Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mechanical Engineering: University of Calicut
Uploaded by
Jacob JoseOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mechanical Engineering: University of Calicut
Uploaded by
Jacob JoseCopyright:
Available Formats
Vidya Digital Library
UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT
SCHEME AND SYLLABI
FOR
SIXTH SEMESTER
OF
BACHELOR OF TECHNOLOGY
IN
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
FROM 2004 ADMISSION ONWARDS
CALICUT UNIVERSITY (P.O), THENHIPALAM
University of Calicut
B. Tech.-Mechanical Engg.
Vidya Digital Library
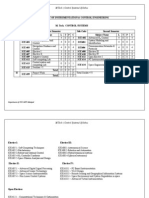
SIXTH SEMESTER Hours/Week L 3 3 3 3 3 3 18 T 1 1 1 1 1 1 6 P/D 3 3 6 Sessional Marks 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 400 University Examination Hrs Marks 3 100 3 100 3 100 3 100 3 100 3 100 3 100 700
Code ME04 601 ME04 602 ME04 603 ME04 604 ME04 605 ME04 606 ME04 607(P) ME04 608(P)
Subject I.C.Engines and Gas Turbines Machine Design Computer Integrated Manufacturing Finite Element Methods Operations Research Dynamics of Machinery CAD/CAM Lab Mini Project TOTAL
University of Calicut
B. Tech.-Mechanical Engg.
Vidya Digital Library
SIXTH SEMESTER ME04 601 : I C ENGINES AND GAS TURBINES 3 hours lecture & 1hour tutorial per week Objective To provide knowledge on air standard cycles,components of IC and CI engines, performance testing of IC engines , theory of combustion in IC engines and gas turbine theory Module I (14 hours) Internal combustion engines Engine components- Engine classification - four stroke and two stroke spark ignition and compression ignition - valve timing diagram - air standard cycles - Otto, diesel and duel combustion cycles - actual engine cycles - effect of dissociation - variable specific heats and heat losses scavenging - objectives - effects and methods Module II (13 hours) Systems and components of IC engines - fuel systems - ignition systems - cooling - starting - lubrication governing of IC engines - supercharging of SI and CI engines - turbocharging - exhaust emissions of IC engines - alternate potential engines - free piston engine - Wankel engine and stratified charged engine automotive transmission systems and its components - engine testing - performance and characteristics of constant speed and variable speed engines - heat balance test - Morse test - retardation test Module III (12 hours) Combustion in IC engines - flame propagation - normal and abnormal combustion - detonation - pre ignition - after burning - fuel rating - additives in petrol - combustion chambers of SI engines Combustion in CI engines - phase of normal combustion - diesel knock - effect of engine variables on diesel knock - cetane number - additives in diesel - combustion chambers of CI engines Module IV (13 hours) Gas turbine plants - open and closed cycles - thermodynamic cycles - regeneration - reheating intercooling - efficiency and performance of gas turbines - rotary compressors - analysis - centrifugal and axial flow compressors - combustion chambers of gas turbines - cylindrical - annular and industrial type combustion chamber - combustion efficiency - axial flow turbines - elementary and vortex theories design of nozzles and blades for turbines - limiting factors in turbine design Text Books Ganesan V Internal Combustion Engines, Tata McGraw Hill Ganesan V Gas Turbines , Tata McGraw Hill Reference books Rogowsky, Elements of Internal Combustion Engines, Tata McGraw Hill Gill, Smith & Ziurys, Fundamentals of Internal Combustion Engines, Oxford and IBH Maleev, Internal Combustion Engine Theory and Design McGraw Hill Judge, Modern Petrol Engines, Chapman & Hall Benson & Whitehouse, Internal Combustion Engines Vol. I & II, Pergamon press Mathur & Mehta, Thermodynamics and Heat Power Engineering, Vol. I & II Cohen & Rogers, Gas Turbine Theory, Longmans Edward F Obert, I.C. Engines & Air Pollution, Harper & Row Publishers Heywood, I.C. Engine Fundamentals, International Edition, McGraw Hill 1988 Sessional work assessment: 2 Assignments = 15 marks = 30 marks 2 Tests (2 15) Regularity = 05 marks Total = 50 marks University examination pattern Q I - 8 short type questions of 5 marks each, 2 from each module Q II - 2 questions A and B of 15marks each from module I with choice to answer any one Q III - 2 questions A and B of 15marks each from module II with choice to answer any one Q IV - 2 questions A and B of 15marks each from module III with choice to answer any one Q V - 2 questions A and B of 15marks each from module IV with choice to answer any one
University of Calicut
B. Tech.-Mechanical Engg.
Vidya Digital Library
ME04 602 : MACHINE DESIGN 3 hours lecture & 1hour tutorial per week Objective To provide knowledge on strength of mechanical elements,theories of failure, design of fasteners,welded joints,springs and power shafts Module I (13 hours) Introduction to design - steps in design process - design factors - tolerances and fits - principles of standardisation - selection of materials - strength of mechanical elements - stress concentration - theories of failure - impact load - fatigue loading - consideration of creep and thermal stresses in design Module II (13 hours) Threaded fasteners - thread standards - stresses in screw threads - preloading of bolts - bolted joints eccentric loading - gasketed joints - analysis of power screws - keys: types of keys and pins - stresses in keys and pins - design of keys - design of cotter and pin joints - riveted joints - stresses in riveted joints strength analysis - boiler and tank joints - structural joints Module III (13 hours) Welded joints - types of welded joints - stresses in butt and fillet welds - torsion and bending in welded joints - welds subjected to fluctuating loads - design of welded machine parts and structural joints springs: stresses in helical springs - deflection of helical springs - extension, compression and torsion springs - design of helical springs for static and fatigue loading - critical frequency of helical springs stress analysis and design of leaf springs Module IV (13 hours) Power shafting - stresses in shafts - design for static loads - reversed bending and steady torsion - design for strength and deflection - design for fatigue loading - critical speed of shafts - stresses in couplings design of couplings Text book Shigley J.E., Mechanical Engineering Design, McGraw Hill Book Company Reference books Siegel, Maleev & Hartman, Mechanical Design of Machines, International Book Company Phelan R.M., Fundamentals of Mechanical Design, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Co. Ltd. Doughtie V.L., & Vallance A.V., Design of Machine Elements, McGraw Hill Book Company Juvinall R.C. & Marshek K.M., Fundamentals of Machine Component Design, John Wiley Data hand books (allowed for reference during examinations) Prof. Narayana Iyengar B. R. & Dr Lingaiah K., Machine Design Data Handbook, Vol. I &II P.S.G., Tech., Machine Design Data Handbook Sessional work assessment: 2 Assignments 2 Tests (2 15) Regularity Total University examination pattern Data hand books (allowed for reference during examinations) Prof. Narayana Iyengar B. R. & Dr Lingaiah K., Machine Design Data Handbook, Vol. I &II P.S.G., Tech., Machine Design Data Handbook Q I - 8 short type questions of 5 marks each, 2 from each module Q II - 2 questions A and B of 15marks each from module I with choice to answer any one Q III - 2 questions A and B of 15marks each from module II with choice to answer any one Q IV - 2 questions A and B of 15marks each from module III with choice to answer any one Q V - 2 questions A and B of 15marks each from module IV with choice to answer any one
= 15 = 30 = 05 = 50
marks (At least one assignment should be Computer based) marks marks marks
University of Calicut
B. Tech.-Mechanical Engg.
Vidya Digital Library
ME04 603 : COMPUTER INTEGRATED MANUFACTURING 3 hours lecture & 1hour tutorial per week Objective To impart knowledge on fundamentals of Numerical Control, NC part programming,controls in Computer Integrated Manufacturing,Material handling , Data Capture,Flexible Manufacturing Systems and Robotics Module I (12 hours) Introduction Fundamentals of numerical control- Advantages of NC systems classification of NC systems point to point and contouring systems NC and CNC Incremental and absolute systems open loop and closed loop systems Features of NC machine tools Fundamentals of machining Design consideration of NC machine tools methods of improving machine accuracy and productivity special tool holders. Module II (15 hours) NC part programming - manual programming tape formats tab sequential fixed block word address and variable block formats part programming examples point to point programming and contour programming computer aided programming concepts post processor program languages APT programming part programming examples Module III (15 hours) Controls in CIM programmable logic controllers components of PLC PLC operating cycle Programming of PLC- Material handling in CIM- AGV- Vehicle guidance vehicle management and safety automated storage systems ASRS- components and operation features of ASRS Automatic data capture barcode technology magnetic strips optical character recognition group technology part families- part classifications and coding features of Opitz classification and multi class coding system Mode IV (12 hours) Flexible manufacturing system types of FMS -components of FMS FMS work stations material handling and storage systems FMS layout configurations computer control systems in FMS applications and benefits of FMS industrial robotics robot anatomy configurations joints- drive systems robot control systems end effectors- sensors in robots industrial robots applications robot programming-on line and off line programming Textbooks 1.Yoram Koran; Computer control of manufacturing systems; Mc Graw -Hill international book Company 2 Mickell .P.Grooer ; Automation, Production Systems and Computer Integrated Manufacturing; Pearson Education References H.M.T, Mechatronics, Tata Mc Graw Hill Groover M.P, Industrial Robotics- Technology, Programming and Applications- Mc Graw Hill. Sessional work assessment: 2 Assignments = 15 marks = 30 marks 2 Tests (2 15) Regularity = 05 marks Total = 50 marks University examination pattern Q I - 8 short type questions of 5 marks each, 2 from each module Q II - 2 questions A and B of 15marks each from module I with choice to answer any one Q III - 2 questions A and B of 15marks each from module II with choice to answer any one Q IV - 2 questions A and B of 15marks each from module III with choice to answer any one Q V - 2 questions A and B of 15marks each from module IV with choice to answer any one
