Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Impact of Gloablisationon Indian Banking Sector
Uploaded by
Vicky MishraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Impact of Gloablisationon Indian Banking Sector
Uploaded by
Vicky MishraCopyright:
Available Formats
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
Chapter 1 The Indian Banking Sector History of Banking in India Banking in India originated in the first decade of 18th century. The oldest bank in existence in India is the State Bank of India being established as "The Bank of Bengal" in Calcutta in June 1806. The first fully Indian owned bank was the Allahabad Bank, which was established in 1865.
By the 1900s, the market expanded with the establishment of banks such as Punjab National Bank, in 1895 in Lahore and Bank of India, in 1906, in Mumbai - both of which were founded under private ownership. The Reserve Bank of India formally took on the responsibility of regulating the Indian banking sector from 1935. After India's independence in 1947, the Reserve Bank was nationalized and given broader powers. The banking in India was controlled and dominated by the presidency banks, namely, the Bank of Bombay, the Bank of Bengal, and the Bank of Madras - which later on merged to form the Imperial Bank of India, which was renamed as the State Bank of India after the independence. There was potential for many new banks as the economy was growing. Lord Curzon had observed then in the context of Indian banking: "In respect of banking it seems we are behind the times. We are like some old fashioned sailing ship, divided by solid wooden bulkheads into separate and cumbersome compartments."
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
Nationalization By the 1960s, the Indian banking industry has become an important tool to facilitate the development of the Indian economy. At the same time, it has emerged as a large employer, and a debate has ensued about the possibility to nationalize the banking industry. Mrs. Indira Gandhi, thethen Prime Minister of India expressed the intention of the GOI in the annual conference of the All India Congress Meeting in a paper entitled "Stray thoughts on Bank Nationalization." The paper was received with positive enthusiasm. Thereafter, her move was swift and sudden, and the GOI issued an ordinance and nationalized the 14 largest commercial banks with effect from the midnight of July 19, 1969. Jayaprakash Narayan, a national leader of India, described the step as a "masterstroke of political sagacity." Within two weeks of the issue of the ordinance, the Parliament passed the Banking Companies (Acquisition and Transfer of
Undertaking) Bill, and it received the presidential approval on 9th August, 1969. A second dose of nationalization of 6 more commercial banks followed in 1980. The stated reason for the nationalization was to give the government more control of credit delivery. With the second dose of nationalization, the GOI controlled around 91% of the banking business of India. After this, until the 1990s, the nationalized banks grew at a pace of around 4%, closer to the average growth rate of the Indian economy.
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
Liberalization In the early 1990s the then Narsimha Rao government embarked on a policy of liberalization and gave licenses to a small number of private banks, which came to be known as New Generation tech-savvy banks, which included banks such as Global Trust Bank (the first of such new generation banks to be set up)which later amalgamated with Oriental Bank of Commerce, UTI Bank(now re-named as Axis Bank), ICICI Bank and HDFC Bank. This move, along with the rapid growth in the economy of India, kick started the banking sector in India, which has seen rapid growth with strong contribution from all the three sectors of banks, namely, government banks, private banks and foreign banks. The new policy shook the Banking sector in India completely. Bankers, till this time, were used to the 4-6-4 method (Borrow at 4%; Lend at 6%; Go home at 4) of functioning. The new wave ushered in a modern outlook and tech-savvy methods of working for traditional banks. All this led to the retail boom in India Functions of Banks today Banks act as payment agents by conducting checking or current accounts for customers, paying cheques drawn by customers on the bank, and collecting cheques deposited to customers' current accounts. Banks also enable customer payments via other payment methods such as telegraphic transfer, EFTPOS, and ATM.
Banks borrow money by accepting funds deposited on current account, accepting term deposits and by issuing debt securities such as banknotes and bonds. Banks lend money by making advances to customers on
3
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
current account, by making installment loans, and by investing in marketable debt securities and other forms of lending.
Banks provide almost all payment services, and a bank account is considered indispensable by most businesses, individuals and
governments. Non-banks that provide payment services such as remittance companies are not normally considered an adequate substitute for having a bank account.
Banks borrow most funds borrowed from households and non-financial businesses, and lend most funds lent to households and non-financial businesses, but non-bank lenders provide a significant and in many cases adequate substitute for bank loans, and money market funds, cash management trusts and other non-bank financial institutions in many cases provide an adequate substitute to banks for lending savings to. The economic functions of banks include: Issue of money -- Issue of money, in the form of banknotes and current accounts subject to cheque or payment at the customer's order. These claims on banks can act as money because they are negotiable and/or repayable on demand, and hence valued at par and effectively transferable by mere delivery in the case of banknotes, or by drawing a cheque, delivering it to the payee to bank or cash.
Netting and settlement of payments -- banks act both as collection agent and paying agents for customers, and participate in inter-bank clearing and settlement systems to collect, present, be presented with, and pay
4
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
payment instruments. This enables banks to economize on reserves held for settlement of payments, since inward and outward payments offset each other. It also enables payment flows between geographical areas to offset, reducing the cost of settling payments between geographical areas.
Credit intermediation -- banks borrow and lend back-to-back on their own account as middle men
Credit quality improvement -- banks lend money to ordinary commercial and personal borrowers (ordinary credit quality), but are high quality borrowers. The improvement comes from diversification of the bank's assets and the bank's own capital which provides a buffer to absorb losses without defaulting on its own obligations. However, since banknotes and deposits are generally unsecured, if the bank gets into difficulty and pledges assets as security to try to get the funding it needs to continue to operate, this puts the note holders and depositors in an economically subordinated position.
Maturity transformation -- banks borrow more on demand debt and short term debt, but provide more long term loans. Bank can do this because they can aggregate issues (e.g. accepting deposits and issuing banknotes) and redemptions (e.g. withdrawals and redemptions of banknotes), maintain reserves of cash, invest in marketable securities that can be readily converted to cash if needed, and raise replacement funding as needed from various sources (e.g. wholesale cash markets and securities markets) because they have a high and more well known credit quality than most other borrowers.
5
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
The Financial and Other services provided by banks Merchant banking: Merchant Banking is an organization which underwrites securities for the company, advises in various activities. Banks provide services to businessmen to promote their business.
Leasing: Banks have started funding the fixed assets through leasing. A written agreement is made in this respect.
Mutual Funds: Banks have floated new subsidiaries to undertake the business of Mutual Funds. The main function of mutual fund is to mobilize the saving of general public and invest them in stock market and money market. Unit Trust of India is the first mutual fund started in India in 1964. The nationalized banks have started their mutual funds through subsidiaries.
Money Transfer: Banks are helping business and society for transfer of money from place to place or person to person.
Housing Finance: There are variety of housing finance schemes stared by banks. Such as purchase of new house, construction of new home, home improvement, repairs, extension, land purchase, Bridge loans, and balance transfer loans.
Portfolio Management: Portfolio management is a process of investment in securities. The portfolio should be reviewed and adjusted from time to time in tune with the market conditions.
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
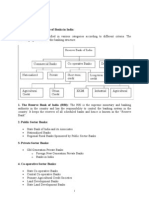
Structure of the Banking System Central Bank (Reserve Bank)
Commercial Bank
Co-operative Bank
Scheduled Bank
Non-Scheduled Bank
Indian Bank Public Sector Bank
Foreign Bank Regional Rural Bank Local Area Bank Private Sector
Bank
SBI& Group
Nationalized Bank
Old Bank
New Bank
Importance of Banks We need banks in our day to day life. Banks cater to the needs of farmers, businessman, traders, industrialists and common people in the society. Common people save money, which they put into bank for safety, security and getting some return out of it. Businessmen, traders and industrialists open their account in the bank and carry out their transactions for receipts of payment of money through cash or cheques. They can also get loans from the bank for financing their business activities. Farmers can borrow money from the bank for seeds, irrigation, fertilizers, etc. They can also save and invest their surplus money in the banks. Thus, banks are needed by every section of our society.
