Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Critical Axial Load For Torsional and Flexural Torsional Buckling Modes
Uploaded by
Pang Sze DaiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Critical Axial Load For Torsional and Flexural Torsional Buckling Modes
Uploaded by
Pang Sze DaiCopyright:
Available Formats
the
NCCI:
Critical
axial
load
for
torsional
and
flexural
torsional
buckling
modes
NCCI: Critical axial load for torsional and flexural torsional buckling modes SN001a-EN-EU
conditions
of
NCCI: Critical axial load for torsional and flexural torsional buckling modes
This NCCI gives the expressions for the critical axial load for the torsional buckling mode and the flexural-torsional buckling mode.
terms
and
Contents
1. 2. General Torsional buckling Flexural-torsional buckling References 2 2 3 4
subject
to
the
3. 4.
04, Created This on material Monday, is October copyright -
all
2010 rights
reserved.
Use
of
this
document
is
Page 1
the
NCCI:
Critical
axial
load
for
torsional
and
flexural
torsional
buckling
modes
NCCI: Critical axial load for torsional and flexural torsional buckling modes SN001a-EN-EU
conditions
of
1.
General
and
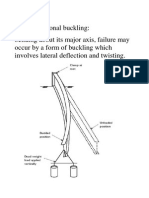
For the following common cases, torsional and flexural torsional buckling will not give a lower mode than flexural buckling : Doubly symmetric I and H sections (provided that both flanges are restrained at positions of lateral restraint) Hollow sections However, in some particular cases, the torsional buckling mode or the flexural-torsional buckling mode of an axially loaded member may correspond to a critical load lower than the one corresponding to the flexural buckling mode, especially for open sections. This document gives rules to determine the critical load for such cases. This document deals with uniform members only and for which the conditions of restraint at each end of the member are at least : restrained against lateral movement restrained against rotation about the longitudinal axis
document
is
subject
to
the
terms
2.
Torsional buckling
2 EI w 1 GI t + 2 2 io lT
this
The critical axial load Ncr.T for torsional buckling mode may be calculated from :
N cr, T =
of
(1)
Use
with:
reserved.
2 2 2 2 io = iy + iz2 + yo + z o
(2)
where:
2010 rights
E G It Iw lT
is the Young modulus (E = 210000 N/mm2) is the shear modulus (G = 80770 N/mm2) is the torsion constant is the warping constant is the buckling length regarding the torsional buckling mode. In general, lT should be taken as the system length, except when a special device prevents the warping at the ends of the member.
04, October copyright -
all
yo and zo are the coordinates of the shear centre with respect to the centroid (see Figure 2.1). For a doubly symmetric cross-section, the shear centre coincides with the centroid; then yo = 0 and zo = 0 iy iz is the radius of gyration of the cross-section about the strong axis is the radius of gyration of the cross-section about the weak axis
Page 2
Created This
on material
Monday, is
the
NCCI:
Critical
axial
load
for
torsional
and
flexural
torsional
buckling
modes
NCCI: Critical axial load for torsional and flexural torsional buckling modes SN001a-EN-EU
conditions
of
S
and
zo
yo
G
y
to
the
terms
Figure 2.1
subject
Coordinates of the shear centre S with respect to the centroid G
3.
Flexural-torsional buckling
is
document
The flexural-torsional buckling mode should be considered only when the shear centre does not coincide with the centroid. The critical axial load Ncr.TF for the flexural-torsional buckling mode is the smallest root of the following cubic equation in N :
2 2 2 io (N N cr, y )(N N cr, z )(N N cr, T ) N 2 yo (N N cr, z ) N 2 zo (N N cr, y ) = 0
this
(3)
of
where
Use
Ncr,y and Ncr,z are the critical axial loads for flexural buckling about yy and zz axes respectively Ncr.T is the critical axial load for torsional buckling mode, see 2. The equation may also be written as follows :
2 iy + iz2 3 1 2 2 2 N + 2 N cr, y zo + N cr, z yo (N cr, y + N cr, z + N cr, T ) N 2 i io o
reserved.
