Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Turbo Super Charger System
Uploaded by
sanju_17Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Turbo Super Charger System
Uploaded by
sanju_17Copyright:
Available Formats
TURBO SUPER CHARGER SYSTEM OBJECTIVE The need of super charging....... Various methods of super charging........
.. Various components of turbo super charger and their duties.......... INTRODUCTION the diesel engine produce mechanical energy by converting heat energy Derived from burning fuel inside the cylinder. For efficient burning of fuel availability of proper ratio is prerequisite..... in natural aspirated engines, during the suction stroke air is being sucked into the cylinder from the atmosphere. Availability of less quantity of air of low density inside the cylinder would limit the scope of burning fuel. More the air breath by engine more will be its efficiency. so super charger is used to provide more air to the engine...... ADVANTAGES OF TURBOSUPER CHARGER IN WDS4 Can give 30 to 40% more power........ Enables to stay in high gear to keep pace with lingering traffic........ Better fuel efficiency due to complete combustion of fuel.......... At higher altitude where air density is low. provide artificial aspiration Only self powered device. No need of power from engine to work...... METHOD OF SUPER CHAGING Most efficient and economical method of super charging is by centrifugal blower Run by exhaust gas driven turbine. In the system the energy left over the exhaust gas Which would have been wasted is to drive the gas turbine. The turbine in turns drive the centrifugal blower. Which suck air from the atmosphere and pressurized it. This does away with need for an additional power required for driving the blower. More over this system can maintain air to fuel ratio at all speed and load condition of engine than any other system.........3
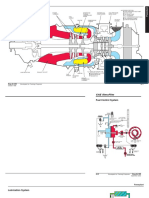
MAIN COMPONENT OF TURBOSUPER CHARGER GAS INLET CASING TURBINE CASING INTERMEDIATE CASING BLOWER CASING WITH DIFFUSER ROTER ASSEMBLY WITH TURBINE AND ROTER ON SAME SHAFT
GAS INLET CASING The inlet casing is of ch20 stainless steel that is highly heat resistant. The Function of the casing is to take hot gases from exhaust manifold and pass them through the nozzle ring. Which is bolted to the casing face. this assembly is Fitted on the turbine casing with cap screw.......... TURBINE CASING The turbine casing houses the turbine inside it and is cored to have circulation of water through it for cooling puposes.it has an oval shape gas outletpassege At top.it is made up of alloy cast iron or fabricated.......... INTERMEDIATE CASING this casing is also water cooled and cored to have circulation and is of alloy cast iron or fabricated like turbine casing. it is placed between turbine casing and the blower casing. It separates the exaust and airside and also support the turbine roter on 2 trimetal bearing. BLOWER HOUSING ASSEMBLY this houses the blower and of 2 part,mainly the blower inlet and the blower housing.air enters through blower inlet axially and discharge radically from the blower through diffuser.the vane diffuser is a precision aluminium casing. ROTOR ASSEMBLY the rotor assembly consist of rotor shaft,rotor blade,thrust collar,inducers, center stud,nose peice and locknut etc..the rotor blade are fitted into fir tree slot and locked by tab lock washers.this is dynamically balanced component,as this has a very high rotational speed.