7
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
Banks are an indispensable part in the modern developing society. They act as an agent of their customers in performing the functions such as collection of dividends, pensions, purchase and sale of securities and payments of salary and other expenses. Banks are also needed by the Government. Banks act as agent as well as banker of the Government. They collect money from the Public, tax payers and businessmen on behalf of the Government and payments are also made through the Government. Only a bank can issue cheque books to the depositors because they are authorized by the Banking Regulations Act. A bank performs a multitude of functions and services which cannot be reached into a single definition. A bank may mean different things for different people. For some it is a store house of money, for others an institution of funding money and to get finance and yet something else to others. Banking today means a lot more . In Current situation, banking in India is generally fairly mature in terms of supply, product range and reach-even though reach in rural India still remains a challenge for the private sector and foreign banks. In terms of quality of assets and capital adequacy, Indian banks are considered to have clean, strong and transparent balance sheets relative to other banks in comparable economies in its region. The Reserve Bank of India is an autonomous body, with minimal pressure from the government. With the growth in the Indian economy expected to be strong for quite some time-especially in its services sector-the demand for banking services, especially retail banking, mortgages and investment services are
8
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
expected to be strong. One may also expect M & As, takeovers, and asset sales. In March 2006, the Reserve Bank of India allowed Warburg Pincus to increase its stake in Kotak Mahindra Bank (a private sector bank) to 10%. This is the first time an investor has been allowed to hold more than 5% in a private sector bank since the RBI announced norms in 2005 that any stake exceeding 5% in the private sector banks would need to be vetted by them. Currently, India has 88 scheduled commercial banks (SCBs) , 28 public sector banks (that is with the Government of India holding a stake), 29 private banks (these do not have government stake; they may be publicly listed and traded on stock exchanges) and 31 foreign banks. They have a combined network of over 53,000 branches and 17,000 ATMs. According to a report by ICRA Limited, a rating agency, the public sector banks hold over 75 percent of total assets of the banking industry, with the private and foreign banks holding 18.2% and 6.5% respectively.
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
Chapter - 3 Globalization Introduction to Globalization Globalization in its literal sense is the process of making, transformation of some things or phenomena into global ones. It can be described as a process by which the people of the world are unified into a single society and function together. This process is a combination of economic, technological, socio-cultural and political forces. Globalization is often used to refer to economic globalization, that is, integration of national economies into the international economy through trade, foreign direct investment, capital flows, migration, and the spread of technology. The concept of Globalization infers that the globe is a single unit which functions as one when it comes to decision-making. In other words, Globalization implies the free movement of goods, services and capital throughout the world. Globalization involves the opening up of national economies to global markets. Many Socialists define Globalization as a primarily economic phenomenon, which involves increasing interaction and integration of national economic systems. This leads in turn to growth in international trade, investment and capital flows. Moreover, there is a rapid increase in cross-border social, cultural and technological exchanges because of the phenomenon of globalization. The sociologist defines globalization as a decoupling of space and time. With the advent of instantaneous communications, knowledge, trade and culture can be shared around the world simultaneously. This will
10
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
ultimately result in an increase in international trade, investment and capital flows. On the other hand, some critics define Globalization as ''the worldwide drive towards a globalize economic system, dominated by supranational corporate trade and banking institutions that are not accountable to the democratic processes or national governments. Due to Globalization, all important institutions like the nation, state, family, work, services, trade, leisure, culture, knowledge etc. are changing. As a result of this, life styles of people throughout the world are also changing, making the world a single unit when it comes to decision making. A Brief History of Globalization The word "globalization" has been used by economists since the 1980s; however, its concepts did not become popular until the latter half of the 1980s and 1990s.
Globalization is viewed as a centuries long process, tracking the expansion of human population and the growth of civilization, that has accelerated dramatically in the past 50 years. Early forms of globalization existed during the Roman Empire, the Parthian empire, and the Han Dynasty, when the silk road started in China, reached the boundaries of the Parthian empire, and continued onwards towards Rome. Global integration continued through the expansion of European trade in the 16th and 17th centuries, when the Portuguese and Spanish Empires expanded to the Americas. Globalization has had a tremendous impact on cultures, particularly indigenous cultures, around the world. Four distinct phases of globalization can be discerned in modern history:11
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
The first phase began in sixteenth century with the passing of premodern localism, improvements in maritime technology leading to great age of maritime exploration and discovery. The second phase from the late eighteenth century was marked by the spread of industrial revolution and vast improvements in human technology, productivity and demand, which lead to mass production. The Industrial Revolution opened up a rapidly and widening income gap between Europe and America on the other hand and the rest of the world on other. During the third phase, merchandise trade resumed its triumphant march as the engine of hyper growth in East Asia from the 1970s. International trade/GDP ratios recovered to their late 19th century level by the last decade of the 20th century. This globalization thrust was led by trans -national corporations (TNCs) that endeavored disseminate international trade and modern technology to every flag on earth. Globalization arguably entered in the frenetic fourth phase from the end of the twentieth century, in which developed and developing countries are becoming more equal partners in the flow of cross border trade and investment, as per capita income between the developed and developing countries of the world rapidly converge, galvanized by the awakening of the ancient sleeping giants, China and India.
12
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
Globalization Understandings "Globalization simply means freedom of movement for goods and people, and it is hard to be violently hostile to that. This term has become a common word within the last few decades. This is a coming event and some people are looking forward to the coming events. Others fear and protest away from it. Some even see it as a defining point soon to come to change our lives.
Pros and Cons of Globalization
The debates are strong and fierce for and against globalization. To take a look closer at this, we view the pros and cons of globalization itself. According to an April 2000 issue of Business Week these are the most common Pros and Cons.
Pros 1. Viewing both the Productivity grows more quickly when countries produce goods and services in which they have a comparative advantage. Living standards can go up faster. 2. Global competition and cheap imports keep a lid on prices, so inflation is less likely to derail economic growth. 3. An open economy spurs innovation with fresh ideas from abroad. 4. Export jobs often pay more than other jobs. 5. Unfettered capital flows give the U.S. access to foreign investment and keep interest rates low.
13
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
The Pros for globalization show that prices will be kept at one set price and that money will be quickly made by all. That help with foreign countries could also speed up technology as well. Technology could help the underdeveloped countries in the long run, and help everyone overall economically.
Cons 1. Millions of domestic people lose their jobs due to imports or production shifts abroad. Most find new jobs - that pay less. 2. Millions of others fear losing their jobs, especially at those companies operating under competitive pressure. 3. Workers face pay-cut demands from employers, which often threaten to export jobs. 4. Service and white-collar jobs are increasingly vulnerable to operations moving offshore. 5. U.S. employees can lose their comparative advantage when companies build advanced factories in low-wage countries, making them as productive as those at home.
The Con list shows that the concerns are that smaller businesses will be put out of business by larger ones. Also stating that only the white-collar or richer people will be making a benefit in the changes.
It can be said that form the above observations made about globalization, both sides have good points. Pro groups are saying there is money for all and that it will help undeveloped countries grow. The anti group in retaliation are saying that only the rich will gain from this globalize
14
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
economy. Both continue to fight for what they see as right in their own ways. But without more facts and effort from the anti-globalist this economy is going to continue towards globalization. Only time will tell what the real outcome really will be
Globalization in the era since World War II is largely the result of planning by economists, business interests, and politicians who recognized the costs associated with protectionism and declining international economic integration. Their work led to the Bretton Woods conference and the founding of several international institutions intended to oversee the renewed processes of globalization, promoting growth and managing adverse consequences. These institutions include the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (the World Bank), and the International Monetary Fund.
