Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SMPF
Uploaded by
John Christopher CadiaoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SMPF
Uploaded by
John Christopher CadiaoCopyright:
Available Formats
SAN MIGUEL COMPANY PUREFOODS COMPANY, INC.
2012
I. INTRODUCTION
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi, and other life forms for food, fiber, biofuel and other products used to sustain life. It is also called farming or husbandry. Generally, it refers to human activities, although it is also observed in certain species of ant and termite. The word agriculture is the English adaptation of Latin agricultra, from ager, "a field", and cultra, "cultivation" in the strict sense of "tillage of the soil".Thus, a literal reading of the word yields "tillage of fields". Agriculture Science is the term used for the study of agriculture. Since the 1940s, agricultural productivity has increased dramatically, due largely to the increased use of energy-intensive mechanization, fertilizers and pesticides. The vast majority of this energy input comes from fossil fuel sources.[128] Between 1950 and 1984, the Green Revolution transformed agriculture around the globe, with world grain production increasing by 250%[129][130] as world population doubled. Modern agriculture's heavy reliance on petrochemicals and mechanization has raised concerns that oil shortages could increase costs and reduce agricultural output, causing food shortages. IAS 41 Agriculture sets out the accounting for agricultural activity. It states the transformation of biological assets into agricultural produce. The standard generally requires biological assets to be measured at fair value less costs to sell. The objective of IAS 41 is to establish standards of accounting for agricultural activity the management of the biological transformation of biological assets (living plants and animals) into agricultural produce (harvested product of the entity's biological assets).
1 ACT143
SAN MIGUEL COMPANY PUREFOODS COMPANY, INC. 2012
II. COMPANY BACKGROUND
HERITAGE
San Miguel Pure Foods integrates two outstanding food institutions, the San Miguel Food Group and Pure Foods Corporation. Both have a rich history and a solid record of experience and expertise spanning nearly six decades of market leadership in the food industry. The San Miguel Food Group had its beginnings in 1953 when San Miguel Polo Brewery started producing animal feeds from protein-rich by-products of beer brewing, laying the groundwork for what would later become San Miguel Foods, Inc. In the 1960s, business operations in feeds, livestock, and dairy were consolidated under San Miguel Feeds and Livestock Division. Integrated poultry operations began a decade later through a breeder farm in Cavite , and the first chicken processing plant was eventually set up in Muntinlupa. Philippine Dairy Products Corporationa precursor to Magnolia, Inc.was established in 1981 as a 70-30 joint venture between San Miguel and New Zealand Dairy Board. San Miguel would eventually attain leadership position in the margarine market following the acquisition of Star and Dari Crme Brands a decade later. In 1991, San Miguel Feeds and Livestock Division was spun off to become San Miguel Foods, Inc., managing both feeds and livestock business. These past decades indeed saw San Miguel Corporations food business expand to include poultry and livestock, dairy products, fresh and processed meats, and agriculture.
2 ACT143
SAN MIGUEL COMPANY PUREFOODS COMPANY, INC. 2012
Meanwhile, Pure Foods was founded in 1956 by a group of leading businessmen who put up a one-building, one-kitchen food facility in Mandaluyong to produce hams, bacon and sausages. It went on to produce quality meats that became household names. Several years later, Hormel Foods International acquired substantial interest in Pure Foods, giving the company exclusive rights to market Hormel products in the country. San Miguel Corporations acquisition of Pure Foods in May 2001 brought together these two food industry leaders, ushering in a new era of growth and market leadership of the integrated businesses.
CORE BUSINESS
SMFI-Feeds drives growth with the proven strength and effectiveness of the B-Meg and Pureblend brands. Combined, these two brands account for the greater share of the commercial feeds market. SMFI-Poultry operations include broiler breeding, hatching, growing, and processing using company-owned and contracted facilities. Flagship brands Magnolia Chicken and Purefoods Supermanok lead the poultry market, being the brands of choice among major food service outlets as well as in supermarkets and wet markets. Monterey Foods Corporation, the Philippiness largest pork and beef producer, manages SMPFCs fresh and semi-processed meats businesses. Montereys fullyintegrated operations cover breeding, growing and slaughtering, marketing and distribution of fresh meats and value-added meat products. Monterey Foods was the first manufacturer of branded fresh meats to expand into franchising operations. These outlets, known as Monterey Neighborhood Meat Shops, conveniently provide Filipinos across the country with readily-accessible sources of safe, clean and top-quality pork and beef as well as opportunities for entrepreneurship.