TURBO SUPER CHARGER ITS WORKING PRINCIPAL the exaust gases discharge from the entire cylinder accumulated in the common exaust manifold at the end of which,turbosupercharger is fitted.the gases under pressure there after enters the turbo super chargers through the torpedo shaped bell mouth connetor and then passes the passes the nozzel ring.then it is directed on turbine. blades at increased pressure and at the most suitable angle to achieve rotary motion of the turbine blade at maximum efficiency. After rotating the turbine, the exhaust gas goes out to the atmosphere through the exhaust chimney. The turbine has a centrifugal blower moutned at the other end of the same shaft and the rotation of the turbine drives the blower at same speed . The blower connected to the atmosphere through the set of oil bath filters, sucks air form from atmosphere and delivers at higher velocity. The air then passcs through the diffuser inside the
turbosuperchargr, where the velocity is diffused to increase the pressure of the air before it is delivered from the turbo-supercharger. Presurizing air increases its dnsity but due to compression heat developes. It causes expansion and reduces the density. This affects supply of high-density air to the engine. To take care of this, air passed through the tubes and around the tubes air pases. The heat in the air is thus transferred to the cooling water and air regains its lost density. From the after cooler air gors to a common inlet valce opens the booster air of higher pressure density rushes in to the cylinder. completing the process of super charging. The engine initially starts as naturlly aspirated engine. With the increased quantity of fuel injection increases the exhaust gas pressure on the turbine. thus the self-adjusting system maintains a prper air and furl ratio under all speed and load conditions of the engine on its own. The maximum rotational speed of the turbine is 18000 RPM for the 720A model turbo supercharger and creates 1.8kg/cm^2 air pressure in air manifold of the diesel engine known as booster pressure. Low booster presure causes black smoke dur to incombustion of fuel. High exhaust gas temperature due to after burning of fuel may result in considerable damage to the turbo supercharfer and the other components in the engine. Turbo Ru- Down Test Turbo run-down test is very common type of test done to cheeck the free running time of turbo rotor. It indicates whether there is any abnormal sound in the turbo , seizer/partial sezer of bearing physical damages to the turbine, or any other abnomality inside it . The engine is started and warmed up to normal working temperature and running at fourth notch speed. Engine is then shut down through the over speed trip mechanism. When the rotation of the crankshaft stops, the free running time of the turbine is watched through the chimney and recorded by a stopwatch. The minimum time allowed for free running is 120 seconds and maximum 240 seconds. Low or high turbo run down time are both considered being harmful for the engine.
FUEL OIL SYSTEM OBJETIVE understand the fuel oil system learn the function of component of fuel oil system learn the concept of fuel feed system and fuel injection system INTRODUCTION all locomotives units have individual fuel oil system is designed to introduce fuel oil into engine cylinder at the correct time,at correct pressure ,at correct quantity,and corretly optimised. the system inject into the system correctly metered quantity of fuel in highly atomised form. the high pressure is required to lift the nozzle valve.and for better penitration of fuel into combustion chamber. high pressuer is also help in proper atomisation so that the small droplets come into better contanct into fresh air in the combustion chamber ,resulting in better combustion, metering of fuel quantity is important because the locomotive engine is variable speed and variable load engine with variable requiment of fuel. FUEL OIL SYSTEM the fuel oil system consist of integrated systems. FUEL FEED SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM FUEL FEED SYSTEM AND ITS ASSOCIATES COPONENT the fuel feed system provide the back up support to the fuel injection pumps by maintaining steady supply of fuel to them at the required pressure so that the fuel pump can meter and deliver the oil to the cylinder at required pressuer and time.the fuel feed system include the following; FUEL OIL TANK a fuel oil tank of required capacity 2700 LITERS is fabricated under the super structure of locomotive and located in 2 different tanks of 1100 and 1400 liters is stoered in the pump due to gravity...... 200 liters in the system itself. FUEL PRIMARY FILTER a filter is provided in the suction side of the fuel transfer pump to allow only filtered oil inside the pump.this enhance the life of the pump. this filter is most often reneable bleaced cotton type filter.commonly known as socks type filter element.for longer service life paper filter is also used.
FUEL TRANSFER PUMPS IT IS USED TO LIFT THE PUMP FUEL RELEASE VALVE passing excess oil to the fuel tank this releasing excess load to the pump means of spring loaded relief valve.it is adjusted to the required pressure 1.2kg/cm^2 and by passes the excess fuel back to the oil tank. FUEL SECONDRY FILTER it is located after the fuel feed pump.it is of paper filter type,cartridge of finer quality renewable at regular interval.it arrest finer dist particle lift over by primary filter. FUEL REGULATING VALVE it is spring loaded valve of similar design as the fuel feed system.this valve is adjusted to required pressure of 0.2kg/cm^2. FUNCTION OF FUEL FEED SYSTEM transfer pump start sucking oil from the fuel tank.filter through primary filter and dilivered.then the fuel feed pumps the fuel upside.then fuel goes to the fuel secondary filter and remaining oil return back to the oil tank through return pipe.then fuel goes to the main header where it is distributed to the FIP.fuel injector pump is used to pump the fuel to the injector.remaning fuel return back to the fuel tank.the fuel injector inject fuel in the cylinder head through a spray pattern. FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM when deisel engine starts all fuel injetion pump starts functioning, according to the firing order all F.I PUMPS starts functioning discharging fuel oil at high pressure to their respective nozzle. FUEL INJECTION PUMP it is constant stroke plunger type with variable quantity of fuel dilivery to suit the demand of the engine.the fuel cam controls the pumping stroke of the plunger.length of the stroke and time of the stroke is depend on the cam angle. plunger spring controls the return stroke.the plunger moves inside the barrel,which has a very close tolerance with the plunger.when the plunger reaches the BDC ,spill ports in the barrel,which are connected to the fuel feed system open up.oil then fills up the empty space inside the barrel.at the correct time in deisel cycle ,the fuel cam pushes the cam forward ad moving plunger covers the pill port.thus trap oil is forced out through the delivery valve to be injected into the combustion chamber through the injection nozzle.the governer for the engine speed control ,on sensing the requirement of fuel,controls the rotary motion of the plunger.while it has also resiprocating pumping stroke.