Critics have observed that the term's contemporary usage comprises several meanings. The term "globalization," like most terms of public discourse, has two meanings: its literal meaning, and a technical sense used for doctrinal purposes. In its literal sense, "globalization" means international integration. In the technical sense defined by the powerful, they are described as "anti-globalization," which means that they favor globalization directed to the needs and concerns of people, not investors, financial institutions and other sectors of power, with the interests of people incidental.
15
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
Measuring globalization Looking specifically at economic globalization, it can be measured in different ways. These center around the four main economic flows that characterize globalization:
1.Goods and services, e.g. exports plus imports as a proportion of national income or per capita of population
2.Labor/people, e.g. net migration rates; inward or outward migration flows, weighted by population
3.Capital, e.g. inward or outward direct investment as a proportion of national income or per head of population
4.Technology, e.g. international research & development flows; proportion of populations (and rates of change thereof) using particular inventions (especially 'factor-neutral' technological advances such as the telephone, motorcar, broadband).
Aspects Of Globalization Globalization has various aspects which affect the world in several different ways such as: Industrial - emergence of worldwide production markets and broader access to a range of foreign products for consumers and companies. Particularly, the movement of material and goods between and within transnational corporations, and access to goods by wealthier nations and
16
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
individuals at the expense of poorer nations and individuals who supply the labor.
Financial - emergence of worldwide financial markets and better access to external financing for corporate, national and sub national borrowers. Simultaneous though not necessarily purely globalize is the emergence of under or un-regulated foreign exchange and speculative markets leading to inflated wealth of investors and artificial inflation of commodities, goods, and in some instances entire nations as with the Asian economic boom-bust that was brought on externally by "free" trade.
Economic - realization of a global common market, based on the freedom of exchange of goods and capital.
Informational - increase in information flows between geographically remote locations. Arguably this is a technological change with the advent of fiber optic communications, satellites, and increased availability of telephony and Internet, to the globalist ideology.
Cultural -growth of cross-cultural contacts; advent of new categories of consciousness and identities such as Globalism - which embodies cultural diffusion, the desire to consume and enjoy foreign products and ideas, adopt new technology and practices, and participate in a "world culture"; loss of languages
Social - increased circulation by people of all nations with fewer restrictions. Provided that the people of those nations are wealthy enough
17
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
to afford international travel, which the majority of the world's population is not. An illusory 'benefit' recognized by the elite and wealthy, and increasingly so as fuel and transport costs rise.
Advantages of Globalization 1. Goods and people are transported with more easiness and speed 2. free trade between countries increases 3. global mass media connects all the people in the world 4. as the cultural barriers reduce, the global village dream becomes more realistic 5. the interdependence of the nation-states increases 6. as the liquidity of capital increases, developed countries can invest in developing ones 7. the communication between the individuals and corporations in the world increases
18
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
Effects of globalization 1. enhancement in the information flow between geographically remote locations 2. the global common market has a freedom of exchange of goods and capital 3. there is a broad access to a range of goods for consumers and companies 4. worldwide production markets emerge 5. free circulation of people of different nations leads to social benefits 6. corporate, national and sub national borrowers have a better access to external finance 7. worldwide financial markets emerge 8. multiculturalism spreads as there is individual access to cultural diversity. This diversity decreases due to hybridization or assimilation 9. international travel and tourism increases 10.worldwide sporting events like the Olympic Games and the FIFA World Cup are held 11.local consumer products are exported to other countries 12.immigration between countries increases 13.cross-cultural contacts grow and cultural diffusion takes place 14.there is an increase in the desire to use foreign ideas and products, adopt new practices and technologies and be a part of world culture 15.free trade zones are formed having less or no tariffs
19
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
16. due to development of containerization for ocean shipping, the transportation costs are reduced. Chapter 4- Impact of Globalization on developing countries Globalization is the new buzzword that has come to dominate the world since the nineties of the last century with the end of the cold war and the break-up of the former Soviet Union and the global trend towards the rolling ball. The frontiers of the state with increased reliance on the market economy and renewed faith in the private capital and resources, a process of structural adjustment spurred by the studies and influences of the World Bank and other International organizations have started in many of the developing countries. Also Globalization has brought in new opportunities to developing countries. Greater access to developed country markets and technology transfer hold out promise improved productivity and higher living standard. But globalization has also thrown up new challenges like growing inequality across and within nations, volatility in financial market and environmental deteriorations. Another negative aspect of globalization is that a great majority of developing countries remain removed from the process. Till the nineties the process of globalization of the Indian economy was constrained by the barriers to trade and investment liberalization of trade, investment and financial flows initiated in the nineties has progressively lowered the barriers to competition and hastened the pace of globalization
Globalization and Inflation Ironically a chief culprit of todays Inflation is the source that has kept inflation low for much of the last two decades. Its long being an article of faith among economists that increasing integration of national
20
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
economies
contributed
heavily
to
global
decline
in
inflation.
Globalization allows domestic companies to hold down labor cost-via outsourcing. Globalization forced the world global bankers to raise their game to ensure that their countries can attract capital and investment. In recent study the more globalize nations tend to pursue policies that achieve faster economic growth, lower inflation, higher income, greater economic freedom.
Globalization means people all over the globe have a greater ability to share common experience of inflation. Globalization has brought about structural changes in the world economy. This includes services particularly banking and finance services is yet to capture the attention of researchers and policy makers in many countries.
Globalization and Poverty: Globalization in the form of increased integration though trade and investment is an important reason why much progress has been made in reducing poverty and global inequality over recent decades. But it is not the only reason for this often unrecognized progress, good national polices, sound institutions and domestic political stability also matter.
Despite this progress, poverty remains one of the most serious international challenges we face up to 1.2 billion of the developing world 4.8 billion people still live in extreme poverty. But the proportion of the world population living in poverty has been steadily declining and since 1980 the absolute number of poor people has stopped rising and appears
21
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
to have fallen in recent years despite strong population growth in poor countries.
It can be said that globalization has both positive and negative impacts on a developing country like India. Pro groups are saying there is money
for all and that it will help undeveloped countries grow. The anti group in retaliation are saying that only the rich will gain from this globalize economy. Both continue to fight for what they see as right in their own ways. But without more facts and effort from the anti-globalist this economy is going to continue towards globalization. Only time will tell what the real outcome really will be. Globalization In India A large number of global multinational brands such as Coca-Cola, Google, Micro-soft and Mercedes-Benz have successfully operating in India. Indian Brands which were operating locally in India earlier have started competing internationally. From New Delhi to New York brands have become global.
Pattern of consumption in India has also changed. Level of spending on the private consumption has been growing significantly. Spending by young consumers in India is regarded as the most powerful consumers.
In an era of globalize environment, the country has become a major player in the socio-economic fields from merely a third world country. BRIC and other reports have forecasted India to be the third largest economy by 2040.
22
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
Globalization in India has transformed the countrys system. Presently India is regarded as an economy dominated country rather than politics driven, as it was earlier. Political dominance has fallen significantly these days. Adoption of Globalization in India and liberalization principles has widened the horizon of country's Consumers worldwide. Consumers in India have become more conscious. Market information in India has become clear.
More over, development in education and awareness is largely marked in the country in the era of Globalization in India
Globalization in India has been advantageous for companies that have ventured in the Indian market. By simply increasing their base of operations, expanding their workforce with minimal investments, and providing services to a broad range of consumers, large companies entering the Indian market have opened up many profitable opportunities.
Indian companies are rapidly gaining confidence and are themselves now major players in globalization through international expansion. From steel to Bollywood, from cars to IT, Indian companies are setting themselves up as powerhouses of tomorrows global economy.
