Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EM-I Lab HOTS Questions
Uploaded by
Joseph HarindranathOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EM-I Lab HOTS Questions
Uploaded by
Joseph HarindranathCopyright:
Available Formats
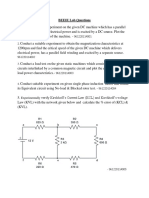
VINAYAKA MISSIONS UNIVERSITY AARUPADAI VEEDU INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, PAIYANOOR ELECTRICAL MACHINES I LAB HOTS (Higher Order Thinking
g Skills) Questions The student is expected to read each of the following questions carefully, identify the machine on which the experiment is to be conducted, the tests to be conducted and then write the aim of the experiment. The hints are given within brackets.
Conduct load test on the DC motor in which flux is practically constant and determine its performance characteristics. (DC shunt motor)
Conduct load test on the DC motor which has a high starting torque and determine its performance characteristics. (DC series motor)
Conduct load test on the DC motor which is used in electric traction and determine its performance characteristics. (DC series motor)
Conduct load test on the DC motor in which the torque is proportional to the square of the armature current before saturation and determine its performance characteristics.(DC series motor)
Control the speed of the given DC shunt motor by varying the armature voltage at constant field current and draw the graph. (Speed control armature control)
Control the speed of the given DC shunt motor by varying the field current at constant armature voltage and draw the graph. (Speed control flux control)
Conduct load test on the given electrical device which works on the principle of mutual induction and determine its efficiency and regulation. (Single phase transformer load test)
Conduct suitable tests to determine the parameters of the equivalent circuit of a static electrical device and draw the equivalent circuit. (OC & SC test on single phase transformer)
Predetermine the efficiencies of the given DC machine, in which flux is practically constant, at different loads indirectly without actually loading it and draw its performance curves (i) as a motor and (ii) as a generator. (Swinburnes test)
Predetermine the efficiencies of the given DC machine, in which flux is practically constant, at (a) (b) (c) of the full load and also at the full load indirectly by estimating the losses and draw its performance curves (i) as a motor and (ii) as a generator. (Swinburnes test)
Conduct a suitable test to determine the no load losses of the given DC machine whose flux is practically constant. (Separation of losses)
Conduct a suitable test on the given DC generator, whose field winding is excited by a separate source, to determine its magnetization characteristics. (DC separately excited generator OCC)
Conduct a suitable test on the given DC generator, whose field winding is excited by a separate source, to determine its load characteristics. (DC separately excited generator Load characteristics)
Conduct a suitable test on the given DC generator, whose field winding is connected in parallel with its armature winding, to determine its magnetization characteristics. (DC shunt generator OCC)
Conduct a suitable test on the given DC generator, whose field winding is connected in parallel with its armature winding, to determine its load characteristics. (DC shunt generator load characteristics)
Conduct a suitable test on the given DC generator which has two field windings, one of which is connected in parallel with the series combination of its armature winding and the other field winding, to determine its load characteristics in the following cases: (i) when the flux of one field winding aids that of the other field winding and (ii) when the flux of one field winding opposes that of the other. (DC Compound generator load test)
You might also like
- Electrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseFrom EverandElectrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseNo ratings yet
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines I Lab Twisted QuestionsDocument4 pagesElectrical Machines I Lab Twisted QuestionsPranav MenonNo ratings yet
- Lab - End QNDocument3 pagesLab - End QNSuresh Sampath SNo ratings yet
- EE232 Electrical Machines Lab IDocument3 pagesEE232 Electrical Machines Lab ISREEHARI S J100% (1)