2010 rights
(4)
04,
+ (N cr,y N cr,z + N cr,z N cr,T + N cr,T N cr,y )N N cr,y N cr,z N cr,T = 0
When the cross-section is symmetric about the y-y-axis (see Figure 3.1), the critical axial load may be obtained from :
October copyright
all
N cr,TF =
Monday, is
2 io N + N cr, y cr,T 2 2 2 i y + iz
(N
cr, y
+ N cr,T ) 4 N cr,y N cr,T
2
2 iy + iz2 2 io
(5)
Created This
on material
When the cross-section is symmetric about the z-z-axis, Ncr.y should be replaced by Ncr.z in the above expression.
Page 3
the
NCCI:
Critical
axial
load
for
torsional
and
flexural
torsional
buckling
modes
NCCI: Critical axial load for torsional and flexural torsional buckling modes SN001a-EN-EU
conditions
of
yo
and
y
terms
the
subject
to
Figure 3.1
Cross-section symmetric about y-y-axis
is
4.
document
References
Timoshenko, S.P. and Gere, J.M.
Theory of elastic stability. 2nd Edition. Mc Graw-Hill. 1961.
04, Created This on material Monday, is October copyright -
all
2010 rights
reserved.
Use
of
this
Page 4
the
NCCI:
Critical
axial
load
for
torsional
and
flexural
torsional
buckling
modes
NCCI: Critical axial load for torsional and flexural torsional buckling modes SN001a-EN-EU
conditions
of
Quality Record
and
terms
RESOURCE TITLE
NCCI: Critical axial load for torsional and flexural torsional buckling modes
Reference(s)
the
ORIGINAL DOCUMENT Name Created by A. BUREAU Y. GALEA D C Iles Company CTICM CTICM SCI Date 02/02/05 02/02/05 2/3/05
subject
to
Technical content checked by Editorial content checked by Technical content endorsed by the following STEEL Partners: 1. UK 2. France 3. Sweden
is
document
G W Owens A Bureau A Olsson C Mueller J Chica G W Owens
SCI CTICM SBI RWTH Labein SCI
1/3/05 1/3/05 1/3/05 1/3/05 1/3/05 21/04/06
this
4. Germany 5. Spain Resource approved by Technical Coordinator TRANSLATED DOCUMENT This Translation made and checked by:
reserved.
Use
of
Translated resource approved by:
04, Created This on material Monday, is October copyright -
all
2010 rights
Page 5
You might also like
- Elastic Lateral Torsional BucklingDocument3 pagesElastic Lateral Torsional BucklingRuchit ParmarNo ratings yet
- Lateral Loads Manual SAP 2000Document316 pagesLateral Loads Manual SAP 2000Nyein Zaw100% (1)
- Hoardings Design Cal FinalDocument10 pagesHoardings Design Cal FinalJay Senjalia100% (1)
- Classification of Cross SectionDocument19 pagesClassification of Cross SectionAmirul Asyraf Bin Mohd BekeriNo ratings yet
- Building Structures and TechnologyDocument98 pagesBuilding Structures and TechnologyBandilung Tz100% (1)
- A Comparison Study of Pressure Vessel Design Using Different StandardsDocument319 pagesA Comparison Study of Pressure Vessel Design Using Different StandardsHyune Boom SheenNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Objective Type Paper - IDocument23 pagesCivil Engineering Objective Type Paper - IVishal RanganathanNo ratings yet
- Aisi Standard: North American Standard For The Design of Profiled Steel Diaphragm PanelsDocument199 pagesAisi Standard: North American Standard For The Design of Profiled Steel Diaphragm PanelsSabdiel Morales100% (1)
- Deep Foundations: Limit State Design, Tensile Load and Load TestsDocument46 pagesDeep Foundations: Limit State Design, Tensile Load and Load TestsSteven KuaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Students Understand The Elastic Neutral Axis But What About The Plastic Neutral AxisDocument9 pagesEngineering Students Understand The Elastic Neutral Axis But What About The Plastic Neutral AxisAnonymous fKv3jsANo ratings yet
- CV6311 Shear Strength Lect1 2012Document38 pagesCV6311 Shear Strength Lect1 2012ikanyu79No ratings yet
