Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Delivery Room Drug Study
Uploaded by
ChinimansiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Delivery Room Drug Study
Uploaded by
ChinimansiCopyright:
Available Formats
Name of Patient: Age:
Ward/Bed Number:
Attending Physician: Impression/Diagnosis:
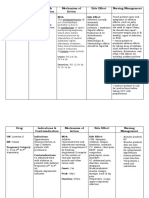
Dosage, Route, Name of Drug Frequency, Timing Available Forms: Generic: Oxytocin 10 units/ml in1ml ampule, vial or syringe Brand: incompatible IV solution Contraindications Hypersensitive to Classification Pharmacologic Class: Posterior pituitary hormone Therapeutic Class: Uterine active agent
Students Name: ___________________________ Clinical Instructor: _________________________ Name of Patient: Attending Physician:
Mechanism of Action
Indication To induce or stimulate labor.
Adverse Reactions
Special Precautions Oxytocin can be very useful for helping labor. However, there are certain risks with using it. Oxytocin
Nursing Responsibilities 1. Continuously monitor contractions, fetal and maternal heart rate, and maternal blood pressure andECG. 2. Discontinueinfusion if uterinehyperactivity occurs. 3. Monitor patientextremely closelyduring first andsecond stages oflabor because of riskof cervical laceration,uterine rupture andmaternal and fetaldeath. 4. Assess fluid intakeand output. Watch forsigns and symptomsof water intoxication
Side Effects CV: Hypertension,increased heartrate, systemicvenous return,cardiac output GI: Nausea,vomiting RESPIRATORY: Anoxia, asphyxia OTHERS: Low APGARscore at 5 mins.
causes contractions of the uterus. In women who are unusually sensitive to its effects, these contractions may become too strong.
drug when vaginal delivery is advisedCPD is presentwhen delivery requires conversion as in transverse lie.
Age:
Ward/Bed Number:
Impression/Diagnosis:
Dosage, Route, Name of Drug Frequency, Timing Oxytocin Generic: Dosage: Causes potent and selective stimulation Brand: Route: Classification Functional: Frequency: of uterine and mammary gland smooth muscles producing sustained contractions Induces labor and milk ejection and reduces post partum bleeding Contraindications
Cardiovascular: hypertension; increased heart rate, systemic venous return, and cardiac output, and arrhytmias CNS: seizures, coma from water intoxication Gastrointestinal: Nausea, vomiting, GU: titanic uterine contractions, abruption placentae, impaired uterine blood flow, pelvic hematoma Respiratory: anoxia, asphyxia
Mechanism of Action
Indication
Adverse Reactions
Special Precautions In rare cases, this may lead to tearing of the uterus. Also, if contractions are too strong, the supply of blood and oxygen to the fetus may be decreased. Oxytocin may cause jaundice and eye problems such as retinal hemorrhage infants
Nursing Responsibilities
Hematologic:afibrinogenemia in some newborn
Chemical:
Timing:
Students Name: ___________________________ Clinical Instructor: _________________________ Name of Patient: Attending Physician:
Age:
Ward/Bed Number:
Impression/Diagnosis:
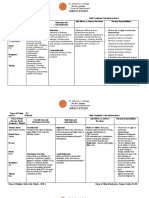
Dosage, Route, Name of Drug Generic:
methylergonovine maleate
Frequency, Timing IV:0.2 mg after delivery of after delivery of
Mechanism of Action Methergin smooth muscles Producing sustained contractions thereby shortens the third stage of labor
Indication Prevention and treatment of postpartum and post abortion hemorrhage caused by uterine atony or sub involution Contraindications
Adverse Reactions
Special Precautions
Caution should be exercised in the presence of sepsis, obliterative vascular disease. Also use with caution during the second stage of labor. The necessity for manual removal of a
Nursing Responsibilities Be alert for adverse reactions and drug interactions. This drug should be used extremely carefully because of its potent vasoconstrictor action. I.V. use may induce sudden hypertension and cerebrovascular accidents. As a last resort, give I.V. slowly over several minutes and monitor blood pressure closely.
anterior shoulder, Stimulates uterine placenta, or during puerperium; may be repeated as
Brand: Methergine
Classification PC: Ergot Alkaloid and Derivative TC: oxytocic, lactation stimulant
required at intervals of 2-4 hours
Side Effects
Nausea; vomiting.
retained placenta should occur only rarely with proper technique and adequate allowance of time for its spontaneous separation.
