Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HL 1 Topic 1 PP Notes
Uploaded by
MrNewbsOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HL 1 Topic 1 PP Notes
Uploaded by
MrNewbsCopyright:
Available Formats
HL 1 Topic 1 Complete the following as you read through the PowerPoint on statistical analysis Slide 1 title slide Slide
e 2 - 3 What is the mean? What are error bars? Error bars can be used to plot How do you know that Set A has the largest mean? How do you know that set B has the greatest variability?
Slide 4 Slide 5 What is a nectarivore? Give 3 examples of nectarivores. Define mutualism (use your understanding not Dr. Googles) Why would the measurement of bill lengths and body size have any insight on the evolutionary history of a hummingbird? What is statistical analysis? Explain why you would not need the bars for the graph provided.
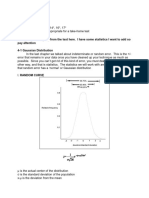
Slide 6 Slide 7 What is uncertainty? In digital measuring devised you use _______________ for uncertainty. Why should the sample size be large? What do you think is the source of uncertainty and error of measurements?
Rulers have uncertainty on both ends explain why. Analogue (non-digital) measurements are usually what?
Slides 8 12 We will practice the use of excel in class you can open up an excel document and copy the steps you read on these slides. Slide 13 The mean is a measure of the. What is range? Explain the differences in the 2 graphs on slide 13.
Slides 14 - 16 Slide 17 What is standard deviation? Explain why this gives us a more reliable view of the true spread of data? How do you calculate the range of data? How do you explain the presence of the 21 data point? What does this do to the data?
Slides 18-19 Why is C the correct answer?
Slides 20-21 Why is B the correct answer?
Slides 22 28 We will go over this in class you may use an excel doc to practice standard deviation and take out your scientific calculator to practice as well.
Slides 29 30 Explain the answer for letter B
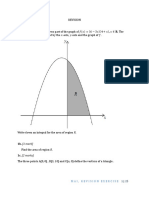
Slides 31 - 32 How can significance be discovered? What defines not likely or likely to be significant?
Slides 33 - 34 What is Range, Standard Deviation, Mean and Frequency? Why does set A have a higher frequency at the mean?
Slide 35 Slide 36 Slide 37 Why start every T-test with a Null Hypothesis? If T-test accepts or rejects the null hypothesis what are we told? What will a T test tell us? Which table has the most similarity? What is a T-test?
Slides 38 40 Flip through these 3 slides multiple times. Each time you flip through study the progression of the image and focus on interpreting the information given in these slides. What P is usually used by Biologists? What does CV stand for? Slides 41 46 What does df stand for?
How do you calculate df? How did the CV (critical value) get identified? How did you know that t was 2.15? How do you know there is a significant difference between wing span?
Slide 47 Why do we reject the null hypothesis is t > cv?
Slide 48 - 49 Explain the acceptance of the Null Hypothesis and how it was acquired?
Slides 50-51 Slide 52 Check em out Explain the rejection of the Null Hypothesis and how it was acquired?
Slides 53 56 We will practice during class you can use the ecxcel document youve been practicing with to practice before class.
Slide 57 Something fun
Slide 58 - 60 What are correlations? Why would the first graph be described as a strong positive?
Slide 61 Why do correlations not prove causality? What is needed?
Slide 62 Slide 63 Slide 64 The end! Nice Job!! Check these out I tend to agree with the graph in the upper right.
