Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Brain Tumors and Epilepsy
Uploaded by
Navjot BrarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Brain Tumors and Epilepsy
Uploaded by
Navjot BrarCopyright:
Available Formats
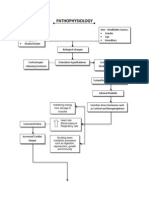
Brain tumors and epilepsy
due to progression of brain tumor
damage to the brain cells as well as morphological and functional changes occur
formation of scar tissue (gliosis)
gliosis interfere with normal structural and chemical environment of brain neurones
increased permeability of cell membrane
excessive discharge of electrical impulses
makes the cell membrane to depolarize
excessive firing and discharge of epileptogenic neurones
repeated jerky movements of muscles
seizures and loss of consciousness
due to causes
hyperplasia of cells of piyuitary gland
pituitary tumors
Increased secretion of pituitary hormones i.e. hyperpituitarism
Compression of optic nerve
Increase GH Increase ACTH Increase TSH Increase gonadotrophin Increase prolactin Increase oxytocin Increase ADH
Blocks transmission of nerve impulse from ganglionic cells in retina to the visual area in cerebrum.
Visual disturbances such as blurred vision and diplopia
Hyper functioning of target glands
As compression increases it cause permanent damage to optic nerve
Blindness
Due to anterior pituitary tumors
Increased anterior pituitary hormones
Increased growth hormone
Increased thyroid stimulating hormone
Increased gonadotrophins
Increased prolactin
Increased adrenocortico trophic hormone
Gigantism, acromegaly, hepatomegaly and elevated blood glucose
Increased stimulation to thyroid gland
Increased production of sex hormones
Stimulate lactogenesis
Increase adrenal gland activity
hyperthyroidism
Increase T3 and T4
Menstrual abnormalities, impotence in male, decrease libido
Galactorrhea
Increase glucocorticoids
Increase BMR, body temperature, catecholamines, weight loss
Increase breakdown of proteins and glucose production, diminished immune response
Increase heart rate and BP
Due to posterior pituitary tumors
Increased production of posterior pituitary hormones
Increased oxytocin
Increase ADH
Increase uterine contractions, increased stimulation to mammary glands
Acts on renal tubules
Dysmennorhea, galactorrhea, abortion
Decreased urine output and increase fluid reabsorption
Sodium and water retention
Edema
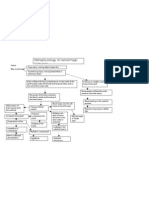
Due to causes
Brain stem tumors
Compression of brain stem
Medulary tumors
Tumors in pons
Tumors in mid brain
Involvement of cardio vascular centre Involvement of respiratory centre Involvement of cranial nerves (VIII, IX, X, XI, XII)
Involvement of pneumotaxic and apneustic area Involvement of cranial nerves (V, VI,VII,VIII)
Impaired reflex centre of visual activities Involve occulomotor and trochlear nerves Involve substantia nigra
Medulla oblongata tumors
Damage to cardiovascular centre
Damage to respiratory centre
Damage to cranial nerves.
Lack of control over heart rate and rhythm.
Lack of regulation of respiratory rhythm
Decreased cardiac contractility
Chienne stroke respiration Cluster breathing
Dysrhythmias As further compression occurs, leads to varying degree of dyspnea and suffocation
Decreased cardiac output
Impaired tissue perfusion
Oxygen insufficiency to tissues
Necrosis and damage
Anaerobic metabolism and lactic acid accumulation
Cell death
Hypoxia and respiratory failure.
