espaol)
THERE IS: Cuando decimos que hay UNA COSA there is a house o algo que NO PODEMOS CONTAR (azcar, agua...) there is water THERE ARE: Cuando decimos que hay VARIAS COSAS there are three houses Forma negativa: THERE ISNT, THERE ARENT Forma interrogativa: IS THERE...? y ARE THERE?
DEMONSTRATIVES: THIS, THAT, THESE, THOSE (esto, eso, estos, esos)
THIS THAT THESE THOSE Esto, a Eso, a Estos, as Esos, as
POSSESSIVE ADJECTIVES (adjetivos posesivos)
I YOU HE SHE IT WE YOU THEY MY YOUR HIS HER ITS OUR YOUR THEIR Mi mis Tutus Su sus (l) Su sus (ella) Su sus (ello) Nuestroaosas Vuestroaosas Su sus (ellos-as)
SAXON GENITIVE (genitivo sajn, para posesin: La casa de Pedro, el libro de Antonio)
POSEEDOR + S (equivalente al de) + COSA POSEDA NO se pone the para indicar LA casa de, sino que se inicia la frase con el nombre del dueo Ejemplo: The Peters house (la casa de Pedro) Si hay varios poseedores: La palabra ya acaba en s, por lo que SLO SE AADE UNA tras la palabra:The boys house (la casa de los chicos)
English grammar for 1 and 2 ESO
English Department. IES Hermgenes Rodrguez
SIMPLE PRESENT (TODOS LOS VERBOS MENOS TO BE / TO HAVE GOT)
Se usa para hbitos y descripciones 1. FORMA
En el afirmativo:
Se pone el verbo tal igual que en infinitivo, pero en he/ she/ it se aade una S al final En los verbos que acaban en S / SH / CH / X se pone es (watchwatches) En los verbos que acaban en O se pone es (do-does) En los verbos que acaban en CONSONANTE + Y la Y se sustituye por ies (study-studies)
En el negativo: se pone sujeto + DONT + verbo
Para la tercera persona: He / she / it + DOESNT + verbo
En el interrogativo: se pone DO + sujeto + verbo
Para la tercera persona: DOES + he / she / it + verbo
EJEMPLO: VERBO RUN (yo corro) AFFIRMATIVE I RUN YOU RUN HE / SHE / IT RUN S WE / YOU / THEY RUN NEGATIVE I DONT RUN YOU DONT RUN HE / SHE / IT DOESNT RUN WE / YOU / THEY DONT RUN INTERROGATIVE DO I RUN? DO YOU RUN? DOES HE / SHE / IT RUN? DO WE / YOU / THEY RUN?
2. FREQUENCY ADVERBS (adverbios de frecuencia)
Always Siempre
Usually / normally
Normalmente
Often A menudo
Sometimes A veces Siempre
Seldom Rarely Hardly ever
Never Nunca
Rara vez
Se ponen DETRS del sujeto y JUSTO DELANTE del verbo Ejemplo: Do you always buy milk? I sometimes buy milk 3. TIME EXPRESSIONS FOR THE PRESENT SIMPLE (expresiones de tiempo)
Once Twice Three times Four times 50 times
a day a week a month a year
Una vez Dos veces Tres veces Cuatro veces Cincuenta veces
al da a la semana al mes al ao
Every + day, week, month In + the morning, afternoon, evening At night
Todos los das, todas las semanas, meses... Por la maana, por la tarde, por la noche Por la noche (al acostarse)
Se ponen al final de la frase Ejemplo: I study French three times a week (yo estudio francs tres veces por semana) 4. DAILY ACTIVITIES (actividades de la vida diaria)
English grammar for 1 and 2 ESO Wake up Get up Have a shower Have breakfast Have lunch Have dinner Get dressed Leave home Go to school / work Study Work Leave school / work
English Department. IES Hermgenes Rodrguez Come back home Watch TV Listen to music Do the homework Do the housework Go shopping Play on the computer Play a musical instrument Meet the friends Go out / party / to the disco Go to bed Sleep
Despertarse Levantarse Ducharse Desayunar Comer (a medioda) Cenar Vestirse Irse de casa Ir al colegio / trabajo Estudiar Trabajar Salir del cole /trabajo
Volver a casa Ver la televisin Escuchar msica Hacer los deberes Hacer las tareas de la casa Ir de compras Jugar con el ordenador Tocar un instrumento Ver a los amigos Salir / ir de fiesta / a la disco Irse a la cama Dormir
LOVE, LIKE, DONT LIKE, HATE (encantar, gustar, no gustar, odiar)