FUEL INJECTION NOZZLE it is fitted in the cylinder head with its tip projected inside the combustion chamber.it remains connected to the fuel injector pump with a steel tube known as high pressure line. FI NOZZLE is of multi hole neddle valve closes the oil hole by blocking due to spring pressure.due to delivery stroke pressure inside the nozzle increases.when pressure is higher then valve spring pressure the small holes in the nozzle tip uncovers.after injection the pressure drops and holes are uncovered and terminate the fuel injection. CALIBRATION OF FUEL INJECTION PUMP Every pump must deliver regulated and equal quantity of fuel at the same time so that the engine output is optimum and at the same time running is smooth with minimum vibration. the calibration and testing is done on specially designed machine. The machine has a 5HP reversible motor to drive the camshaft through vbelt.the blended oil of recommended viscosity under controlled temperature is circulated through a pump at a specified pressure for feeding the pump under test. The pump is fixed on the top of cam box and its rack is set at a particular position to find out the quantum of fuel delivery at the position. Machine is then switch on. A revolution counter set to 400 rpm.oil is diverted until 100 strokes are completed. A counter check is also done by reversing the position of the of the motor that simulates slow running of engine. If the test result is not in stipulated limit as indicated by the makers then adjustment of the fuel rack position is required by moving the rack pointer, or by addition and removal of shims behind it. PHASING OF FUEL INJECTION PUMPS every fuel injection pump after repair and overhouling needs phasing while fitted on the engine.in course of working the drive mechenism of fip suffers from wear and cause loss of motion.this may cause the shorter length of plunger stroke and lesser fuel deliveryadjustment is provided in the valve lifter mechenism to adjust the marking between the guide cap and the sight window so that they coinside with each other after positioning the engine.this adjustment is known as phasing of the pump and to make up the waer losses. FUEL INJECTION NOZZLE TEST the criteria of good nozzle are good atomisation,correct spray pattern and no leakage or dribling.before the nozzle put to test the assembly must be rinsed in the fuel oil.nozzle holes are cleaned with wire brush and spray hole are cleaned with steel wire to correct thickness. SPRAY PATTERN TEST spray should be uniform and properly atomised.atomisation can been seen through the glass jar,an impression taken on a sheet of blotting paper at a distance of 1 and 1.5 inch also gives a clear impression of the spray pattern. SPRAY PRESSURE
the spray should be takes place 3900-4050 psi for new and 3700-3800 psi for reconditioned nozzle.if pressure is down to 3600 psi the nozzle spring increses or decreses the pressure. DRIBBLING there should be no loose drops of fuel coming out of the nozzle before and after the injections.the nozzle tip of good nozzle always remain dry.the pressure of checking dribling during testingare by having injection manully done couple of times quickly and check the nozzle tip wheater leaky.raising the pressure within 100 psi of set injection pressure and holding for about 10 seconds may also give a clear idea. NOZZLE CHATTER the chattering sound is a sort of cracking noise created due to free movement of nozzle valve inside the valve body.if it is not proper means that valve is not moving freely inside the nozzle. SILENT FEATURE compressed air pressure 450-550psi temprature of the compressure 800-1000F fuel injection pressure 300kg/cm^2
TRANSMISSION OBJECTIVEThe objective of this unit is to make you understand about folowing The need for transission in a diesel engine Various mode of transmission and their working princile The application of hydraulic transmission in diesel locomotive. INTRODUCTIONA diesel locomotive must fulfill the following essential requirements1- It should be able to start a heavy load and hence should exert a very high starting torque at the axles. 2- It should ve able to cover a very wide speed range. 3- It shoukd be able to ren in either direction with ease. Further the diesel enine has the following drawbaks It cannot start on its own. To start the engine, it has to be cranked at a particular speed, known as a starting speed. Once the engine is started , it cannot be kept running below a certain speed known as the lower critical speed normally 30-40 % of the rated speed . Low critical speed means thet speed at wich the engine can keep itself running along with its auxiliaries and accessories without smoke and vibrations. The engine cannot be allowed to run above the cetain speed known as high critical speed. It is 112 to 115% of rated speed. The hifh critical is the speed at which the engine can keep itself running without damaging itself due to thermal loading and centrifugal forces. It is constant torque engine for a particular fuel setting irrespective of its speed. It can develop rated power at rated speed and fuel stting only. It is unidirectional. To satisfy the above operating requirements of the locomotives, it become necessary to introduce and intermediate device vetween the diesel engine and the locomotive wheels. This device in called transmission. should accept whether the diesel engine gives,with all its limitations mentioned above and be able to feed the axels in such a way that the locomotive fulfill the essential requirements.