You might also like
- Berengueres J. Introduction To Data Visualization... Guide... 2020Document189 pagesBerengueres J. Introduction To Data Visualization... Guide... 2020Marof KhalifaNo ratings yet
- Statistics Formulas: ParametersDocument3 pagesStatistics Formulas: ParametersRidwan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Impact of Merger and AcquisitionDocument11 pagesImpact of Merger and Acquisitionmonu67% (3)
- Lab1: Scientific Method: Biology 6A/ Bruce Heyer & Brian Mccauley September 24 & 25, 2007Document10 pagesLab1: Scientific Method: Biology 6A/ Bruce Heyer & Brian Mccauley September 24 & 25, 2007Ku Nurul Afiqah50% (2)
- Stats & Maths Workbook Edition1Document54 pagesStats & Maths Workbook Edition1Jonathan JNo ratings yet
- Statistics Interview QuestionsDocument5 pagesStatistics Interview QuestionsARCHANA R100% (1)
- Mathematics: Quarter 4 - Module 1 Illustrating The Measures of Position For Ungrouped DataDocument16 pagesMathematics: Quarter 4 - Module 1 Illustrating The Measures of Position For Ungrouped DataPol Zeretnev85% (13)
- A Level Further Mathematics For AQA - Discrete Student Book (AS - A Level)Document268 pagesA Level Further Mathematics For AQA - Discrete Student Book (AS - A Level)NghiaNo ratings yet
- Conducting & Reading Research in Kinesiology - Ted, PHD & Weimo Zhu, PHD & Pamela Hodges Kulinna, PHDDocument844 pagesConducting & Reading Research in Kinesiology - Ted, PHD & Weimo Zhu, PHD & Pamela Hodges Kulinna, PHDMUIslamNo ratings yet
- T TestDocument25 pagesT TestTanvi Sharma50% (2)
- T TestDocument3 pagesT TestEvan Swager0% (1)
- To The Learners:: NAME: - YR & SECDocument11 pagesTo The Learners:: NAME: - YR & SECG01-Azurin, Keisha Denise T.No ratings yet
- The Effect of Using Cubing Strategy Toward StudentsDocument18 pagesThe Effect of Using Cubing Strategy Toward StudentsFiqri Muharam100% (2)
- MYP Science Practice Questions - Explain and EvaluateDocument6 pagesMYP Science Practice Questions - Explain and Evaluateoc0% (1)
- EPSO Assistant Exam WorkbookDocument7 pagesEPSO Assistant Exam Workbookeuinmotion33% (3)
- AIRs-LM - Math 10 QUARTER 4-Weeks 6-7 - Module 5Document20 pagesAIRs-LM - Math 10 QUARTER 4-Weeks 6-7 - Module 5joe mark d. manalang100% (4)
- IB Biology Internal Assessment Lab FormatDocument3 pagesIB Biology Internal Assessment Lab Formatk_oonnNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: 4 QUARTER - Module 3Document12 pagesDepartment of Education: 4 QUARTER - Module 3Krystal BuenaobraNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Interpretation of Assessment ResultsDocument84 pagesAnalysis and Interpretation of Assessment ResultsAlyanna Clarisse Padilla CamposNo ratings yet
- Mean Is Meaningless: Guide For Interpretinng Likert ScaleDocument3 pagesMean Is Meaningless: Guide For Interpretinng Likert ScaleRJ Bedaño100% (1)
- PEDSQL Generic N CancerDocument17 pagesPEDSQL Generic N CancerJimmy Oi SantosoNo ratings yet
- CS001-B03 - Exploratory Data Analysis 20Document7 pagesCS001-B03 - Exploratory Data Analysis 20Viswa SpiritualNo ratings yet
- The Many Meanings of QuartileDocument9 pagesThe Many Meanings of QuartilealbgomezNo ratings yet
- Seminar QuestionsDocument5 pagesSeminar Questionsabdulwahabsaid26No ratings yet
- 1 e ExercisesDocument31 pages1 e ExerciseszubairulhassanNo ratings yet
- Statistics in DetailsDocument283 pagesStatistics in Detailsyousef shaban100% (1)
- Howweendureenduranceportfolio JenniferdabbertDocument3 pagesHowweendureenduranceportfolio Jenniferdabbertapi-270329172No ratings yet
- Grade 8 Math Silly PuttyDocument4 pagesGrade 8 Math Silly Puttyrurbanik100% (2)
- Accuracy vs. Precision and The Scientific MethodDocument41 pagesAccuracy vs. Precision and The Scientific MethodDionel RizoNo ratings yet
- Revised Wheres WaldoDocument5 pagesRevised Wheres Waldoapi-284026302No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Triangle InequLITYDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Triangle InequLITYachumbreNo ratings yet
- MPC 006Document19 pagesMPC 006Swarnali MitraNo ratings yet