3 ACT143
SAN MIGUEL COMPANY PUREFOODS COMPANY, INC. 2012
The Purefoods-Hormel Company, Inc., a joint venture with Hormel USA, produces and markets processed meats which account for nearly two-thirds of the processed meats market, leading both the refrigerated and canned segments. Among its well-loved brands is Purefoods Tender Juicy Hotdog, the countrys largest-selling hotdog. Other popular products are Purefoods Corned Beef, Purefoods Carne Norte, Purefoods Fiesta Ham, Beefies Hotdog, Moby Hotdog, Purefoods Classic Honeycured Bacon, and Lean and Mean Bacon. San Miguel Mills, Inc. produces and markets flour, with its mill in Mabini, Batangas as its main flour production facility. This is the first flour mill in the country to receive an ISO 9002 certification. Its acquisition of the assets of Pacific Flour Mills, Inc., a pioneer in the flour industry, further strengthened the Companys hold of the market. The power of its combined brandsEmperor Hard Flour, Queen Soft Flour, Baron AllPurpose Flour, King Hard Flour, Pacific Hard Flour, Red Dragon Soft Flour, together with other specialty flour productsmake the company the acknowledged industry leader. The introduction of Magnolia Pancake Plus and waffle mix likewise strengthened the companys position in the branded food category. Magnolia, Inc. manufactures and markets butter, cheese, margarine, milk, jellyace and cooking oil. With its well-established leading brands, the company comprises over 90% of the non-refrigerated margarine market and over 80% of refrigerated margarine. Magnolia Ice Cream is the brand that immediately comes to a consumers mind when it comes to ice cream. In 2004, the Magnolia brand proved its strong brand equity upon its return from a 10-year absence in the market with the favorite classic ice creams that Filipinos have grown up with in the 60s and 70s. It quickly regained market footing in bulk ice cream through innovations in product packaging and introducing value-for-money premium quality products. Magnolia has introduced in the
4 ACT143
SAN MIGUEL COMPANY PUREFOODS COMPANY, INC. 2012
market the 21st century in-mould scratch-proof labeling, typical of packaging materials in Europe and North America. San Miguel Super Coffeemix Company, Inc., San Miguel Pure Foods joint venture with Super Coffeemix Manufacturing Limited of Singapore, engages in the importation, packaging (including toll-packaging), manufacture, sales, marketing and distribution of coffee and coffee-related food products in the Philippines and other countries in the Asia Pacific region. The San Mig Coffee mother brand has gained considerable share of the coffee market in the Philippines with the introduction of its San Mig Coffee Instant 3in1 Coffeemix and Sugar Free variants. Great Food Solutions provides institutional outlets with customized food products, employing the full range of San Miguel Pure Foods products. The company enjoys preferred status with many of the countrys leading fast food chains, cafes and bars, and full service restaurants. The Culinary Center is a facility composed of well-equipped modern kitchens catering to three different types of customers. The Consumer Kitchen is designed to be a housewifes dream, where all the recipes for the homes are developed and standardized. The Institutional Kitchen simulate the set-up of a typical modern restaurant, where recipes are developed and cooking procedures for meat and poultry products are standardized. Training for restaurant and canteen staffers are also held there. A wellequipped bakeshop typically samples the baked goodies as technologists develop institutional recipes. It is also an excellent venue for baking classes for clients. The Culinary Center conducts mall cooking demonstrations, culinary workshops, cooking contests, livelihood and educational seminars, and the distribution of newsletters to keep the consumers updated on the latest trends in food. They respond to the many requests for recipes and homemaking tips from consumers.
5 ACT143
SAN MIGUEL COMPANY PUREFOODS COMPANY, INC. 2012
CORE PURPOSE
Nourishing and Nurturing Families World Wide It is our fundamental belief that everything is loaned to us by our Creator, to grow and multiply them for the good of everyone. As such, we value and take care of what has been entrusted to us - malasakit. It is the core value that permeates all other values that we espouse: Customer focus, Social Responsibility, Passion for Success, Integrity, Respect for our People, Innovation, and Teamwork. It is in this spirit that we will look after the welfare and interest of our stakeholders. We will delight our Customers with products and services of uncompromising quality, great taste and value, and are easily within their reach. We will create value and provide fair returns on our Shareholders investments. We will work hand-in-hand with our Suppliers and other Business Partners, helping them grow with us and assuring them of reasonable returns. We will develop and motivate our Employees to become best-in-class through cognitive and affective programs, competitive compensation and benefits, and diverse career growth opportunities. We will help improve the quality of life in Communities where we operate. Collectively, we will give and do what is right and become proponents of good stewardship.
6 ACT143
SAN MIGUEL COMPANY PUREFOODS COMPANY, INC. 2012
ENVISIONED PURPOSE
BHAG By 2020, San Miguel Purefoods Company, Inc. will be a P520 billion company with an income of P42 billion
Vivid Description We will intimately understand our consumers, winning ther hearts by providingtasting and innovative products and services that anticipate and respond to their needs. We will ensure that our products are of uncompromising quality and easily within reach. We will be the leading provider of good nutrition for families, offering a wide spectrum of products. And, to complete our portfolio, we will engage in nutraceuticals and organic food segments. We will revolutionize the foodservice and retail industries. We will aggressively bring our products and services worldwide, spanning the AsiaPacific, Middle East, South Africa, and Europe. We will develop a regional network of manufacturing capabilities that will provide us with least cost advantage in raw material sourcing, production, and logistics costs. We will develop a regional network of manufacturing capabilites that will provide us with least cost advantage in raw material sourcing, production, and logistics costs.
7 ACT143
SAN MIGUEL COMPANY PUREFOODS COMPANY, INC. 2012
We will become the benchmark of innovation, systems and technology, and people development in the industry. We will play an active role in improving the lives of the communities where we operate. We will be the Filipino company that nurtures families worldwide.
III.
AGRICULTURAL FARMS PECULIAR TRANSACTIONS III.I PECULIAR ACCOUNTS
In the study of an agricultural entity, we should notice the distinguishing accounts it maintains. Most accounts of an agricultural entity are similar to that of a manufacturing concern. A manufacturing entity converts raw material and labor to produce goods. Hence, accounts such as raw materials, direct labor and manufacturing overhead can be seen as distinguishing accounts that differentiate it from a merchandising entity. In addition, work-in-process and finished goods inventory are also some peculiar accounts that distinguishes a manufacturing entity from a merchandising entity. Basically, manufacturing companies in general has same accounts as with that of the agricultural entity. The main difference is within the content of inventories of the agricultural entity. In addition to those accounts peculiar to a manufacturing from a merchandising entity, an agricultural entity maintains the following accounts. Raw Materials, Feeds, and Feed Ingredients. This account contains compound feeds which are commercial pelleted food produced in a feed mill and fed to domestic livestock; fodder, food given to domestic livestock, including plants cut and carried to them; forage, a growing plants eaten by domestic livestock.
