Professional Documents
Culture Documents
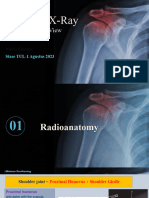
Normal Shoulder Xrays: True AP in Neutral Rotation (Taken in The Plane of The
Uploaded by
ต๋องแต๋ง กะต๋องกะแต๋งOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Normal Shoulder Xrays: True AP in Neutral Rotation (Taken in The Plane of The
Uploaded by
ต๋องแต๋ง กะต๋องกะแต๋งCopyright:
Available Formats
Normal Shoulder Xrays
True AP in neutral rotation (taken in the plane of the scapula) (Grashey view)
Helpful for: GH arthritis, Coracoid fx,Glenoid fx, Proximal humerus fx.Posterior shoulder dislocation. Evaluate: humeral head postion relative to glenoid; AC joint position/arthritis; RTC calcifications, acromial spurring Acromiohumeral interval: normal = 7-14mm. <7mm indicates massive RTC tear. (Weiner DS, JBJS 1970;52B:524). May appear falsely decreased with posterior subluxation of the humeral head.
Blue dot = Greater Tuberosity Red dot = Lesser Tuberosity Position: Patient erect, turned 3035 toward the side being xrayed Tube: Perpendicular to plate AP in External rotation (taken in the plane of the scapula)
Helpful for: GH arthritis, Coracoid fx,Glenoid fx, Proximal humerus fx, compression fracture of humeral head.
Blue dot = Greater Tuberosity Red dot = Lesser Tuberosity Position: Patient erect, turned 3035 toward the side being xrayed; arm maximally externally rotated Tube: Perpendicular to plate
AP in Internal rotation (taken in the plane of the scapula)
Helpful for: Hill-Sachs lesions, GH arthritis, Coracoid fx, Glenoid fx,Proximal humerus fx.
Blue dot = Greater Tuberosity Red dot = Lesser Tuberosity Position: Patient erect, turned 3035 toward the side being xrayed; arm maximally internally rotated Beam: aimed perpendicular to plate
Scapular Y
Demonstrates: lateral projection of scapular body and humeral head overlapping the glenoid. Helpful for: Shoulder dislocation;Proximal humerus fx. ; scapular body fracture
Position: Erect with anterior aspect of affected shoulder against x-ray plate and rotating other shoulder out 40 deg. Beam: aimed from posteriorly along scapular spine
Axillary
Demonstrates: glenohumeral joint narrowing (best view), Os Acromionale, glenoid version, glenoid erosion, humeral head subluxation. Helpful for: determining the amount of acromion which remains in patients who have undergone previous surgery; relation of humeral head to glenoid; Hill-Sachs lesions, Os Acromionale, AC joint, Shoulder dislocation,
Position: Patient seated at side of radiographic table with the arm abducted and axilla over the cassette.
Beam:angle 5-10 toward the elbow, central beam directed at the shoulder joint. Many alternative postions for similar xray, can be supine etc.
Supraspinatus Outlet view
Demonstrates: outlet/impingement of the supraspinatus and coracoacromial arch. Helpful for: Subacromial impingement, assessing acromial morphology, unfused acromial epiphysis.
Position: Erect with anterior aspect of affected shoulder against x-ray plate and rotating other shoulder out 40 deg. Beam: aimed from posteriorly along scapular spine but with the beam aimed with 10 caudal tilt Zanca View
Demonstrates: AC joint and distal clavicle Helpful for: AC arthritis, AC separations, dista l clavicle osteolysis. AC joint spurring and cystic changes indicates AC arthritis Distal clavicle elevation indicates AC separations.
Position: Erected with cassette behind shoulder. Beam:Xray beam aimed at the AC joint in 10 to 15 cephalic tilt. Xray penetration should be 1/2 normal to avoid overpenetration of AC joint.
West Point Axillary View
Demostrates: anteroinferior glenoid rim., best for osseous Bankart lesion. Helpful for: Shoulder Instability, Glenoid fractures, osseous Bankart lesion.
Postion:Patient prone with affected shoulder resting on a pad @8cm for the table top. Casette positioned against the superior apsect of the shoulder. Beam: aimed 25 from horizontal (to tables surface) and 25 medially (to patients midline). (Rokous JR, CORR 1972;82:84) Stryker Notch View
Demonstrates: humeral head Helpful for: Hill-Sachs lesions (best view), Bankart lesion.
Position: Patient supine with cassette posterior to the shoulder. The hand placed on top of the head. The elbow should point straight upward. Beam directed 10 superiorly/toward the head, centered over the coracoid process. (Hall RH, JBJS 1959;41-A:489-94)
Serendipity View
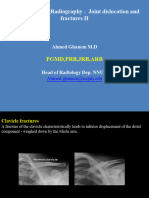
Demonstrates: sternoclavicular joints and medial 1/3 of the clavicles. Helpful for: Clavicle Fracture, Distal Clavicle Fracture, Sternoclavicular Dislocation,
Postion: supine with cassette under upper chest Beam aimed at clavicle or manubrium (SC pathology) with a 40 cephalic tilt.
Bennett's View (modified)
Obtained by angling the tube 5 cephalad with the arm abducted 45. Approximates an AP in ER view. Wright RW, AJSM 2004;32:121
Bennett's view
External rotation of the humerus with tilting of the xray tube 5 cephalad Bennett GE: Elbow and shoulder lesions of baseball players. Am J Surg 98: 484 492, 1959
Acromiohumeral Interval
average = 10.5mm. <7mm=full-thickness RTC tear. Measure on Grashey view. (Cotty P, J Radiol 1988;16:633).
Garth View (apical oblique)
Demostrates: the full extent of the glenoid rim bone loss and Hill-Sachs lesions Helpful for: Shoulder Instability, Glenoid fractures, osseous Bankart lesion. HillSachs lesions.
Postion: Seated with shoulder adjacent to cassette and arm adducted and internally rotated (place hand over heart). Chest rotated 45 Beam: beam perpendicular to the anterior-inferior glenoid rim and posterior-superior humeral head. (45 to the coronal plane and 45 caudally). Rollover for example rendition. Garth WP Jr, JBJS1984;66A:1450 Site Terms | Copyright Information | Contacts | Advertisements
Copyright 2008 by eORIF.com LLC. All Rights Reserved.
http://eorif.com/Shoulderarm/XrayShoulder.html
You might also like
- Alphabetical List of Named Radiographic ProjectionsDocument27 pagesAlphabetical List of Named Radiographic Projectionsimran sheriff100% (1)
- What Process Is Best Seen Using A Perpendicular CR With The Elbow in Acute Flexion and With The Posterior Aspect of The Humerus Adjacent To The Image ReceptorDocument22 pagesWhat Process Is Best Seen Using A Perpendicular CR With The Elbow in Acute Flexion and With The Posterior Aspect of The Humerus Adjacent To The Image ReceptorKalpana ParajuliNo ratings yet
- Shoulder GirdleDocument7 pagesShoulder GirdleGynewNo ratings yet
- ReviewrDocument47 pagesReviewrPaw Cortez100% (2)
- radio-UL, Pelvic, LLDocument125 pagesradio-UL, Pelvic, LLsirfayNo ratings yet
- Grashey ViewDocument23 pagesGrashey Viewsindami.nabilaNo ratings yet
- Bankurt RadiologyDocument22 pagesBankurt RadiologyVajja SwatiNo ratings yet
- Skyline Projections of Knee JointDocument11 pagesSkyline Projections of Knee JointKiran Kumar TNo ratings yet
- X-Ray Rounds: (Plain) Radiographic Evaluation of The ShoulderDocument58 pagesX-Ray Rounds: (Plain) Radiographic Evaluation of The ShoulderYeonseun KimNo ratings yet
- Tenth Edition Merrill's Atlas Radiographic Postions and Radiologic ProceduresDocument7 pagesTenth Edition Merrill's Atlas Radiographic Postions and Radiologic ProceduresIsmael AlexNo ratings yet
- ShoulderDocument91 pagesShoulderRazan AlayedNo ratings yet
- AP Elbow Analysis CriteriaDocument4 pagesAP Elbow Analysis CriteriaVivNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The HipDocument76 pagesDisorders of The HipMohamad RamadanNo ratings yet
- FR dISLOKASI BAHUDocument39 pagesFR dISLOKASI BAHUnurul azizaNo ratings yet
- Radiography of The Thoracic SpineDocument59 pagesRadiography of The Thoracic SpineEzra NserekoNo ratings yet
- Knee Joint RadiographyDocument50 pagesKnee Joint RadiographyRitu pantaNo ratings yet
- Rendgen Karlice I KukovaDocument49 pagesRendgen Karlice I KukovadrbaneNo ratings yet
- 1 Shoulder Radiography: 1.1 Examination Technique and Shoulder ViewsDocument11 pages1 Shoulder Radiography: 1.1 Examination Technique and Shoulder ViewsdevantyNo ratings yet
- Management of Anterior Shoulder Instability Ask TheDocument10 pagesManagement of Anterior Shoulder Instability Ask Themarcelogascon.oNo ratings yet
- Kamars RadiologyDocument135 pagesKamars RadiologyNayantara Nair100% (1)
- Pelvic RadiologyDocument30 pagesPelvic RadiologyGayle Grey100% (1)
- Shoulder Bankart Lesion With Posterior Instability A Case Report of Ultrasound DetectionDocument5 pagesShoulder Bankart Lesion With Posterior Instability A Case Report of Ultrasound DetectionSheila Setiawati TanzilNo ratings yet
- TM Shoulder Exam-1Document36 pagesTM Shoulder Exam-1ratkhiaberNo ratings yet
- Elbowjointjino 141121231122 Conversion Gate02 PDFDocument81 pagesElbowjointjino 141121231122 Conversion Gate02 PDFjiniNo ratings yet
- The Elbow - Radio Graphic Imaging Pearls and PitfallsDocument25 pagesThe Elbow - Radio Graphic Imaging Pearls and PitfallsDarko IllusionNo ratings yet
- 009 MSK - Joint Dislocation and Fractures 2Document33 pages009 MSK - Joint Dislocation and Fractures 2نوال سائد عبداللطيف مسلماني نوال سائد عبداللطيف مسلمانيNo ratings yet
- Femoroacetabular Impingement: DR Sandeep SinghDocument33 pagesFemoroacetabular Impingement: DR Sandeep Singhsandy singhNo ratings yet
- Presentation1 150221070554 Conversion Gate01Document75 pagesPresentation1 150221070554 Conversion Gate01yellymarlianapatuNo ratings yet
- Ortho Xray MeasurmentsDocument110 pagesOrtho Xray MeasurmentsPriza RazunipNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1: CHIR12007 Clinical Assessment and Diagnosis Portfolio Exercises Week 7Document9 pagesExercise 1: CHIR12007 Clinical Assessment and Diagnosis Portfolio Exercises Week 7api-455408952No ratings yet
- Skull: DR / Mohamed Shawky MDDocument92 pagesSkull: DR / Mohamed Shawky MDMohamed Ragab 3mmarNo ratings yet
- Shoulder DislocationDocument6 pagesShoulder DislocationRizki IrwansyahNo ratings yet
- Xray ViewsDocument81 pagesXray ViewsvipinNo ratings yet
- Paul in 1981Document4 pagesPaul in 1981RobertoNo ratings yet
- 5 Radiographicpositionsandprocedures 2011 SkullDocument80 pages5 Radiographicpositionsandprocedures 2011 SkulldimasfebrianpNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal NPTE Prep Flashcards - QuizletDocument10 pagesMusculoskeletal NPTE Prep Flashcards - Quizletakheel ahammed100% (4)
- Jarrett 2013Document20 pagesJarrett 2013aliNo ratings yet
- 6 - Right-Sided Valve Disease TEEDocument36 pages6 - Right-Sided Valve Disease TEECarlos Perez CastroNo ratings yet
- Elbow TestsDocument12 pagesElbow TestsAqsa ZaheerNo ratings yet
- Radiography of Forearm and Upper ArmDocument35 pagesRadiography of Forearm and Upper ArmsaurabhmhshwrNo ratings yet
- ElbowDocument7 pagesElbowapi-302398226No ratings yet
- Analisa X-Ray Fraktur Pada Tulang BelakangDocument77 pagesAnalisa X-Ray Fraktur Pada Tulang BelakangKurniadi BiasasajaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Shoulder Dislocation - PendekDocument84 pagesJurnal Shoulder Dislocation - PendekCliff LewisNo ratings yet
- Double Contrast CT Arthrography of The Glenoid Labrum and Shoulder GirdleDocument11 pagesDouble Contrast CT Arthrography of The Glenoid Labrum and Shoulder GirdlemasakishilaNo ratings yet
- 2017 OITE ReviewDocument105 pages2017 OITE ReviewJayNo ratings yet
- Ortho PE NotesDocument35 pagesOrtho PE NotesSudesna Roy ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- 24.9 Sternoclavicular Dislocation (A) (B) : Tio Erecta) Nearly Always The Arm Then Drops, BringingDocument10 pages24.9 Sternoclavicular Dislocation (A) (B) : Tio Erecta) Nearly Always The Arm Then Drops, BringingClaudios CANo ratings yet
- Deutsch1996 PDFDocument8 pagesDeutsch1996 PDFAlexandraNo ratings yet
- Recurrent Dislocation of The ShoulderDocument31 pagesRecurrent Dislocation of The ShoulderDiana AstriaNo ratings yet
- Shoulder DislocationDocument44 pagesShoulder DislocationMazvita Maz MatipiraNo ratings yet
- Role of Xray in NoseDocument13 pagesRole of Xray in NoseUmang UpadhyaNo ratings yet
- Dislocation of Hip-1Document44 pagesDislocation of Hip-1lionhearteagleNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Positioning of Humerus and Shoulder Elbow ForearmDocument63 pagesRadiographic Positioning of Humerus and Shoulder Elbow ForearmMohamed Ragab 3mmarNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Dislocation: Orthopedics Department DR Kilian K.KDocument32 pagesShoulder Dislocation: Orthopedics Department DR Kilian K.KInnocentNo ratings yet
- Study of LS Pelvis Sacrum-CoccyxDocument5 pagesStudy of LS Pelvis Sacrum-CoccyxZihad DmrtNo ratings yet
- The Shoulder Anatomy & Approaches: Abdulaziz F. Ahmed, MBBS PGY-2Document61 pagesThe Shoulder Anatomy & Approaches: Abdulaziz F. Ahmed, MBBS PGY-2Abdulaziz Al-Akhras100% (1)
- Pelvis-2019 AbadierrrtDocument47 pagesPelvis-2019 AbadierrrtGenevieve Marie MacabudbudNo ratings yet
- Orthopedics Notes for Medical StudentsFrom EverandOrthopedics Notes for Medical StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Musculoskeletal Ultrasound for the Orthopaedic Surgeon OR, ER and Clinic, Volume 2From EverandMusculoskeletal Ultrasound for the Orthopaedic Surgeon OR, ER and Clinic, Volume 2No ratings yet
- Kine 3301 Anatomy Exam ReviewDocument1 pageKine 3301 Anatomy Exam Reviewsep91No ratings yet
- Biomechanics of Patellofemoral JointDocument44 pagesBiomechanics of Patellofemoral JointMaluNo ratings yet
- Joints & Movement Worksheet PDFDocument4 pagesJoints & Movement Worksheet PDFRanulfo Mayol100% (1)