Impact on India: India opened up the economy in the early nineties following a major crisis that led by a foreign exchange crunch that dragged the economy close to defaulting on loans. The response was a slew of Domestic and external sector policy measures partly prompted by the immediate needs and partly by the demand of the
23
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
multilateral organizations. The new policy regime radically pushed forward in favor of amore open and market oriented economy.
Major measures initiated as a part of the liberalization and globalization strategy in the early nineties included scrapping of the industrial licensing regime, reduction in the number of areas reserved for the public sector, amendment of the monopolies and the restrictive trade practices act, start of the privatization program, reduction in tariff rates and change over to market determined exchange rates.
Over the years there has been a steady liberalization of the current account transactions, more and more sectors opened up for foreign direct investments and portfolio investments facilitating entry of foreign investors in telecom, roads, ports, airports, insurance and other major sectors.
Globalization and the future of Indian economy: Globalization is an inevitable, irreversible process despite some vested interests trying to thwart it and some other vested interests trying to take better advantage of globalization than others. This is because the increasing prosperity of people at large of each and every country in the World is dependent on global trade, economic cooperation and global integral of economic activities in all spheres- trade, commerce, financial services, technology commercialization, conservation of exhaustible resources, information and knowledge acquisition, protection of environment, ecology, food and health security, enrichment of cultural diversity, tourism, travel, and so on. This is being increasingly realized by
24
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
more and more common citizens of almost every country. The vested interests of military/ dynastic ideological exploitation and oppression are getting exposed and will not be able to keep common people away from globalization and its benefits for long.
Indian economy will also benefit and grow at a rapid rate, ensuring radical improvements in standards of living and quality of life for more than 1.1 billion Indians over the years. The increasing trend towards regional trade agreements and bilateral trade agreements will make India realize that India is already on the fast march on the path of globalization. India is becoming more expert in sorting out issues at WTO. This may create problems for politicians and their parties, they will not be able to live the comfortable luxurious lives and enjoy the privileges of power to control the lives of the masses, keeping them at their mercy for long.
Importers have strong financial interest in globalize economy. But the greater danger posed by unrestricted globalization is that it may exacerbate problem of nagging poverty and uneven development. It is already evident that Indian Economy has become more dependent on imports which have brought pressure on value of rupee, leading to high Inflation.
For coping with risk that arise out of globalization Banks have adopted reforms in calibrated manner. Due to globalization not only the GDP has increased but also the direction of growth in the sectors has also been changed. Earlier the maximum part of the GDP in the economy was generated from the primary sector but now the service industry is
25
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
devoting the maximum part of the GDP. The services sector remains the growth driver of the economy with a contribution of more than 57 per cent of GDP. India is ranked 18th among the worlds leading exporters of services with a share of 1.3 per cent in world exports. The service sector is expected to benefit from the ongoing liberalization of the foreign investment regime into the sector.
The Faces Of Globalization: A Dilemma For India It's good for the economy; it creates employment, lots of it, and working nights at India's back offices is pleasing and financially rewarding for a huge number of young Indians. However, while India's money-spinning industry of taking service jobs from overseas is turning out to be a source of discomfort for U.S. and European politicians, the subcontinent is fast realizing that its now-famed success in so-called Business Process Outsourcing may have come at the cost of a generation's mental well-being. Owing to the 10 1/2 hour time difference between the Western Hemisphere, particularly the United States, which sends more service jobs abroad than anyone else, almost all Indian back office operations have to work at shifts typically running from 5 p.m. to 3 a.m. local time to coincide with the daytime office hours in the United States. And it's this working at nights that requires adjusting the biological clock and social practices to a different time, which is turning out to be a major cause for health-related and social problems.
26
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
Still, even as the money and the act of donning an American life-style through their working hours continues to be the initial draw for many youngsters in the country's numerous back offices and call centers, a worry that is looming large is: high social and health costs that the country is paying for raking in billions of dollars, spoil India's back office party sooner rather than later. Cases of successful Mergers in India as a result of globalization Globalization and mergers in India are among the most popular issues in India and there has been plenty of debate surrounding these issues. Of late, several sectors of the economy are heating up with numerous mergers and global alliances. According to a recent review, this will improve the economy of the country.
Mergers in India have led to a massive upsurge in the Indian economy. Numerous companies in the auto sector, steel sector, cement sector, pharmaceutical sector, petrochemical sector, and many more have experienced mergers with the global companies. Among all the industrial sectors in India, these are the few sectors which have witnessed the maximum profit brought in by globalization and mergers with global associations. The automotive sector is on the top list among the mergers in India with Maruti Udyog Pvt. Ltd. and Tata Motors ruling the sector. Tata Motors, one of the leading organizations in the auto sector has had the maximum mergers and deals with trucks and agricultural machinery besides cars and motors. The Fiat Company is looking forward to some big-time trade through mergers in India as well and is already being distributed by Tata Motors in India.
27
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
The mergers and acquisitions done by the global companies in India are susceptible to continuous change in practicing the same. Globalization and mergers in India is an influential perspective of any corporate executive on every detail of mergers and acquisitions exercised around the world. The transactions in the mergers in India include governing mergers, joint ventures, acquisitions, takeovers, and other kinds of crossborder transactions.
According to the expert knowledge of domestic markets, it is mandatory to have International Mergers & Acquisitions Law for any company or occupational group who is pursuing a global business strategy. The trends and growth of mergers and acquisition dealings, changes in regulative sector, and restructuring of the already modified associates led to a marked increase in the globalization and mergers in India.
28
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
Chapter 5 - Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector The term globalization connotes enhanced connectivity among people across the national borders. The nature and pace of globalization depends on the combined effect of technology and the public policy both at the national and international levels. With the growing integration of economies and the markets around the world, global banking has arrived and is here to stay. Globalization will further fillip with the opening of financial services under WTO. India, being one of the signatories of financial services agreement of 1997, is poised to expand the reach of its financial services, including banking, on a reciprocal basis to many countries.
The process of globalization will increase the presence of international players in the banking arena in India. Similarly, some of the Indian banks will become global players. So, the banks will perforce spread their net beyond borders in their quest for new markets, customers and profit. Against this backdrop, banks in India must not only prepare themselves to retain business back home but also to capture business in hithertounexplored markets by competing with their global counterparts. Size is not the only problem. Indian banks are considered to be lacking in necessary products, skill sets on the part of their human resources and risk-taking. The implementation of Basel II norms in right earnest is, therefore, critical for Indian banks seeking an international presence. It is felt that top international banks will enjoy lesser capital requirements on
29
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
the back of their superior risk management practices. This will enable them to price their products aggressively when compared to the banks in India. Another key issue facing banks planning to go global is having a real knowledge of the foreign market and making the best preparation possible for an entry into it. Banks must be focused and disciplined. They need a long-term plan, know what they want to achieve, consider the strategic benefits, assess the risks and identify the competencies and challenges. This global move may be achieved through joint venture or an acquisition or any other route, but not before analyzing the market and competitors. The challenges do not stop with successful market entry. The banks must continuously evaluate and update their operations and optimize the business processes to main competitive. The Reserve Bank of India has, however, prepared sufficient ground on domestic turf so that the aspiring Indian banks will not be left behind in their bid to become truly global players. As pointed out by V Leeladhar, Deputy Governor of The RBI, in a speech delivered to Kanara chamber of commerce and Industry in March, Indian Banking Sector has already implemented internationally followed prudential accounting norms for the
classification of assets, income recognition and loan-loss provisioning. Currently, the banking sector in India complies with transparency and disclosure norms comparable with the best international practices.