8 ACT143
SAN MIGUEL COMPANY PUREFOODS COMPANY, INC. 2012
Formulas and Recipes. This account is included in the intangible assets of the company. These are sets of instructions for preparing a particular dish, product, including a list of the ingredients required. Biological Assets. This account includes plants and animals. The common examples of biological assets include animals such as goats, sheep, cows, buffaloes, calves, and fish. Biological assets include plants such as vegetables, crops, vineyards, trees, and fruit orchards. Depreciation and Amortization Biological Assets. This account is the allocation of the cost of the tangible asset over its useful life.
III.II CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ACCOUNTS
The agricultural entity is substantially a manufacturing entity. However, as stated earlier, their difference lies between the contents of inventories and assets. An agricultural entity has biological assets which are sources of finished products in the form of a produce or harvest. The inventory of an agricultural entity forms material part of its total assets for about 26%. It contains raw material, feeds, and finished goods. Like a normal manufacturing entity, inventory is very significant. It can be observed that SMPFC engages in a significant derivatives transaction. This is used to help the company to reduce risks from different exposures from financial risks such as interest rate risk, foreign currency risk, commodity price risk, liquidity risk, and credit risk. The entitys derivative comprises of commodity options to protect it from exposures to commodity price risks arising from its operations. Some other characteristics that are observed by the researchers are provided in the ratio analysis part of this paper.
9 ACT143
SAN MIGUEL COMPANY PUREFOODS COMPANY, INC. 2012
IV. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS ANALYSIS IV.I. COMPARATIVE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
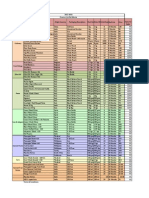
SAN MIGUEL PURE FOODS COMPANY, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES Comparative Balance Sheet - Increase (Decrease) Method As of December 31 (In Thousands) ASSETS Current Assets Cash and cash equivalents Trade and other receivables Inventories - net Biological assets Derivative assets
Prepaid expenses and other current assets
Three Years Ended December 31 Increase (Decrease)
2010 2009 Amount Percent
7,041,345 7,760,271 12,123,435 3,266,564 107,633 1,765,748
3,950,346 9,023,953 11,804,099 2,524,510 47,070 1,245,674 28,595,652 108,065 8,294,593 1,285,125 167,562 170,792 1,219,676 334,408 11,580,221 40,175,873
3,090,999 (1,263,682) 319,336 742,054 60,563 520,074 3,469,344 4,953 811,490 194,126 3,257,948 245,518 (619,785) (21,378) 3,872,872 7,342,216
78.25% -14.00% 2.71% 29.39% 128.67% 41.75%
12.13% 4.58% 9.78% 15.11% 1944.32% 143.75% -50.82% -6.39% 33.44% 18.28%
Total Current Assets 32,064,996 Noncurrent Assets Investment properties - net 113,018 Property, plant and equipment - net 9,106,083 Biological assets - net 1,479,251 Intangible assets 3,425,510 Goodwill - net 416,310 Deferred tax assets 599,891 Other noncurrent assets 313,030 Total Noncurrent Assets 15,453,093 Total Assets 47,518,089 LIABILITIES AND EQUITY Current Liabilities Notes Payable 5,172,538 Trade payables and other current liabilities 15,145,969 Income tax payabe 162,159 Total Current Liabilities 20,480,666 Noncurrent Liabilities Long-Term debt - net of debt issue costs 4,460,807 Deferred tax liabilities 271,074 Other noncurrent liabilities 87,544 Total Noncurrent Liabilities 4,819,425 Total Liabilities 25,300,091 Equity Attributable to Parent Capital stock 1,708,748 Additional paid-in capital 5,821,288 Revaluation surplus 18,219 Cumulative translation adjustments (92,492) Retained earnings 11,773,185 Treasury stock (182,094)
19,046,854
8,816,090 12,667,086 466,920 21,950,096 399,040 181,487 580,527 22,530,623
(3,643,552) 2,478,883 (304,761) (1,469,430) 4,460,807 (127,966) (93,943) 4,238,898 2,769,468
-41.33% 19.57% -65.27% -6.69%
-32.07% -51.76% 730.18% 12.29%
1,454,510 5,821,288 18,219 (48,278) 8,181,278 (182,094) 15,244,923 2,400,327 17,645,250 40,175,873
254,238 (44,214) 3,591,907 3,801,931 770,817 4,572,748 7,342,216
17.48% 0.00% 0.00% 91.58% 43.90% 0.00% 24.94% 32.11% 25.91% 18.28%
Non-controlling interests Total Equity Total Liabilities and Equity
3,171,144 22,217,998 47,518,089
10 ACT143
SAN MIGUEL COMPANY PUREFOODS COMPANY, INC. 2012
IV.I.I. SHORT-TERM SOLVENCY ANALYSIS As shown in the Statement of Financial position, the percentage of increase in total current assets (12.13%) was favorable against the decrease in the percentage in current liabilities (-6.69%). It can be observed that the percentage of cash and cash equivalents increased significantly (78.25%). This may indicate that the company is turning to a more conservative way of financing its current assets or the company is expected to purchase new assets. Income tax payable also decreased significantly which shows that the company is effective in avoiding its taxes. Trade and other receivables together with inventories have lower percentage than the percentage increase in sales revenue (5.63%). This indicates faster conversion of inventory and receivables to cash. The changes mentioned resulted to the improvement in the short-term solvency position of the company as of the end of year 2010 compared with year 2009. IV.I.II. LONG-TERM FINANCIAL POSITION ANALYSIS Intangible assets and goodwill increased in value intensely. Non-current liabilities increased dramatically (730.18%) due to the issuance of long-term debt by SMPF. The company now is shifting its long-term position through borrowing funds instead of capital provided by profitable operations. This change can be viewed as unfavorable because it can indicate weakening of the long-term financial position by end of year 2010. Stockholders can also be threatened because of this debt issuance because if the company collapses, they are the ones who will receive less because liabilities should be settled first
11 ACT143
SAN MIGUEL COMPANY PUREFOODS COMPANY, INC. 2012
before they can divide the remaining shares. The company should have very good investment opportunities to counter the effect of this long-term debt that will eventually increase the cost of interest expenses.
