Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2010-01-18 191618 11 Weaponeer 8542008B407
Uploaded by
browar4440 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views1 pageIn this research a rifling tool is designed and manufactured according to electrochemical basic theories. The results are compared with those of simulation and experimental methods. Increasing the linear speed of the tool decreases the machining depth. This increasing causes the reduction in machining time and subsequently decreases the depth.
Original Description:
Original Title
2010-01-18_191618_11_weaponeer_8542008B407
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIn this research a rifling tool is designed and manufactured according to electrochemical basic theories. The results are compared with those of simulation and experimental methods. Increasing the linear speed of the tool decreases the machining depth. This increasing causes the reduction in machining time and subsequently decreases the depth.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views1 page2010-01-18 191618 11 Weaponeer 8542008B407
Uploaded by
browar444In this research a rifling tool is designed and manufactured according to electrochemical basic theories. The results are compared with those of simulation and experimental methods. Increasing the linear speed of the tool decreases the machining depth. This increasing causes the reduction in machining time and subsequently decreases the depth.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
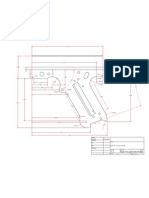
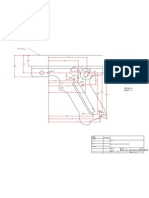
ECM rifling tool design and manufacturing
351
7. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION
In this research a rifling tool is designed and manufactured according to electrochemical basic theories. The results are compared with those of simulation and experimental methods. The linear speed of the tool and the depth of the rifles are compared with the results of simulation and experimental methods. The linear speed of the tool and also the depth of the rifle, as two major machining parameters, were under consideration. Increasing the linear speed of the tool decreases the machining depth (Fig. 9).This increasing causes the reduction in machining time and subsequently decreases the machining depth. It can be inferred that increasing the voltage decreases the machining depth (Fig. 10). The theoretical and experimental rifling depth variations are shown in Figs. 12 and 13. Comparison between the two shows a difference in the range of 0-0.025mm. The tolerance domain for this depth, as indicated in Fig. 12, is 0.06mm. This difference is very small and can be neglected. This means that the theoretical and experimental values are almost the same. The error could be due to: 1) Reading voltage and current values from analogue systems are not precise. 2) Different linear speed of the tool is obtained via the variations in the gearbox and also transmission speed pulleys from the motor to gearbox. This speed is calculated via the measurement of the distance and time which have their own cumulative errors. 3) The spiral shape of rifling depth is complex and the measurement of these slots is prone to errors. 4) The setting up of some machining parameters such as the density and the temperature of electrolyte and their control during the machining process. Two theoretical and one experimental result show a very good agreement (Fig. 12 and 13).
0.25
Solution 1 Solution 2 Experimental data
0.225
0.2
0.175
0.15
ch
0.1 6 7
0.125
ive
8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
a ( mm )
Ar
a ( mm )
Fig. 12. Rifling depth variations with electrical voltage according to; Computer simulation (solution 1), Electro chemical theories (solution 2), Experimental results
0.35
Solution 1 Solution 2 Experimental data
0.3
0.25
0.2
0.15
0.1
of
U(v)
3 4 5 6
V ( mm / sec )
Fig. 13. Rifling depth variations with linear speed of tool according to; Computer simulation (solution 1) Electro chemical theories (solution 2), Experimental results