Overall, the Indian Banking sector is stronger today than it was a decade ago. The focus on the microfinance and lending to small and medium enterprise firms welcome change for the banking sector as well as the economy and society as a whole. Finding opportunities at the bottom of
30
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
the pyramid rather than regulator-mandated loan-publishing is likely to help in better distribution of the economic gains as well as opportunities. Managing the risk through the implementation of the Basel II is likely to be an important step of Indian Banking Sector in the future. Banks and financial institutions will continue to experiment with new technologies and electronic, information based services to serve their customers better. The potential is great, yet the return on investment will be realized only in the long term. Proper alignment of technology strategies with business goals will ensure commensurate value addition to banks.
Also, banks are rediscovering the need for more brick-and-mortar branches as the most effective touch points for building relationships, marketing and selling. Advancements in technology like data mining and business intelligence will enable and empower branch personnel to realize higher customer life cycle value. The information-intensive nature of banking and financial service is unlikely to change. Banks will continue to find new and innovative ways to put technology and business risks associated with these investment proactively.
Globalization of Banking in India Integration of economies leads to integration of financial markets catalyzing the globalization process. The growing role of the financial sector in allocation of resources has significant potential advantages for the efficiency with which our economy functions. Consequently, the adverse consequences of malfunction of the financial system are likely to be more severe than they used to be in the past. Hence, all our efforts today are focused at ensuring greater financial stability. Given the
31
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
significance of the Indian banking system, one cannot afford to underplay the importance of a robust and resilient banking system. The enhanced role of the banking sector in the Indian economy, the increasing levels of deregulation along with the increasing levels of competition have facilitated globalization of the India banking system and placed numerous demands on banks. Operating in this demanding environment has exposed banks to various challenges. The last decade has witnessed major changes in the financial sector - new banks, new financial institutions, new instruments, new windows, and new opportunities - and, along with all this, new challenges. While deregulation has opened up new vistas for banks to augment revenues, it has entailed greater competition and consequently greater risks. Demand for new products, particularly derivatives, has required banks to diversify their product mix and also effect rapid changes in their processes and operations in order to remain competitive in the globalize environment.
The benefits vis--vis Costs To derive maximum advantage from technology investments, banks should use technology as a strategic resource and align it well with their business strategies and objectives. The strategic plan should clearly spell out how much business value it can enhance and it should not be used as mere publicity stunt. It is crucial that experts who have sufficient exposure to both banking and technology domains formulate the strategic planning. It is difficult to measure productivity in financial services unlike in the rest of the service sector, since there is a constant improvement in the quality of service in the quality of service in his sector due to greater convenience, speed and lower risk. Moreover,
32
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
measuring the inputs used to produce outputs is not easy. Lack of consistent data also hampers researchers from analyzing the cost and benefits reliably. However, investments in the IT is justified by most CEOs as the cost for retaining good customers, if not attracting new ones, and for the better competitive advantage it provides.
Significance of Service Quality in Banking With continuous growth of competition in market place, understanding the customer has become more and more important. Research show that high quality contributes significantly to Profitability. The result of the present study shows that the Internet is a convenience tool available whenever and wherever customers need it. It is also found that the Internet has improved the factors in service quality like responsiveness, communication and access. It is concluded that the Internet has an important and positive effect on customer perceived banking services and the service quality has been improved since the Internet has been used in banking sector. Furthermore, the study offers suggestions to banking managers to allocate their resources on the dimensions i.e., reliability, responsiveness, security, communication and access to improve service quality according to its relative importance since the Internet has been used.
Now a days incredible growth of technology-intensive- new delivery channels has liberalized the customers from the constraints of time and space. Thanks to the high-level of service quality and standard, ATMs have transformed the sway the customers carry out their banking
33
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
transactions. Quality initiatives like Six Sigma can go a long way in controlling this variance to ensure uniform customer experience.
Infusion of Technology made a Difference Unlike the global banks, Indian banks have hooked on to the computerization drive rather late, i.e., by the 1980s and 1990s. They began with PC-based system, moved on to total branch automation and later to networking and implementation of centralized/Core Banking Solution (CBS).Banks tend to use information technology more intensively and practice niche banking. Efficiency ladder has been driven almost exclusively by the new private banks ICICI, UTI, HDFC, etc. Some new technologies introduced are: Core banking solutions(CBS) The concept of CBS, which allows a customer to fulfill a wide range of banking operations online, has come alive during past four years. The number of branches providing CBS has grown rapidly to 44 percent since last years. The combination of a centralized database and browser client is a powerful enabler of business process changes, as the processes can be centralized, decentralized, split across locations or completely outsourced at short notice to improve efficiency, enhance quality or reduce risk. Core Banking Platform's open architecture ensures easy interface to third party systems. The product can be interfaced with various delivery channels like ATM, Internet Banking and Phonebanking. It has a common set of service components that provide a uniform customer experience across all channels. It has a user-friendly,
34
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
browser-based interface and operates in a truly 24 x 7 x 365 basis with uninterrupted transaction execution.
Instant Fund Transfer: RTGS and NEFT National Electronic Fund Transfer(NEFT) enables us to transfer funds electronically from our bank account to an account in an other bank. Typically it takes a day for an account to be debited and other to be credited. There are no lower or upper limits for NEFT and generally banks do not charge their customers who avail this facility.
Real Time Gross Settlement is where money is actually transferred instantly to beneficiary account. If the amount is not transferred to the beneficiary account within two hours for some reason the money is credited back to your account. High tech banking ATMs: With growing technological innovations, banks have significantly expanded their ATM network over the past three years. According to RBI data as of end June2008, the number of ATMs in the country had climbed to 36314 compare to 27088 at end March 2007 respectively.
Loan Disbursement: Technology has facilitated the growth in loan disbursement also, making the whole process simpler and faster. The sector has delivered a growth of 30% a year over last 4-5 years. The Impact on Customers
35
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
The shift from branch counter to e-channels has indeed enhanced customer service and convenience. The dream of anytime, anywhere banking is a reality now. With facilities like mobile alerts, customers can get real-time information about transactions in their accounts. The warmth and human touch is missing because of the mechanical media, leaving many a customer to contemplate the benefits of talking to the good old banker. The silver lining for customers is that they can shift to competitors banks easily if they are not satisfied with the services from the present bank.
Innovation and Branding the Product Experts opine that innovation is the key to the sustained growth of the banking industry in future. However, innovation cannot be limited to products and brands. Successful financial service players are required to embed innovation in every aspect of their functioning, ranging from products and processes to even people, system and business partners.
However, product innovation is important and such innovative products need to be tailor-made for different customer segments; for example specific to age groups, regions and so on. However, a bank should develop a clear vision on the various parameters of innovations. Banking Then and Now Indian villages were deprived of various financial products like MF, insurance and equity trading, which are now accessible through proxy banking in form of ATMs and kiosks. This is possible because banking
36
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
transactions are stored in a centrally located server with which all other branches are connected.
Chapter 6- Implication of Globalization Globalization has had an impact on different cultures around the world. The seeds of globalization have been sowed with the introductions of financial sector reforms. These include the following:
1) Deregulation of interest rates, 2) Capital Adequacy norms, 3) Internationally accepted accounting norms, 4) Asset classification, 5) Entry of Private Banks, 6) Reduction of Government stake in banks.
With reforms and the rapid globalization the very character of banks underwent a fundamental change. Enhancing the profit and profitability has become one of the major concerns for the banks. The prime driver behind the reduction of cost is the increase of operational efficiency of the banks. With the advent of Internet banking, the path for tremendous cost saving was paved.