- Overview of EurocodesDocument27 pagesOverview of EurocodesbsitlerNo ratings yet
- SN001a (NCCI - Critical Axial Load For Torsional and Flexural Torsional Buckling Modes)Document5 pagesSN001a (NCCI - Critical Axial Load For Torsional and Flexural Torsional Buckling Modes)Hamati RamiNo ratings yet
- Portal frame eaves connection designDocument3 pagesPortal frame eaves connection designCenascenascenascenas100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - Design of Steel Frames by Second-Order Analysis Fulifilling Code RequirementsDocument54 pagesChapter 3 - Design of Steel Frames by Second-Order Analysis Fulifilling Code RequirementsIvan KlyuchkaNo ratings yet
- Beam DesignDocument84 pagesBeam DesignFoo He XuanNo ratings yet
- Understanding Heat Exchanger Reading 01Document87 pagesUnderstanding Heat Exchanger Reading 01charliechong100% (2)
- Example: Fire Engineering A Composite SHS ColumnDocument10 pagesExample: Fire Engineering A Composite SHS ColumnCatalin234No ratings yet
- Afcen Etc-C 2010Document409 pagesAfcen Etc-C 2010Vinh LENo ratings yet
- Seismic Design of Composite Metal Deck and Concrete Filled Diaphragms A Discussion Paper Cowie Hicks Macrae Clifton FussellDocument11 pagesSeismic Design of Composite Metal Deck and Concrete Filled Diaphragms A Discussion Paper Cowie Hicks Macrae Clifton Fussellmongkol_1001No ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Solids and AcousticsDocument56 pagesMechanical Properties of Solids and AcousticsMayank Agarwal100% (3)
- SN001a-En-EU - NCCI - Critical Axial Load For Torsional and Flexural TorsionalDocument5 pagesSN001a-En-EU - NCCI - Critical Axial Load For Torsional and Flexural TorsionalJ ZhangNo ratings yet
- 114 (STD)Document13 pages114 (STD)roshniNo ratings yet
- Bernt - EC3 1 5Document44 pagesBernt - EC3 1 5Rosario BlancaNo ratings yet
- SX004a-En-EU-Example - Pinned Column Using Non Slender H-Section or RHSDocument5 pagesSX004a-En-EU-Example - Pinned Column Using Non Slender H-Section or RHSKen OkoyeNo ratings yet
- DS - en 1999-1-1 DK Na - 2007 eDocument6 pagesDS - en 1999-1-1 DK Na - 2007 ep_meulendijks108No ratings yet
- Tài Liệu 1 PDFDocument122 pagesTài Liệu 1 PDFThanh HuyNo ratings yet
- EC3 - Tension Member - 2021Document27 pagesEC3 - Tension Member - 2021MUHAMMAD AMIRUL ASYRAF BIN MOHD RANINo ratings yet
- Bs Na en 1993 - 1-2 2005Document8 pagesBs Na en 1993 - 1-2 2005Chicho PopovNo ratings yet
- Prof - Tamura July19 APSS2010 Wind-Universitatea TokyoDocument156 pagesProf - Tamura July19 APSS2010 Wind-Universitatea TokyoPasc Oana JianinaNo ratings yet
- SN017 (NCCI - Shear Resistance of A Fin Plate Connection)Document13 pagesSN017 (NCCI - Shear Resistance of A Fin Plate Connection)Hamati Rami100% (2)
- E 720Document50 pagesE 720Shama100% (2)
- European Recommendations On Sandwich Structures PDFDocument71 pagesEuropean Recommendations On Sandwich Structures PDFSigfridoLogesNo ratings yet
- Chapter05 - Plane Frame and Grid EqDocument63 pagesChapter05 - Plane Frame and Grid EqAgus BaeNo ratings yet
- Critical Axial Load For Torsional and Flexural Torsional Buckling ModesDocument5 pagesCritical Axial Load For Torsional and Flexural Torsional Buckling ModesBobaru MariusNo ratings yet
- Sn027a-Design of TrussDocument14 pagesSn027a-Design of Trussdeepak_dce_meNo ratings yet
- DS - en 1999-1-2 DK Na - 2007 eDocument3 pagesDS - en 1999-1-2 DK Na - 2007 ep_meulendijks108No ratings yet
- DWM Holdings Provides Quick Response to Vibration IssueDocument5 pagesDWM Holdings Provides Quick Response to Vibration IssueHussain AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Response of Structures To DynaDocument61 pagesChapter 3 Response of Structures To DynaSayyadh Rahamath BabaNo ratings yet