SAN MIGUEL PURE FOODS COMPANY, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES Comparative Income Statement - Increase (Decrease) Method As of December 31 (In Thousands) Three Years Ended December 31 Increase (Decrease)
2010 2009
75,042,967 61,447,996 13,594,971 (8,957,347) (751,042) 69,141 (24,663) (88,968) 3,842,092 (1,183,625) 2,658,467
Amount
4,226,793 1,843,090 2,383,703 (1,119,558) 391,627 36,347 (7,949) 186,834 1,871,004 (470,582) 1,400,422
Percent
5.63% 3.00% 17.53% 12.50% -52.14% 52.57% 32.23% -210.00% 48.70% 39.76% 52.68%
Revenues Cost of sales Gross Profit Selling, general and administrative Interest expense and other financing charges Interest income Gain (loss) on sale of property and equipment Other income (charges) Income before income tax Income tax expense Net Income Attributable to: Equity holders of the parent company Non-controlling interests Basic and Diluted Earnings per share attributable to equity holders of the parent company
79,269,760 63,291,086 15,978,674 (10,076,905) (359,415) 105,488 (32,612) 97,866 5,713,096 (1,654,207) 4,058,889
3,846,145 212,744
2,596,963 61,504
P 23.08
P 15.58
12 ACT143
SAN MIGUEL COMPANY PUREFOODS COMPANY, INC. 2012
IV.I.III. OPERATING EFFICIENCY AND PROFITABILITY ANALYSIS Sales revenues increased by (5.63%) while cost of goods sold increased by only (3.00%). The is favorable because this could indicate that the company was able to adjust the selling price of the goods commensurate to the increase in cost of goods purchased or manufactured or it was able to control the price factor of its cost of sales. These changes resulted to growth in the gross profit rate which is favorable. The increase in sales was accompanied by a (12.5%) increase in selling and administrative expenses which is unfavorable because this could indicate managements inefficiency in keeping expenses within control. On an overall basis, operating performance could be considered as very satisfactory because of the increase in net income of (52.68%).
IV.II. FINANCIAL RATIO ANALYSIS
I. Analysis of Liquidity or Short-Term Solvency Current Ratio Formula = Current Assets Current Liabilities 32,064,996.00 20,480,666.00 28,595,652.00 21,950,096.00 1.57 times 1.30 times
2010 2009
13 ACT143
SAN MIGUEL COMPANY PUREFOODS COMPANY, INC. 2012
Quick or Acid Test Ratio Formula = Quick Assets Current Liabilities 14,801,616.00 20,480,666.00 12,974,299.00 21,950,096.00 0.72 times 0.59 times
2010 2009
Cash-Flow Liquidity Ratio Cash + Marketable Securities+ Cash flow from Operating Acts Formula = Current Liabilities 2010 2009 11,857,216.00 20,480,666.00 9,486,553.00 21,950,096.00 0.58 times 0.43 times
Working Capital to Assets Formula = Working Capital Total Assets 11,584,330.00 47,518,089.00 6,645,556.00 40,175,873.00 0.24 times 0.17 times
2010 2009
14 ACT143
SAN MIGUEL COMPANY PUREFOODS COMPANY, INC. 2012
IV.II.I. ANALYSIS OF LIQUIDITY OR SHORT-TERM SOLVENCY Current assets increased because of significant increase in cash and cash equivalents that may indicate conservatism or as a reserve for buying an asset or investing in new business opportunities. The increase in cash and cash equivalent increased the current ratio, quick ratio, working capital ratio and cash-flow liquidity ratio which strengthen the short-term solvency of SMPF. This increase signifies the increasing capability of the company to pay its currently maturing debts but may also signify lesser money making activities because of stagnant cash which do not earn high interest. Presently, there appears to be no major problems with the firms short-term liquidity position.