Students Name: ___________________________ Clinical Instructor: _________________________ Name of Patient: Attending Physician:
Age:
Ward/Bed Number:
Impression/Diagnosis:
Dosage, Route, Name of Drug Frequency, Timing
Cardiovascular:
Mechanism of Action
Indication
Adverse Reactions
Special Precautions
Nursing Responsibilities
Generic:
Dosage:
Contraindications
Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to methy lergonovine or any component of theformulation. ergot alkaloids are contraindicated with potent inhibitors of
hypertension, temporary chest pain, palpitation CNS: Hallucinations, dizziness, seizure, headache Gastrointestinal: Nausea, vomiting ,diarrhea, foul taste Local: Thrombophlebitis Otic: Tinnitus Renal: Hematuria Respiratory: Dyspnea, nasal congestion Miscellaneous: Diaphoresis
Brand: Route: Classification Functional: Frequency:
CYP3A4 (includes protease inhibitors, azole antifungals, and some macrolide
Chemical:
Timing:
antibiotics hypertension toxemia; pregnancy
Students Name: ___________________________ Clinical Instructor: _________________________
Name of Patient:
Attending Physician:
Age:
Ward/Bed Number:
Impression/Diagnosis:
Dosage, Route, Name of Drug Frequency, Timing 5mL Generic: 2% Lidocaine Brand: (100mg/5mL) An amide type local anaesthetic. It stabilizes the neuronal membrane and inhibits sodium are necessary for Classification Antiarrhythmic, Anesthetic (local and general) conduction of impulses. In the heart, lidocaine reduces phase 4depolarisation and automaticity. Duration of action potential and effective refractory period are also reduced.
Students Name: ___________________________ Name of Patient: Clinical Instructor: _________________________ Attending Physician:
Mechanism of Action
Indication Pulse less ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia block Contraindications Hypovolemia Heart block or other conduction disturbances
Adverse Reactions Dizziness, Paraesthesia, Drowsiness, Confusion, Respiratory depression Convulsions
Special Precautions Hepatic or renal impairment CHF and following cardiacsurgery Bradycardia Respiratory
Nursing Responsibilities Additive cardiac effects with IV phenytoin Effects antagonized by hypokalaemia caused by acetazolamide, loop diuretics and thiazides.
ion movements, which Sympathetic nerve
Side Effects Potentially fatal: Hypotension and bradycardia leading to cardiac arrest Anaphylaxis
depression Porphyria Elderly or debilitated patients Pregnancy
Dose requirements may be increased with long-term use of phenytoin and other enzyme-inducers.
Age:
Ward/Bed Number:
Impression/Diagnosis:
Dosage, Route, Name of Drug Frequency, Timing
Child 6-12 yr 1 tab
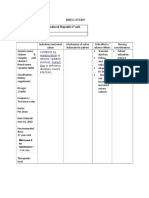
Mechanism of Action May be taken with or without food. Swallow whole, do not break/crush/chew.
Indication Tab GIT & GUT spasm. Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Amp Acute GI, biliary & genito-urinary spasm, including biliary & renal colic. As an aid in diagnostic & therapeutic procedures where spasm may be a problem eg gastroduodenal endoscopy & radiology.
Adverse Reactions Tachycardia, dizziness, dry mouth, dishydrosis, urinary retention. Tab Allergic reactions, dyspnea, painful red eye w/ loss of vision. Amp Anaphylactic reactions, accomodation disorders, mydriasis, increased IOP, decreased BP, flushing.
Special Precautions Tachycardia or other cardiac problems. Thyroid gland problems. Urinary retention, constipation, fever. May impair ability to drive or operate machinery. Pregnancy & lactation
Nursing Responsibilities Asses for eyepain; d/c use Asses for parkinsonism, extra pyramidalsymptoms Asses for urinary hesitancy, retention, palpate bladder of retention occurs. Asses for constipation Asses for tolerance overlong term therapy Asses for mental status.
Generic: Hyoscine
tds. Amp Adult & adolescent >12 yr 1-2 amp (20-40 mg). Max 100 mg/day. Infants & childn Severe cases: 0.3-0.6 mg/kg body wt. Max 1.5 mg/kg
Brand: Buscopan
Classification Functional: Anticholinergic/ antispasmodic
body wt/day. To be administered via slow IV, IM or SC inj several times daily
Students Name: ___________________________ Clinical Instructor: _________________________ Name of Patient: Attending Physician:
Age:
Ward/Bed Number:
Impression/Diagnosis:
Dosage, Route, Name of Drug Frequency, Timing Generic: Dosage: Contraindications Megacolon, myasthenia gravis, Brand: Route: Classification Functional: Frequency: glaucoma. Women of child-bearing potential. Amp Untreated narrow angle glaucoma, prostate hypertrophy w/ urinary retention, mechanical stenosis in GIT, tachycardia, Chemical: Timing: IM inj in patients on anticoagulants.