August 2008 Iranian Journal of Science & Technology, Volume 32, Number B4
SI
www.SID.ir
You might also like
- A 518298Document19 pagesA 518298browar444No ratings yet
- MAC 10 CookbookDocument90 pagesMAC 10 Cookbookbrowar44472% (32)
- Mechanism of Action of Presynaptc Neurotoxins. Annual Report 1985 PDFDocument34 pagesMechanism of Action of Presynaptc Neurotoxins. Annual Report 1985 PDFbrowar444No ratings yet
- Ruger 10-22 Rifle Receiver 1 - BlueprintDocument1 pageRuger 10-22 Rifle Receiver 1 - BlueprintAride4ever100% (2)
- Firearms - Blueprint - Ruger 10-22 Rifle Receiver 2Document1 pageFirearms - Blueprint - Ruger 10-22 Rifle Receiver 2browar444100% (2)
- M 1911 A 1Document62 pagesM 1911 A 1Michael C. Burgess88% (16)
- Stinger Rifles FamilyDocument7 pagesStinger Rifles Familybrowar44467% (9)
- Firearms - Blueprint - Owen MK II, H&R Reising Submachine Guns and Springfield M60 RifleDocument12 pagesFirearms - Blueprint - Owen MK II, H&R Reising Submachine Guns and Springfield M60 Riflebrowar44484% (19)
- SVT40 ManualDocument23 pagesSVT40 Manualandy2205No ratings yet
- Beretta 38A 38-44 SMG Receiver BlueprintDocument1 pageBeretta 38A 38-44 SMG Receiver Blueprinth762x39100% (3)
- PPSH41 Assault Rifle BlueprintDocument12 pagesPPSH41 Assault Rifle Blueprinth762x3992% (12)
- UZI ReceiverDocument7 pagesUZI Receiverbrowar444No ratings yet
- 223 Silencer DesignDocument1 page223 Silencer DesignFlavio MarçalNo ratings yet
- Post-14-01138-M 14 Receiver Ordnance PrintsDocument5 pagesPost-14-01138-M 14 Receiver Ordnance PrintsJustus Pradana AdityawanNo ratings yet
- Home Workshop - Vol 5 - AR-15, M-16 - Bill Holmes - Paladin Press PDFDocument110 pagesHome Workshop - Vol 5 - AR-15, M-16 - Bill Holmes - Paladin Press PDFCarlaAndrade100% (2)
- Ruger Mk1 Right Side Grip FrameDocument1 pageRuger Mk1 Right Side Grip Framebrowar444No ratings yet
- UZI SMG ReceiverDocument7 pagesUZI SMG Receiverbrowar444100% (6)
- TM-9-1005-301-30 Repair Wood Fibre Plastic Components of Weapons Part2Document18 pagesTM-9-1005-301-30 Repair Wood Fibre Plastic Components of Weapons Part2browar444No ratings yet
- Nangant Pistol HistoryDocument67 pagesNangant Pistol Historygorlan100% (1)
- TM-9-1005-301-30 Repair Wood Fibre Plastic Components of Weapons Part1Document19 pagesTM-9-1005-301-30 Repair Wood Fibre Plastic Components of Weapons Part1browar444No ratings yet
- Spring RatingDocument6 pagesSpring Ratingbrowar444No ratings yet
- MAC-11 9mm Construction Conversion Iron Wulf PublishingDocument86 pagesMAC-11 9mm Construction Conversion Iron Wulf PublishingJordan Voller100% (5)
- Metal Casting Basics Book 2Document67 pagesMetal Casting Basics Book 2browar444100% (2)
- Shotgun Based Pistol BlueprintDocument6 pagesShotgun Based Pistol BlueprintGonzoGranello0% (1)
- Ruger Mk1 Grip Frame Left SideDocument1 pageRuger Mk1 Grip Frame Left Sidebrowar444100% (1)
- Ruger Mk1 Grip Frame Left Hole DetailDocument1 pageRuger Mk1 Grip Frame Left Hole Detailbrowar444100% (1)
- Metal Casting Basics Book 1Document57 pagesMetal Casting Basics Book 1browar444100% (1)
- Mac-10 SMG Lower-Upper Receiver - BlueprintsDocument2 pagesMac-10 SMG Lower-Upper Receiver - Blueprintsbrowar44489% (9)
- Machinist Drawings For SMG Frames - MAC10, MAC11, Cobray M11-9, CobrayM12Document13 pagesMachinist Drawings For SMG Frames - MAC10, MAC11, Cobray M11-9, CobrayM12Aride4ever89% (73)
- Full Auto Volume Three Semi Auto Mac 10 SMG Modification ManualDocument29 pagesFull Auto Volume Three Semi Auto Mac 10 SMG Modification ManualJerry Becraft85% (13)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Ipecacuanha Liquid Extract - British Pharmacopoeia 2017Document1 pageIpecacuanha Liquid Extract - British Pharmacopoeia 2017Social Service (V)No ratings yet
- SITI SOLEHAH BINTI OMAR (2015834112) /EH224 7A1 Heuristics of ReactorDocument2 pagesSITI SOLEHAH BINTI OMAR (2015834112) /EH224 7A1 Heuristics of ReactorSolehah OmarNo ratings yet