Commercial bank through out the world has been undergoing a major transformation. Traditional banks have long been exposed to strong external pressures brought about the influence of worldwide globalization
37
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
and unceasing technological development. Banks have been rapidly expanding the menu of financial services they offer to their customers. This proliferation of services has accelerated over the years under the pressure of increasing competition from other financial firms. It has also increased bank costs and posed a greater risk of bank failure. The new services have had a positive effect on the industry through a new source of bank revenue (interest income). Interest Rates; likely Scenario Interest rates are currently on the rise mainly on account of high oil and commodity prices coupled with high inflation. Also, problems due to erratic monsoon and its corresponding effect on agriculture production, along with higher-than-anticipated money supply growth, are putting an upward bias to the yield curve across maturities. The impact of this rising interest rates on the banks will lead to reprising of the portfolio of the banks on both asset and liability sides. The banks net interest margin may be affected as liabilities in general get reprised faster than its assets. As a whole, banks must develop a short, medium and long term views on interest rates in their corporate planning exercise, wherein adverse impact of a rising interest rate scenario can be taken care of through advance planning. Such measures vary from bank to bank depending on the composition of the portfolio. Opportunity for Private Sector This is the most visible change in Indian financial system. With the emergence of new private sector banks and the entry of foreign banks, the Indian banking is quickly getting drawn into globalize financial system.
38
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
Emphasis on Professionalism The spirit of competition and the emphasis on profitability are also driving PSBs towards greater profit-orientation from the socialistic approach that was followed earlier. In general, it seems that the emergence of new private banks and the increased participation of foreign banks have increased professionalism in the banking sector as a whole.
One of the major forces of globalization in India has been in the growth of outsourced IT and business process outsourcing (BPO) services. The last few years have seen an increase in the number of skilled professionals in India employed by both local and foreign companies to service customers in the US and Europe in particular. Taking advantage of Indias lower cost but educated and English-speaking work force, and utilizing global communications technologies such as voice-over IP (VOIP), email and the internet, international enterprises have been able to lower their cost base by establishing outsourced knowledge-worker operations in India.
Healthy Competition would Increase Competition has clearly increased with the Herfindahi Index for advances and assets dropping by over 28% and 20% respectively during 1991-92 and 2000-01. Over the period, The State Bank of India, the largest Indian Bank, witnessed a decline in asset market share from 28% to 24% while its loan market share dropped from 27% to 22%. The deposit share, on the other hand, stayed pretty much the same at 23%. The asset, loan and deposit shares of the top 10 banks all fell from close to 70% to below
39
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
60%. Nevertheless, the PSBs still enjoy a preeminent position in the Indian banking sector today, accounting for over 80% of deposits and credit. There is, however, a noticeable trend of private banks gradually eroding the market share of the public sector. Software Packages for Banking Applications in India had their beginnings in the mid 80''s. This move was spurred on by RBI and the C Rangarajan Committee Report which decided to computerize the Indian Banking branches in a limited manner. This move was aimed at promoting competition and allows an easy assessment of relative vendor capabilities. Gradually, even those who opposed computerization in government and banks changed their perspective and within a few years our country became a superpower in Information technology. The early 90s saw a fall in hardware prices and the advent of cheap and inexpensive but high-powered PCs and servers. Banks went in for what was called Total Branch Automation (TBA) Packages. We are now at the point when we have accepted the use of computers in every sphere of our activity today. Opportunities In Todays Scenario The entire banking sector has undergone a restructuring during recent years as a result of Globalization. The I-T revolution has made it possible to provide ease and flexibility in operations to customers thus making life simpler and easier. Rapid strides in information technology have, in fact, redefined the role and structure of banking in India. Further, due to exposure to global trends after Information explosion led by Internet, customers - both Individuals and Corporate - are now demanding better services with more products from their banks. The financial market has
40
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
turned into a buyer's market. Banks are also coping and adapting with time and are trying to become one-stop financial supermarkets. The market focus is shifting from mass banking products to class banking with the introduction of value added and customized products. Public Sector Banks like SBI have also started focusing on this area. SBI plans to open 100 new branches called Personal Banking Branches (PBB) this year. Customized banking products, such as Investment Advisory Services; photo-credit cards; cash Management services; Investment products and Tax Advisory services have already been introduced by a few foreign and private sector banks. A few banks have gone in to market mutual fund schemes. The bank of the future has to be essentially a marketing organization that also sells banking products. New distribution channels are being used; more & more banks are introducing services like disbursement and servicing of consumer loans, Credit card business. Direct Selling Agents (DSAs) of various Banks go out and sell their products. They make house calls to get the application form filled in properly and also take your passport-sized photo. Home banking has already become common. Now, you can order a draft or cash over the phone or internet and have it delivered home. ICICI was the first among the new private banks to launch its net banking service, called Infinity. It allows the user to access account information over a secure line, request cheque books and stop payment, and even transfer funds between ICICI Bank accounts. Citibank has been offering net banking to customers.
41
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
Chapter 7- Challenges to Banking due to Globalization Globalization a Challenge as well as an Opportunity The benefits of globalization have been well documented and are being increasingly recognized. Globalization of domestic banks has also been facilitated by tremendous advancement in information and
communications technology. Globalization has thrown up lot of opportunities but accompanied by concomitant risks. There is a growing realization that the ability of countries to conduct business across national borders and the ability to cope with the possible downside risks would depend, inter-alia, on the soundness of the financial system and the strength of the individual participants. Adoption of appropriate prudential, regulatory, supervisory, and technological framework on par with international best practices enables strengthening of the domestic banking system, which would help in fortifying it against the risks that might arise out of globalization.
In India, we had strengthened the banking sector to face the pressures that may arise out of Opening up of the frontiers for globalization by adopting the banking sector reforms in a has to necessarily follow a carefully laid out policy. As evidenced in our country, we took to reforms in early nineties, strengthened the banking system, opened up in calibrated manner, which followed the twin governing principles of allowed the competition to sink in and tone up the efficiency and service quality.
42
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
The entire reform process the content, pace and sequencing, was undertaken in such a manner that change was achieved in a nondisruptive progress and consultative process manner and the result is indeed very evident. The market participants and the regulator act in tandem to bring about resilience in the financial system, shoring up the confidence levels which are imperative for tapping the fruits of globalization.
Global challenges in banking: Recently a few broad challenges faced by the Indian banks in the following areas viz. enhancement of customer service; application of technology; improvement of risk management systems; implementation of new accounting standards; enhancement of transparency & disclosures; and compliance with KYC aspects. If we were to identify a few global challenges which banks face today, I am sure we would cover some common ground. Hence it can be said that, The global challenges which banks face are not confined only to the global banks. These aspects are also highly relevant for banks which are part of a globalize banking system. Further, overcoming these challenges by the other banks is expected to not only stand them in good stead during difficult times but also augurs well for the banking system to which they belong and will also equip them to launch themselves as a global bank.