Students Name: ___________________________ Clinical Instructor: _________________________ Name of Patient: Attending Physician:
Mechanism of Action
Indication
Adverse Reactions
Special Precautions
Nursing Responsibilities
Side Effects Constipation, dry mouth, trouble urinating, or nausea could occur.
Age:
Ward/Bed Number:
Impression/Diagnosis:
Dosage, Route, Name of Drug Frequency, Timing Generic: Dosage: Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing Responsibilities
Brand: Route: Classification Functional: Frequency: Contraindications Side Effects
Chemical:
Timing:
Students Name: ___________________________ Clinical Instructor: _________________________ Name of Patient: Attending Physician:
Age:
Ward/Bed Number:
Impression/Diagnosis:
Dosage, Route, Name of Drug Frequency, Timing Generic: Dosage: Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing Responsibilities
Brand: Route: Classification Functional: Frequency: Contraindications Side Effects
Chemical:
Timing:
Students Name: ___________________________ Clinical Instructor: _________________________ Name of Patient: Attending Physician:
Age:
Ward/Bed Number:
Impression/Diagnosis:
Dosage, Route, Name of Drug Frequency, Timing Generic: Dosage: Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing Responsibilities
Brand: Route: Classification Functional: Frequency: Contraindications Side Effects
Chemical:
Timing:
Students Name: ___________________________ Clinical Instructor: _________________________ Name of Patient: Attending Physician:
Age:
Ward/Bed Number:
Impression/Diagnosis:
Dosage, Route, Name of Drug Frequency, Timing Generic: Dosage: Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing Responsibilities
Brand: Route: Classification Functional: Frequency: Contraindications Side Effects
Chemical:
Timing:
Students Name: ___________________________ Clinical Instructor: _________________________
You might also like
- OxytocinDocument1 pageOxytocinJoi Danielle Tabares IsturisNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DRDocument6 pagesDrug Study DRBheigh Lomitao AlbueraNo ratings yet
- Oxytocin Generic Name Action and ContraindicationsDocument2 pagesOxytocin Generic Name Action and ContraindicationsJoanne Kaye TaylorNo ratings yet
- Fentanyl Citrate Drug StudyDocument1 pageFentanyl Citrate Drug StudyArthur Christopher CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Vit K Drug StudyDocument2 pagesVit K Drug StudyKrisha AristonNo ratings yet
- Promethazine (Phenergan)Document1 pagePromethazine (Phenergan)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Carboprost Drug StudyDocument3 pagesCarboprost Drug StudyAjay SupanNo ratings yet
- Methergine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMethergine Drug StudyjoshNo ratings yet
- Vit K Drug Study PDFDocument2 pagesVit K Drug Study PDFA sisonNo ratings yet
- WESLEYAN UNIVERSITY-PHILIPPINES CONAMS (College of Nursing) DRUG STUDY CARD NURSING IMPLICATIONSDocument3 pagesWESLEYAN UNIVERSITY-PHILIPPINES CONAMS (College of Nursing) DRUG STUDY CARD NURSING IMPLICATIONSPrince Juzzel BanagNo ratings yet
- Oxytocin Drug StudyDocument9 pagesOxytocin Drug StudyAyessah Mapa100% (1)
- Timolol MaleateDocument3 pagesTimolol MaleateAP TOROBXNo ratings yet
- Terbutaline SulfateDocument2 pagesTerbutaline SulfateRhoellet VenzonNo ratings yet
- AztreonamDocument2 pagesAztreonamHannahShaeHayesNo ratings yet
- A Drug Study On Evening Primrose OilDocument5 pagesA Drug Study On Evening Primrose OilAlexis Khalyl Y. MontejoNo ratings yet
- Vii. Drug Study Drug Mechanism of ActionDocument7 pagesVii. Drug Study Drug Mechanism of ActionRifa'atul MahmudahNo ratings yet
- Drug Study...Document5 pagesDrug Study...Ezra Dizon ManzanoNo ratings yet
- BetamethasoneDocument3 pagesBetamethasoneMichael KuzbytNo ratings yet
- Levalbuterol (Xopenex)Document1 pageLevalbuterol (Xopenex)ENo ratings yet
- Methyldopa nursing management for hypertensionDocument4 pagesMethyldopa nursing management for hypertensionRico Mae ValenciaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Diphenhydramine)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY (Diphenhydramine)Avianna CalliopeNo ratings yet