ANY TRANSMISSION SHOULD FULFILL THE REQUIRMENTS1- It must transmit the power from the diesel engine to the wheels. 2- It must have a provision to connect and disconnect the engine from the axles for startng and stopping the locomotive----3- It must corrporate a mechanism to revrse the direction of motion of the locomotive. 4- It must provide a permanent speed reduction, as he axle speed are normallu very low when compared with the speed of the crankshaft of the diesel engine. ' 5- It must provide high torque multiplication at staru, whidch should gradully fall as the vehicle picks up speed and veice-versa. TYPE OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMMechanical Transmission Gear Fructuib Clutch Belt and pulley Chain and sprocket Hydrodynamic Transmission Fluid Coupling Torque converter
Electrical transmission DC Electrical AC/DC Electrical AC Electrical
PRINCIPLES OF MECHANICAL TRANSMISSIONIn this system of transmission, a clutch and a multi ratio gearvox are employed. The multi ratio gearbox consists of several gear trains. the engine power is transmitted through one gear pair at a time, As the engine is rigidly connected to the wheels through a fixed gear ratio in each gear, the vehivle speed varies directly with the engibne speed. As the power out put of the engine is proportional to the engine speed. the power delivered by the vehicle also varies with the engine spees. The transmission efficiency of he mechanical transmission efficiency of the mechanical transmission is the highest, as there is no conversion of energy during the power transmission process. But the other parameters are ingerior when compared with other types of transmission system. Types of transmission used in railways1- Voith German Company 2- Mekydro German Company 3- Twin Disk American Design 4- Suri Transmission Indian
You might also like
- Below Is An Overview of The Fuel System Intake OperationDocument8 pagesBelow Is An Overview of The Fuel System Intake OperationchigauNo ratings yet
- Marvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SFrom EverandMarvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SNo ratings yet
- 01.main Engine ManualDocument64 pages01.main Engine ManualwilfredNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesFrom EverandComparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- 03 Principle of TurbochargerDocument19 pages03 Principle of TurbochargerSky RNo ratings yet
- AEH307 3 Fuel SystemsDocument50 pagesAEH307 3 Fuel SystemssiphulwazijamesNo ratings yet
- Turbo Charger NoteDocument9 pagesTurbo Charger NoteShovon SanaNo ratings yet
- EMEg 5221 Chapter 12 13 14Document51 pagesEMEg 5221 Chapter 12 13 14Yoseph MershaNo ratings yet
- How A Turbo WorksDocument2 pagesHow A Turbo WorksSubhojit SamontaNo ratings yet
- SI Engine Mixture PreparationDocument107 pagesSI Engine Mixture PreparationSabyasachi Ghosh100% (1)
- SI Engine Mixture PreparationDocument93 pagesSI Engine Mixture PreparationSabyasachi GhoshNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document21 pagesModule 2NithinNo ratings yet
- TurbochargerDocument21 pagesTurbochargerJo VialNo ratings yet
- Turbochargers in Diesel EnginesDocument5 pagesTurbochargers in Diesel Enginesmister_no34No ratings yet
- Fuel Supply System: Unit 1 BDocument23 pagesFuel Supply System: Unit 1 BAnubhav SinghNo ratings yet
- 1434533907018-Diesel Engine Mechanical Sub-Systems - ALCODocument28 pages1434533907018-Diesel Engine Mechanical Sub-Systems - ALCOsandeep kumar vishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Turbochargers in Diesel EnginesDocument6 pagesTurbochargers in Diesel EnginesSrini VasanNo ratings yet
- TurbochargersDocument8 pagesTurbochargersEddy ErmanNo ratings yet
- Turbo Charger1Document21 pagesTurbo Charger1rameshkumaratvelloreNo ratings yet
- Turbocharger 2NDDocument6 pagesTurbocharger 2NDkyaw yaNo ratings yet