II. Analysis of Asset Liquidity and Asset Management Efficiency Accounts Receivable Turnover Net Sales Formula = Average Accounts Receivable Balance 2010 2009 79,269,760.00 8,392,112.00 75,042,967.00 9,023,953.00 9.45 times 8.32 times
15 ACT143
SAN MIGUEL COMPANY PUREFOODS COMPANY, INC. 2012
Average Collection Period / DSO 365 days Formula = Accounts Receivable Turnover 2010 2009
365.00
9.45
365.00
38.64 days 43.89 days
8.32
Inventory Turnover Formula = Cost of Goods Sold Average Inventory Balance 63,291,086.00 11,963,767.00 61,447,996.00 11,804,099.00 5.29 times 5.21 times
2010 2009
Average Sale Period Formula = 365 days Inventory Turnover
365.00
2010 2009
5.29
365.00
69.00 days 70.12 days
5.21
16 ACT143
SAN MIGUEL COMPANY PUREFOODS COMPANY, INC. 2012
Fixed Asset Turnover Formula = Net Sales Average PPE 79,269,760.00 8,700,338.00 75,042,967.00 8,294,593.00 9.11 times 9.05 times
2010 2009
Total Asset Turnover Formula = Net Sales Average Total Assets 79,269,760.00 43,846,981.00 75,042,967.00 40,175,873.00 1.81 times 1.87 times
2010 2009
IV.II.II. ANALYSIS OF ASSET LIQUIDITY AND ASSET MANAGEMENT EFFICIENCY SMPF converted accounts receivable into cash 9.45 times in2010, up from 8.32 times in 2009. The turnover has improved and this may indicate better quality of receivable and improvement of the firms collection and credit policies. The ratios of SMPF indicated that during 2010, the firm collected its accounts in 39 days, an improvement over the 44 day collection period in 2009. This is a sign of improving credit management such as adequate checks and follow-ups on slow accounts. In terms of Inventory turnover, SMPF increased 5.29 times from
17 ACT143
SAN MIGUEL COMPANY PUREFOODS COMPANY, INC. 2012
5.21 this is an indication of efficient inventory management and profit for the firm. SMPFs average sale or conversion period decreased from 70 days in 2009 to 69 days in 2010. The decrease shows that inventories are sold faster and fewer funds are tied up in inventory and more profits will be generated by the company. On average, the company increased its fixed asset turnover and total asset turnover. The investments of the company in assets are very well utilized which means that the company is effective in generating sales from its assets. On an overall basis, the company makes proper use of its resources which eventually led to higher returns.
III. Analysis of Leverage: Debt Financing and Coverage Debt Ratio Formula = Total Liabilities Total Assets 25,300,091.00 47,518,089.00 22,530,623.00 40,175,873.00 0.53 53.24% 0.56 56.08%
2010 2009
18 ACT143
SAN MIGUEL COMPANY PUREFOODS COMPANY, INC. 2012
Debt to Equity Ratio Formula = Total Liabilities Total Equity 25,300,091.00 22,217,998.00 22,530,623.00 17,645,250.00 1.14 113.87% 1.28 127.69%
2010 2009
Times Interest Earned Formula = Operating Profit Interest Expense 5,901,769.00 359,415.00 4,637,624.00 751,042.00 16.42 times 6.17 times
2010 2009
IV.II.III. ANALYSIS OF LEVERAGE: DEBT FINANCING AND COVERAGE SMPFs debt ratio declined its ratio compare to previous year. This may indicate lesser risk of interest charged which are fixed which if not satisfied will ultimately result in bankruptcy. This is in contrary to the issuance of debt by the company which increases non-current liabilities by 730%. The company issued a significant amount of long-term debt but this was subsided by the increase in income from operations and eventual decrease in other liabilities of the company. Debt to equity ratio increased in spite of debt issuance but this is mainly because of issuance of capital, income from operations and decrease in
19 ACT143
SAN MIGUEL COMPANY PUREFOODS COMPANY, INC. 2012
other liabilities of the company. The decrease in debt to equity ratio is insignificant and it still shows that creditors are still the holder of the biggest chunk of resources used by the company in operating its business. Times interest earned by the company increased significantly by 16.42 times from 6.17 times which means that the companys operating income can cover its interest expense by 16 times which is also an advantage to stockholders because of lesser risk of bankruptcy from non-payment of fixed interest charges. As an overall analysis, the company is still dependent on its creditors that make the risk higher for stockholders. The company should focus on using its income from operations to capitalize its operations and lessen the dependency to liabilities.
IV. Operating Efficiency and Profitability Gross Profit Margin Formula = Gross Profit Net Sales 15,978,674.00 79,269,760.00 13,594,971.00 75,042,967.00 0.20 20.16% 0.18 18.12%
2010 2009
20 ACT143
SAN MIGUEL COMPANY PUREFOODS COMPANY, INC. 2012
Operating Profit Margin Formula = Operating Profit Net Sales 5,901,769.00 79,269,760.00 4,637,624.00 75,042,967.00 0.07 7.45% 0.06 6.18%
2010 2009
Net Profit Margin Formula = Net Income Net Sales 4,058,889.00 79,269,760.00 2,658,467.00 75,042,967.00 0.05 5.12% 0.04 3.54%
2010 2009
Cash Flow Margin Cash flow from Operating Acts Formula = Net Sales 2010 2009 4,815,871.00 79,269,760.00 5,536,207.00 75,042,967.00 0.06 6.08% 0.07 7.38%
21 ACT143
SAN MIGUEL COMPANY PUREFOODS COMPANY, INC. 2012
Return on Assets (ROA) Formula = Net Income Average Total Assets 4,058,889.00 43,846,981.00 2,658,467.00 40,175,873.00 0.09 9.26% 0.07 6.62%
2010 2009
Return on Equity (ROE) Net Income Formula = Average Stockholder's Equity 2010 2009 4,058,889.00 19,931,624.00 2,658,467.00 17,645,250.00 0.20 20.36% 0.15 15.07%
Financial Leverage Index Formula = Return on Equity Return on Assets
0.2036 0.0926 0.1507 0.0662
2010 2009
2.20 2.28
22 ACT143
SAN MIGUEL COMPANY PUREFOODS COMPANY, INC. 2012
IV.II.IV. OPERATING EFFICIENCY AND PROFITABILITY SMPFs gross profit margin increased as a result of the companys ability to both control costs of products sold and inventories or manufacturing of products and to pass along price increases through sales to customers. SMPFs operating profit margin improved from 6.18% in 2009 to 7.45% in 2010. This is favorable because it indicates ability of the company to control its operating expenses while sharply increasing sales. SMPFs net profit margin significantly increased despite increase in tax expenses and selling and administrative expenses. The companys cash flow margin in 2010 was lower than the operating margin. This indicates a negative impression because of weak generation of cash. SMPFs financial leverage is greater than 1 indicating the return on equity exceeds return on assets, the firm is using debt effectively although borrowing increased. This ratio also showed that the company succeeded in generating profits from its investments and management strategies. The firm has generated sufficient operating returns to more than cover the interest payments on borrowed funds. There has been substantial sales growth which suggests future performance potential. IV.II.V. CONCLUSION OF ANALYSIS SMPF is well positioned for future growth. Continued advertisement will attract customers to both new and old areas which will eventually lead to expansion. SMPF has financed much of its operations and expansion with debt, and so far, its shareholders have benefited from it. The company however should
23 ACT143
SAN MIGUEL COMPANY PUREFOODS COMPANY, INC. 2012
be cautious of the increased risk associated with debt financing and should focus more in utilizing stock or income as capital for its operations and new investments. This will increase shareholders confidence in the sustenance of the companys short and long term operations.