- ANNA UNIVERSITY PRACTICAL EXAM ON DC MACHINES AND TRANSFORMERSDocument4 pagesANNA UNIVERSITY PRACTICAL EXAM ON DC MACHINES AND TRANSFORMERSnandhakumarmeNo ratings yet
- BEEIE Lab ExperimentsDocument6 pagesBEEIE Lab Experiments961220205018 MANOJ KUMAR C100% (1)
- Aim/Principle/Apparatus Required/procedure Tabulation/Circuit/ Program/Drawing Calculation & Results Viva-Voce Record Total 20 35 25 10 10 100Document2 pagesAim/Principle/Apparatus Required/procedure Tabulation/Circuit/ Program/Drawing Calculation & Results Viva-Voce Record Total 20 35 25 10 10 100Durai MuruganNo ratings yet
- Electric Drives Experiment List Cycle 1Document1 pageElectric Drives Experiment List Cycle 1Ashish KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Lab Compre Question Bank 2017 2018Document4 pagesLab Compre Question Bank 2017 2018Vaibhav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sample QuestionsDocument4 pagesSample QuestionsdubstepoNo ratings yet
- Cycle 1 Experiment No. 4 Study of The Steady State Performance of A Separately Excited DC GeneratorDocument4 pagesCycle 1 Experiment No. 4 Study of The Steady State Performance of A Separately Excited DC GeneratorVIJAY KUMARNo ratings yet
- Ee 502Document1 pageEe 502lucky250No ratings yet
- Machine GcetDocument1 pageMachine GcetJason RathorNo ratings yet
- NARES Group of Institutions Electrical Engineering Lab ExperimentsDocument1 pageNARES Group of Institutions Electrical Engineering Lab ExperimentssunilkumareceNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of DC Motor Using Chopper: Presented byDocument17 pagesSpeed Control of DC Motor Using Chopper: Presented bydeviselva75No ratings yet
- BEEE Lab QuestionsDocument2 pagesBEEE Lab QuestionsThangaraj KNo ratings yet
- PSD Course File 2011-12Document40 pagesPSD Course File 2011-12Sethupathi CmNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines - I Lab Manual GuideDocument61 pagesElectrical Machines - I Lab Manual GuideraniaNo ratings yet
- Transformers and Induction Machine Lab: I-Load Test On 1-Phase TransformerDocument4 pagesTransformers and Induction Machine Lab: I-Load Test On 1-Phase TransformerChithra ManivelanNo ratings yet
- Em II Lab QDocument1 pageEm II Lab QThangaraj KNo ratings yet
- EMS Lab Manual Ver 1.0 (Fall 2016)Document69 pagesEMS Lab Manual Ver 1.0 (Fall 2016)Fahad MahmoodNo ratings yet
- List of ExperimentsDocument1 pageList of ExperimentsMahesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Electrical (09) /power Electronics (24) : Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument4 pagesElectrical (09) /power Electronics (24) : Gujarat Technological UniversityKeyur PatelNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine Lab D.C Shunt Generator No-Load Test: University of Kirkuk Mechanical DepartmentDocument5 pagesElectrical Machine Lab D.C Shunt Generator No-Load Test: University of Kirkuk Mechanical Departmentعبدالمؤمن خالد محمودNo ratings yet
- Motor, Electric Traction and Electrical Control Trainer YL-195Document41 pagesMotor, Electric Traction and Electrical Control Trainer YL-195jhgffdfdffNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power and Machines Testing (1) EPE 323a: Title Load Test On A Self - Excited DC Compound GeneratorDocument12 pagesElectrical Power and Machines Testing (1) EPE 323a: Title Load Test On A Self - Excited DC Compound Generatorabdalghny073No ratings yet
- DC Machines and Transformers Lab ManualDocument50 pagesDC Machines and Transformers Lab ManualSuseel MenonNo ratings yet
- Ee2259 Set1Document11 pagesEe2259 Set1kaliappan45490No ratings yet
- DC Machines Test QuestionsDocument1 pageDC Machines Test QuestionsVeera ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual Electrical Machines and Applications LaboratoryDocument40 pagesLaboratory Manual Electrical Machines and Applications LaboratoryRamez MezNo ratings yet
- EE258 2024 CoursePlan - SubjectedToDUGCapprovalDocument3 pagesEE258 2024 CoursePlan - SubjectedToDUGCapprovalSumukha ShettyNo ratings yet
- Em 1Document1 pageEm 1Mou LaliNo ratings yet
- Gnerator +motor RevisedDocument182 pagesGnerator +motor RevisedkkNo ratings yet
- Electric Machines Virtual Laboratory Testing of DC MotorDocument11 pagesElectric Machines Virtual Laboratory Testing of DC Motora78492431No ratings yet
- Electromechanical Energy Conversion Lab ManualDocument61 pagesElectromechanical Energy Conversion Lab Manualprathyush srinivasanNo ratings yet