- SN002a (NCCi - Determination of Non-Dimensional Slenderness of I and H Sections)Document11 pagesSN002a (NCCi - Determination of Non-Dimensional Slenderness of I and H Sections)Hamati RamiNo ratings yet
- Part 1-8 Joint DesignDocument8 pagesPart 1-8 Joint DesignChweNo ratings yet
- TCVN 7571-2006 Thep Hinh Can Nong Kich Thuoc Dung Sai Dac Tinh Mat CatDocument24 pagesTCVN 7571-2006 Thep Hinh Can Nong Kich Thuoc Dung Sai Dac Tinh Mat CatgiangleohartNo ratings yet
- (EXTRACT) Etabs Analysis Reference v18 - Friction Pendulum - Single, Double & TripleDocument13 pages(EXTRACT) Etabs Analysis Reference v18 - Friction Pendulum - Single, Double & TripleO SNo ratings yet
- 07 Axisymmetric Finite Element ModelingDocument14 pages07 Axisymmetric Finite Element ModelingSchubertDeierlein100% (1)
- EN 1991-1-4 Denmark NADocument10 pagesEN 1991-1-4 Denmark NAcpm101No ratings yet
- Free Vibration of SDF SystemsDocument14 pagesFree Vibration of SDF Systemspattrapong pongpattraNo ratings yet
- Ramset Specifiers Anchoring Resource Book ANZ Chemical Anchoring Anchor StudsDocument59 pagesRamset Specifiers Anchoring Resource Book ANZ Chemical Anchoring Anchor StudsjlolhnpNo ratings yet
- Column Splices Not Requiring Full Continuity of StiffnessDocument6 pagesColumn Splices Not Requiring Full Continuity of StiffnessBobaru MariusNo ratings yet
- CE5108 Earth Retaining StructuresDocument1 pageCE5108 Earth Retaining StructuresbsitlerNo ratings yet
- 98s11 PDFDocument11 pages98s11 PDFpaulkohanNo ratings yet
- DS - en 1993-1-4 DK Na - 2007 eDocument4 pagesDS - en 1993-1-4 DK Na - 2007 ep_meulendijks108No ratings yet
- 2 Local Buckling and Section Classification - 2011Document21 pages2 Local Buckling and Section Classification - 2011Melinda GordonNo ratings yet
- Bridge Design DataDocument1 pageBridge Design DataKw TseNo ratings yet
- Tying Resistance 635Document7 pagesTying Resistance 635jo0rodriguesNo ratings yet
- DS - en 1993-1-7 DK Na - 2007 eDocument4 pagesDS - en 1993-1-7 DK Na - 2007 ep_meulendijks108No ratings yet
- Eccentric ShearDocument20 pagesEccentric ShearbsitlerNo ratings yet
- Flexure: European Standards CEN/TC 250 Structural Eurocodes (EN 1992-1-1)Document22 pagesFlexure: European Standards CEN/TC 250 Structural Eurocodes (EN 1992-1-1)Alican TörenNo ratings yet
- Effective LengthsDocument8 pagesEffective Lengthsberto2008No ratings yet
- Lateral-torsional buckling of beamsDocument27 pagesLateral-torsional buckling of beamsYoussef AliNo ratings yet
- Homework 2Document7 pagesHomework 2Chinny LyheangNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4B.5: Calculation Examples: Example 1: Critical Temperature of Tension MemberDocument6 pagesLecture 4B.5: Calculation Examples: Example 1: Critical Temperature of Tension MemberMihajloDjurdjevicNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Axial Load Limit (Columns EC2)Document1 pageUltimate Axial Load Limit (Columns EC2)dhanya1995No ratings yet
- Structural Dynamics Response ForcesDocument4 pagesStructural Dynamics Response ForcesMD NayeemNo ratings yet
- CH 24Document25 pagesCH 24Sanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Design of Shaft TransmissionDocument20 pagesDesign of Shaft TransmissionPranav BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Elastic Critical Moment For Lateral Torsional BucklingDocument14 pagesElastic Critical Moment For Lateral Torsional BucklingAndrey SemjonovNo ratings yet
- Vibrations AssignmentDocument6 pagesVibrations AssignmentEe JehanabadNo ratings yet