Son verbos que indican lo que nos gusta o nos disgusta y los solemos utilizar en presente simple. 1. USO: I love pasta (me encanta la pasta) I like pizza (me gusta la pizza) Ms nombre I dont like broccoli (no me gusta el brcoli) I hate carrots (odio las zanahorias) I love EATING pasta (me encanta COMER pasta) I like EATING pizza (me gusta COMER pizza) Ms verbo (TIENE QUE IR EN -ING) I dont like EATING broccoli (no me gusta COMER brcoli) I hate EATING carrots (odio COMER zanahorias)
WOULD + LOVE, LIKE (me encantara, me gustara)
Esta forma es el CONDICIONAL de los verbos love o like, por lo que indica lo que nos gustara. 1. FORMA: Sujeto + WOULD + love / like + TO+ VERBO EN INFINITIVO WOULD se puede contraer en la forma d 1. USO: Deseos Id love to go to the theatre (me encantara ir al teatro) Ofrecimientos (te gustara?) Would you like to go to the cinema? (te gustara ir al cine?) Aceptacin del ofrecimiento Yes, please!, Id love to! (S, por favor!, me encantara)
English grammar for 1 and 2 ESO
English Department. IES Hermgenes Rodrguez
ASKING FOR THE TIME (pedir la hora)
A: Excuse me, what time is it? / whats the time?, please: Disculpe, qu hora es, por favor? B: Its (ms la hora): Son las Siempre se dicen los minutos ANTES que la hora, excepto cuando es la hora en punto A: Thank you: Gracias B: Youre welcome: De nada
HORA + OCLOCK
A QUARTER TO + HORA SIGUIENTE
MINUTOS +TO+ HORA SIGUIENTE
MINUTOS +PAST+ HORA
A QUARTER PAST + HORA
HALF PAST + HORA
TIMETABLES (horarios)
A: What time do you usually + (INFINITIVE)?: A qu hora sueles t + (INFINITIVO) B: I usually + (INFINITIVE) + AT... + TIME: Normalmente yo + (INFINITIVO) a las + HORA I usually go to school at seven oclock (normalmente voy al colegio a las siete en punto) I always study French at half past five (siempre estudio francs a las cinco y media)
SOME and ANY (algunos, algunas, ningunos, ningunas, algo de, nada de)
Some Afirmativas Interrogativas Any Negativas Algunos, algunas Algo de Algunos, algunas Algo de Ningunos, ningunas Nada de
There ARE SOME books on the shelf There IS SOME water in the jar ARE there ANY books on the shelf? IS there ANY water in the jar? There ARENT ANY books on the shelf There ISNT ANY water in the jar
MODAL VERBS (verbos modales)
Si van solos NO tienen ningn significado. Por ello, les sigue un infinitivo SIN TO Para hablar de habilidades Para pedir permiso Para dar permiso Para hablar de deberes Para dar prohibiciones
CAN / CANT MUST MUSTNT
I can play the guitar Can I go to the toilet, please? Yes, you can / No, you cant I must study hard I mustnt smoke
PRESENT CONTINUOUS
English grammar for 1 and 2 ESO English Department. IES Hermgenes Rodrguez Se usa para hablar de: Acciones en el momento de hablar (I am talking=estoy comiendo) Planes futuros (en ese caso se traduce como ir a + verbo): Im travelling tomorrow=voy a viajar maana. Esto no lo vamos a estudiar ahora, pero os lo digo para que lo sepis para otro ao Se traduce por estoy comiendo, est hablando, etc. OJO: En este tiempo verbal, en espaol utilizamos el GERUNDIO (aquellos verbos que acaban en ando / -endo, como cantando, escribiendo, corriendo, etc. Este gerundio lo hacemos en ingls aadiendo ING al verbo (singing, writing, running) 1. FORMA: SUJETO + TO BE EN PRESENTE (afirmativo, negativo o interrogativo)+ VERBO EN ING AFFIRMATIVE I am studying You are studying He / she / it is studying We are studying You are studying They are studying NEGATIVE Im not studying You arent studying He / she / it isnt studying We arent studying You arent studying They arent studying INTERROGATIVE Am I studying ? Are you studying ? Is he / she / it studying ? Are we studying? Are you studying? Are they studying?