The Indian banking sector is currently redefined as it faces myriad challenges and opportunities, especially after 2009, when they will be fully exposed to competition from here global counterparts. Banks are
43
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
bracing themselves to face the competition through the adoption of novel technology and by strengthening their capital base. They are minimizing their Non Performing Asset (NPAs), bringing down operating cost, enhancing corporate governance and alignments, undertaking
organizational restructuring and sharpening their customer-centric initiatives. Consolidation through the merger and acquisition route to effectively compete with large global banks may not be far off, when viewed against such preparedness and positive signs from regulators. Technology is clear a prerequisite for growth and scale. Overcoming Challenge Development in technology also offer potential opportunities for banks to develop and improve their retail distribution channels. Coming to important trends in India, ICICI and several other DFIs have made inroads into universal banking. The opening up of the insurance sector has provided ample opportunities for the banks. ICICI Bank, HDFC Bank, UTI Bank and several other foreign banks have exploited the highly profitable end of banking business i.e. the retail segment. Globalization brings new technology. But today, almost no advocate of globalization is calling for selectivity. For instance Coca-Cola, Pepsi were welcomed in country even though they offered little in terms of new technology. The same can be said of advertising companies and manufacturers of consumer non-durable goods like soap, detergent, cereals toothpaste etc. According to Chris Patten, Chancellor of University of Oxford and former Governor of Hong Kong globalization that triggered the flow of investments and growth in the developing nations brought millions out of
44
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
poverty, particularly in India and China. After the Indian economy opened up, the level of poverty in the country declined, and had the reforms been pursued further and faster, the results would have been better. The untapped potential of the economy remained and there was immense scope for improvement in the bureaucracy and labor reforms in order to sustain the economic reforms. Technology Infusion and Up gradation Challenges Reluctance to adopt the best practices envisaged by the standard CBS packages has forced them to resort to heavy customization, leading to reduced effectiveness and efficiency of the solution. Many large banks have confined the CBS facility to only 20% or 30% of their branches with the justification that it will cover 70% to 80% business of the bank. This has deprived the mass customers of rural branches of the fruits of modern technology. Underutilized and unknown to many, there exists a huge potential at the bottom of the pyramid for banks. It is proved that convenient and anytime banking channels like Automated Teller Machines serve as good avenues for the banking system to procure large amount of cash stacked by the rural folk. It calls for some out-of-the-box solutions to achieve costeffective results. Smart cards can come to the help of the remote villages. Perhaps, the true spirit of financial inclusion can be achieved only when banks use modern technology extensively.
45
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
Conclusion Benefits reaped by Indian Banking sector as a result of globalization is much more than the setbacks To conclude, it can be said that unfortunately, several concerns related to the banking sector still remain. The chief among these is the matter of ownership and control. In the near future, India will be forced to apply the norms of developed countries to the Banking Industry. Consequently, many Indian banks (including some of the biggest) will show very poor return ratios and dozens of banks will go bankrupt. Thus, it becomes imperative that the Banking Industry should streamline itself and become more compatible with global norms in the fields of operation and services. Globalization is a theoretical construct. Its open to various meanings and inflection. It can be described positively, negatively to describe complex process in the economy, culture and everyday life. Globalization has caused suffering to domestic industry, economic crisis in some countries. Globalization created new risks as well as opportunities. Globalization is integration of various markets of world into an international market.
Indian Banks have huge financial resources at their disposal. Indian banks started with aggregate deposits of about 5000 Crores in the Sixties which increased to 10 Lakh Crores this millennium. This denotes a 20046
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
hundred-fold growth in three decades. A major tool which banks have at their disposal is our knowledge capital-something which is being grossly under utilized currently. This is an extremely valuable type of capital. In banking they are short of intangible assets. Our knowledge capital is quite crucial to the success of banking in India. For this banks cannot garner it from outside; neither can they go in for a public issue to mobilize intangible assets.
Therefore banking employees have to embrace the need for higher learning and better knowledge. Banking in India has immense potential given the population figures in our country. With a little effort, careful planning and timely legislation this industry can be brought on par with the best banks in the world. NRI look forward to new business opportunities in a globalize India. Another outcome of globalization has been a huge increase in salaries of senior mangers, accountants, lawyers and public relation personnel working for MNCs. For the IT literate, job opportunities have plentiful, and there are opportunities to live and earn abroad. For the English speaking upper middle class, this has come as boon.To an end note it can also be said that thorough instant transfers, the banking sector has facilitated enormous benefits in terms of convenience and efficiency.
47
Impact of Globalization on Indian Banking Sector
48
You might also like
- Organizational Structure, Development of Banks in IndiaDocument54 pagesOrganizational Structure, Development of Banks in Indiaanand_lamani100% (1)
- Investment Analysis ReportDocument52 pagesInvestment Analysis ReportTanu BansalNo ratings yet
- Energy Audit and Energy SavingDocument21 pagesEnergy Audit and Energy SavingPrafulla Mandlekar100% (2)
- Development Banking in IndiaDocument54 pagesDevelopment Banking in IndiaNitesh GoruleNo ratings yet
- Banking and InsuranceDocument11 pagesBanking and InsuranceGanpat SoundaleNo ratings yet
- Introduction to the Indian Banking SectorDocument94 pagesIntroduction to the Indian Banking SectorDinesh ChahalNo ratings yet
- Indian Finacial System Cia-IiiDocument20 pagesIndian Finacial System Cia-IiiMathew KanichayNo ratings yet
- Introduction to BankingDocument31 pagesIntroduction to BankingRavi Kashyap506No ratings yet
- Executive Summary Credit Management Can Be Defined As "Management of Loans andDocument100 pagesExecutive Summary Credit Management Can Be Defined As "Management of Loans andchowdary368No ratings yet
- Indian Financial System: Role of Commercial BanksDocument11 pagesIndian Financial System: Role of Commercial BanksRohit GoyalNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument11 pagesUnit IShahid AfreedNo ratings yet
- NPA PROJECT For Surat Dist Co-Op BankDocument62 pagesNPA PROJECT For Surat Dist Co-Op BankVijay Gohil33% (3)
- Banking in IndiaDocument25 pagesBanking in IndiaanviNo ratings yet
- BankingDocument7 pagesBankingAnkur Kasliwal JainNo ratings yet
- Banking LawDocument52 pagesBanking LawKillspreeNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Banking Sector & Functions of Banks in IndiaDocument57 pagesIntroduction to Banking Sector & Functions of Banks in IndiaShweta Yashwant Chalke0% (1)
- Chapter-1 Introduction 1.1 Introduction About The SectorDocument60 pagesChapter-1 Introduction 1.1 Introduction About The SectorGaurav Goyal100% (2)
- 12 - Chapter 2 PDFDocument32 pages12 - Chapter 2 PDFManali ShahNo ratings yet
- Dena BankDocument37 pagesDena Bankamit_ruparelia28100% (2)
- Capstone Project PGDM 2992 f3Document12 pagesCapstone Project PGDM 2992 f3pinka02No ratings yet
- State BanksDocument6 pagesState BanksVikram LodhaNo ratings yet