- Assignment (60%) : ESE 633 Statistics in EducationDocument11 pagesAssignment (60%) : ESE 633 Statistics in EducationFatin Zain0% (1)
- Intro To Modelling - W1Document31 pagesIntro To Modelling - W1CatNo ratings yet
- Safari - 23-Mar-2019 at 1:49 PMDocument1 pageSafari - 23-Mar-2019 at 1:49 PMRakesh ChoNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION OF ASSESSMENT RESULTS (Autosaved)Document85 pagesANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION OF ASSESSMENT RESULTS (Autosaved)Alyanna Clarisse Padilla CamposNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability: Quarter 3 - Module 7: Percentiles and T-DistributionDocument17 pagesStatistics and Probability: Quarter 3 - Module 7: Percentiles and T-DistributionYdzel Jay Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Assignment (60%) : ESE 633 Statistics in EducationDocument11 pagesAssignment (60%) : ESE 633 Statistics in EducationPrisca Susella Welbe Tanis100% (1)
- Comparing The Means Using The TtestDocument25 pagesComparing The Means Using The TtestAngelica AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Thesis With Chi-Square TestDocument7 pagesThesis With Chi-Square TestWhatIsTheBestPaperWritingServiceCanada100% (2)
- Chi-Square Statistic: How To Calculate It / DistributionDocument9 pagesChi-Square Statistic: How To Calculate It / Distributionk767No ratings yet
- Pca TutorialDocument27 pagesPca TutorialGregory A Perdomo PNo ratings yet
- Ukcat DetailsDocument15 pagesUkcat DetailsvishaljalanNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Test of Significance/Hypothesis Testing (Topics 20, 22, 23)Document24 pagesUnit 5: Test of Significance/Hypothesis Testing (Topics 20, 22, 23)Riddhiman PalNo ratings yet
- Hemh105 PDFDocument20 pagesHemh105 PDFhoneygarg1986No ratings yet
- Assignment (100%) : ESE 633 Statistics in EducationDocument13 pagesAssignment (100%) : ESE 633 Statistics in EducationMaria FlorinaNo ratings yet
- ds15 13-14 Experimental Design Graph PracticeDocument10 pagesds15 13-14 Experimental Design Graph Practiceapi-110789702No ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Measures of Central Tendency and Variability 2Document31 pagesLesson 7 Measures of Central Tendency and Variability 2loysaserentas27No ratings yet
- Q3 - W2 - Theorems On The Different ParallelogramsDocument26 pagesQ3 - W2 - Theorems On The Different ParallelogramsatNo ratings yet
- MTH302 FAQsDocument18 pagesMTH302 FAQsRamesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Final Stats Intrerview Q&ADocument12 pagesFinal Stats Intrerview Q&AVamsi Krishna Y NNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: 4 QUARTER - Module 3Document10 pagesDepartment of Education: 4 QUARTER - Module 3ERVIN DANCANo ratings yet
- Bluman Stats Brief 6e CH01 (Jang)Document23 pagesBluman Stats Brief 6e CH01 (Jang)Das ChimeraNo ratings yet
- 30C00200 Problem Set 1Document4 pages30C00200 Problem Set 1wazaawazaaNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Lab ReportDocument5 pagesHow To Write A Lab Reportapi-298351628No ratings yet
- Statistics For Data Science Quiz Questions: Section 1 - IntroductionDocument9 pagesStatistics For Data Science Quiz Questions: Section 1 - IntroductionMhamed ErrajiNo ratings yet
- Lab 12 PracticeDocument3 pagesLab 12 PracticececilrwNo ratings yet
- Basic Statistics Week 5 & 6Document10 pagesBasic Statistics Week 5 & 6Jessa Bienel Biagtas OlescoNo ratings yet
- Assignment #1 The Scientific MethodDocument3 pagesAssignment #1 The Scientific MethodSharon Rose Genita MedezNo ratings yet
- Workshop 1 Statistical SupplementDocument5 pagesWorkshop 1 Statistical Supplementazazel666No ratings yet
- Taylors Math 3 Pow 3Document3 pagesTaylors Math 3 Pow 3api-481780857No ratings yet
- PPT. Mode of Ungrouped DataDocument27 pagesPPT. Mode of Ungrouped DataJayson GeranceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 StatisticsDocument11 pagesChapter 4 Statisticszaheer abbasNo ratings yet
- Chapters 1 and 2Document12 pagesChapters 1 and 2tarek mahmoudNo ratings yet