2. REGLAS ORTOGRFICAS AL PONER ING: Verbos que acaban en e muda: sta desaparece al aadir ing: come-coming Verbos que acaban en ie: la ie se cambia por y antes de aadir ing: lie-lying Verbos de una slaba que acaban en CONSONANTE+VOCAL+CONSONANTE: Se dobla la ltima consonante al aadir ing: plan-planning, stop-stopping Excepcin: Verbos que acaban en w, x, y: fix-fixing, play-playing 3. EXPRESIONS DE TIEMPO DE PRESENTE CONTINUO: Se ponen al final de la frase, y son: Now Right now At this moment At present Today Ahora Ahora mismo En este momento Ahora Hoy
English grammar for 1 and 2 ESO
English Department. IES Hermgenes Rodrguez
TO BE (SIMPLE PAST): Era, estaba / fue, estuvo
Significa era, estaba, fue, estuvo. Es la NICA forma en pasado que se forma de manera DISTINTA al resto de los verbos Funciona igual que el to be en presente para hacer el negativo (con nt) y para hacer la pregunta (verbo+sujeto). AFFIRMATIVE I was You were He / she / it was We / you / they were NEGATIVE I was nt You werent He / she / it wasnt We / you / they werent INTERROGATIVE Was I ? Were you ? Was he / she / it ? Were we / you / they ?
REST OF THE VERBS: SIMPLE PAST (pasado simple del resto de los verbos)
Para hacer el pasado del resto de los verbos tenemos que distinguir entre verbos regulares e irregulares. La dificultad slo existe en el afirmativo, puesto que en la forma negativa o interrogativa se usa LA MISMA FORMA para todos los verbos. No hay un mtodo para distinguir entre verbos regulares e irregulares. Los verbos irregulares son los de la segunda columna de la lista de verbos irregulares. El resto que estudiemos sern regulares. 1. SIMPLE PAST. AFFIRMATIVE: 1.a. PASADO DE LOS VERBOS REGULARES: Se aade ed a la palabra en infinitivo (forma que nos dan siempre para estudiar). EJEMPLO: FINISH = acabar. FINISH-ED = acabar en pasado NUNCA SE AADE OTRA COSA, NI SIQUIERA HAY CAMBIOS EN HE / SHE / IT Ejemplo: I studied Yo estudiaba-estudi You studied T estudiabas-estudiaste He / she / it studied l, ella, ello estudiaba-estudi We / you / they studied Nosotros-as, vosotros-as, ellos-as estudiaban-estudiaron Reglas ortogrficas de formacin del pasado regular: Verbos que acaban en e muda: slo se aade -d: bake-baked; hope-hoped Verbos que acaban en consonante + y: la y se cambia por i antes de aadir ed: study-studied; copy-
copied
Verbos formados por CONSONANTE+VOCAL+CONSONANTE: se dobla la ltima consonante al aadir ed: plan-planned, stop-stopped
1.b. PASADO DE LOS VERBOS IRREGULARES: Se usa la forma de la segunda columna de la lista de verbos irregulares para todos los pronombres (I, you, he...) Ejemplo: Verbo BUY (comprar): La 2 columna de la lista de los verbos es BOUGHT (compraba, comprabas) I bought Yo compraba-compr You bought T comprabas-compraste He / she / it bought l, ella, ello compraba-compr We / you / they bought Nosotros-as, vosotros-as, ellos-as compraban-compraron
English grammar for 1 and 2 ESO English Department. IES Hermgenes Rodrguez 2. SIMPLE PAST. AFFIRMATIVE AND INTERROGATIVE: Tiene dos ventajas: No tienes problemas de que el verbo sea regular o irregular porque usamos el infinitivo del verbo Funciona muy parecido al presente simple, porque necesita de AUXILIAR (recordad el DO, DOES, DONT, DOESNT), pero es an ms fcil porque no hacemos diferenciacin de tercera persona. 1. FORMA: Negativo: SUJETO + DIDNT + VERBO EN INFINITIVO + COMPLEMENTOS Interrogativo: DID + SUJETO + VERBO EN INFINITIVO + COMPLEMENTOS + ? Ejemplos: GO (ir) AFFIRMATIVE I went to school yesterday NEGATIVE I didnt go to school yesterday INTERROGATIVE Did you go to school yesterday?