- Vibrations AssignmentDocument6 pagesVibrations AssignmentEe JehanabadNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialFormulas Short NotesDocument19 pagesStrength of MaterialFormulas Short NotesRavindra DevireddyNo ratings yet
- SOM 2 Lecture Notes PDFDocument163 pagesSOM 2 Lecture Notes PDFRajiv KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Static Analysis of Circular Cylindrical Shell Under Hydrostatic and Ring ForcesDocument10 pagesStatic Analysis of Circular Cylindrical Shell Under Hydrostatic and Ring ForcestevredeNo ratings yet
- DESIGN OF TIMBER COLUMNSDocument40 pagesDESIGN OF TIMBER COLUMNSMuhd FaridNo ratings yet
- CAC Handbook Chapter 11 Seismic DesignDocument27 pagesCAC Handbook Chapter 11 Seismic DesignthailecanadaNo ratings yet
- Simple Shear DesignDocument57 pagesSimple Shear DesignWilliam MataNo ratings yet
- CIV-MSE-R19 WWW - Mepcoeng.ac - inDocument95 pagesCIV-MSE-R19 WWW - Mepcoeng.ac - inAnonymous Qm0zbNkNo ratings yet
- High-Strength Concrete in U.S. Codes and Standards S.K. GhoshDocument16 pagesHigh-Strength Concrete in U.S. Codes and Standards S.K. GhoshGuilhermeFregoneziNo ratings yet
- Raftsundet Bridge in Lofoten, Norway. A Cantilevered Bridge With A Lightweight Concrete Main Span of 298mDocument13 pagesRaftsundet Bridge in Lofoten, Norway. A Cantilevered Bridge With A Lightweight Concrete Main Span of 298mJose Manuel Gonzalez Contreras100% (1)
- Analysis and Optimization of Connecting Tie Rod Assembly in Agriculture ApplicationDocument5 pagesAnalysis and Optimization of Connecting Tie Rod Assembly in Agriculture ApplicationYehualaw AyresamNo ratings yet
- Tensile Test ResultsDocument7 pagesTensile Test ResultsImran QayyumNo ratings yet
- University of Kerala: Syllabus For Viii Semester Mechanical EngineeringDocument81 pagesUniversity of Kerala: Syllabus For Viii Semester Mechanical EngineeringJephinSJohnNo ratings yet
- Designing Effective Static Tests For Spacecraft Structures - Sarafin (Ler) - Part6Document1 pageDesigning Effective Static Tests For Spacecraft Structures - Sarafin (Ler) - Part6JizzPontesNo ratings yet
- SOM One Linear PDFDocument88 pagesSOM One Linear PDFDinuSkyNo ratings yet
- Column B-4 Load Takeoff: 3 Floor 2 Floor RoofDocument9 pagesColumn B-4 Load Takeoff: 3 Floor 2 Floor Roofclam2014No ratings yet
- The New Guide To Stability Design Criteria For Metal StructuresDocument3 pagesThe New Guide To Stability Design Criteria For Metal StructuresBilly BobNo ratings yet
- Magee Forth BridgeDocument10 pagesMagee Forth BridgeVali MirzaNo ratings yet
- Ultra-High Strength Concrete Filled Composite Columns For Multi-Storey Building Construction, 2012 (Liew JYR)Document17 pagesUltra-High Strength Concrete Filled Composite Columns For Multi-Storey Building Construction, 2012 (Liew JYR)Phan Đào Hoàng HiệpNo ratings yet
- Herbert E. Lindberg, Alexander L. Florence Auth. Dynamic Pulse Buckling Theory and ExperimentDocument394 pagesHerbert E. Lindberg, Alexander L. Florence Auth. Dynamic Pulse Buckling Theory and ExperimentJulio VergaraNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Column and StrutDocument69 pagesModule 7 Column and StrutRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- Steel Shear Walls For Existing BuildingsDocument8 pagesSteel Shear Walls For Existing BuildingsOscar SanabriaNo ratings yet
- Arthur W. Leissa (Auth.), I. H. Marshall (Eds.) - Composite Structures 4 - Volume 1 Analysis and Design Studies (1987, Springer Netherlands)Document647 pagesArthur W. Leissa (Auth.), I. H. Marshall (Eds.) - Composite Structures 4 - Volume 1 Analysis and Design Studies (1987, Springer Netherlands)Shivareddy KondakindiNo ratings yet