- Oxytocin Drug Study for Labor Augmentation and Postpartum BleedingDocument3 pagesOxytocin Drug Study for Labor Augmentation and Postpartum BleedingJustin AncogNo ratings yet
- Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: EGAO, Vanessa Jones C. - Section:260Document1 pageMindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: EGAO, Vanessa Jones C. - Section:260Vanessa EgaoNo ratings yet
- Nifedepine Drug StudyDocument1 pageNifedepine Drug StudyMa. Sheenadel ZamudioNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyKristine Young100% (1)
- Name: Micaela Andrea C. Cielo Date: Year & Section: BS Nursing 2A Drug Study: AlbendazoleDocument2 pagesName: Micaela Andrea C. Cielo Date: Year & Section: BS Nursing 2A Drug Study: AlbendazoleMicaela Andrea CieloNo ratings yet
- Beractant for treatment of respiratory distress syndrome in premature infantsDocument2 pagesBeractant for treatment of respiratory distress syndrome in premature infantssyafiraNo ratings yet
- BricanylDocument4 pagesBricanylianecunarNo ratings yet
- ErythromycinDocument6 pagesErythromycinapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug Studykit genitaNo ratings yet
- NifedipineDocument3 pagesNifedipineNovi YulianaNo ratings yet
- DORMICUMDocument1 pageDORMICUMArian Rose100% (1)
- Furosemide ChlorthalidoneDocument5 pagesFurosemide ChlorthalidoneLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Drug Study - DelanDocument3 pagesDrug Study - DelanJuliana Sophia DelanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CefradoxilDocument13 pagesDrug Study - CefradoxilJohara G'naid0% (1)
- Name of Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesName of Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesMinaNo ratings yet
- A Drug Study On MISOPROSTOLDocument6 pagesA Drug Study On MISOPROSTOLAlexandrea MayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Form OxyDocument3 pagesDrug Study Form OxyRyan OdioNo ratings yet
- Generic Name (Brand Name) Methergine (Methylergonovine Maleate)Document3 pagesGeneric Name (Brand Name) Methergine (Methylergonovine Maleate)jennix_030883% (6)
- CefuroximeDocument11 pagesCefuroximeAlmira Ballesteros CestonaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudymYiE23No ratings yet
- Drug Study Delivery RoomDocument7 pagesDrug Study Delivery RoomkhleeoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - TerbutalineDocument2 pagesDrug Study - TerbutalineRock With YouNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Hep BDocument4 pagesDrug Study Hep BSawada TsunayoshiNo ratings yet
- MetamucilDocument1 pageMetamucilSheri490No ratings yet
- OfloxacinDocument2 pagesOfloxacinCarla Arciaga100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyEvangeline Anne MacanasNo ratings yet
- Drug CelexaDocument1 pageDrug CelexaSrkocher100% (1)
- Drug Study (Room 104)Document4 pagesDrug Study (Room 104)Maeshe Pryll TanamorNo ratings yet
- DocetaxelDocument4 pagesDocetaxelfnurdiansah002No ratings yet
- Duavent Drug Study - CunadoDocument3 pagesDuavent Drug Study - CunadoLexa Moreene Cu�adoNo ratings yet
- Journal PediaDocument2 pagesJournal PediapeteiroNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyJenivic Empig PuedanNo ratings yet
- Cephalexin Drug Study RNpedia ComDocument2 pagesCephalexin Drug Study RNpedia ComTaraKyleUyNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Misoprostol)Document3 pagesDrug Study (Misoprostol)Danica NuevaexcijaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SummaryDocument7 pagesDrug Study SummaryKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Labor and Delivery DrugsDocument8 pagesLabor and Delivery DrugsDing EmilyNo ratings yet
- Tramadol, Ketorolac, EterocoxibDocument4 pagesTramadol, Ketorolac, EterocoxibEric de JulianNo ratings yet
- CHH Drug Study Week 2Document25 pagesCHH Drug Study Week 2maryxtine24No ratings yet
- Labor and Delivery MedsDocument12 pagesLabor and Delivery MedsSam DanaNo ratings yet
- Doppler US Validates Portal Vein Flow in CirrhosisDocument5 pagesDoppler US Validates Portal Vein Flow in CirrhosisL0v3B00k5No ratings yet
- Basic Anatomical Terms PPTDocument30 pagesBasic Anatomical Terms PPTInsatiable Clee100% (1)
- Personal IdentificationDocument13 pagesPersonal IdentificationJose Li ToNo ratings yet
- Importance of Functional Groups in Drug SelectionDocument6 pagesImportance of Functional Groups in Drug SelectionNuruel HassanNo ratings yet
- A New Furileusaurian Abelisaurid From La Invernada Upper Cretaceous Santonian Bajo de La Carpa Formation Northern Patagonia ArgentinaDocument29 pagesA New Furileusaurian Abelisaurid From La Invernada Upper Cretaceous Santonian Bajo de La Carpa Formation Northern Patagonia ArgentinaStuff NewsroomNo ratings yet
- Poster 10 NLS 01 01 ENG V20100927 PDFDocument1 pagePoster 10 NLS 01 01 ENG V20100927 PDFAndy XiaoNo ratings yet
- CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR UpdatedDocument66 pagesCONSUMER BEHAVIOUR UpdatedUmer AzizNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Question Booklet: Name . .Document16 pagesPhotosynthesis Question Booklet: Name . .ajithaNo ratings yet
- Super 108 DR LalDocument8 pagesSuper 108 DR Lalarkaprava paulNo ratings yet
- AP PSYCHOLOGY EXAM REVIEW SHEETDocument6 pagesAP PSYCHOLOGY EXAM REVIEW SHEETNathan HudsonNo ratings yet
- The Normal Anterior Inferior Cerebellar ArteryDocument19 pagesThe Normal Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery16fernandoNo ratings yet
- Lipid Membrane Composition and SignificanceDocument4 pagesLipid Membrane Composition and SignificanceZainab AliNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Review of Temporal Lobe EpilepsyDocument36 pagesComprehensive Review of Temporal Lobe Epilepsyyohanes0gadiNo ratings yet
- 8Document6 pages8rajanNo ratings yet
- FORENSIC SEROLOGY AND BLOOD ANALYSISDocument16 pagesFORENSIC SEROLOGY AND BLOOD ANALYSISBARCELON, CHRISTOPHER JAMESNo ratings yet
- NCM 100 H.A Procedure DPPER 3Document51 pagesNCM 100 H.A Procedure DPPER 3Richelle Joy Durano RegatunaNo ratings yet
- PharmD 1st Year SyllabusDocument21 pagesPharmD 1st Year SyllabusAshwat ANo ratings yet
- Modul Anatomi Blok 7Document27 pagesModul Anatomi Blok 7Dewandaru I A BNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi Patient Monitor: Draeger - Vista 120S: Type Parameter Merk FeaturesDocument3 pagesSpesifikasi Patient Monitor: Draeger - Vista 120S: Type Parameter Merk Featuresflorensia shielyNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Compartment SyndromeDocument15 pagesAbdominal Compartment SyndromePierinaNo ratings yet
- Manajemen Pre-Operatif Pasien Dengan DMDocument12 pagesManajemen Pre-Operatif Pasien Dengan DMyanayas28No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document7 pagesChapter 4R LashNo ratings yet
- CP On AmoebiasisDocument77 pagesCP On Amoebiasiskathy100% (1)
- Arthropod-Plant Interactions Novel Insights and Approaches For IPMDocument238 pagesArthropod-Plant Interactions Novel Insights and Approaches For IPMAnonymous T9uyM2No ratings yet
- CSIR UGC JRF Subjetive Model Test PaperDocument17 pagesCSIR UGC JRF Subjetive Model Test PaperManu Mallahalli ShanthappaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease : Hypertensive and Diabetic Retinopathy in PatientsDocument7 pagesChronic Kidney Disease : Hypertensive and Diabetic Retinopathy in PatientsAnonymous FgT04krgymNo ratings yet
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument4 pagesRisk For Decreased Cardiac Outputapi-283482759No ratings yet
- Francisco Aboitiz (Auth.) - A Brain For Speech - A View From Evolutionary Neuroanatomy-Palgrave Macmillan UK (2017)Document515 pagesFrancisco Aboitiz (Auth.) - A Brain For Speech - A View From Evolutionary Neuroanatomy-Palgrave Macmillan UK (2017)TecuitlatlNo ratings yet
- Kotlyar 2016Document1 pageKotlyar 2016dasdsaNo ratings yet
- Excretory System QuizDocument17 pagesExcretory System QuizShadab HanafiNo ratings yet