V.
CONCLUSION
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi, and other life forms for food, fiber, biofuel and other products used to sustain life. It is also called farming or husbandry. Generally, it refers to human activities, although it is also observed in certain species of ant and termite. The word agriculture is the English adaptation of Latin agricultra, from ager, "a field", and cultra, "cultivation" in the strict sense of "tillage of the soil".Thus, a literal reading of the word yields "tillage of fields". Agriculture Science is the term used for the study of agriculture.
San Miguel Purefoods Company is the agricultural company chosen by the students to be documented. San Miguel Purefoods Company, Inc. (PF) is in the business of manufacturing and marketing of processed meat products. PF is a 100% subsidiary of San Miguel Corporation (SMC). Its operations are classified into great food solutions and condiments. The first one is a food service unit that caters to institutional accounts for their poultry and flour-based needs while the second produces cane vinegar under the brand Supremo.
24 ACT143
SAN MIGUEL COMPANY PUREFOODS COMPANY, INC. 2012
The Agriculturals Peculiar accounts are Raw Materials, Feeds, and Feed Ingredients, Formulas and Recipes, Biological Assets and Depreciation and Amortization Biological Assets. Fundamentally, manufacturing companies in general has same accounts as with that of the agricultural entity. The main difference is within the content of inventories of the agricultural entity.
The Characteristics of the Accounts are also described. It is stated that the difference between the manufacturing and agricultural entity lies between the contents of inventories and assets. Some other characteristics that are observed by the researchers are provided in the ratio analysis part of this paper.
25 ACT143
You might also like
- San Miguel Pure Foods CompanyDocument4 pagesSan Miguel Pure Foods CompanyErica Mae VistaNo ratings yet
- Economics MilkDocument23 pagesEconomics MilkSamuel LeonardNo ratings yet
- Lessons From Millionaire Chicken Farmers: Cracking The Code To Poultry ProfitsFrom EverandLessons From Millionaire Chicken Farmers: Cracking The Code To Poultry ProfitsNo ratings yet
- San Miguel PurefoodsDocument128 pagesSan Miguel PurefoodsSanta Anna SinagaNo ratings yet
- Final Feasib!!!!Document42 pagesFinal Feasib!!!!James WilliamNo ratings yet
- Strama Final PDFDocument36 pagesStrama Final PDFNicki SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Home Depot Strategic Audit Reveals Strengths Under CEO NardelliDocument18 pagesHome Depot Strategic Audit Reveals Strengths Under CEO NardellikhtphotographyNo ratings yet
- Typhon Food Inc Business Plan - EditedDocument14 pagesTyphon Food Inc Business Plan - EditedMeshack MateNo ratings yet
- Chicken Broiler Production Is One of The Most Progressive Animal Enterprises in The Philippines TodayDocument8 pagesChicken Broiler Production Is One of The Most Progressive Animal Enterprises in The Philippines TodayEmamMsHome-hyhyNo ratings yet
- Shell Comprofile MapDocument4 pagesShell Comprofile MapEasy WriteNo ratings yet
- All HomeDocument5 pagesAll HomeallhomephNo ratings yet
- STRAMADocument7 pagesSTRAMACheryl Arcega PangdaNo ratings yet
- Wilfred Corrigan's global financing strategy for LSI Logic CorpDocument2 pagesWilfred Corrigan's global financing strategy for LSI Logic Corpvikas joshiNo ratings yet
- Meat One ReportDocument13 pagesMeat One ReportMOIZ ALI KHAN50% (2)
- Shell Ems - EditedDocument14 pagesShell Ems - EditedGeovanie LauraNo ratings yet
- REPUBLIC FLOUR MILLS CORPORATION - Financial AnalysisDocument46 pagesREPUBLIC FLOUR MILLS CORPORATION - Financial Analysiskirt diazNo ratings yet
- The End of Hanjin ShippingDocument8 pagesThe End of Hanjin ShippingAna VBNo ratings yet
- Ai 410 e 00Document27 pagesAi 410 e 00Lukman PitonoNo ratings yet
- Generoso Pharmaceutical and Chemicals, Inc.: Background of The StudyDocument7 pagesGeneroso Pharmaceutical and Chemicals, Inc.: Background of The StudyKristine Joy Serquina67% (3)
- Philippine Christian University: Senior High School Department Dasmariñas CampusDocument15 pagesPhilippine Christian University: Senior High School Department Dasmariñas Campusrehina lopez100% (1)
- International StrategyDocument23 pagesInternational StrategyKendrew SujideNo ratings yet