University of Calicut
B. Tech.-Mechanical Engg.
Vidya Digital Library
ME04 604 : FINITE ELEMENT METHODS 3 hours lecture & 1hour tutorial per week Module I (13 hours) Review : Matrices and matrix operations solution of system of linear equations Gauss elimination Basic equations of elasticity strain-displacement relations- stress-strain relationship theorem of potential energy principle of virtual work St. Venants principle. Matrix method of structural analysis Flexibility matrix method stiffness matrix method Steady state heat conduction. (No direct questions from the above part) Introduction : Finite element method as a numerical tool for design basic concepts formulation procedures historical development current trends free and commercial FE packages. FE modeling Direct approach : 1-D bar element stiffness assembly of elements properties of [K] matrix treatment of boundary conditions temperature effects stress computation support reaction. Analogus problems in 1-D : Torsion heat conduction laminar pipe flow DC networks. Module II (12 hours) FE modeling Direct approach : Plane truss : Displacement based formulation for trusses Elements nodes degree of freedom connectivity element stiffness matrix - assembly of elements global stiffness matrix stress calculation - treatment of boundary conditions coordinate transformation local and global coordinates band width of the stiffness matrix node numbering to exploit matrix sparsity conservation of computer memory. Beam problems : Beam relationships 1-D beam element FE formulation - element stiffness matrix load considerations boundary conditions member end forces. Module III (12 hours) FE modeling Direct approach : 2-D stress and deformation analysis : FE discretization constant strain triangle strain-disp relation in an element stress-nodal force relations element stiffness matrix material property matrix global stiffness matrix load considerations boundary conditions stress evaluation modeling aspects symmetry element size and shape convergence. 2-D heat transfer : FE formulation for 2-D steady state heat transfer triangular element conductivity matrix boundary conditions. Module IV (15 hours) Variational approach : Variational methods weak and strong form Principle of stationary potential energy Rayleigh-Ritz method - FE formulation from a functional interpolation shape function for 1D and 2D element stiffness matrices consistent elemental nodal loads equilibrium and compatibility in the solution convergence requirements patch test. Weighted residual methods : Galerkin FE formulation axially loaded bar heat flow in a bar. Isoparamteric formulation : Linear and bilinear isoparametric elements jacobian matrix - Gauss quadrature requirements for isoparamteric elements accuracy and mesh distortion. Advanced topics : Introduction to non-linear and dynamic finite element procedures, error estimation, coupled problems (only brief details are needed).
Text books Chandrupatla T.R., Finite element analysis for engineering and technology, University Press. Cook R.D., Malkus D.S. & Plesha M.F., Concepts & Applications of Finite Element Analysis, John Wiley. Reference books Reddy J.N., An Introduction to the Finite Element Method, McGraw Hill International Edition Chandrupatla T.R. & Belegundu A.D., Introduction to Finite Elements in Engineering, Prentice Hall of India. Bathe K.J., Finite Element Procedures in Engineering Analysis, Prentice Hall of India. Zienkiewics O.C. & Taylor R.L., The Finite Element Method, Vol I & II, McGraw Hill.
University of Calicut
B. Tech.-Mechanical Engg.
Vidya Digital Library
Sessional work assessment 3 Tests 2 x 15 = 30 2 Assignments 2 x 10 = 20 Total marks = 50 Note : Assignments should be computer based problems. University examination pattern Q I - 8 short type questions of 5 marks each, 2 from each module Q II - 2 questions A and B of 15marks each from module I with choice to answer any one Q III - 2 questions A and B of 15marks each from module II with choice to answer any one Q IV - 2 questions A and B of 15marks each from module III with choice to answer any one Q V - 2 questions A and B of 15marks each from module IV with choice to answer any one
ME04 605 : OPERATIONS RESEARCH 3 hours lecture & 1hour tutorial per week Objective To provide knowledge on Linear algebra,linear programming, transportation, assignment and game problems and queing theory Module I: Linear algebra (13 hours) Vectors - vector space and Euclidean space - vector operations - matrix operations - unit vector - sum vector - linear dependence - bases - spanning set - rank - simultaneous equations - basic solutions - point sets - lines and hyper planes - linear inequalities - convex sets - extreme points - fundamental theorem of linear programming Module II: Linear programming (13 hours) Statement of the LP problem - slack and surplus variables - basic feasible solutions - reduction of a feasible solution to basic feasible solution - artificial variables - optimality conditions - unbounded solutions - Charnes M method - two phase method - degeneracy - duality Module III: Transportation, assignment and game problems (13 hours) Transportation problem - coefficient matrix and its properties - basic set of column vectors - linear combination of basic vectors - tableau format - stepping stone algorithm - UV method - inequality constraints - degeneracy in transportation problems - assignment problem as a maximally degenerate transportation problem - Knings method - rectangular zero sum games - von Neumans theorem - saddle points - pure and mixed strategies - formulation of the primal and dual LP problem for fixed strategies dominance - graphical solutions Module IV: Queuing theory (13 hours) Basic structure of queuing models - exponential and Poisson distributions - birth and death processes queuing models based on Poisson inputs and exponential service times - basic model with constant arrival rate and service rate - finite queue - limited source queue models involving non-exponential distributions single service model with Poisson arrival and any service time distribution - Poisson arrival with constant service time - Poisson arrival and Erlang service times - priority disciplines - dynamic programming Bellmans principle of optimality - formulation and solution of simple problems Text books Hadley G., Linear Programming, Addison Wesley Hillier & Liberman, Operations Research, Holden Day Inc. Ravindran, Solberg & Phillips, Operations Research, John Wiley Reference books Saskieni, Yaspen & Friedman, Operations Research: Methods and Problems, Wiley Toppan Wagner, Principles of Operations Research, Prentice Hall of India Sessional work assessment: 2 Assignments = 15 marks = 30 marks 2 Tests (2 15) Regularity = 05 marks Total = 50 marks
University of Calicut
B. Tech.-Mechanical Engg.
Vidya Digital Library
University examination pattern Q I - 8 short type questions of 5 marks each, 2 from each module Q II - 2 questions A and B of 15marks each from module I with choice to answer any one Q III - 2 questions A and B of 15marks each from module II with choice to answer any one Q IV - 2 questions A and B of 15marks each from module III with choice to answer any one Q V - 2 questions A and B of 15marks each from module IV with choice to answer any one
ME04 606: DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY 3 hours lecture & 1hour tutorial per week Objective To impart knowledge on force analysis of machinery, balancing of rotating and reciprocating masses ,vibration analysis, coordinate transformation, axial vibration of rods, bending vibration of bars and non linear vibration Module I (13 hours) Force analysis of machinery - static and dynamic force analysis of plane motion mechanisms - graphical method - principle of superposition - matrix methods - method of virtual work - complex number method Force Analysis of Spur- Helical - Bevel and Worm gearing Module II (13 hours) Flywheel analysis - balancing - static and dynamic balancing - balancing of masses rotating in several planes - balancing of reciprocating masses - balancing of multicylinder engines, V Engines - balancing machines. Gyroscope. Module III (13 hours) Introduction to vibrations Free and Forced vibrations of single degree freedom system Energy Method - Damped vibrations Coulomb damping - Logarithmic decrement Vibration Isolation Structural Damping - Transverse vibrations - support excitation - whirling of shafts torsional vibrations inertia effect of mass of shaft torsionally equivalent systems two rotor systems three rotor systems. Module IV (13 hours) Two degree of freedom systems - coordinate transformations - coupling - natural coordinates - beat phenomenon - undamped vibration absorbers. Vibration of continuous systems - exact methods - boundary value problem - Eigenvalue problem - axial vibration of rods - bending vibration of bars. Introduction to nonlinear vibration vibration measurements - accelerometer seismometer. Text books 1. Shigley J.E. & Uicker J.J. Jr., Theory of Machines and Mechanisms, McGraw Hill 2. A Ghosh & Asok Kumar Malik, Theory of Mechanisms and Machines. 3. Thompson W T , Theory of Vibrations with Applications , Prentice Hall of India. Reference books 1. Hollowenko, Dynamics of Machinery, McGraw Hill, Modules 2. Rao. S. S , Mechanical Vibrations, Pearson Education. Sessional work assessment: 2 Assignments = 15 marks = 30 marks 2 Tests (2 15) Regularity = 05 marks
University of Calicut
B. Tech.-Mechanical Engg.
Vidya Digital Library
Total = 50 marks Note: Computer based assignments are to be included. University examination pattern Q I - 8 short type questions of 5 marks each, 2 from each module Q II - 2 questions A and B of 15marks each from module I with choice to answer any one Q III - 2 questions A and B of 15marks each from module II with choice to answer any one Q IV - 2 questions A and B of 15marks each from module III with choice to answer any one Q V - 2 questions A and B of 15marks each from module IV with choice to answer any one
ME04 607(P) : CAD/CAM LABORATORY 3 hours lecture per week Objectives: At the end of this laboratory course you must be able to Create and Edit solid models and working drawings Perform Static and Dynamic analysis using FEM Program and Simulate CNC machine tool operations Program an industrial robot for simple material handling tasks Demonstrate the capabilities of a CMM for quality control 1. Exercises on solid modeling (12 hours) Introduction to computer graphics - viewing transformations, curves and surfaces generation, curve fitting and curve fairing techniques - 2D, wire frame, 3D shading - familiarity with Boolean operations - sweep, revolve, loft, extrude, filleting, chamfer, splines etc. - windowing, view point, clipping, scaling and rotation transformations using commercial solid modeling packages 2. Exercises on finite element analysis (12 hours) Introduction to FEM - 1D, 2D and 3D elements - shape functions - preprocessing - boundary conditions, structured and free mesh generation - analysis - linear and non linear analysis - static and dynamic analysis - post processing - display, animation, extraction of nodal data - exercises on heat conduction and elasticity may be given using commercial FEM packages 3. Assembly and mechanism design (6 hours) Assembling of various parts and tolerance analysis - synthesis and design of mechanisms - animations exercises on various mechanisms like four bar linkages and its variations - cam and follower - two and four stroke engines 4. Computer aided manufacturing (9 hours) Part programming fundamentals - manual part programming and computer aided part programming hands on training in computer controlled turning and milling operations - familiarity with windows based software packages - tool path generation and simulation - exercises on CNC lathe and machining center/milling machines 5. Programming of industrial robots (6 hours) Introduction to robotics - structure, workspace analysis and various components - actuators - sensors encoders - end effectors - applications - hands on training on industrial robots - manual and programmed path planning 6. Computer aided inspection and quality control (3 hours) Introduction to CMM - classification - structure - components - familiarity with measurement software packages and its modules - demonstration of the capability of coordinate measuring machine using a sample component e.g. - engine block - concepts of reverse engineering and rapid prototyping technology Reference books Rogers D.F. & Adams J.A., Mathematical Elements for Computer Graphics, McGraw Hill Rogers David F., Procedural Elements for Computer Graphics, McGraw Hill Cook, Robert Davis et al., Concepts and Applications of Finite Element Analysis, John Wiley
University of Calicut
B. Tech.-Mechanical Engg.
Vidya Digital Library
Koren Yoram, Computer Control of Manufacturing Systems, McGraw Hill Kundra Rao & Tewari, Numerical Control and Computer Aided Manufacturing, Tata McGraw Hill Ramamurthy V., Computer Aided Mechanical Design, Tata McGraw Hill Fu K.S., Gonzalez R.C. & Lee C.S.G., Robotics: Control, Sensing, Vision and Intelligence, McGraw Hill Koren Yoram, Robotics for Engineers, McGraw Hill Bosch J.A., Coordinate Measuring Machines and Systems, Marcel Decker Inc. Sessional work assessment Two tests = 25 Two assignments = 20 Regularity = 05 Total marks = 50
ME04 608(P) : MINI PROJECT 3 hours per week The project work can be a design project, experimental fabrication project or software development project on any of the topics of mechanical engineering interest - it can be allotted as a group project with groups consisting of three or four students The assessment of all the mini projects should be done by a committee consisting of three or four faculty members specialised in the various fields of mechanical engineering - the students will present their project work before the committee - the relative gradings and group average marks for the various projects will be fixed by the committee - the guides will award the marks for the individual students in the project maintaining the group average - each group will prepare the project report and submit to the department through the guide - the head of the department will certify the copies and keep them in the departmental library. Sessional work assessment Presentation = 30 Report = 20 Total marks = 50
University of Calicut
10
B. Tech.-Mechanical Engg.
You might also like
- Mechanical Engineering: University of CalicutDocument17 pagesMechanical Engineering: University of CalicutJacob JoseNo ratings yet
- Lbs College of Engineering: KasaragodDocument14 pagesLbs College of Engineering: KasaragodshobithNo ratings yet
- knrS7 & S8Document94 pagesknrS7 & S8Raavan LankaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Applications: A Project Resource BookFrom EverandEngineering Applications: A Project Resource BookRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (1)
- Mechanical Engineering Branch: Mahatma Gandhi University B.Tech. Degree Course 5 Semester Scheme & Syllabus 2002Document11 pagesMechanical Engineering Branch: Mahatma Gandhi University B.Tech. Degree Course 5 Semester Scheme & Syllabus 2002JOSEPH VARGHESENo ratings yet
- CIM SYSTEMS DESIGN MACHINE ELEMENTSDocument6 pagesCIM SYSTEMS DESIGN MACHINE ELEMENTSBala NarayanasamyNo ratings yet
- Practical Control of Electric Machines: Model-Based Design and SimulationFrom EverandPractical Control of Electric Machines: Model-Based Design and SimulationNo ratings yet
- Calicut University BTech Mechanical Engineering Scheme and CurriculumDocument4 pagesCalicut University BTech Mechanical Engineering Scheme and CurriculumAnish SukumarNo ratings yet
- Mech 5semDocument16 pagesMech 5sembhuvansparksNo ratings yet
- University of Kerala: Syllabus For Vii SemesterDocument43 pagesUniversity of Kerala: Syllabus For Vii SemesterSreekanthKottavilayilNo ratings yet
- Automobile 5th Syllabus CsvtuDocument9 pagesAutomobile 5th Syllabus CsvtuTejasvi AnantNo ratings yet
- AU010 702 Advanced Automotive TechnologyDocument2 pagesAU010 702 Advanced Automotive TechnologyVaisakVenugopalNo ratings yet
- University of Mumbai Scheme of Instruction and Evaluation for B.E. Mechanical EngineeringDocument82 pagesUniversity of Mumbai Scheme of Instruction and Evaluation for B.E. Mechanical EngineeringJayesh NavareNo ratings yet
- Ic Engines and Gas TurbineDocument3 pagesIc Engines and Gas TurbineLippin PaulyNo ratings yet
- Kannur University BTech EE VIII Sem SyllabusDocument14 pagesKannur University BTech EE VIII Sem SyllabusManu K M100% (1)
- Mechanical Engineering: University of CalicutDocument20 pagesMechanical Engineering: University of CalicutJacob JoseNo ratings yet
- Anna University Coimbatore REGULATIONS 2007-08 B.E - Mechanical EngineeringDocument28 pagesAnna University Coimbatore REGULATIONS 2007-08 B.E - Mechanical EngineeringRaajeshkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Chhattisgarh Technical University B.E. Mechanical 5th Sem Subject SchemeDocument14 pagesChhattisgarh Technical University B.E. Mechanical 5th Sem Subject Schemeveer_sNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesLesson Planshweta_770587No ratings yet
- S8Document7 pagesS8Gopu KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Auto-Syllab MTech Admission 2012-13Document25 pagesAuto-Syllab MTech Admission 2012-13Ratnakar PatilNo ratings yet
- Course Plan and Syllabus for Computer Aided ManufacturingDocument5 pagesCourse Plan and Syllabus for Computer Aided ManufacturingABHINAV20239No ratings yet
- r17 III-i SyllabusDocument19 pagesr17 III-i SyllabusAvinash RNo ratings yet
- B.E. Automobile Engineering Course DocumentsDocument73 pagesB.E. Automobile Engineering Course Documentssss0987654321No ratings yet
- M.E. Mech (Prod Des & Devp)Document41 pagesM.E. Mech (Prod Des & Devp)Peter PushpanathanNo ratings yet
- 6 Sem SyllabusDocument7 pages6 Sem SyllabusAjinkya NawghareNo ratings yet
- Third Year Second Semester: Department of Mechanical Engineering - Course CatalogueDocument8 pagesThird Year Second Semester: Department of Mechanical Engineering - Course CatalogueSudeep GamerNo ratings yet
- Course Module (VI Sem)Document7 pagesCourse Module (VI Sem)Vijay KumawatNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Automobile EngineeringDocument54 pagesSyllabus Automobile EngineeringmechanzsNo ratings yet
- R16 B.Tech Mechanical EnggDocument34 pagesR16 B.Tech Mechanical EnggmechhodNo ratings yet
- AutomobileDocument33 pagesAutomobilemarinerajesh3022No ratings yet
- M.E. AutomobileDocument33 pagesM.E. AutomobileJeyaram KumarNo ratings yet
- Syllabus-MDU-ME 5 Sem FDocument13 pagesSyllabus-MDU-ME 5 Sem Fraul2speedNo ratings yet
- Lbs College of Engineering: KasaragodDocument13 pagesLbs College of Engineering: KasaragodDamodar S PrabhuNo ratings yet
- JNTUK-DAP-B.tech (Mechanical Engineering) - Syllabus of B.tech III Year - I SemesterDocument20 pagesJNTUK-DAP-B.tech (Mechanical Engineering) - Syllabus of B.tech III Year - I SemesterSwamy RakeshNo ratings yet
- KANNUR UNIVERSITY BTech.S8 ME. SyllabusDocument13 pagesKANNUR UNIVERSITY BTech.S8 ME. SyllabusManu K MNo ratings yet
- Anna Univ Syllabus For EIE 3rd To 8th Sem Syllabus - WWW - Annaunivedu.infoDocument58 pagesAnna Univ Syllabus For EIE 3rd To 8th Sem Syllabus - WWW - Annaunivedu.infosudentsideaNo ratings yet
- B.E Mechnical2009Document64 pagesB.E Mechnical2009akshaybj4396No ratings yet
- MCE 417 Course CompactDocument7 pagesMCE 417 Course CompactKEHINDE BABALOLANo ratings yet
- AU401 Automotive System DesignDocument2 pagesAU401 Automotive System DesignAJIN ELIAS ALEXNo ratings yet
- B Tech Semester 5 2015-19Document30 pagesB Tech Semester 5 2015-19api-294538209No ratings yet
- 2nd Semester SyllabusDocument6 pages2nd Semester SyllabusNitin RathoreNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Vjti Structural EnggDocument276 pagesSyllabus Vjti Structural EnggPravin AwalkondeNo ratings yet
- E-4 Me Sem-1 SyllabusDocument14 pagesE-4 Me Sem-1 SyllabusraviNo ratings yet
- Shivaji University, Kolhapur Syllabus Structure of Second Year (S.E. Auto.) Automobile Engineering Course SchemeDocument45 pagesShivaji University, Kolhapur Syllabus Structure of Second Year (S.E. Auto.) Automobile Engineering Course SchemeAmol KharatNo ratings yet
- Cse Eme NotesDocument65 pagesCse Eme NotesVedNo ratings yet
- 6th Sem. Syllabus.Document13 pages6th Sem. Syllabus.ashutosh.vssplNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - B.E. Mechanical - 2009 RegulationDocument161 pagesSyllabus - B.E. Mechanical - 2009 RegulationshivakumarNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-11-30 at 5.53.13 PMDocument20 pagesScreenshot 2023-11-30 at 5.53.13 PMtextkapishhNo ratings yet
- Kannur University: B.Tech Degree Programme inDocument94 pagesKannur University: B.Tech Degree Programme inMuzammil MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Bmee301l Design-Of-Machine-Elements TH 1.0 67 Bmee301lDocument3 pagesBmee301l Design-Of-Machine-Elements TH 1.0 67 Bmee301lKrijayNo ratings yet
- GTU MECHATRONICS SYLLABUSDocument2 pagesGTU MECHATRONICS SYLLABUSpmagrawalNo ratings yet
- M.e.,cim SyllabusDocument44 pagesM.e.,cim SyllabusSiva PrakashNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument18 pagesDepartment of Mechanical EngineeringBrandon AllenNo ratings yet
- M.Tech Control Systems Syllabi MANIPAL UNIVERSITYDocument41 pagesM.Tech Control Systems Syllabi MANIPAL UNIVERSITYJacob Jose100% (1)
- MEM201 L6-Tolerance RCDocument31 pagesMEM201 L6-Tolerance RCKaliya PerumalNo ratings yet
- Ex 1435Document3 pagesEx 1435Jacob JoseNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Servo MotorsDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Servo MotorsJacob JoseNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Mechanical Echanical Properties and Grain Rain Structure of 5xxx AluminiumDocument4 pagesInvestigation of Mechanical Echanical Properties and Grain Rain Structure of 5xxx AluminiumJacob JoseNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering: University of CalicutDocument20 pagesMechanical Engineering: University of CalicutJacob JoseNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering: University of CalicutDocument12 pagesMechanical Engineering: University of CalicutJacob JoseNo ratings yet
- s3 s4Document26 pagess3 s4Jacob JoseNo ratings yet
- 03 ForecastingDocument29 pages03 ForecastingJacob JoseNo ratings yet
- s1 s2Document18 pagess1 s2Jacob JoseNo ratings yet
- Break Even Analysis of Mining ProjectsDocument60 pagesBreak Even Analysis of Mining ProjectsAnil Kumar100% (1)
- Fea 2 Marks and AnswersDocument20 pagesFea 2 Marks and AnswerssnvijayanNo ratings yet
- Wataru Mizumachi Electric Atomic Power Division, Tokyo, JapanDocument17 pagesWataru Mizumachi Electric Atomic Power Division, Tokyo, JapanRajat MalikNo ratings yet
- Mfelab PDFDocument246 pagesMfelab PDFbekjuNo ratings yet
- JNTU Hyderabad FEM exam questionsDocument8 pagesJNTU Hyderabad FEM exam questionsvenkiscribd444No ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Isoparametric Elements Chapter 6: Isoparametric ElementsDocument10 pagesChapter 6: Isoparametric Elements Chapter 6: Isoparametric ElementsAryan BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To AE, MSNT, ME)Document3 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To AE, MSNT, ME)Sreedhar MNo ratings yet
- Static Condensation and SubstructuringDocument2 pagesStatic Condensation and Substructuringrf123_456No ratings yet
- Structural and Thermal Analysis of Disc Brake RotorsDocument9 pagesStructural and Thermal Analysis of Disc Brake RotorsgnanesqNo ratings yet
- Global Analysis of Tall Buildings With Tubed Mega Frame StructuresDocument154 pagesGlobal Analysis of Tall Buildings With Tubed Mega Frame Structuresdxzaber100% (2)
- Vehicle-Bridge Interaction Analysis by Dynamic Condensation MethodDocument9 pagesVehicle-Bridge Interaction Analysis by Dynamic Condensation MethodHuda AlrikabiNo ratings yet
- Ce4257 1 IntroductionDocument27 pagesCe4257 1 IntroductionLiew Yen ChingNo ratings yet
- NX Nastran Model Checks: WhitepaperDocument10 pagesNX Nastran Model Checks: Whitepaperstefanos axiosNo ratings yet
- R18 B.Tech 3-2 MechanicalEngg SyllabusDocument20 pagesR18 B.Tech 3-2 MechanicalEngg SyllabusGovar AnjaneyuluNo ratings yet
- Code Conversion FEM - XFEMDocument6 pagesCode Conversion FEM - XFEMjacobessNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Modelling of Insulation Thicknesses For Cryogenic Products in Spherical Storage Pressure VesselsDocument5 pagesFinite Element Modelling of Insulation Thicknesses For Cryogenic Products in Spherical Storage Pressure VesselsAdityaShetgaonkarNo ratings yet
- Fem Assignment Question Bank Unit 1&2 PDFDocument1 pageFem Assignment Question Bank Unit 1&2 PDFSudhakar UppalapatiNo ratings yet
- 10 BirthDeathDocument20 pages10 BirthDeathChetan B ArkasaliNo ratings yet
- Fem Objective QuestionsDocument7 pagesFem Objective Questionsbharathkumar03100% (2)
- MSC Nastran 2012 Linear Static Analysis User's GuideDocument772 pagesMSC Nastran 2012 Linear Static Analysis User's GuideMSC Nastran Beginner100% (2)
- ME1401 Finite Element AnalysisDocument10 pagesME1401 Finite Element AnalysisSarathiraja SekarNo ratings yet
- DKT 3-node triangular element for composite platesDocument44 pagesDKT 3-node triangular element for composite platesMiguel SerraNo ratings yet
- Advanced Finite Element Methods For Engineers: Exercise 3Document31 pagesAdvanced Finite Element Methods For Engineers: Exercise 3Sangram BhosaleNo ratings yet
- Question Repository for JUNE/JULY 2022 ExamsDocument43 pagesQuestion Repository for JUNE/JULY 2022 ExamsAravind KumarNo ratings yet
- Fast MATLAB Assembly of FEM Matrices in 2D and 3D - Nodal ElementsDocument13 pagesFast MATLAB Assembly of FEM Matrices in 2D and 3D - Nodal ElementsOndelettaNo ratings yet
- TahaDocument12 pagesTahaTaha ShalabiNo ratings yet
- ADA173823Document138 pagesADA173823vuilehaidNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Stiffness (Displacement) Method: Analysis of A System of SpringsDocument42 pagesIntroduction To The Stiffness (Displacement) Method: Analysis of A System of SpringsFaryal BatoolNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis of Car Disk BrakeDocument73 pagesStructural Analysis of Car Disk BrakeAkesh KakarlaNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Maxwell's EquationsDocument6 pagesFinite Element Maxwell's EquationsHFdzAlNo ratings yet
- M.Tech Scheme and Syllabus for Mechanical EngineeringDocument72 pagesM.Tech Scheme and Syllabus for Mechanical EngineeringNithul DasNo ratings yet
- Practical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsFrom EverandPractical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Hyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionFrom EverandHyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Piping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationFrom EverandPiping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (18)
- Einstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseFrom EverandEinstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (50)
- The Laws of Thermodynamics: A Very Short IntroductionFrom EverandThe Laws of Thermodynamics: A Very Short IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Pressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedFrom EverandPressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Introduction to Applied Thermodynamics: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionFrom EverandIntroduction to Applied Thermodynamics: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Handbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringFrom EverandHandbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Quantum Mechanics 4: Spin, Lasers, Pauli Exclusion & Barrier PenetrationFrom EverandQuantum Mechanics 4: Spin, Lasers, Pauli Exclusion & Barrier PenetrationRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Rolling Bearing Tribology: Tribology and Failure Modes of Rolling Element BearingsFrom EverandRolling Bearing Tribology: Tribology and Failure Modes of Rolling Element BearingsNo ratings yet
- 1,001 Questions & Answers for the CWI Exam: Welding Metallurgy and Visual Inspection Study GuideFrom Everand1,001 Questions & Answers for the CWI Exam: Welding Metallurgy and Visual Inspection Study GuideRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (7)
- Waves and Beaches: The Powerful Dynamics of Sea and CoastFrom EverandWaves and Beaches: The Powerful Dynamics of Sea and CoastRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Formulas and Calculations for Drilling, Production, and Workover: All the Formulas You Need to Solve Drilling and Production ProblemsFrom EverandFormulas and Calculations for Drilling, Production, and Workover: All the Formulas You Need to Solve Drilling and Production ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignFrom EverandOperational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Machinery Failure Analysis Handbook: Sustain Your Operations and Maximize UptimeFrom EverandMachinery Failure Analysis Handbook: Sustain Your Operations and Maximize UptimeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Basic Alarm Electronics: Toolbox Guides for Security TechniciansFrom EverandBasic Alarm Electronics: Toolbox Guides for Security TechniciansJohn SangerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)