- What Is An Engine ?: Is A Machine That Converts Heat Energy To Mechanical Energy Which Can Be Harnessed For UsefulDocument38 pagesWhat Is An Engine ?: Is A Machine That Converts Heat Energy To Mechanical Energy Which Can Be Harnessed For UsefulEtulan AduNo ratings yet
- Power Plant EngineeringDocument158 pagesPower Plant EngineeringtamilvananirttNo ratings yet
- Bme - 9Document4 pagesBme - 9snehamariam2023No ratings yet
- Engine Lubrication System: The Importance of LubricationDocument4 pagesEngine Lubrication System: The Importance of LubricationPyae Sone LonnNo ratings yet
- What Is Forced Induction?Document15 pagesWhat Is Forced Induction?Fugaru Paul - AlexandruNo ratings yet
- Aircraft System Prelim Module 3 Induction System RevisedDocument31 pagesAircraft System Prelim Module 3 Induction System RevisedGertrudeshane IletoNo ratings yet
- Turbocharger: - Power of A Two Stroke Diesel EngineDocument28 pagesTurbocharger: - Power of A Two Stroke Diesel EngineShraddha Kant SinghNo ratings yet
- TurbochargingDocument11 pagesTurbochargingtiamiyusefiu95No ratings yet
- Engine Turborging23Document2 pagesEngine Turborging23Pagg Dē TygerNo ratings yet
- Valve Timing DiagramDocument43 pagesValve Timing Diagramѕυdeѕн ĸNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine Start UpDocument131 pagesGas Turbine Start UpBaharudin Bin Kamarul Baharin100% (3)
- cm142 1 0Document122 pagescm142 1 0dudleydoright100% (1)
- Chapter 12 Supercharging TurbochargingDocument33 pagesChapter 12 Supercharging Turbochargingdesie yalewNo ratings yet
- Automobile EnggDocument43 pagesAutomobile EnggV V DEVADASNo ratings yet
- Locomotive - Charge Air SystemDocument4 pagesLocomotive - Charge Air SystemArpan MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Description: Necessity of Turbocharger and SuperchargerDocument16 pagesDescription: Necessity of Turbocharger and SuperchargerNazrul Aizat ZunaidiNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engine: Heavy VehiclesDocument33 pagesDiesel Engine: Heavy VehiclesAvinash GangadharanNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbines - Hassan ElBanhawiDocument3 pagesGas Turbines - Hassan ElBanhawijesus_manrique2753No ratings yet
- Turbo Charger PresentationDocument22 pagesTurbo Charger PresentationPragyan Kumar0% (1)
- Unit - 3 Types of Gas Turbine EnginesDocument4 pagesUnit - 3 Types of Gas Turbine EnginesAnonymous VKv75qe98100% (1)
- Supercharging and Turbocharging: High Performance Aircraft EnginesDocument42 pagesSupercharging and Turbocharging: High Performance Aircraft EnginesBalachander RkNo ratings yet
- 3.the CarburetorDocument90 pages3.the CarburetorBikash sharrfNo ratings yet
- Turbocharger and SuperchargerDocument65 pagesTurbocharger and Superchargerzia malikNo ratings yet
- 13 PowerplantDocument18 pages13 Powerplantfevary100% (4)
- Engine 114E-3 Series: 10 Structure, Function and Maintenance StandardDocument14 pagesEngine 114E-3 Series: 10 Structure, Function and Maintenance StandardGiancarlo Cardenas NinaNo ratings yet
- Ic Engine m2Document19 pagesIc Engine m2Amal MonichanNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Turbo Chargers (WGT, VGT), Engine Emission Control by Three Way Catalytic Converter System, Emission Norms (Euro and BS) .Document20 pages2.3 Turbo Chargers (WGT, VGT), Engine Emission Control by Three Way Catalytic Converter System, Emission Norms (Euro and BS) .DEEPAK S SEC 2020No ratings yet
- Turbo Charger - ProjectDocument36 pagesTurbo Charger - ProjectSam Sams100% (2)
- Turbo ChargerDocument19 pagesTurbo ChargerHamimi AkmalNo ratings yet
- Fuel Injection System For Ci Engines PDFDocument6 pagesFuel Injection System For Ci Engines PDFmark mutimushiNo ratings yet
- Ch-12 - Turbocharger & Super MecDocument29 pagesCh-12 - Turbocharger & Super Mecahmed jemalNo ratings yet
- Diesel Fa19Document35 pagesDiesel Fa19Muhammad JunaidNo ratings yet