- Exp-4 (DC Generator OCC)Document3 pagesExp-4 (DC Generator OCC)SHAJEDA AKTHER 2102154No ratings yet
- 19EE211Document3 pages19EE211chaitanya200039No ratings yet
- Electrical Devices & Applications Course OverviewDocument4 pagesElectrical Devices & Applications Course OverviewTimothy FieldsNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Analysis On The Performance of Universal Motor When Driven by Alternating Current/direct CurrentDocument6 pagesA Comparative Analysis On The Performance of Universal Motor When Driven by Alternating Current/direct CurrentKeshavNo ratings yet
- Regulations - 2008 Fifth SemesterDocument6 pagesRegulations - 2008 Fifth Semesterkaliappan45490No ratings yet
- ELE3114 Tutorial April 2022Document6 pagesELE3114 Tutorial April 2022Sahiil MauriceNo ratings yet
- Department Of: Electronics & Communication EnggDocument2 pagesDepartment Of: Electronics & Communication Enggarifiqbal74No ratings yet
- Traction Induction Drive For Railway CHUEV DenisDocument9 pagesTraction Induction Drive For Railway CHUEV DenisPABLO MAURONo ratings yet
- Machine Based Experiments Lab Report-1 Name: Karthickeien E BY: CH - EN.U4CCE21024 Group: A TopicDocument14 pagesMachine Based Experiments Lab Report-1 Name: Karthickeien E BY: CH - EN.U4CCE21024 Group: A TopicKartheepan KaNo ratings yet
- List of Experiments - Spring 2017Document1 pageList of Experiments - Spring 2017VatteVineethNo ratings yet
- GROUP 3 - Experiment 6Document13 pagesGROUP 3 - Experiment 6Ervin James AbulocNo ratings yet
- QP. Code: Third Semester Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument2 pagesQP. Code: Third Semester Electrical and Electronics EngineeringarwinNo ratings yet
- Manual EEE2003Document64 pagesManual EEE2003rishanNo ratings yet
- Questions 1Document11 pagesQuestions 1anvithaNo ratings yet
- 3-Starting and Braking, Introduction to DC Motors-19-01-2024Document35 pages3-Starting and Braking, Introduction to DC Motors-19-01-2024AYUSH GOYALNo ratings yet
- Lab 3abDocument16 pagesLab 3abLiaqat AliNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument2 pagesQuestion BankRahul CNo ratings yet
- DC Machine and TransformerDocument4 pagesDC Machine and TransformermitulNo ratings yet
- Homwork May DienDocument2 pagesHomwork May DienBk DecNo ratings yet
- Ee2304 Set3Document4 pagesEe2304 Set3kaliappan45490No ratings yet
- Dhifa Haris Mohammad - Prak Pengemudian Listrik (I)Document6 pagesDhifa Haris Mohammad - Prak Pengemudian Listrik (I)dhifa harisNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Modeling and Analysis of Three Phase Self-Excited Induction Generator Using Generalized State Space ApproachDocument8 pagesDynamic Modeling and Analysis of Three Phase Self-Excited Induction Generator Using Generalized State Space ApproachAnonymous On47lKiNo ratings yet
- Ee LabDocument1 pageEe LabNarasimman DonNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1-Lecture 1 Introduction of Electrical Drives and ControlDocument19 pagesUNIT 1-Lecture 1 Introduction of Electrical Drives and Controlanandlm710No ratings yet
- EM-II Assignment-2 - IV Sem EEE - 25.02.13Document1 pageEM-II Assignment-2 - IV Sem EEE - 25.02.13Joseph HarindranathNo ratings yet
- Synchronous GeneratorsDocument62 pagesSynchronous GeneratorsAkira ZamudioNo ratings yet
- University Practical Examination Questions - EM-II Lab Latest 22.03.11 Ver-3 HOTS With KeysDocument4 pagesUniversity Practical Examination Questions - EM-II Lab Latest 22.03.11 Ver-3 HOTS With KeysJoseph HarindranathNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines-II Units-III & IV Questions and AnswersDocument4 pagesElectrical Machines-II Units-III & IV Questions and AnswersJoseph Harindranath100% (2)
- EMD Important Questions Unit IV - Conventional Speed ControlsDocument3 pagesEMD Important Questions Unit IV - Conventional Speed ControlsJoseph HarindranathNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Alternator (Synchronous Generator) : StructureDocument29 pagesUnit 6 Alternator (Synchronous Generator) : StructureMahir Asif Shadman100% (1)
- Regulation of AlternatorsDocument3 pagesRegulation of Alternatorsrakeshkr07No ratings yet
- Synchronous Generators - 2 Marks Questions and AnswersDocument3 pagesSynchronous Generators - 2 Marks Questions and AnswersJoseph Harindranath67% (3)
- Regulation of Alternators by M.venkateshDocument6 pagesRegulation of Alternators by M.venkateshKrishnamoorthi DuraisamyNo ratings yet