- Thesis With T-TestDocument4 pagesThesis With T-Testjillbellmilwaukee100% (1)
- Biological Diversity Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesBiological Diversity Practice ProblemsMrNewbs100% (1)
- The Unmotivated StudentDocument1 pageThe Unmotivated StudentMrNewbsNo ratings yet
- Essential Biology 2.2 and 2.3Document7 pagesEssential Biology 2.2 and 2.3MrNewbsNo ratings yet
- BiolH U3Document35 pagesBiolH U3MrNewbs100% (1)
- BiolH U3Document35 pagesBiolH U3MrNewbs100% (1)
- T-Tests For DummiesDocument10 pagesT-Tests For DummiesMeganAislingNo ratings yet
- 2018 - Barriers To The Integration of BIM and Sustainability Practices in Construction Projects - A Delphi Survey of International ExpertsDocument35 pages2018 - Barriers To The Integration of BIM and Sustainability Practices in Construction Projects - A Delphi Survey of International ExpertsAli J. LubbadNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 RevisionDocument15 pagesGrade 12 RevisionMariam KhalilNo ratings yet
- HackingDocument431 pagesHackingPsyartCenter Cabinet Psihologic100% (2)
- Integromics QPCR Statistics White PaperDocument9 pagesIntegromics QPCR Statistics White Paperdrahmed1212No ratings yet
- Impact of School Location On Academic Ac PDFDocument4 pagesImpact of School Location On Academic Ac PDFMorrison Omokiniovo Jessa SnrNo ratings yet
- Determining The Effectiveness of Neem and Papaya L-2Document8 pagesDetermining The Effectiveness of Neem and Papaya L-2Ariana hazelNo ratings yet
- Body Image in Obese Women Before, During, and After Weight Loss TreatmentDocument4 pagesBody Image in Obese Women Before, During, and After Weight Loss Treatmentsaqib ghiasNo ratings yet
- Descriptives: Descriptives Variables Pre Post /statistics Mean Stddev Min Max SkewnessDocument3 pagesDescriptives: Descriptives Variables Pre Post /statistics Mean Stddev Min Max Skewnessputri anisahNo ratings yet
- 7608-Article Text-13581-1-10-20210613Document20 pages7608-Article Text-13581-1-10-20210613SuniNo ratings yet
- Childbirth Self-Efficacy Inventory and Childbirth Attitudes Questionner Thai LanguageDocument11 pagesChildbirth Self-Efficacy Inventory and Childbirth Attitudes Questionner Thai LanguageWenny Indah Purnama Eka SariNo ratings yet
- Testing Hypothesis With One SampleDocument10 pagesTesting Hypothesis With One SampleStephanie Danielle HizoleNo ratings yet
- Microfinance and The Rural Poor:: Impact Assessment Based On Fieldwork in Madhya Pradesh, IndiaDocument32 pagesMicrofinance and The Rural Poor:: Impact Assessment Based On Fieldwork in Madhya Pradesh, Indiaju1daNo ratings yet
- MITIGATING THE DIFFICULTIES OF FOURTH YEAR STUDENTS OF LAOANG NATIONAL TECHNICAL HIGH SCHOOL IN ANSWERING WRITTEN EVALUATIONS IN PHYSICS USING AN INTRINSIC ACADEMIC MOTIVATION MODEL (Loreta N. Ada)Document50 pagesMITIGATING THE DIFFICULTIES OF FOURTH YEAR STUDENTS OF LAOANG NATIONAL TECHNICAL HIGH SCHOOL IN ANSWERING WRITTEN EVALUATIONS IN PHYSICS USING AN INTRINSIC ACADEMIC MOTIVATION MODEL (Loreta N. Ada)John Paul Nuguit AdaNo ratings yet
- Latest by Nana LR Metrix 8-6-2021 9Document28 pagesLatest by Nana LR Metrix 8-6-2021 9api-552883952No ratings yet
- Data Science Interview Preparation (30 Days of Interview Preparation)Document27 pagesData Science Interview Preparation (30 Days of Interview Preparation)Satyavaraprasad BallaNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis Using SPSS - Evsu PDFDocument201 pagesData Analysis Using SPSS - Evsu PDFMary Michael BactongNo ratings yet
- Sas Ron CodyDocument35 pagesSas Ron Cody王No ratings yet
- Math 107 - Problem Set 1Document5 pagesMath 107 - Problem Set 1Smartcool So0% (1)
- Internet Based Machinery Health MonitoringDocument8 pagesInternet Based Machinery Health Monitoringabc_123_mnoNo ratings yet
- Water Bill Perception in Brazil Do Households Get It RightWP1336May2022Document32 pagesWater Bill Perception in Brazil Do Households Get It RightWP1336May2022Narcizo AlvesNo ratings yet
- Purpose of The Study and Research DesignDocument11 pagesPurpose of The Study and Research DesignJep Jep Panghulan100% (2)