- Turbo Charged Engine: Presenting by M. Sumanth Reddy 16701A0344 Under Guidance of M. Maruthi PrasadDocument21 pagesTurbo Charged Engine: Presenting by M. Sumanth Reddy 16701A0344 Under Guidance of M. Maruthi PrasadSumanthNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engine Tune UpDocument10 pagesDiesel Engine Tune UpMaher MarquezNo ratings yet
- Fuel Injectors For Marine Diesel EngineDocument5 pagesFuel Injectors For Marine Diesel EngineParthivNo ratings yet
- Lubrication and Cooling SystemDocument11 pagesLubrication and Cooling Systemrongphar9alon100% (1)
- DG SetDocument103 pagesDG Setlvsaru67% (3)
- Diesel Engine TechnologyDocument59 pagesDiesel Engine TechnologyAnonymous f2zDTm7kmNo ratings yet
- Cse 2015Document12 pagesCse 2015sanju_17No ratings yet
- SteamDocument24 pagesSteamsanju_17No ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Compressed Air EngineDocument4 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Compressed Air Enginesanju_17No ratings yet
- The Life Line of Delhi.: Delhi Metro Rail Corporation LTDDocument5 pagesThe Life Line of Delhi.: Delhi Metro Rail Corporation LTDsanju_17No ratings yet
- Tea LeavesDocument1 pageTea Leavessanju_17No ratings yet
- 3.2 Properties of DeterminantsDocument15 pages3.2 Properties of Determinantssanju_17No ratings yet
- Main Particulars of WDS-4Document6 pagesMain Particulars of WDS-4sanju_17No ratings yet
- Summer Training ProjectDocument2 pagesSummer Training Projectsanju_17No ratings yet
- Diagrama 1 EGR VOLUME CONTROL..Document1 pageDiagrama 1 EGR VOLUME CONTROL..Gustavo PérezNo ratings yet
- TCM Torque SB96 7DDocument14 pagesTCM Torque SB96 7DИван КоньковNo ratings yet
- Carb TuningDocument2 pagesCarb TuningBrand Str100% (1)
- HDMaster Cam SpecsDocument10 pagesHDMaster Cam Specspipeman61No ratings yet
- Engine Theory and Calculations: Four Stroke Cycle EngineDocument4 pagesEngine Theory and Calculations: Four Stroke Cycle EngineSitanshu ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- D4FDocument97 pagesD4Fcatant86% (7)
- 773E (Bda) Tier Ii 775E (Bec) Tier I Emissions Off-Highway TrucksDocument37 pages773E (Bda) Tier Ii 775E (Bec) Tier I Emissions Off-Highway TrucksWilliams ArayaNo ratings yet
- Perkins 1104C-44TA Parts Manual 161182Document140 pagesPerkins 1104C-44TA Parts Manual 161182Vlad Ptashnichenko100% (5)
- Maxx Force 9Document4 pagesMaxx Force 9John MkCito KI100% (1)
- Main Engine Logic Pneumatic ControlDocument1 pageMain Engine Logic Pneumatic ControlVadim LioutiNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi Diesel Engine Repair ManualDocument3 pagesMitsubishi Diesel Engine Repair Manualbernad evendi36% (14)
- Renegade Sport S 300 Epa 2017 Parts Catalogue 2016 09 05Document33 pagesRenegade Sport S 300 Epa 2017 Parts Catalogue 2016 09 05JeovannyAlexanderMatamorosSanchezNo ratings yet
- Indenor InfDocument2 pagesIndenor InfRetíficaitatibaNo ratings yet
- C20 25 30 33 35L PDFDocument374 pagesC20 25 30 33 35L PDFVanessa RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Cylinder Head 26916Document2 pagesCylinder Head 26916Wilheam MamaniNo ratings yet
- QSK78 G-Drive Mechanical ProductDocument24 pagesQSK78 G-Drive Mechanical Productquang_dtd09100% (2)
- REG841 - Disassembly and Assembly (D6C TRACTOR ENGINE)Document178 pagesREG841 - Disassembly and Assembly (D6C TRACTOR ENGINE)jeffreyguy1No ratings yet
- MAN Hitachi S50MC C ManualsDocument7 pagesMAN Hitachi S50MC C ManualsVaibhav Sarda100% (2)
- Service Parts Manual: April, 2004Document60 pagesService Parts Manual: April, 2004Miguel MeloNo ratings yet
- Solex Adj ProcedureDocument6 pagesSolex Adj Procedureprivate 2No ratings yet
- Camless EngineDocument19 pagesCamless EngineNitesh GoelNo ratings yet
- Deutz 226b Euro II Engine ManualDocument46 pagesDeutz 226b Euro II Engine Manualmarcosluna6871% (7)
- Mercedes-Benz Sprinter Engine TypesDocument2 pagesMercedes-Benz Sprinter Engine TypesJack Norhy100% (1)
- Wa470 6Document9 pagesWa470 6chaky212No ratings yet
- Toyota ECU ChartDocument8 pagesToyota ECU ChartChonseyNo ratings yet