- Financial Management & Control FinalDocument25 pagesFinancial Management & Control FinalAnees Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Catfish Farming: Water Recirculatory SystemDocument6 pagesCatfish Farming: Water Recirculatory SystemMarkNo ratings yet
- Project Profile For Lyantonde Animal Feed Mill - Table of ContentsDocument4 pagesProject Profile For Lyantonde Animal Feed Mill - Table of ContentsInfiniteKnowledge100% (1)
- Poultry ButcheryDocument110 pagesPoultry ButcheryBernard PalmerNo ratings yet
- Strategic Improvement Plan for Company ADocument7 pagesStrategic Improvement Plan for Company AGel AlivioNo ratings yet
- Product List-Del Monte 2013-2014 Canned Fruit Drinks Canned Fruits Fruit Fillings Corn Olives & Jalapenos Olive Oil Cullinary PastaDocument2 pagesProduct List-Del Monte 2013-2014 Canned Fruit Drinks Canned Fruits Fruit Fillings Corn Olives & Jalapenos Olive Oil Cullinary PastaNaveenbabu Soundararajan100% (1)
- BCG Space Tow SCPMDocument5 pagesBCG Space Tow SCPMDanica Rizzie TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Brief History and Services of 2GO Group IncDocument5 pagesBrief History and Services of 2GO Group IncJohn Patrick ReynosNo ratings yet
- Financial Management of Phoenix Petroleum Philippines Inc. BodyDocument29 pagesFinancial Management of Phoenix Petroleum Philippines Inc. BodyAl Therese R. CedeñoNo ratings yet
- Itlogan Sa Dabaw FarmDocument15 pagesItlogan Sa Dabaw FarmMicka EllahNo ratings yet
- HONEY DUCK EGG PRODUCTION FEASIBILITY STUDYDocument34 pagesHONEY DUCK EGG PRODUCTION FEASIBILITY STUDYJurie BalandacaNo ratings yet
- Financial Analyses On The Various Davao City-Based CompaniesDocument24 pagesFinancial Analyses On The Various Davao City-Based CompaniesmasterdrewsNo ratings yet
- Buffalo Wild Wings Marketing Plan: Megan Hamik Justin Butchert Recreation Administration 135Document29 pagesBuffalo Wild Wings Marketing Plan: Megan Hamik Justin Butchert Recreation Administration 135Natividad, Marry Ave Paula B.No ratings yet
- Final - Lucid Timber Liquid Wax Feasib UpdatedDocument518 pagesFinal - Lucid Timber Liquid Wax Feasib UpdatedCristofer MatunogNo ratings yet
- ArpDocument44 pagesArpAnnamaAnnama100% (1)
- Guidelines for Establishing Poultry and Piggery FarmsDocument5 pagesGuidelines for Establishing Poultry and Piggery FarmsKimm Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Robina 130310091148 Phpapp02Document9 pagesRobina 130310091148 Phpapp02Robert MaganaNo ratings yet
- Josfin's Smoked Fish Marketing ProjectDocument21 pagesJosfin's Smoked Fish Marketing ProjectLandoNo ratings yet
- Acquarius Case AnalysisDocument6 pagesAcquarius Case AnalysisEarl MarquezNo ratings yet
- Retail Performance Leads Virginia Farms' GrowthDocument3 pagesRetail Performance Leads Virginia Farms' Growthleahdorado_picNo ratings yet
- Poultry Farm Business PlanDocument20 pagesPoultry Farm Business PlanGizachew NadewNo ratings yet
- PreliminaryProspectus - CenturyDocument650 pagesPreliminaryProspectus - CenturykazimirkiraNo ratings yet
- Econ Midterm MontereyDocument3 pagesEcon Midterm MontereyArnold NiangoNo ratings yet
- Fruitien Operations AnalysisDocument10 pagesFruitien Operations AnalysisMuhammadSufianNo ratings yet
- 004b3c6a9860493197879aba7fcc3661Document41 pages004b3c6a9860493197879aba7fcc3661Chrissel Joy Lascuña PalacaNo ratings yet
- Marby Strama FaithDocument6 pagesMarby Strama FaithEllyse De Leon0% (1)
- Emperador 2013Document114 pagesEmperador 2013collieNo ratings yet
- Dole Heart Fresh: Marketing PlanDocument54 pagesDole Heart Fresh: Marketing PlanMargaret LachoNo ratings yet
- Max's Group Inc in Consumer Foodservice (Philippines)Document2 pagesMax's Group Inc in Consumer Foodservice (Philippines)MikanLeachonNo ratings yet
- Fresh Fruit Exports From The Philippines:: The Lapanday Foods OpportunitiesDocument34 pagesFresh Fruit Exports From The Philippines:: The Lapanday Foods OpportunitiesWalther Hontiveros0% (1)
- IDLS PiggeryDocument4 pagesIDLS PiggeryOmar RodriguezNo ratings yet
- "On The Water" Business PlanDocument22 pages"On The Water" Business Planmohammad10000100% (2)
- Adjusted Feasibility Study of Kimcs AbujaDocument64 pagesAdjusted Feasibility Study of Kimcs AbujaHomework PingNo ratings yet
- Halal Meat Sector Time To Make The Most of The Edge Jul 2016Document15 pagesHalal Meat Sector Time To Make The Most of The Edge Jul 2016waqarNo ratings yet