- Organic Pigments - The Basics - SII - Dec 2008Document298 pagesOrganic Pigments - The Basics - SII - Dec 2008Prince Jannisari100% (1)
- Chemsheets As 1038 Le Chatelier 1Document1 pageChemsheets As 1038 Le Chatelier 1Дильназ БолатбеккызыNo ratings yet
- Dissolution Improvement of Telmisartan by Surface Solid Dispersion MethodDocument5 pagesDissolution Improvement of Telmisartan by Surface Solid Dispersion MethodHafidz PrasetyaNo ratings yet
- Feasibility of Using Lightweight Eps Based Partitions For Washrooms of ApartmentsDocument6 pagesFeasibility of Using Lightweight Eps Based Partitions For Washrooms of ApartmentsVishnuNo ratings yet
- OIL-Xplus Filtros Aire ComprimidoDocument8 pagesOIL-Xplus Filtros Aire ComprimidoMario Vazquez BNo ratings yet
- Cyproheptadine Hydrochloride WordDocument4 pagesCyproheptadine Hydrochloride WordFathur Rahman YusufNo ratings yet
- Detection of Porcine DNA in Gelatine and Gelatine-Containing Processed Food Products-Halal - Kosher AuthenticationDocument4 pagesDetection of Porcine DNA in Gelatine and Gelatine-Containing Processed Food Products-Halal - Kosher AuthenticationekosaputrobbppbatuNo ratings yet
- AFLAS Technical DatasheetDocument13 pagesAFLAS Technical DatasheetManual SourceNo ratings yet
- IB Biology HL IA (MAY 2021)Document14 pagesIB Biology HL IA (MAY 2021)Insiyah Huzefa BasraiNo ratings yet
- EspecificacionesDC Axial Fan 4114NH6 ENGDocument4 pagesEspecificacionesDC Axial Fan 4114NH6 ENGFabrizio DandreamatteoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 Activity Sheet Quarter 2-MELC 12 Week 6Document9 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 Activity Sheet Quarter 2-MELC 12 Week 6Joshua De La VegaNo ratings yet
- Airfoil Lift Procedures PDFDocument12 pagesAirfoil Lift Procedures PDFmatthias.s.sommer3656No ratings yet
- Optical Properties of Semiconductor NanocrystalsDocument259 pagesOptical Properties of Semiconductor Nanocrystalsanhthigl25No ratings yet
- What Is Calcium Oxalate PrecipitationDocument3 pagesWhat Is Calcium Oxalate PrecipitationluismiguelmmercadoNo ratings yet
- Oxygen MSDS Safety GuideDocument4 pagesOxygen MSDS Safety Guidelutfi_thalib3175No ratings yet
- Mechanical EngineeringDocument94 pagesMechanical EngineeringAnandu ANo ratings yet
- Spectrophotometric Determination of The Equilibrium Constant of A Reaction DraftDocument3 pagesSpectrophotometric Determination of The Equilibrium Constant of A Reaction DraftFem T. BartolomeNo ratings yet
- BMW Fault Codes OBDDocument15 pagesBMW Fault Codes OBDtitibacsiNo ratings yet
- ZirconiaDocument12 pagesZirconiaAna Massiel NarváezNo ratings yet
- Russell J. Donnelly - Fifty-Five Years of Taylor - Couette FlowDocument35 pagesRussell J. Donnelly - Fifty-Five Years of Taylor - Couette FlowQMDhidnwNo ratings yet
- Indonesian Journal of Chemical Science and Technology: State University of MedanDocument7 pagesIndonesian Journal of Chemical Science and Technology: State University of Medanrizky bungaNo ratings yet
- Groundwater Fluoride in Haryana State: A Review On The Status and Its MitigationDocument5 pagesGroundwater Fluoride in Haryana State: A Review On The Status and Its MitigationSEP-PublisherNo ratings yet
- Protocol Calcofluor MutDocument3 pagesProtocol Calcofluor Mutrck46No ratings yet
- Watson and Crick 1953 Molecular Structure of Nucleic AcidsDocument2 pagesWatson and Crick 1953 Molecular Structure of Nucleic AcidsFabio KochanowskiNo ratings yet
- SPM 4551 2006 Biology k2 BerjawapanDocument15 pagesSPM 4551 2006 Biology k2 Berjawapanpss smk selandarNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Catabolism 2013Document108 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism Catabolism 2013Anonymous nErkwtXnuS100% (1)
- Copper (II) Sulfate - Reagent - Anhydrous 98 - Acros OrganicsDocument5 pagesCopper (II) Sulfate - Reagent - Anhydrous 98 - Acros OrganicsGaryoNo ratings yet
- Vibration Isolation PDFDocument9 pagesVibration Isolation PDFl8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet