Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 2 Notes
Uploaded by
hero_spaceboy3600Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 2 Notes
Uploaded by
hero_spaceboy3600Copyright:
Available Formats
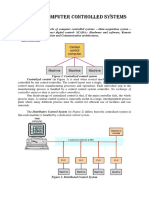
The hardware assembly that houses I/O modules, processor modules, and power supplies is referred to as the chassis.
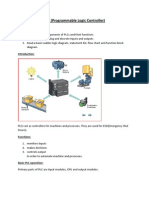
One benefit of a PLC system is the ability to locate the I/O modules near the field devices in order to minimize the amount of wiring. A rack is referred to as a remote rack when it is located away from the processor module. To communicate with the processor, the remote rack uses a special communications network. The PLCs memory system stores information about the status of all the inputs and outputs. To keep track of all this information, it uses a system called addressing. An address is a label or number that indicates where a certain piece of information is located in a PLCs memory. In general, rack/slot-based addressing elements include: TypeThe type determines if an input or output is being addressed. SlotThe slot number is the physical location of the I/O module. This may be a combination of the rack number and the slot number when using expansion racks. Word and Bitthe word and bit are used to identify the actual terminal connection in a particular I/O module. A discrete module usually uses only one word, and each connection corresponds to a different bit that makes up the word. Read page 24. Discrete input modules perform four tasks in the PLC control system. They: Sense when a signal is received from a field device. Convert the input signal to the correct voltage level for the particular PLC. Isolate the PLC from fluctuations in the input signals voltage or current. Send a signal to the processor indicating which sensor originated the signal.
Output modules can be purchased with transistor, triac, or relay output as illustrated in Figure 2-19. Triac outputs can be used only for control of AC devices, whereas transistor outputs can be used only for control of DC devices. The discrete relay contact output module uses electromechanical as the switching element. These relay outputs can be used with AC or DC devices, but they have a much slower switching time compared to solid- state outputs. Certain DC I/O modules specify whether the module is designed for interfacing with current-source or current-sink devices. If the module is a current-sourcing module, then the input or output device must be a current-sinking device. Conversely, if the
module is specified as current-sinking, then the connected device must be currentsourcing. Some modules allow the user to select whether the module will act as current sinking or current sourcing, thereby allowing it to be set to whatever the field devices require. Field devices connected to the positive side of the field power supply are classified as sourcing field devices. Conversely, field devices connected to the negative side or DC common of the field power supply are sinking field devices. Flash memories do not need to be physically removed from the processor for reprogramming; this can be done using the circuitry within the processor module in which they reside. Through personal computerbased setup software, you can configure display screens of an human machine interface (HMI) to: Replace hardwired pushbuttons and pilot lights with realistic-looking icons. The machine operator need only touch the display panel to activate the pushbuttons. Show operations in graphic format for easier viewing. Allow the operator to change timer and counter pre- sets by touching the numeric keypad graphic on the touch screen. Show alarms, complete with time of occurrence and location. Display variables as they change over time.
You might also like
- IA Lab Manual.1pdf-1Document64 pagesIA Lab Manual.1pdf-1Harsh GajjarNo ratings yet
- PLC m4Document17 pagesPLC m4Goutham KNo ratings yet
- PLC NotesDocument35 pagesPLC Notesmanisha daundNo ratings yet
- Answers For QuestionnsDocument101 pagesAnswers For QuestionnsfitzgeraldNo ratings yet
- PLC and PLC TechnologiesDocument28 pagesPLC and PLC Technologieskatjinomasa kavetuNo ratings yet
- Programmable Logic Controller: Need For PLCDocument20 pagesProgrammable Logic Controller: Need For PLCmkumar_234155No ratings yet
- Distributed Control System AssignmentDocument11 pagesDistributed Control System AssignmentGhulam Mustaqeem100% (1)
- 04 Chapter 1 - PLCDocument36 pages04 Chapter 1 - PLCsaliana binti sanusi100% (3)
- Vehicle Speed Control System Using RF CommunicationDocument80 pagesVehicle Speed Control System Using RF CommunicationSaheb Amrinder100% (6)
- Answers To Question-2Document350 pagesAnswers To Question-2Dev KumarNo ratings yet
- PLC QuestionsDocument17 pagesPLC QuestionsbahyNo ratings yet
- Industrial Automation - Final PDFDocument153 pagesIndustrial Automation - Final PDFTanvir KhanNo ratings yet
- Industrial AutomationDocument16 pagesIndustrial Automationvivek6681No ratings yet
- CHP 2Document9 pagesCHP 2BRIAN CLIFFNo ratings yet
- PLC Report FileDocument36 pagesPLC Report FileRajat100% (2)
- Plcman - Co.uk PLC GuideDocument27 pagesPlcman - Co.uk PLC GuideBharat SharmaNo ratings yet
- How To Communicate PLC To VFDDocument9 pagesHow To Communicate PLC To VFDAPLOGANNo ratings yet
- AU2 PLC Conveyo 28may2010Document13 pagesAU2 PLC Conveyo 28may2010scribdweeNo ratings yet
- C - 2 - PLC Hardware ComponantsDocument69 pagesC - 2 - PLC Hardware ComponantsShreesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Plugin-DCS Write UpDocument16 pagesPlugin-DCS Write Upnainesh goteNo ratings yet
- Assignment A PCIDocument20 pagesAssignment A PCISanjay SundaralingamNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii - Computer Controlled Systems: SyllabusDocument74 pagesUnit Iii - Computer Controlled Systems: SyllabusAravinthNo ratings yet
- Special Function IODocument31 pagesSpecial Function IOِAbdul-Rahman Al-magidiNo ratings yet
- Interfacing ConceptsDocument17 pagesInterfacing Conceptsanon_61073984100% (1)
- PLCDocument14 pagesPLCPrateek S VirdiNo ratings yet
- 777D Monitoring SystemDocument8 pages777D Monitoring Systemzawmoe aungNo ratings yet
- Basic of P.L.C. TechnologyDocument12 pagesBasic of P.L.C. TechnologycataiceNo ratings yet
- PLC and SCADADocument77 pagesPLC and SCADAIshwari GhuleNo ratings yet
- PLCDocument36 pagesPLCsonhack96No ratings yet
- Programmable Logic Controller and Its ApplicationsDocument5 pagesProgrammable Logic Controller and Its Applicationssumit100% (1)
- Solution Manual For Programmable Logic Controllers 5Th Edition Petruzella 0073373842 9780073373843 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Programmable Logic Controllers 5Th Edition Petruzella 0073373842 9780073373843 Full Chapter PDFjohn.rosenstock869100% (10)
- Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) : The Need For PlcsDocument6 pagesProgrammable Logic Controller (PLC) : The Need For Plcsaditya bhandakkarNo ratings yet
- AnswersDocument60 pagesAnswersEng ForQ3No ratings yet
- Ch1 Overview 4502734Document51 pagesCh1 Overview 4502734khaled99No ratings yet
- UNIT 4 MechatronicsDocument21 pagesUNIT 4 MechatronicsMuthuvel M100% (1)
- How Plcs WorkDocument8 pagesHow Plcs WorkRajreddyNo ratings yet
- Relay 543 - 545 ManualDocument70 pagesRelay 543 - 545 ManualVenkatesh Rao100% (2)
- REM 543 Motor Protection Relay: ApplicationDocument24 pagesREM 543 Motor Protection Relay: ApplicationPrateek SinghNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics (302050) Lecture Notes / PPT Unit IvDocument63 pagesMechatronics (302050) Lecture Notes / PPT Unit IvSwapvaibNo ratings yet
- PLC NittDocument58 pagesPLC NittVignesh Meyyappan100% (1)
- Dasar Dasar PLCDocument65 pagesDasar Dasar PLCAgie FernandezNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis 2Document65 pagesFinite Element Analysis 2Theerkka TharisananNo ratings yet
- PLCDocument13 pagesPLCChalez ZengeretsiNo ratings yet
- What Is PLCDocument8 pagesWhat Is PLCkunjiayman2No ratings yet
- PLC NotesDocument170 pagesPLC NotesBikasita Talukdar100% (2)
- Architecture of Specific PLC ControllerDocument11 pagesArchitecture of Specific PLC ControllerDazuky UkyNo ratings yet
- Components of A PLCDocument7 pagesComponents of A PLCJCABRACHY ABNo ratings yet
- Programmable Logic ControlDocument136 pagesProgrammable Logic Controljoshbinmollel112No ratings yet
- Report On PLCDocument17 pagesReport On PLCRahul SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Basic Instructions of Siemens PLCDocument15 pagesBasic Instructions of Siemens PLCPaul OyukoNo ratings yet
- UNIT 22: Programmable Logic Controllers Unit Code: A/601/1625 QCF Level: 4 Credit Value: 15 Outcome 1Document11 pagesUNIT 22: Programmable Logic Controllers Unit Code: A/601/1625 QCF Level: 4 Credit Value: 15 Outcome 1Yellaji AllipilliNo ratings yet