Tumors in mid brain
Compression of visual reflex centre
Damaged substantia nigra
Compression of cranial nerves
Inability to control head and neck movements in response to visual activities
Depletion of dopamine stores
Absent startle reflex,
Imbalance in excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters
Damage to extrapyramidal tracts which control complex body movements
Bradykinesia, tremors and rigidity
Parkinsons disease
You might also like
- Vibrato Michael Trimble PDFDocument7 pagesVibrato Michael Trimble PDFCinqMars100% (1)
- Principles of Managent of Hypovolemic Shock in ADocument43 pagesPrinciples of Managent of Hypovolemic Shock in Aasi basseyNo ratings yet
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Cerebellum & Brain-Stem AnatomyDocument23 pagesCerebellum & Brain-Stem AnatomyMuhammad ShahzaibNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CAP and HTNDocument5 pagesPathophysiology CAP and HTNLeonaPunzalanNo ratings yet
- InfertilityDocument58 pagesInfertilityNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- Capillary Blood CollectionDocument8 pagesCapillary Blood CollectionARIF AHAMMED P100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Cva-Hpnii-Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Cva-Hpnii-Hemorrhagic StrokeLarisse de Leon82% (11)
- ICP Head InjuryDocument57 pagesICP Head InjuryWengel RedkissNo ratings yet
- Stroke: Pathophysiology, Types, Management Categories, and Vascular SyndromesDocument49 pagesStroke: Pathophysiology, Types, Management Categories, and Vascular Syndromesrabia khalidNo ratings yet
- Presented by DR Mohammed AtifDocument42 pagesPresented by DR Mohammed AtifUmer HussainNo ratings yet
- Chest InjuriesDocument8 pagesChest InjuriesNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- Focus On StrokeDocument92 pagesFocus On StrokeDIAH RETNO WULAN100% (2)
- Introduction To Clinical Neurology - 2018Document68 pagesIntroduction To Clinical Neurology - 2018Alberto MayorgaNo ratings yet
- Genetics in Blood BankingDocument47 pagesGenetics in Blood BankingMandy A. Delfin100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Endocrine SystemDocument37 pagesPathophysiology of Endocrine SystemRodriguez Vivanco Kevin DanielNo ratings yet
- Concept Map of Subarachnoid Hemmorhage by Rhealyn NograDocument3 pagesConcept Map of Subarachnoid Hemmorhage by Rhealyn NograRhealyn NograNo ratings yet
- Brain TumorsDocument19 pagesBrain TumorsNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- Brain TumorsDocument19 pagesBrain TumorsNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- Meniere DiseaseDocument16 pagesMeniere DiseaseNavjot Brar100% (2)
- Hypertension Is ADocument4 pagesHypertension Is Aperny karaiNo ratings yet
- DBs MethodsDocument20 pagesDBs Methodscoctyus100% (4)
- Cortical Dipole and Clinical SignificanceDocument15 pagesCortical Dipole and Clinical SignificanceManamitaNo ratings yet
- BLS Provider Manual PDFDocument21 pagesBLS Provider Manual PDFAmany Al Mahgoob100% (1)
- Hands On-Equine Craniosacral NHMDocument4 pagesHands On-Equine Craniosacral NHMapi-237342656100% (1)
- NCPDocument14 pagesNCPkristapot80% (10)
- Pathophysiology of Brain TumorsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Brain TumorsNavjot Brar92% (13)
- 1 - Endocrine DisordersDocument55 pages1 - Endocrine Disorderscephas chinkoliNo ratings yet
- Shock PresentationDocument21 pagesShock Presentationapi-283170120No ratings yet
- CVD Infarct-HpniiDocument3 pagesCVD Infarct-HpniilarissedeleonNo ratings yet
- Cerebral EdemaDocument37 pagesCerebral EdemaTenywa AllyNo ratings yet
- Shock: by Simranpreet KaurDocument10 pagesShock: by Simranpreet Kaurpreet kaurNo ratings yet
- D.5. Oxygenation and PerfusionDocument98 pagesD.5. Oxygenation and PerfusionTricia Denise EstabilloNo ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument9 pagesHead InjuryRaveen mayiNo ratings yet
- Physiology Exchange of AgingDocument31 pagesPhysiology Exchange of Agingnurul dwi ratihNo ratings yet
- Concept Map AAADocument6 pagesConcept Map AAASandrine BarredoNo ratings yet
- Shock: Shock Can Refer To A Range of Related Medical Conditions in Which The Victim's Heart, Lungs andDocument16 pagesShock: Shock Can Refer To A Range of Related Medical Conditions in Which The Victim's Heart, Lungs andLucreatia RynjahNo ratings yet
- Dengue Symptom A To LogyDocument1 pageDengue Symptom A To LogyJet Acido GalloNo ratings yet
- Brain Attack: NR-75D Diana Diaz RN, MSDocument66 pagesBrain Attack: NR-75D Diana Diaz RN, MSJoshua SmithNo ratings yet
- Cases 1-6Document21 pagesCases 1-6angelica dizonNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Non-Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsDocument3 pagesPathophysiology Non-Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsErrol B. TiozonNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland Diseases: Cushing's SyndromeDocument12 pagesPituitary Gland Diseases: Cushing's SyndromeAsh AshNo ratings yet
- TN1Document13 pagesTN1InactiveAccountNo ratings yet
- Hypoxia Ischemic Encephalopathy and Congenital AnomaliesDocument36 pagesHypoxia Ischemic Encephalopathy and Congenital AnomaliesVarna MohanNo ratings yet
- Humoral and Intra Cardiac Mechanism of Heart' RegulationDocument23 pagesHumoral and Intra Cardiac Mechanism of Heart' RegulationAman singhNo ratings yet
- Brunner Normal Intracranial Pressure 10-20 MMHGDocument16 pagesBrunner Normal Intracranial Pressure 10-20 MMHGlovely99_dyahNo ratings yet
- Causes of Hypovolemic Hypernatremia Include The FollowingDocument2 pagesCauses of Hypovolemic Hypernatremia Include The FollowingYOS HANANo ratings yet
- In The Name of Allah, The Most Beneficent, The Most MercifulDocument40 pagesIn The Name of Allah, The Most Beneficent, The Most MercifulISMAILNo ratings yet
- Icp NewDocument50 pagesIcp Newanon_411736789No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Hemorrhagic ContusionDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Hemorrhagic ContusionMaria ClaritaNo ratings yet
- Ans05 HormonesDocument5 pagesAns05 Hormonesngsuan.2020No ratings yet
- Types of Shock: Cardiovascular Dysfunction Chapter 48Document1 pageTypes of Shock: Cardiovascular Dysfunction Chapter 48meeeenonNo ratings yet
- Mid Term III Theory PhysioDocument12 pagesMid Term III Theory PhysioSyeda AlizaNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA) : The BrainDocument6 pagesCerebrovascular Accident (CVA) : The BrainBrenn Marie RamosNo ratings yet
- ICS - 1st LeDocument4 pagesICS - 1st LeAbigail Mayled LausNo ratings yet
- HemodynamicDocument20 pagesHemodynamicمحمد آل راشدNo ratings yet
- Cerebro Vascular DiseaseDocument25 pagesCerebro Vascular DiseaseMuhammad Asif NizamiNo ratings yet
- Medical DictionaryDocument10 pagesMedical DictionaryevacawleyNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Nursing InterventionDocument6 pagesPathophysiology Nursing Interventionjphernandez_2002No ratings yet
- Chapter 57 - ICPDocument32 pagesChapter 57 - ICPJanyll PerezNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular DiseaseDocument19 pagesCerebrovascular DiseaseSurkhali BipanaNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Failure 2'to BACTERIAL MeningitisDocument19 pagesAcute Respiratory Failure 2'to BACTERIAL MeningitislpetalloNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Endocrine Anatomy and Physiology Review & Pituitary DisturbancesDocument27 pagesWeek 2 Endocrine Anatomy and Physiology Review & Pituitary DisturbancesZiqri Dimas SandyNo ratings yet
- Acute Pulmonary Edema: Purwoko Sugeng HDocument25 pagesAcute Pulmonary Edema: Purwoko Sugeng HBee DanielNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Mechanical Ventilation Part IDocument39 pages4.1 Mechanical Ventilation Part IMohamedNo ratings yet
- Perinatal AsphyxiaDocument24 pagesPerinatal AsphyxiaZazzZaffaNo ratings yet
- Increased Intracranial Pressure: CEU ProfessorDocument9 pagesIncreased Intracranial Pressure: CEU ProfessorJah AcabNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System DisorderDocument16 pagesEndocrine System DisorderAnonymous KnlqfUtNo ratings yet
- KC PathoDocument7 pagesKC PathoLomie GumayagayNo ratings yet
- Neuro 2012 Halliday PresentationDocument31 pagesNeuro 2012 Halliday PresentationNugroho HarsonoNo ratings yet
- Kebutuhan Dasar Manusia OksigenasiDocument117 pagesKebutuhan Dasar Manusia Oksigenasiintanputri ramadhaniNo ratings yet
- Oncology ReportDocument2 pagesOncology ReportLinda OrdanzaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal Failure-7Document5 pagesChronic Renal Failure-7GERA SUMANTHNo ratings yet
- Neurologic AL Disorders: Aka: CephalgiaDocument19 pagesNeurologic AL Disorders: Aka: CephalgiaNicole AlcoberNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure NarrativeDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure NarrativeAlfred BucabucaNo ratings yet
- Giant Cell Arteritis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandGiant Cell Arteritis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive DiseasesDocument82 pagesMale Reproductive DiseasesNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal SystemDocument56 pagesMusculoskeletal SystemNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- Cerebral AneurysmDocument6 pagesCerebral AneurysmNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- 10 Mcqs Canada For SampleDocument5 pages10 Mcqs Canada For SampleNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- MeningitisDocument20 pagesMeningitisNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocument8 pagesSubarachnoid HemorrhageNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- Neurological AssessmentDocument23 pagesNeurological AssessmentNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia GravisDocument1 pageMyasthenia GravisNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- Bulbar PalsyDocument14 pagesBulbar PalsyNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- Alzheimer's Disease: Pre Dementia Early Moderate AdvancedDocument7 pagesAlzheimer's Disease: Pre Dementia Early Moderate AdvancedNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- Movement DisordersDocument43 pagesMovement DisordersNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- Alternative System of MedicineDocument8 pagesAlternative System of MedicineNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- Carpal Tunnel SyndromeDocument7 pagesCarpal Tunnel SyndromeNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- Anti Scabies DrugsDocument4 pagesAnti Scabies DrugsNavjot Brar100% (2)
- Anti HistaminesDocument5 pagesAnti HistaminesNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- Antidiuretic DrugsDocument4 pagesAntidiuretic DrugsNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- Anti Asthmatic DrugsDocument8 pagesAnti Asthmatic DrugsNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- A Study To Evaluate Effectiveness of Cold Application and Magnesium Sulphate Application On Superficial Thrombophlebitis Among Patients Receiving Intravenous Therapy in Selected Hospitals Amritsar.Document25 pagesA Study To Evaluate Effectiveness of Cold Application and Magnesium Sulphate Application On Superficial Thrombophlebitis Among Patients Receiving Intravenous Therapy in Selected Hospitals Amritsar.Navjot Brar71% (14)
- Alzheimer's Disease: Pre Dementia Early Moderate AdvancedDocument7 pagesAlzheimer's Disease: Pre Dementia Early Moderate AdvancedNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- Review of Anatomy and Physiology of Reproductive SystemDocument26 pagesReview of Anatomy and Physiology of Reproductive SystemNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes ImbalanceDocument13 pagesFluid and Electrolytes ImbalanceNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- Aqueous Humor Outflow:: Anterior Cavity: The Lens Divides The Anterior Cavity Into Further Two ChambersDocument20 pagesAqueous Humor Outflow:: Anterior Cavity: The Lens Divides The Anterior Cavity Into Further Two ChambersNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of BrainDocument21 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of BrainNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- Urinary Disorders 2Document19 pagesUrinary Disorders 2ula mdiNo ratings yet
- 613 Case Study EssayDocument13 pages613 Case Study EssaysheemalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Circulatory SystemJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- GENITOURINARYDocument24 pagesGENITOURINARYrlinaoNo ratings yet
- Bio 130 Chapter 4 NotesDocument12 pagesBio 130 Chapter 4 Notesgilissa100% (1)
- Uog15821 Online PDFDocument17 pagesUog15821 Online PDFernestosandNo ratings yet
- ANAT1012.1019 Example Regional Upper Limb SAQ's - 2022Document4 pagesANAT1012.1019 Example Regional Upper Limb SAQ's - 2022Grace YNo ratings yet
- Peng Kaji AnDocument54 pagesPeng Kaji Anmabuhay crewNo ratings yet
- Regulation of BPDocument17 pagesRegulation of BPLemon CatbaganNo ratings yet
- 294 Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring. Principles and Interpretation of Cardiotocography LR PDFDocument9 pages294 Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring. Principles and Interpretation of Cardiotocography LR PDFelenNo ratings yet
- Lumbar Traction Review2Document9 pagesLumbar Traction Review2Phooi Yee LauNo ratings yet
- Acist Cvi Brochure Us 2014 LRDocument4 pagesAcist Cvi Brochure Us 2014 LRloulou1306No ratings yet
- ECG (Cardiology Clinic 2006)Document127 pagesECG (Cardiology Clinic 2006)VuqarNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication, Translation, and TranscriptionDocument43 pagesDna Replication, Translation, and TranscriptionMaria VisitacionNo ratings yet
- VO Basics of Neuroscience WS 22Document4 pagesVO Basics of Neuroscience WS 22Sina HsNo ratings yet
- ScriptDocument5 pagesScriptViviNo ratings yet
- A Multi-Dimensional Model of Dysfunctional BreathiDocument4 pagesA Multi-Dimensional Model of Dysfunctional Breathimari_kundera19No ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument5 pagesTransport in PlantsAlex LochaiNo ratings yet
- 10752-02 CH02 Final PDFDocument28 pages10752-02 CH02 Final PDFDejan MilenkovicNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument27 pagesExamKashish HoraNo ratings yet