2. TIME EXPRESSIONS FOR THE PAST TENSE: Yesterday (+ morning, afternoon, evening, night) Last + day/ night/week/month/year/ Monday, May, summer, night Two days / weeks/months/years + ago
Ayer (+ por la maana, tarde, noche) El pasado + da, noche, semana, mes, ao, lunes, mayo, verano, anoche... Hace + dos das, semanas, meses, aos...
PAST CONTINUOUS (pasado continuo)
Se usa para hablar de acciones que estaban A MEDIAS en un momento del pasado (I was talking = estaba comiendo) 1. FORMA: SUJETO + WAS / WERE + VERBO EN ING AFFIRMATIVE I was studying You were studying He / she / it was studying We/you/ they were studying NEGATIVE I wasnt studying You werent studying He / she / it wasnt studying We / you / they werent studying INTERROGATIVE Was I studying? Were you studying? Was he / she / it studying? Were we / you / they studying?
Se suele encontrar en frases: Para acciones que SE VEN INTERRUMPIDAS por algn suceso inesperado De pasado continuo I was having a shower WHEN the telephone rang con pasado simple (accin que est en desarrollo) (accin que interrumpe) Para acciones que se desarrollan al mismo tiempo SIN INTERRUMPIRSE De dos I was having a shower WHILE my dad was reading pasados continuos Ninguna accin interrumpe el desarrollo de la otra Las expresiones de tiempo son las MISMAS que las de pasado simple.
English grammar for 1 and 2 ESO
English Department. IES Hermgenes Rodrguez
THE FUTURE TENSE (el tiempo futuro)
Se puede realizar con TODOS estos tiempos verbales: Present Continuous Future of intention (TO BE GOING TO) Future with WILL
Expresiones de tiempo Necesidad de expresin de tiempo + ? Traduccin
Tomorrow Maana Next+day/week/month/year el prximo + da / semana / mes / ao Soon pronto In + 1,2,3 seconds /minutes/days/ weeks en 1,2,3 segundos / minutos / das SIEMPRE (para NO es necesario (el tiempo NO es necesario (el tiempo distinguirlo del presente verbal ya nos indica que es verbal ya nos indica que es continuo del momento de futuro) futuro) hablar) S+to be pres+v-ing. S+to be pres+going to+inf. S+will/ll+inf.
I am running
S+to be pres neg+v-ing.
Im going to run
S+to be neg pres+going to+inf.
Ill study
S+wont+inf.
Im not running
To be pres+S+v-ing.
I wont study
Will+S+inf.
Im not going to run
To be pres+S+going to+inf.
Are you running? Voy a correr
Are you going to run? Voy a correr
Will you study? Correr
EJEMPLOS: PRESENTE CONTINUO TO BE GOING TO WILL
Planes para un futuro CERCANO Planes para un futuro CERCANO o LEJANO Predicciones CON PRUEBAS Predicciones SIN PRUEBAS
Tracy is starting a new job on Saturday I am going to travel to Mexico next summer Look at those clouds! It is going to rain Im sure that the teacher will be angry today
English grammar for 1 and 2 ESO
English Department. IES Hermgenes Rodrguez
TELLING THE WAY (indicar el camino)
TURN LEFT TURN RIGHT DIALOGUE: A B A B B A B Gira a la IZQUIERDA Gira a la DERECHA GO STRAIGHT ON STOP Sigue recto Para
Can you tell me where the is, please? Yes, of course. Its in (street) How do I get there? Go straight on and take the first, second, third street on the left-right The is opposite-next to the Thank you! You are welcome. Bye!