- Active/intelligent Packaging For Meat IndustryDocument49 pagesActive/intelligent Packaging For Meat IndustryIslemYezza100% (16)
- Marketing Plan for Philippine Dried FruitDocument9 pagesMarketing Plan for Philippine Dried FruitJordy Verdadero0% (1)
- SMC - Leading Philippine ConglomerateDocument3 pagesSMC - Leading Philippine Conglomeratemark_torreonNo ratings yet
- Oral Test KFCDocument8 pagesOral Test KFCrooney_mu21100% (1)
- Guidelines for African Swine Fever (ASF) prevention and Control in Smallholder Pig Farming in Asia: Clean Chain Approach for African Swine Fever in Smallholder SettingsFrom EverandGuidelines for African Swine Fever (ASF) prevention and Control in Smallholder Pig Farming in Asia: Clean Chain Approach for African Swine Fever in Smallholder SettingsNo ratings yet
- Portfolio FOR ANADocument6 pagesPortfolio FOR ANAholdap toNo ratings yet
- Amnesia With Focus On Post Traumatic AmnesiaDocument27 pagesAmnesia With Focus On Post Traumatic AmnesiaWilliam ClemmonsNo ratings yet
- Bill 192: An Act To Ensure Student Health and Safety in The Classroom by Regulating Ambient Air Quality in SchoolsDocument8 pagesBill 192: An Act To Ensure Student Health and Safety in The Classroom by Regulating Ambient Air Quality in SchoolsCtv MontrealNo ratings yet
- Food ProcessingDocument5 pagesFood ProcessingMarycris Doria100% (2)
- ESP Guidance For All Ships V13.7Document53 pagesESP Guidance For All Ships V13.7Jayasankar GopalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Summative Exam. First QuarterDocument5 pagesPhysical Science Summative Exam. First QuarterIsagani WagisNo ratings yet
- GP Series Portable Generator: Owner's ManualDocument48 pagesGP Series Portable Generator: Owner's ManualWilliam Medina CondorNo ratings yet
- Refrigerant Color Code ChartDocument11 pagesRefrigerant Color Code ChartJeffcaster ComelNo ratings yet
- Louise L HAY AffirmationsDocument10 pagesLouise L HAY AffirmationsEvi Kutasi100% (2)
- Chapter 1: Abnormal Behavior in Historical ContextDocument22 pagesChapter 1: Abnormal Behavior in Historical ContextEsraRamos100% (2)
- Form16 (2021-2022)Document2 pagesForm16 (2021-2022)Anushka PoddarNo ratings yet
- SpokenEnglish Section1 TheSoundSystemOfEnglishDocument132 pagesSpokenEnglish Section1 TheSoundSystemOfEnglishRaj Yash100% (1)
- Deltair BrochureDocument4 pagesDeltair BrochureForum PompieriiNo ratings yet
- F 204 (AutoRecovered)Document27 pagesF 204 (AutoRecovered)safiqulislam100% (1)
- Ipao Program Flyer 17novDocument1 pageIpao Program Flyer 17novapi-246252391No ratings yet
- Electric Vehicle BatteryDocument15 pagesElectric Vehicle BatteryTotal Acess100% (1)
- Bio23 LindenDocument34 pagesBio23 LindenDjamal ToeNo ratings yet
- IEC60947 3 Approved PDFDocument3 pagesIEC60947 3 Approved PDFosmpotNo ratings yet
- Role of Perioperative NurseDocument30 pagesRole of Perioperative Nursealiyemany23No ratings yet
- Photodegradation and Photoprotection of Wood SurfaceDocument14 pagesPhotodegradation and Photoprotection of Wood Surfaceichsan hakimNo ratings yet
- Proceedings of BUU Conference 2012Document693 pagesProceedings of BUU Conference 2012Preecha SakarungNo ratings yet
- Physical Security Audit Checklist PDFDocument3 pagesPhysical Security Audit Checklist PDFHendrawan StbNo ratings yet
- Ethics and Disasters: Patricia Reynolds Director, Bishopric Medical Library Sarasota Memorial Hospital Sarasota, FLDocument61 pagesEthics and Disasters: Patricia Reynolds Director, Bishopric Medical Library Sarasota Memorial Hospital Sarasota, FLChandra Prakash JainNo ratings yet
- 4front Projects: BbbeeDocument12 pages4front Projects: BbbeeBrand Media OfficeNo ratings yet
- Cyril Cromier, Frost & SullivanDocument24 pagesCyril Cromier, Frost & SullivanGaurav SahuNo ratings yet
- Community Medicine DissertationDocument7 pagesCommunity Medicine DissertationCollegePaperGhostWriterSterlingHeights100% (1)
- NTFPP-Module 3 Microwave Processing of Foods - AjitKSinghDocument12 pagesNTFPP-Module 3 Microwave Processing of Foods - AjitKSinghKeshav RajputNo ratings yet
- Gimnazjum Exam Practice GuideDocument74 pagesGimnazjum Exam Practice GuideVaserd MoasleNo ratings yet
- Will BrinkDocument10 pagesWill BrinkJoao TorresNo ratings yet
- DepEd Region I Summative Test in Cookery 9Document2 pagesDepEd Region I Summative Test in Cookery 9Jessel Mejia OnzaNo ratings yet