- Auto and ControlDocument54 pagesAuto and Controlsupriya kharageNo ratings yet
- PLC Programming Using SIMATIC MANAGER for Beginners: With Basic Concepts of Ladder Logic ProgrammingFrom EverandPLC Programming Using SIMATIC MANAGER for Beginners: With Basic Concepts of Ladder Logic ProgrammingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Preliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960From EverandPreliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960No ratings yet
- Arduino Measurements in Science: Advanced Techniques and Data ProjectsFrom EverandArduino Measurements in Science: Advanced Techniques and Data ProjectsNo ratings yet
- HW 1Document6 pagesHW 1hero_spaceboy3600No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 NotesDocument2 pagesChapter 2 Noteshero_spaceboy3600No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 NotesDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Noteshero_spaceboy3600No ratings yet
- Lab 1Document8 pagesLab 1hero_spaceboy3600No ratings yet
- Midterm NotesDocument4 pagesMidterm Noteshero_spaceboy3600No ratings yet
- Paul Spicker - The Welfare State A General TheoryDocument162 pagesPaul Spicker - The Welfare State A General TheoryTista ArumNo ratings yet
- Rotating Equipment & ServiceDocument12 pagesRotating Equipment & Servicenurkasih119No ratings yet
- DNA Vs RNA - Introduction and Differences Between DNA and RNADocument10 pagesDNA Vs RNA - Introduction and Differences Between DNA and RNAKienlevyNo ratings yet
- Spare Part PhilosophyDocument27 pagesSpare Part Philosophyavaisharma50% (2)
- Toshiba MotorsDocument16 pagesToshiba MotorsSergio Cabrera100% (1)
- Alphabetic KnowledgeDocument8 pagesAlphabetic KnowledgejsdgjdNo ratings yet
- CTS2 HMU Indonesia - Training - 09103016Document45 pagesCTS2 HMU Indonesia - Training - 09103016Resort1.7 Mri100% (1)
- Vocabulary FceDocument17 pagesVocabulary Fceivaan94No ratings yet
- Data Network Unit 6 - UCDocument15 pagesData Network Unit 6 - UCANISHA DONDENo ratings yet
- Project ProposalDocument4 pagesProject Proposaljiaclaire2998100% (1)
- ইসলাম ও আধুনিকতা – মুফতি মুহম্মদ তকী উসমানীDocument118 pagesইসলাম ও আধুনিকতা – মুফতি মুহম্মদ তকী উসমানীMd SallauddinNo ratings yet
- Aribah Ahmed CertificateDocument2 pagesAribah Ahmed CertificateBahadur AliNo ratings yet
- UAV Design TrainingDocument17 pagesUAV Design TrainingPritam AshutoshNo ratings yet
- Guncha Arora: Professional Profile Career HistoryDocument1 pageGuncha Arora: Professional Profile Career HistoryNitin MahawarNo ratings yet
- Nutrition 2022 PIRDocument22 pagesNutrition 2022 PIRAlmira LacasaNo ratings yet
- Brosur YSIO X.preeDocument20 pagesBrosur YSIO X.preeRadiologi RSUD KilisuciNo ratings yet
- Designing and Drawing PropellerDocument4 pagesDesigning and Drawing Propellercumpio425428100% (1)
- Transparency and Digitalization in The Public Administration of RomaniaDocument8 pagesTransparency and Digitalization in The Public Administration of RomaniaMădălina MarincaşNo ratings yet
- ABI TM 13 16 SL - EngDocument1 pageABI TM 13 16 SL - EngJuan Carlos Benitez MartinezNo ratings yet
- MDI - Good Fellas - ScriptDocument20 pagesMDI - Good Fellas - ScriptRahulSamaddarNo ratings yet
- Advocacy Firm Business Plan by SlidesgoDocument40 pagesAdvocacy Firm Business Plan by SlidesgoirinaNo ratings yet
- I Pmtea 2020 HandoutDocument94 pagesI Pmtea 2020 HandoutAbhijeet Dutta100% (1)
- WBCS 2023 Preli - Booklet CDocument8 pagesWBCS 2023 Preli - Booklet CSurajit DasNo ratings yet
- Pedagogy MCQS 03Document54 pagesPedagogy MCQS 03Nawab Ali MalikNo ratings yet
- Outline Calculus3Document20 pagesOutline Calculus3Joel CurtisNo ratings yet
- Bioinformatics Computing II: MotivationDocument7 pagesBioinformatics Computing II: MotivationTasmia SaleemNo ratings yet
- Spectacle Blinds - Closed Blinds Open Blinds (Ring Spacer)Document2 pagesSpectacle Blinds - Closed Blinds Open Blinds (Ring Spacer)Widiyanto WiwidNo ratings yet
- Veritas™ High Availability Agent For WebSphere MQ Installation and Configuration Guide / WebSphere MQ InstallationDocument64 pagesVeritas™ High Availability Agent For WebSphere MQ Installation and Configuration Guide / WebSphere MQ InstallationkarthickmsitNo ratings yet
- Amritsar Police StationDocument5 pagesAmritsar Police StationRashmi KbNo ratings yet
- BÀI TẬP LESSON 7. CÂU BỊ ĐỘNG 1Document4 pagesBÀI TẬP LESSON 7. CÂU BỊ ĐỘNG 1Yến Vy TrầnNo ratings yet