Puede decirme dnde est el, por favor? S, claro. Est en la calle Cmo llego all? Sigue recto y coge la primera, segunda, tercera... calle a la izquierda-derecha. El est enfrente-junto al Gracias De nada. Adios
EJEMPLOS: THE LIBRARY THE POST OFFICE THE POLICE STATION THE PARK THE CINEMA THE SPORTS SHOP HOME
SCHOOL
THE SUPERMARKET
THE TOWN HALL
THE COFFEE SHOP
WORK
The town hall: ______________________________________________________________ The police station: ___________________________________________________________ The post office: ____________________________________________________________
10
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Oliver Twist WorksheetDocument2 pagesOliver Twist WorksheetAnastasia GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Basic Qur'aanic Arabic Grammar ChartDocument1 pageBasic Qur'aanic Arabic Grammar Chartlalukhan0% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Sherlock Holmes and The Mystery of Boscombe Pool: Activity WorksheetsDocument3 pagesSherlock Holmes and The Mystery of Boscombe Pool: Activity WorksheetsAnastasia García67% (3)
- 11573894Document155 pages11573894Karthikeyan100% (1)
- 11573894Document155 pages11573894Karthikeyan100% (1)
- Final Quiz 2 Video Tutorial RubricDocument1 pageFinal Quiz 2 Video Tutorial RubricRaven ClawNo ratings yet
- Dracula Final WorksheetDocument2 pagesDracula Final WorksheetAnastasia GarcíaNo ratings yet
- AK-RomeoJuliet KEY ACTIVITIES PDFDocument2 pagesAK-RomeoJuliet KEY ACTIVITIES PDFAnastasia García100% (1)
- Adverbs TheoryDocument4 pagesAdverbs TheoryAnastasia García100% (1)
- AK Dracula PDFDocument3 pagesAK Dracula PDFAnastasia GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Important Lesson Planning For The Teacher and The Learners: InteractiveDocument19 pagesImportant Lesson Planning For The Teacher and The Learners: InteractivejosephkondoNo ratings yet
- Academic Writing - Writing and Reading Across The DisciplinesDocument6 pagesAcademic Writing - Writing and Reading Across The Disciplinesathia007No ratings yet
- Oliver Twist: Penguin Readers Answer KeyDocument3 pagesOliver Twist: Penguin Readers Answer KeyAnastasia GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Three Great Plays of Shakespeare LEVEL 4Document43 pagesThree Great Plays of Shakespeare LEVEL 4taze100% (2)
- Degree ModifiersDocument6 pagesDegree ModifiersoliramNo ratings yet
- Oliver Twist Episode 01Document7 pagesOliver Twist Episode 01AB CDNo ratings yet
- Begin Your Year With The Classics!: "Write Like The Dickens" ... and Win A Trip To LondonDocument8 pagesBegin Your Year With The Classics!: "Write Like The Dickens" ... and Win A Trip To LondonAnastasia GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Teens Shakespeare Extension Activities - 1 PDFDocument14 pagesTeens Shakespeare Extension Activities - 1 PDFAnastasia GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Warmer - Impossible Love A. Read The First Text, and Talk About The Questions With A PartnerDocument5 pagesWarmer - Impossible Love A. Read The First Text, and Talk About The Questions With A PartnerAnastasia GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Warmer - Impossible Love A. Read The First Text, and Talk About The Questions With A PartnerDocument5 pagesWarmer - Impossible Love A. Read The First Text, and Talk About The Questions With A PartnerAnastasia GarcíaNo ratings yet
- School FacilitiesDocument2 pagesSchool FacilitiesAnastasia GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Warmer - Impossible Love A. Read The First Text, and Talk About The Questions With A PartnerDocument5 pagesWarmer - Impossible Love A. Read The First Text, and Talk About The Questions With A PartnerAnastasia GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Romeo & Juliet Lesson Plan - 0Document3 pagesRomeo & Juliet Lesson Plan - 0Anastasia GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Penguin Readers Answer Key: Romeo and JulietDocument1 pagePenguin Readers Answer Key: Romeo and Julietlord byronNo ratings yet