- Colles's Fracture: B (Hons.) PhysiotherapyDocument36 pagesColles's Fracture: B (Hons.) PhysiotherapySafwan Idham RamlanNo ratings yet
- Art:10.1007/s00167 016 4132 ZDocument9 pagesArt:10.1007/s00167 016 4132 ZBenito CameloNo ratings yet
- Dr. Med Medical & OrthosisDocument2 pagesDr. Med Medical & OrthosisDedy setiawanNo ratings yet
- Muscle Chart Upper ExtremityDocument3 pagesMuscle Chart Upper Extremitykep1313100% (1)
- Wrist WikiRadDocument34 pagesWrist WikiRadGriggrogGingerNo ratings yet
- Ankle AnatomyDocument59 pagesAnkle AnatomyAsmat Ullah QureshiNo ratings yet
- Blades and Burs: Pocket Reference GuideDocument8 pagesBlades and Burs: Pocket Reference GuideJosé Roberto MuraNo ratings yet
- 19 - Lats & Upper BackDocument29 pages19 - Lats & Upper Backbreinfout fotos100% (1)
- Vertical Humeral Osteotomy For Stem Revision in Total Shoulder ArthroplastyDocument5 pagesVertical Humeral Osteotomy For Stem Revision in Total Shoulder ArthroplastyngoyalnNo ratings yet
- Medial Collateral Ligament InjuriesDocument14 pagesMedial Collateral Ligament InjuriesJeetendra SoniNo ratings yet
- Rom MMT Study Sheet ShoulderDocument3 pagesRom MMT Study Sheet Shoulderapi-242502967No ratings yet
- Hand (Palm)Document1 pageHand (Palm)Drnarendra KumarNo ratings yet
- MRI-confirmed Tear and Spontaneous Healing of The Anterior Cruciate LigamentDocument4 pagesMRI-confirmed Tear and Spontaneous Healing of The Anterior Cruciate LigamentBhim SinghNo ratings yet
- Orthopedics MCQs With AnswersDocument32 pagesOrthopedics MCQs With AnswerslanghalilafaNo ratings yet
- Myers 2005 - Glenohumeral Range of Motion Deficits and Posterior Shoulder Tightness in Throwers With Internal ImpingementDocument8 pagesMyers 2005 - Glenohumeral Range of Motion Deficits and Posterior Shoulder Tightness in Throwers With Internal ImpingementWallison LeaoNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Mandibular Movement: OlehDocument44 pagesMechanics of Mandibular Movement: Olehgaluh dharmapatniNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Physical TherapyDocument8 pagesFaculty of Physical Therapyhesham33usNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Orthopedic ExaminationDocument11 pagesShoulder Orthopedic ExaminationSherief MansourNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Biomechanics of The Meniscus, Allen, OTO95+Document8 pagesAnatomy and Biomechanics of The Meniscus, Allen, OTO95+Ana María RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Fma Ue English PDFDocument3 pagesFma Ue English PDFnistaraNo ratings yet
- Frozen Shoulder DessertationDocument61 pagesFrozen Shoulder DessertationPoorvin ShahNo ratings yet
- Articulations: Clinical Case StudyDocument37 pagesArticulations: Clinical Case Studyodiseu81No ratings yet
- JointsDocument28 pagesJointsS.I. G.T.No ratings yet
- CarpusDocument4 pagesCarpusCarolus Augustus100% (1)
- NASM-CPT OHS Compensations and Translations PDFDocument6 pagesNASM-CPT OHS Compensations and Translations PDFPhong Bụi100% (2)
- Fracture Des Plateaux Tibiaux Yao 2018Document41 pagesFracture Des Plateaux Tibiaux Yao 2018KhalilNo ratings yet
- Subscapularis Sy DonatelliDocument12 pagesSubscapularis Sy DonatelliDusan OrescaninNo ratings yet