- EMD Important Questions Unit-III Starting MethodsDocument9 pagesEMD Important Questions Unit-III Starting MethodsJoseph HarindranathNo ratings yet
- Short Questions and Answers Electrical Machines IIDocument16 pagesShort Questions and Answers Electrical Machines IILata SharmaNo ratings yet
- EM-I Unit-III Questions & AnswersDocument13 pagesEM-I Unit-III Questions & AnswersJoseph HarindranathNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines and Drives/Electrical Drives and Control Third Semester Mechanical Engineering 2 Marks (Questions & Answers)Document7 pagesElectrical Machines and Drives/Electrical Drives and Control Third Semester Mechanical Engineering 2 Marks (Questions & Answers)Joseph HarindranathNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits - ResonanceDocument28 pagesElectric Circuits - ResonanceJoseph HarindranathNo ratings yet
- EM-I Unit-IV Questions & AnswersDocument9 pagesEM-I Unit-IV Questions & AnswersJoseph HarindranathNo ratings yet
- High Side Current Sense CircuitDocument6 pagesHigh Side Current Sense Circuitabhay pandeyNo ratings yet
- AIX I/O Performance TuningDocument16 pagesAIX I/O Performance TuningSubbarao AppanabhotlaNo ratings yet
- Electronics Circuits and Devices SyllabusDocument3 pagesElectronics Circuits and Devices SyllabusBineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- OFDM PAPR ReductionDocument5 pagesOFDM PAPR ReductionAnuj KalraNo ratings yet
- RF Chain - WikipediaDocument15 pagesRF Chain - WikipediaVasikaran PrabaharanNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Current Vs Voltage PDFDocument4 pagesLab 4 Current Vs Voltage PDFAnonymous lm3GIU45No ratings yet
- LM5068 Negative Voltage Hot Swap Controller: General Description FeaturesDocument26 pagesLM5068 Negative Voltage Hot Swap Controller: General Description FeaturesRohit SinghNo ratings yet
- ft7 ManualDocument1 pageft7 Manualscrapper_zipmailNo ratings yet
- 800-10766 Kaherin Antenna PDFDocument2 pages800-10766 Kaherin Antenna PDFLakshmanan ThirupathiNo ratings yet
- Improving Bandwidth Rectangular Patch Antenna Using Different Thickness of Dielectric SubstrateDocument6 pagesImproving Bandwidth Rectangular Patch Antenna Using Different Thickness of Dielectric SubstrateMohd Zubair KhanNo ratings yet
- GSM Channel StructureDocument4 pagesGSM Channel Structurebdrajubd0% (1)
- Association Rule MiningDocument2 pagesAssociation Rule MiningDhruTheGamer100% (2)
- RCI510 Setup PDFDocument10 pagesRCI510 Setup PDFDaniel Castillo PeñaNo ratings yet
- 2-W Stereo Audio Power Amplifier With Mute: Description FeaturesDocument23 pages2-W Stereo Audio Power Amplifier With Mute: Description FeaturesOtoniel CardenasNo ratings yet
- Labview+pulse Shaping and Matched FilteringDocument12 pagesLabview+pulse Shaping and Matched FilteringcarolmNo ratings yet
- Frenophone 1923Document1 pageFrenophone 1923raineymj100% (1)
- Smart Mailbox NotificationsDocument7 pagesSmart Mailbox NotificationsFaiz YunNo ratings yet
- Handover Control Parameters of CellDocument55 pagesHandover Control Parameters of CellAsraful AlamNo ratings yet
- SeminarDocument14 pagesSeminarKumar RaviNo ratings yet
- Benq MP515 DLP ProjectorDocument1 pageBenq MP515 DLP ProjectorGenee IndiaNo ratings yet
- Datasheet 7408Document9 pagesDatasheet 7408Antony ZiimerNo ratings yet
- 02 Medium Pressure Accel Valves Celeris - (MKT 0277)Document6 pages02 Medium Pressure Accel Valves Celeris - (MKT 0277)VICTOR MANUEL SALAZAR GARCIANo ratings yet
- Radio Network Optimization Guideline (HAY) (R)Document40 pagesRadio Network Optimization Guideline (HAY) (R)Hiep Nguyen Dinh100% (1)
- EC1308 Principles of Communication EngineeringDocument107 pagesEC1308 Principles of Communication EngineeringaaparumugamNo ratings yet
- Awpl PDFDocument5 pagesAwpl PDFSHAMUS DANINo ratings yet
- RF - 5G Parameter SettingsDocument4 pagesRF - 5G Parameter SettingsAkhtar Khan100% (1)
- Error Code 14 Hi I Was Wondering What Error Code 14 Was On My Matrix Printer Model DFXDocument3 pagesError Code 14 Hi I Was Wondering What Error Code 14 Was On My Matrix Printer Model DFXJohny AllNo ratings yet
- 449 261 FDocument4 pages449 261 Fqais652002No ratings yet
- Modulator High Powered Omni Speaker: Model MOD SeriesDocument2 pagesModulator High Powered Omni Speaker: Model MOD SeriesCarlos LeyvaNo ratings yet
- DitchWitch 750 Tracker User Manual PDFDocument41 pagesDitchWitch 750 Tracker User Manual PDFmzahidbNo ratings yet