- Romeo and Juliet: Penguin Readers FactsheetsDocument4 pagesRomeo and Juliet: Penguin Readers FactsheetsAnastasia GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Dracula JuniorDocument16 pagesDracula JuniorAnastasia GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Dracula: Summary-Based ActivitiesDocument11 pagesDracula: Summary-Based ActivitiesAnastasia GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Future: INTERMEDIATE - TENSESDocument3 pagesFuture: INTERMEDIATE - TENSESdelvinNo ratings yet
- School SubjectsDocument3 pagesSchool SubjectsAnastasia GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Dracula: Summary-Based ActivitiesDocument11 pagesDracula: Summary-Based ActivitiesAnastasia GarcíaNo ratings yet
- 03 Confusing Verbs - BBC English Learning - Quizzes & VocabularyDocument3 pages03 Confusing Verbs - BBC English Learning - Quizzes & Vocabularyreshmii_123No ratings yet
- DraculaDocument1 pageDraculaAnastasia GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Check Your Vocabulary For IELTSDocument45 pagesCheck Your Vocabulary For IELTSAnastasia GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Useful PhrasesDocument6 pagesUseful PhrasesAnastasia GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Dracula JuniorDocument16 pagesDracula JuniorAnastasia GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Reading Part 6 Cross Text Multiple Matching PDFDocument14 pagesReading Part 6 Cross Text Multiple Matching PDFMiriam ChiovettaNo ratings yet
- EAPP Reviewer For 3rd QuarterDocument2 pagesEAPP Reviewer For 3rd QuarterMarielle BaldivinoNo ratings yet
- Peet CurriculumvitaeDocument7 pagesPeet Curriculumvitaeapi-405364092No ratings yet
- Chapter 13 PhonologyDocument6 pagesChapter 13 PhonologyDaneryRodriguezValerioNo ratings yet
- Politeness in English and Syriac - A Comparative StudyDocument141 pagesPoliteness in English and Syriac - A Comparative StudySalam Neamah HakeemNo ratings yet
- Clow Chapter1Document27 pagesClow Chapter1Malika MatniyazovaNo ratings yet
- Name: - Brittany Duncan, Heather Decarlo - Grade Level: - 2Nd - Lesson Title: - Deaf and Blind - Lesson Length (Ie. 30 Minutes) : - 30-45 MinutesDocument7 pagesName: - Brittany Duncan, Heather Decarlo - Grade Level: - 2Nd - Lesson Title: - Deaf and Blind - Lesson Length (Ie. 30 Minutes) : - 30-45 Minutesapi-321539120No ratings yet
- EltDocument5 pagesEltShane Thea AbejarNo ratings yet
- Gramatica Complementaria BasicaDocument10 pagesGramatica Complementaria Basicaricharth cabreraNo ratings yet
- The Tempest Lesson Plan - 0Document3 pagesThe Tempest Lesson Plan - 0Chaithra GowdaNo ratings yet
- Asmtreport Allie Final DraftDocument15 pagesAsmtreport Allie Final Draftapi-457149143No ratings yet
- How To Communicate With Your Subordinates EffectivelyDocument10 pagesHow To Communicate With Your Subordinates EffectivelyPranati JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Japanese Verb Tenses 031414Document5 pagesJapanese Verb Tenses 031414Peace MantraNo ratings yet
- Expression of Wish English and Arabic PDFDocument86 pagesExpression of Wish English and Arabic PDFmuhannadNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Iv-A Calabarzon Division of RizalDocument4 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Iv-A Calabarzon Division of RizalAbdul Ferran SalameroNo ratings yet
- Rubric For Impromptu SpeechDocument1 pageRubric For Impromptu SpeechthatcatwomanNo ratings yet
- French Numerical AdjectivesDocument1 pageFrench Numerical Adjectivesdiah_mulcil06No ratings yet
- ENG 101 - Fragments - ExplanationDocument18 pagesENG 101 - Fragments - ExplanationSELAHIKHAN100% (1)
- Essay On Social NetworkingDocument2 pagesEssay On Social NetworkingDenish Nadarajan0% (1)
- Yolanda Soyrl 11th August 2017Document18 pagesYolanda Soyrl 11th August 2017Anonymous o5kZfSjERNo ratings yet
- 10th Grade Study Guide Part 2Document7 pages10th Grade Study Guide Part 2api-311995468No ratings yet
- StructuralismDocument2 pagesStructuralismWisnu WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Model Driven ArchitectureDocument34 pagesModel Driven ArchitecturemelguisoNo ratings yet
- The Skeptical Intelligencer 16.4Document23 pagesThe Skeptical Intelligencer 16.4Alan LibertNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Culture On Arabic/English/Arabic Translation of Idioms and ProverbsDocument69 pagesThe Influence of Culture On Arabic/English/Arabic Translation of Idioms and ProverbsSonia MiminNo ratings yet