- Perkins 2800 Series WorkshopmanualDocument10 pagesPerkins 2800 Series Workshopmanualmarylee100% (43)
- 1 ZzfeDocument8 pages1 ZzfeScuderia Redin100% (1)
- Performance Fuel Injection Systems hp1557 How To Design Build Modify and Tune Efi and Ecu Systemscov 191024034015Document6 pagesPerformance Fuel Injection Systems hp1557 How To Design Build Modify and Tune Efi and Ecu Systemscov 191024034015SenghakPhallyNo ratings yet
- Yanmar 2GM20Document70 pagesYanmar 2GM20tnvd420No ratings yet
- 393 TVH 22304331Document462 pages393 TVH 22304331Chester Dalitso MwanzaNo ratings yet
- Hyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionFrom EverandHyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- The Laws of Thermodynamics: A Very Short IntroductionFrom EverandThe Laws of Thermodynamics: A Very Short IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- How to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerFrom EverandHow to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (54)
- Pressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedFrom EverandPressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Faster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestFrom EverandFaster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (28)
- Bulk Material Handling: Practical Guidance for Mechanical EngineersFrom EverandBulk Material Handling: Practical Guidance for Mechanical EngineersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- How to Fabricate Automotive Fiberglass & Carbon Fiber PartsFrom EverandHow to Fabricate Automotive Fiberglass & Carbon Fiber PartsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Modern Engine Blueprinting Techniques: A Practical Guide to Precision Engine BlueprintingFrom EverandModern Engine Blueprinting Techniques: A Practical Guide to Precision Engine BlueprintingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Powder Coating: A How-to Guide for Automotive, Motorcycle, and Bicycle PartsFrom EverandPowder Coating: A How-to Guide for Automotive, Motorcycle, and Bicycle PartsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (17)
- Vibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisFrom EverandVibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Allison Transmissions: How to Rebuild & Modify: How to Rebuild & ModifyFrom EverandAllison Transmissions: How to Rebuild & Modify: How to Rebuild & ModifyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chasing the Demon: A Secret History of the Quest for the Sound Barrier, and the Band of American Aces Who Conquered ItFrom EverandChasing the Demon: A Secret History of the Quest for the Sound Barrier, and the Band of American Aces Who Conquered ItRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (25)
- Basic Digital Signal Processing: Butterworths Basic SeriesFrom EverandBasic Digital Signal Processing: Butterworths Basic SeriesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Machinery's Handbook Pocket Companion: Quick Access to Basic Data & More from the 31st EditionFrom EverandMachinery's Handbook Pocket Companion: Quick Access to Basic Data & More from the 31st EditionNo ratings yet
- Pilot's Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge (2024): FAA-H-8083-25CFrom EverandPilot's Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge (2024): FAA-H-8083-25CNo ratings yet
- Small Engines and Outdoor Power Equipment: A Care & Repair Guide for: Lawn Mowers, Snowblowers & Small Gas-Powered ImplementsFrom EverandSmall Engines and Outdoor Power Equipment: A Care & Repair Guide for: Lawn Mowers, Snowblowers & Small Gas-Powered ImplementsNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting and Repair of Diesel EnginesFrom EverandTroubleshooting and Repair of Diesel EnginesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Einstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseFrom EverandEinstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (51)