- Winter ProjectDocument25 pagesWinter ProjectKishan gotiNo ratings yet
- Untitled 1Document14 pagesUntitled 1Tushar BhatiNo ratings yet
- Banking Fundamentals and Evolution in IndiaDocument29 pagesBanking Fundamentals and Evolution in Indiashivam kumarNo ratings yet
- 35 Modernization and Innovation in Banking Sector Repaired)Document85 pages35 Modernization and Innovation in Banking Sector Repaired)Hema Golani100% (2)
- Scenario of Foreign Banks in IndiaDocument62 pagesScenario of Foreign Banks in IndiaYesha Khona100% (1)
- UNIT-1 Overview of Banking System in India 1-History of Banking in IndiaDocument14 pagesUNIT-1 Overview of Banking System in India 1-History of Banking in Indiaaanya meenaNo ratings yet
- BIFS - CompleteDocument170 pagesBIFS - CompleteAvinesh curseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction 1.1 Meaning and Definition of BankDocument6 pagesChapter 1: Introduction 1.1 Meaning and Definition of BankdineshNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of HDFC Bank and SBIDocument37 pagesComparative Analysis of HDFC Bank and SBIsiddhantkamdarNo ratings yet
- A Study On Project Report On Commercial BankDocument8 pagesA Study On Project Report On Commercial BankGAME SPOT TAMIZHANNo ratings yet
- Commercial Banking MAYURDocument86 pagesCommercial Banking MAYURShama Jain100% (1)
- What Is A BankDocument13 pagesWhat Is A BankShivkumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chapter: 1 Introduction: Services Provided by Banking OrganizationsDocument56 pagesChapter: 1 Introduction: Services Provided by Banking OrganizationsAmol RaksheNo ratings yet
- Project - Loans and AdvancesDocument60 pagesProject - Loans and AdvancesRajendra Gawate75% (12)
- Introduction To Ozone Layer DepletionDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Ozone Layer DepletionPlease let me knowNo ratings yet
- Project On Credit Scheme Offered by State Bank of India and HDFC Bank in Coimbatore CityDocument63 pagesProject On Credit Scheme Offered by State Bank of India and HDFC Bank in Coimbatore Cityprakalya100% (1)
- Project On Credit Management 222Document82 pagesProject On Credit Management 222Karthik Kartu J71% (7)
- Banking Industry: Definition of BankDocument10 pagesBanking Industry: Definition of BankNikhitha ShettyNo ratings yet
- Impact of Technology On Indian BanksDocument63 pagesImpact of Technology On Indian BanksAnoop Chahal0% (1)
- Project On Andhra Bank: Chapter: 1. Introduction of BankDocument47 pagesProject On Andhra Bank: Chapter: 1. Introduction of BankMukesh ManwaniNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Current Scenario:-: Repayable On Demand or Otherwise and Withdrawal by Cheque, Draft or Otherwise"Document7 pages1.3 Current Scenario:-: Repayable On Demand or Otherwise and Withdrawal by Cheque, Draft or Otherwise"balenappasNo ratings yet
- Innovative Services in Banking SectorDocument32 pagesInnovative Services in Banking SectormeghkumawatNo ratings yet
- Tech-Savvy Banks, and Included Global Trust Bank (The First of Such New Generation Banks ToDocument9 pagesTech-Savvy Banks, and Included Global Trust Bank (The First of Such New Generation Banks ToAbhik RoyNo ratings yet
- History of Commercial Banking in India: DividendsDocument24 pagesHistory of Commercial Banking in India: DividendsMohan KumarNo ratings yet
- 180 Sample-Chapter PDFDocument15 pages180 Sample-Chapter PDFhanumanthaiahgowdaNo ratings yet
- Types of Bank DepositsDocument55 pagesTypes of Bank DepositsrocksonNo ratings yet
- Banking Sector Lifeline Modern EconomyDocument36 pagesBanking Sector Lifeline Modern Economykhatiwada2005No ratings yet
- Centurion University of Technology and Management: Project Report OnDocument23 pagesCenturion University of Technology and Management: Project Report OnKING ZINo ratings yet
- Q1 Banking 1Document18 pagesQ1 Banking 1Adarsh ShetNo ratings yet
- Banking Innovation.: EtymologyDocument78 pagesBanking Innovation.: EtymologyFaisal AnsariNo ratings yet
- Industr Y Profil EDocument73 pagesIndustr Y Profil Esaramitha4910No ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument43 pagesResearch PaperJankiNo ratings yet
- BankinglawDocument86 pagesBankinglawrahul singhNo ratings yet
- History and Evolution of Banking in IndiaDocument65 pagesHistory and Evolution of Banking in IndiaKomal MansukhaniNo ratings yet
- Indian Banking System: An IntroductionDocument67 pagesIndian Banking System: An IntroductionamitNo ratings yet
- All Types of Bank Report SumeshDocument30 pagesAll Types of Bank Report Sumeshsumesh894No ratings yet
- Chapter - 1Document32 pagesChapter - 1raj tripathiNo ratings yet
- Banking India: Accepting Deposits for the Purpose of LendingFrom EverandBanking India: Accepting Deposits for the Purpose of LendingNo ratings yet
- Effective SAP SD PDFDocument54 pagesEffective SAP SD PDFAjitabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Sales and DistributionDocument5 pagesSales and DistributionVicky MishraNo ratings yet
- Service MarketingDocument10 pagesService MarketingVicky MishraNo ratings yet
- Employee EngagementDocument10 pagesEmployee Engagementsrikanth351gmailNo ratings yet
- An Operating SystemDocument3 pagesAn Operating SystemVicky MishraNo ratings yet
- Reliance Life InsuranceDocument101 pagesReliance Life InsuranceVicky Mishra100% (2)
- Role of LICDocument23 pagesRole of LICBhagwan Sangle77% (13)
- Curriculum Vitae (CV)Document6 pagesCurriculum Vitae (CV)Adriana DumitriuNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument21 pagesPresentationFaisal MahamudNo ratings yet
- Bahco Chile 2021Document160 pagesBahco Chile 2021victor guajardoNo ratings yet
- Commercial BanksDocument9 pagesCommercial BanksPrathyusha ReddyNo ratings yet
- MEC 1st Year 2020-21 EnglishDocument16 pagesMEC 1st Year 2020-21 EnglishKumar UditNo ratings yet
- Eric Stevanus - LA28 - Cost AnalysisDocument8 pagesEric Stevanus - LA28 - Cost Analysiseric stevanusNo ratings yet
- Lead Dev Talk (Fork) PDFDocument45 pagesLead Dev Talk (Fork) PDFyosiamanurunNo ratings yet
- Marketing Plan - NikeDocument32 pagesMarketing Plan - NikeHendra WijayaNo ratings yet
- Taxes are the Lifeblood of GovernmentDocument23 pagesTaxes are the Lifeblood of GovernmentVikki AmorioNo ratings yet
- Corporation Law - Atty. Zarah Villanueva (Case List)Document3 pagesCorporation Law - Atty. Zarah Villanueva (Case List)leizzhyNo ratings yet
- Global Market Segmentation TechniquesDocument84 pagesGlobal Market Segmentation TechniquesRica de los SantosNo ratings yet
- Proforma LocDocument3 pagesProforma LocPooja MohiteNo ratings yet
- Finance Process & Terms & ConditionsDocument3 pagesFinance Process & Terms & ConditionsPalash PatankarNo ratings yet
- Forest Restoration and Rehabilitation in PHDocument45 pagesForest Restoration and Rehabilitation in PHakosiwillyNo ratings yet
- Market Structure and Game Theory (Part 4)Document7 pagesMarket Structure and Game Theory (Part 4)Srijita GhoshNo ratings yet
- Is the Over-Diversified Birla Conglomerate Good for Aditya Birla GroupDocument8 pagesIs the Over-Diversified Birla Conglomerate Good for Aditya Birla GroupDebalina Ghosh0% (1)
- Lecture Var SignrestrictionDocument41 pagesLecture Var SignrestrictionTrang DangNo ratings yet
- Basel III: Bank Regulation and StandardsDocument13 pagesBasel III: Bank Regulation and Standardskirtan patelNo ratings yet
- The Investment Method of Sir John Maynard KeynesDocument3 pagesThe Investment Method of Sir John Maynard KeynesRiselda Myshku KajaNo ratings yet
- World Bank Review Global AsiaDocument5 pagesWorld Bank Review Global AsiaRadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Examiners' Report June 2017: GCE Economics A 9EC0 03Document62 pagesExaminers' Report June 2017: GCE Economics A 9EC0 03nanami janinaNo ratings yet
- Legal NoticeDocument7 pagesLegal NoticeRishyak BanavaraNo ratings yet
- Amb 336 Case Study AnalysisDocument10 pagesAmb 336 Case Study Analysisapi-336568710No ratings yet
- High Potential Near MissDocument12 pagesHigh Potential Near Missja23gonzNo ratings yet
- 5d7344794eaa11567835257 1037739Document464 pages5d7344794eaa11567835257 1037739prabhakaran arumugamNo ratings yet
- Tutorial1 SolutionsDocument5 pagesTutorial1 Solutionsfgdfdfgd3No ratings yet
- 6021-P3-Lembar KerjaDocument48 pages6021-P3-Lembar KerjaikhwanNo ratings yet
- IAS 2 InventoriesDocument13 pagesIAS 2 InventoriesFritz MainarNo ratings yet
- CI Principles of MacroeconomicsDocument454 pagesCI Principles of MacroeconomicsHoury GostanianNo ratings yet